Microbiology - Prokaryotic Anatomy
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prokaryotic Cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
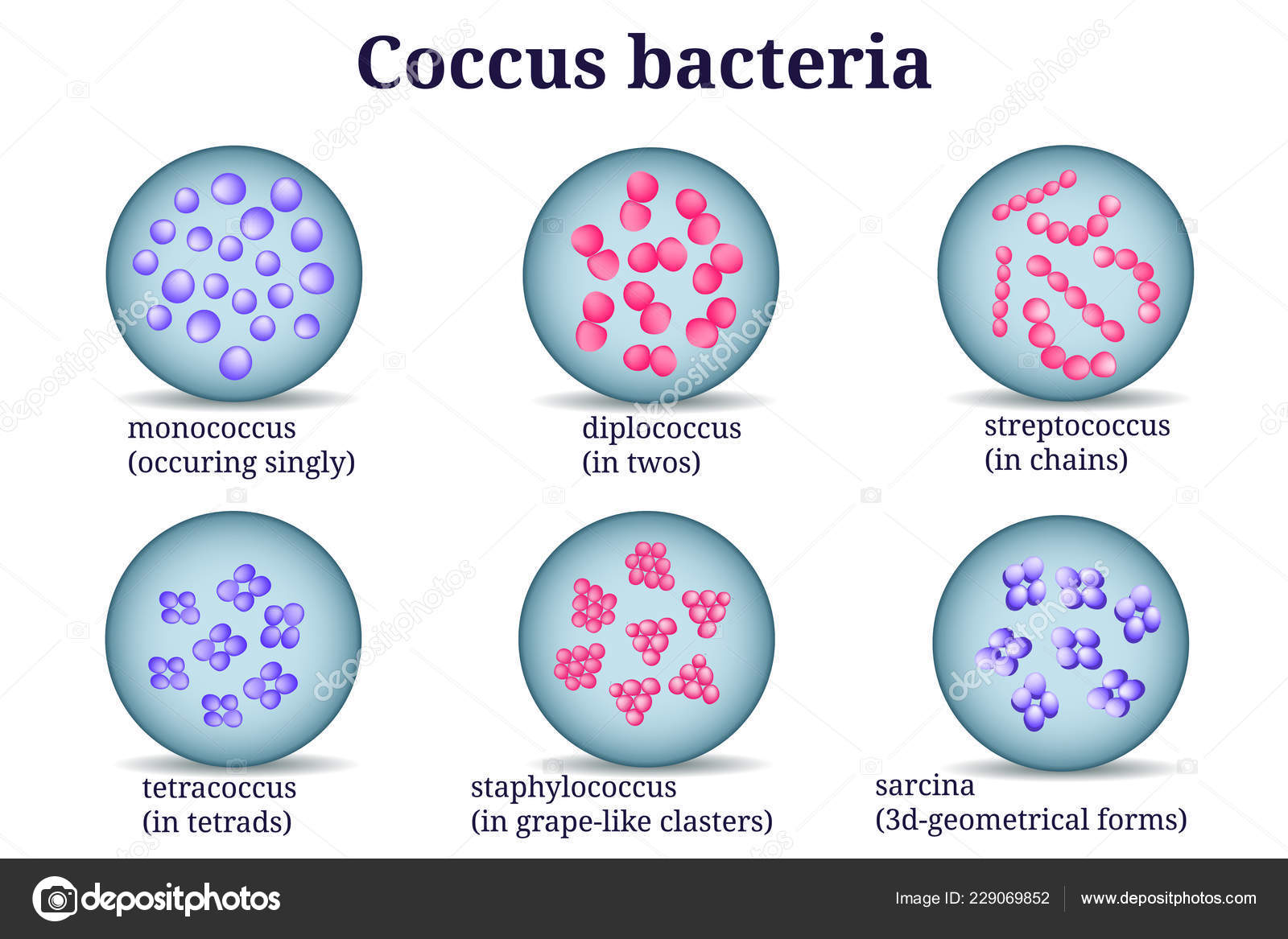
Coccus
Berry looking
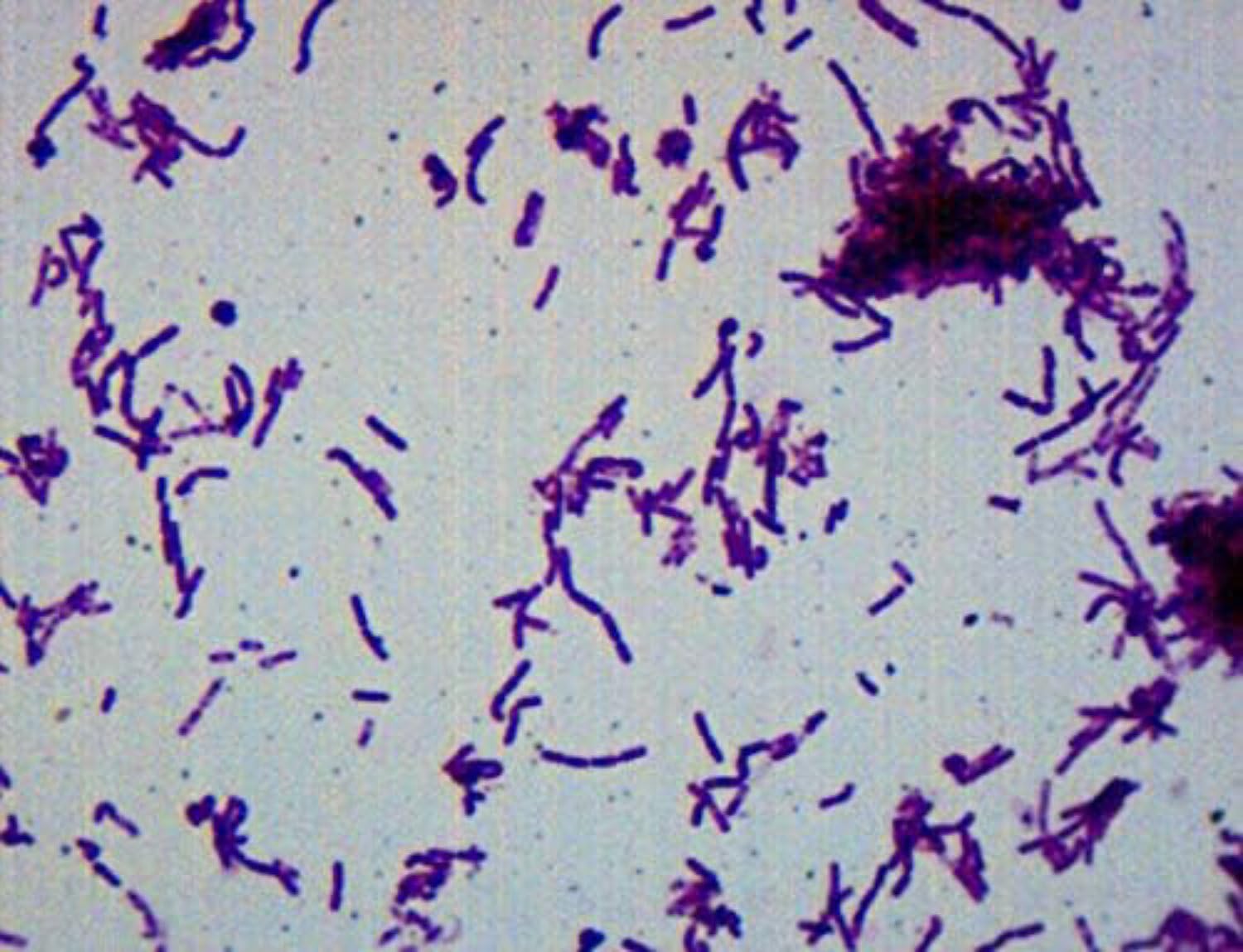
Bacillus
Rods
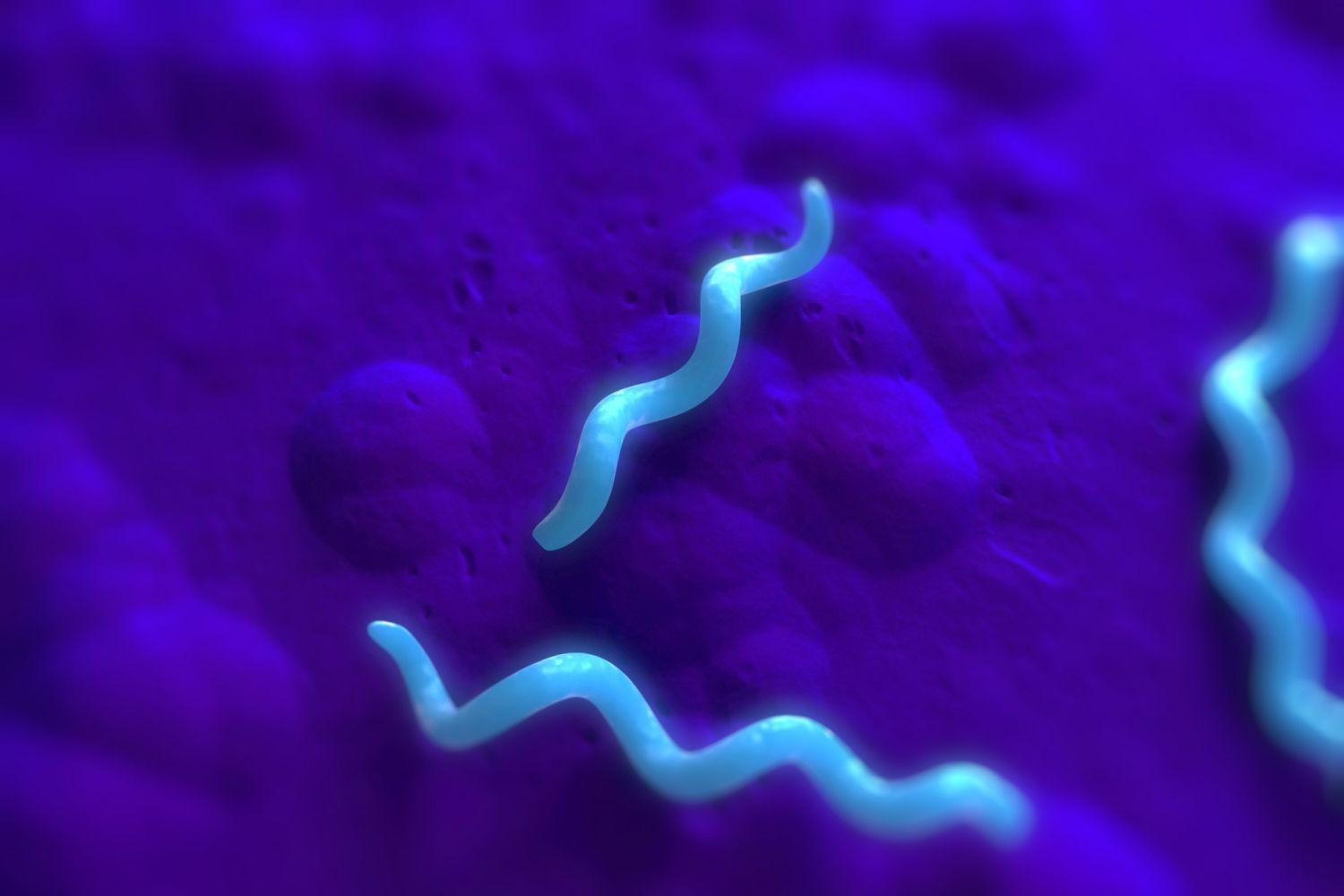
Spirilla
Spiral
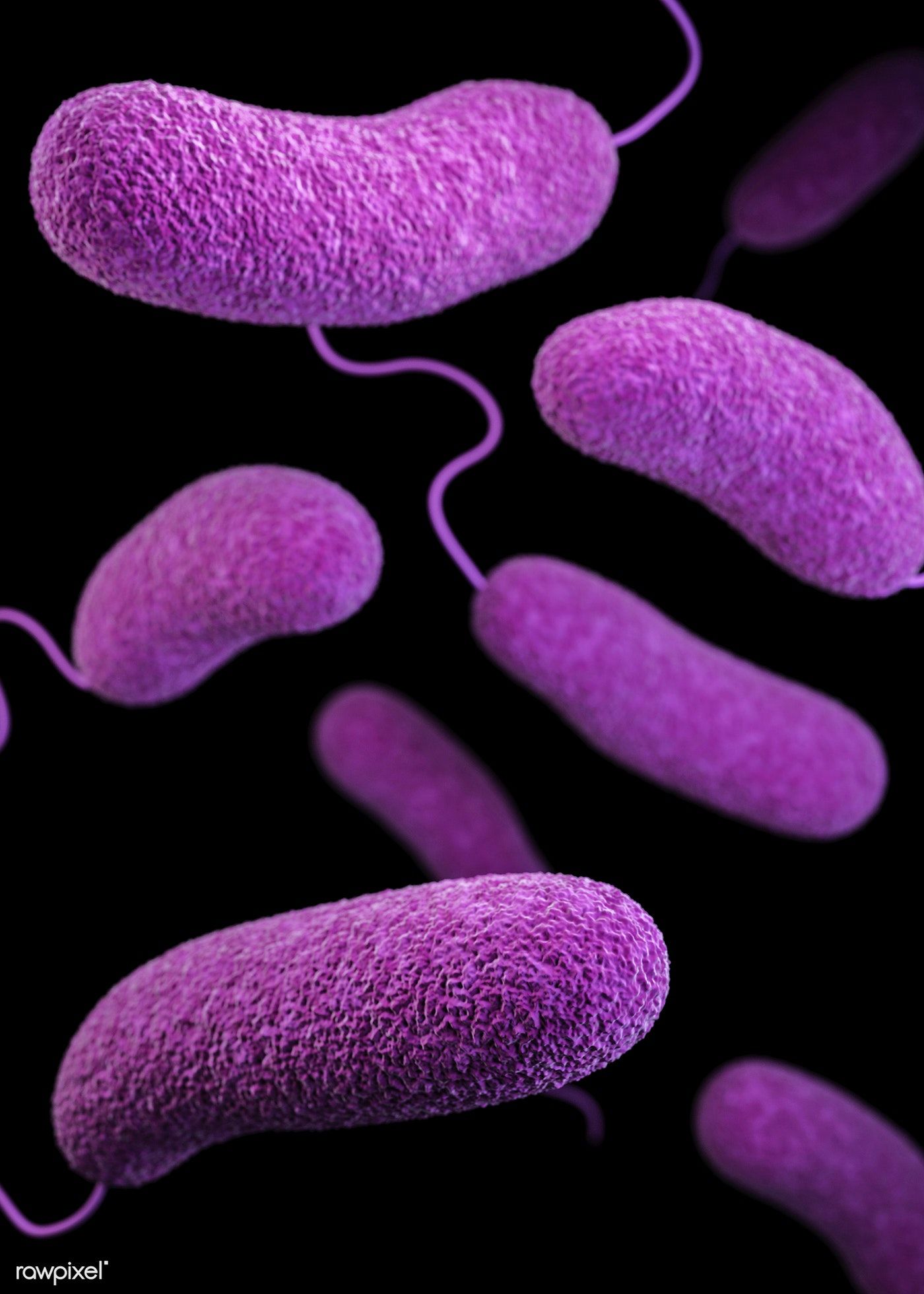
Vibrios
tails!
Pleomorphic
Abnormal cells
Clusters
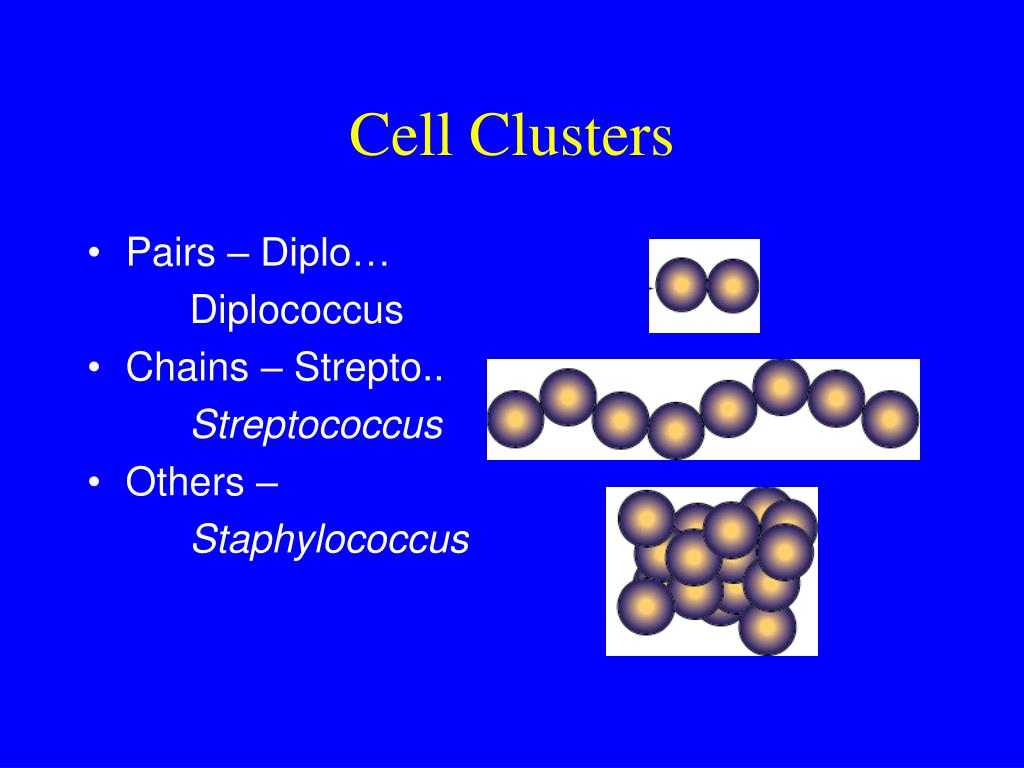
Staphylococcus
many
Diplococcus
Pairs

Streptococcus
Chains

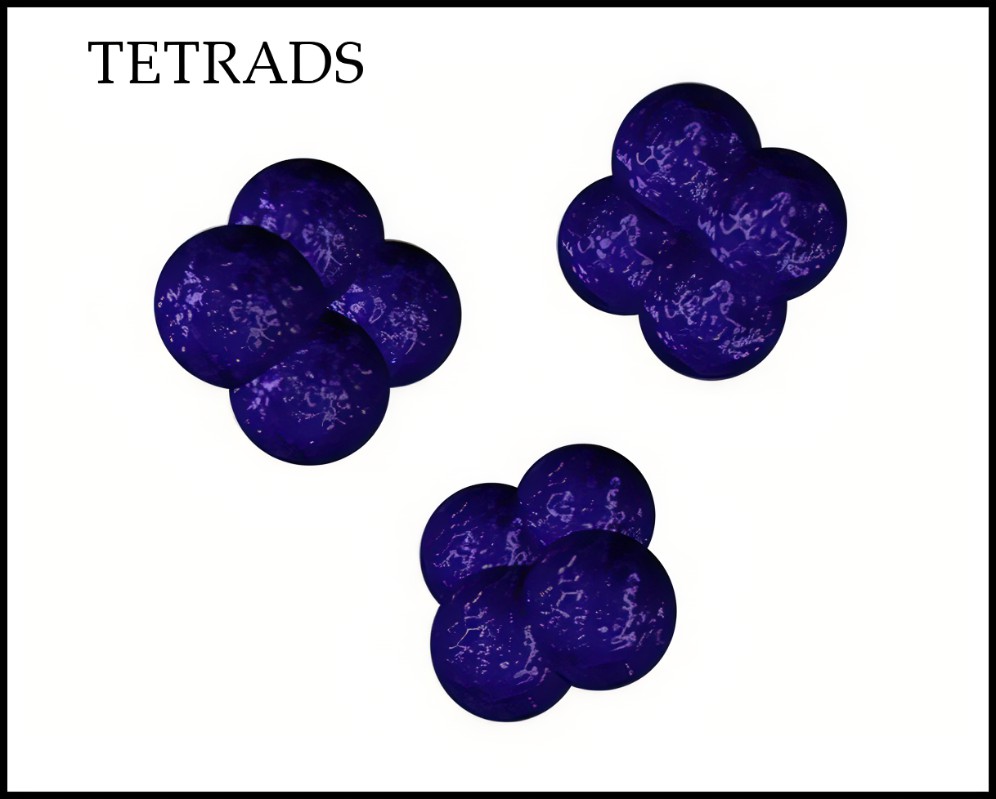
Tetrads
What are prokaryotic membranes called
Cytoplasmic membranes; homeostasis and make ATP
Capsule
Dense/organized glycocalyx
Is prokaryotic G+ or G-
gram positive (thick wall w/peptidoglycan and teichoic acids)
Thin cell wall w/LITTLE peptidoglycan/repels water/toxic effect/outer membrane called lipopolysaccharide
Gram Negative
Prokaryotes don’t have nucleus, but ____
nucleoid
What do prokaryotes’ granules do?
Store glycogen/iron
Cranberry juice helps w/bladder infection
TRUE
What is secondary source of DNA for
Plasmid, not needed for life
Some bacteria have _____ to help transfer plasmid to another bacteria
sex pilus
What are prokaryotic cells surrounded by
Glycocalyx (sugar coat)
Slime layer
Diffused/unorganized glycocalyx
Capsule purpose
Resist phagocytosis; aka encapsulated, as it can be dangerous
Biofilm
Slime layers overlap → work together.
Biofilm example
Dental plaque
Archaea characteristics
Non-pathogenic/has pseudopeptidoglycan/extremophiles (handle extreme conditions)
Alkalophile
Live in very alkaline pH
Picrophiles
Live very cold temps
Halophiles
Live very salty conditions
Methanogens
produce methane from carbon dioxide/hydrogen
What ribosomes?
70s