AP Psych Modules 14-15
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Read Modules 14-15 in “Myers, Psychology for AP, 3e” if you need clarification >_<
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Heredity (Nature)
The genetic transfer of characteristics from parent to offspring
Environment (Nurture)
Every non-genetic influence
Prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us
Behavior Geneticist
They study the relative power and limits of heredity and environmental influences on behavior
What comes built on and what is nurtured — and how?
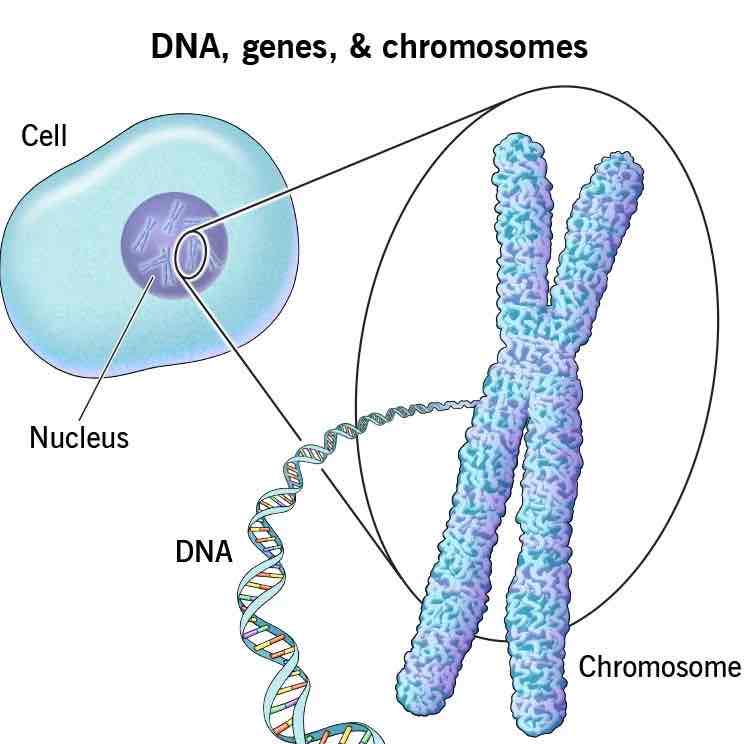
Chromosome
Threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes.
Each person has 46 chromosomes – you inherit 23 from your mother and 23 from your father.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up chromosomes
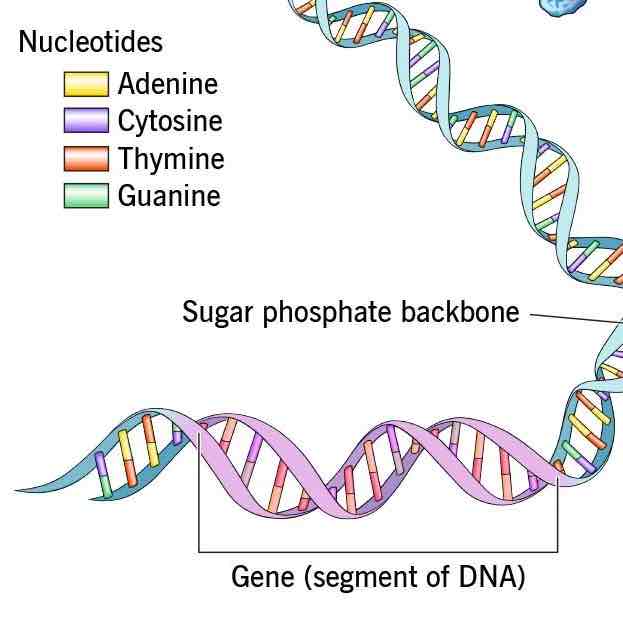
Genes
The biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosome
segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
You have ~20,000 genes
Human Genome
Instructions for making a human organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that human’s chromosomes.
Researchers have discovered a common sequence within human DNA.
This shared genetic profile is what makes us humans, rather than tulips, bananas, or chimpanzees.

Identical (Monozygotic) Twins
A single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms

Fraternal (Dizygotic) Twins
Separate fertilized eggs that share a maternal prenatal environment
no more alike than siblings
Identical Twins Reared Apart Studies
Thomas Bouchard and his colleagues located and studied 74 pairs of identical twins raised apart.
They found similarities of tastes and physical attributes, personality, abilities, attitudes, interests, and even fears.
Adoption Studies
People who grow up together, whether biologically related or not, do not much resemble one another in personality.
Two adopted children raised in the same home are no more likely to share personality traits with each other than with the child down the block.
The environment shared by a family’s children has virtually no discernible impact on their personalities
Heritability
How much of the variation that exists between a group of individuals is due to genetics
EX: Intelligence is ~60% heritable, so genetic influence explains about 66% of the observed variation among people
DOES NOT MEAN YOUR INTELLIGENCE IS 60% GENETIC
Increases when differences in environment decrease
Molecular genetics
The study of the molecular structure and function of genes
Molecular Behavioral Genetics
The further study of how the structure and function of genes interact with our environment to influence behavior
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
EX: Researchers have found the effects of childhood trauma, poverty, or malnutrition may last a lifetime
How do evolutionary psychologists use natural selection to explain behavior?
Darwin’s principles of natural selection guide evolutionary psychologists in understanding what makes humans so much alike
Natural Selection
the principle that inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will (in competition with other trait variations) most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
Survival of the Fittest
Darwin’s Basic Principles
Organisms’ varied offspring compete for survival.
Certain biological and behavioral variations increase organisms’ survival chances in their particular environment.
Offspring that survive are more likely to pass their genes to the next generation.
Over time population characteristics may change.
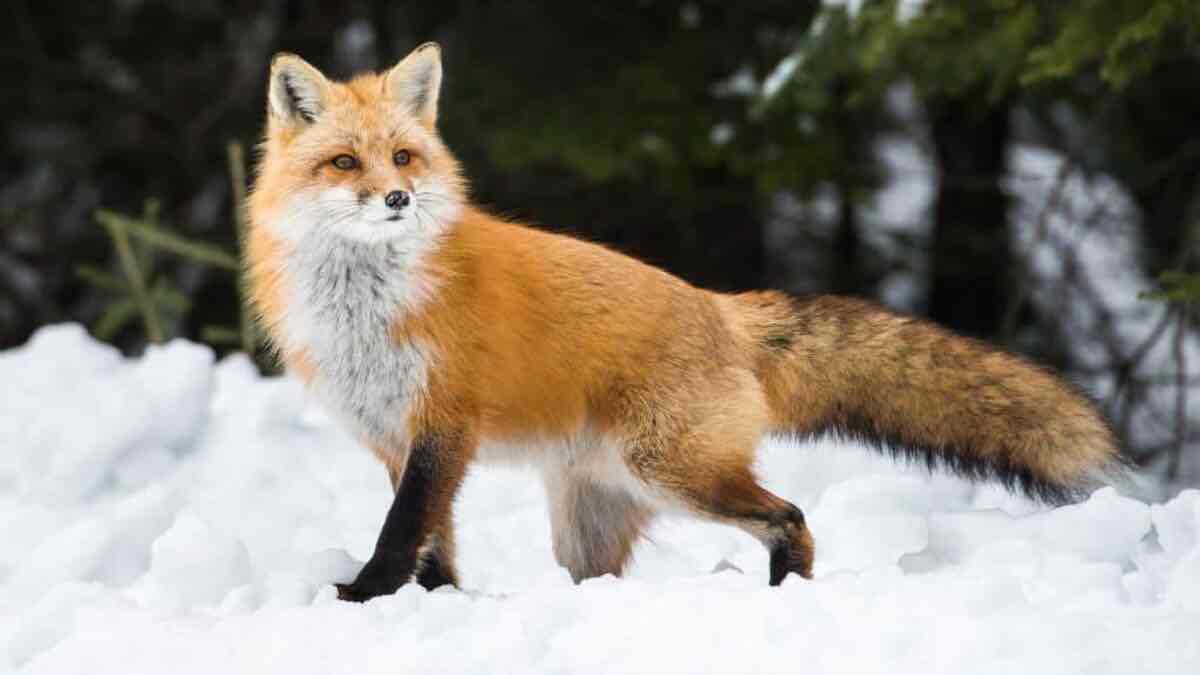

Fox (Evolutionary Psych) Study
Researchers Belyaev and Trut selectively bred the tamest foxes and after 30 generations (40 years) were able to produce “docile, eager to please, domesticated” animals.
psychological traits can be selected as well as physical traits
Naturally Occurring Selection
People’s adaptive flexibility in responding to different environments contributes to our fitness—our ability to survive and reproduce
Genes and experience together wire the brain.
Male Sexuality
May be more likely to initiate sexual activity
May perceive women’s friendliness for sexual interest
Female Sexuality
Tendency toward tall men with slim waists and broad shoulders
May prefer men who are mature, dominant and bold
Social Scripts
a culturally modeled guide for how to act in various situations
EX: There are unspoken rules to eating a restaurant: Enter, Sit down, Read menu, Order food, etc
Criticism of the evolutionary perspective on sexuality
Start with the effect and work backward to explain what happened.
Try to explain today’s behavior with decisions made thousands of years ago.
There are social consequences to accepting evolutionary explanations.
How do evolutionary psychologists respond to criticism?
Much of who we are is NOT hardwired...genes are NOT destiny.
Men and women are far more alike than different.
Some traits and behaviors are hard to explain in terms of natural selection.
Biopsychosocial Approach
Genes, environment and our culture all combine to influence our development