entropy
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
thermodynamics
study of energy and its transformation.
-deals with energy(E), entropy(H) and GIbbs free energy (G)
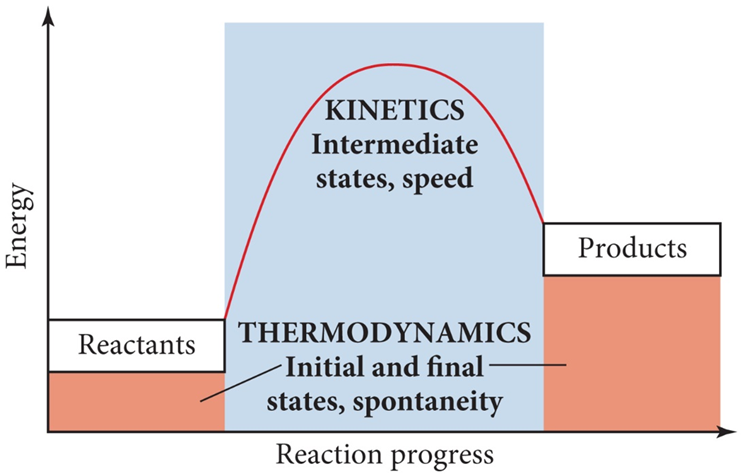
-A fundamental goal of thermodynamics is to predict spontaneity
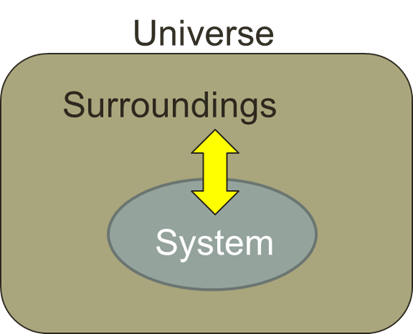
system
what we want to study within thermodynamics, including its interactions with surroundings.
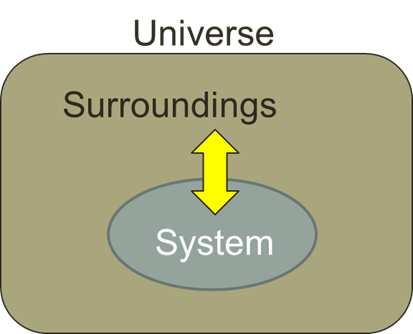
surroundings
is everything else outside the system that interacts with it, including energy and matter exchanges.
first law of thermodynamics
the total energy of the universe constant
and can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
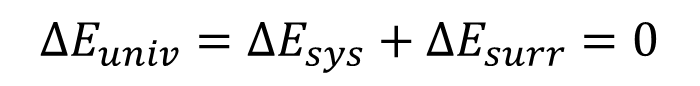
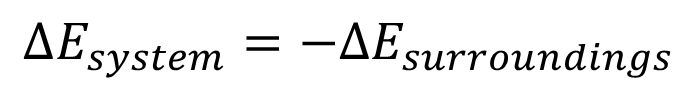
internal energy (E)
is the total energy of the system
-•Energy can be transferred via heat (q) and work (w)

Enthalpy (H)
Heat exchanged under constant pressure condition
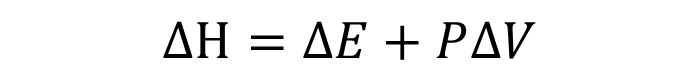
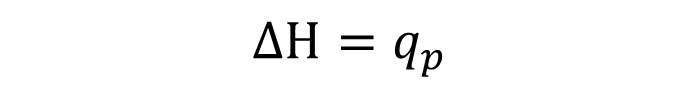
Positive ∆H
is an endothermic reaction
-system gains heat from it surrounding
negative ∆H
is exothermic reaction
-system gives off heat to surroundings
-system loses heat to its surroundings
spontaneous process
A process that occurs without external intervention, resulting in an increase in the total entropy of the system and its surroundings.
nonspontaneous process
A process that does not occur without external intervention, often resulting in a decrease in the total entropy of the system and its surroundings.
what makes reaction spontaneous
is related to the increase in entropy and the decrease in free energy. A reaction is spontaneous if it results in a net gain of entropy.
-entropy
Entropy(s)
thermodynamic function that increases the number of energectical equivalent ways to arrange the components of a system to achieve the same state