PK Bioavailability & Half-Life
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Pharmacokinetics
The study and characterization of the time course of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion and is the basis for drug dosage regimens in various species
Bioavailability
The rate and extent to which a drug administered in a particular dosage form enters the systemic circulation
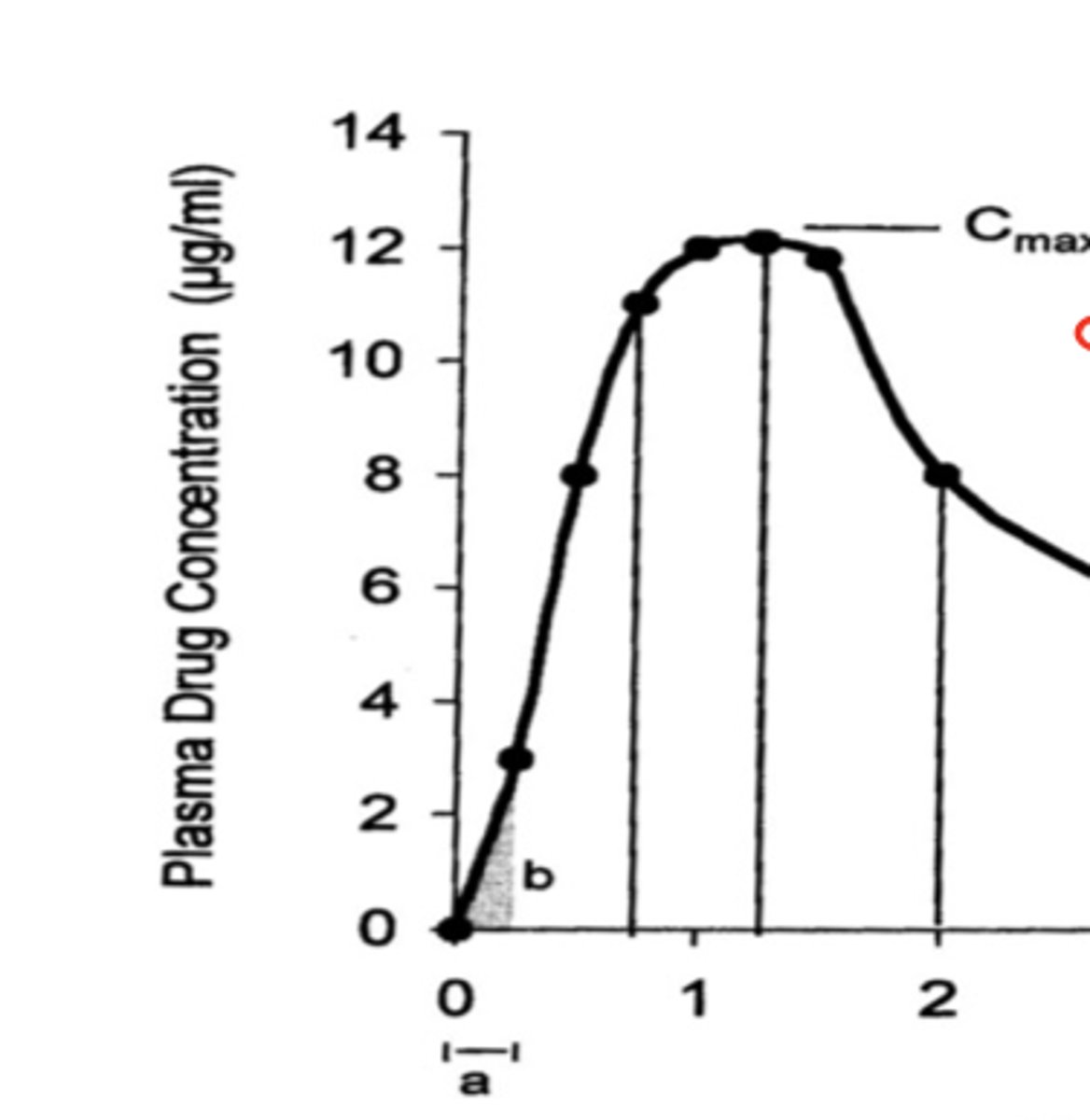
1) Peak plasma concentration (Cmax)
2) Time to reach peak concentration
3) Area under the curve (bioavailability)
What are the three things that bioavailability is described by?
Disposition curve
Graphically defines the time course of the drug in the plasma
ORAL because the plasma drug concentration starts at 0 and in IV it would start at a high number peak
Is this curve IV or oral administration?
Elimination (beta) phase
Phase of the IV administration that removal of the drug is by biotransformation and excretion
Distribution (alpha) phase
Phase of the IV administration that is attributed to the rapid distribution of it into tissues and organs
Liver metabolism will break it down for by mouth administration where it will not in IV
What likely account for the difference in the absolute bioavailability of by mouth compared to IV administration buprenorphine?
Because the pH of transmucosal is much more similar to drug and therefore it crosses the membrane much easier
Why is transmucosal administration so much more effective for bup than oral or transdermal?
Rate of drug elimination (Kel)
Fraction of drug eliminated per unit time
Elimination rate constant (Kel)
What is the slope of the beta phase (elimination phase) referred to as?
It shortens and so does the Kel (rate of elimination)
If the terminal slope of the disposition curve is steep, what happens to the half-life?
Metabolism and excretion
What are the two major determinants of drug elimination half-life?
Steady-state
Point at which the amount of drug leaving the body during each dosing interval is equal to the amount of drug entering the body with each dose
Half-life
What determines the time to steady-state?