AP Bio: Unit 4 Cell Signaling and Cell Cycle Diagram | Quizlet
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Chromosome
A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
Chromatin
Substance found in eukaryotic chromosomes that consists of DNA tightly coiled around histones
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
Autosome
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
Gamete
specialized cell involved in sexual reproduction
Cell cycle
The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
G1 phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
M phase
mitosis and cytokinesis
G0 phase
A nondividing state occupied by cells that have left the cell cycle, sometimes reversibly.
Checkpoint
A control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle.
Cyclin
one of a family of closely related proteins that regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
Cancer
any malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division
Contact inhibition
a process that stops additional cell growth when cells become crowded; cancer cells are immune to contact inhibition
Angiogenesis
formation of new blood vessels
Metastasize
the process by which cancer spreads from one place in the body to another
Benign tumor
An abnormal mass of cells that remains at its original site in the body.
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
Interphase
period of the cell cycle between cell divisions (G1, S, and G2 phase)
Mitosis
a type of eukaryotic cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
TERM
Prophase
DEFINITION
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
TERM
Metaphase
DEFINITION
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Metaphase plate
Plane midway between the two poles of the cell where chromosomes line up during metaphase.
TERM
Anaphase
DEFINITION
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
TERM
Telophase
DEFINITION
After the chromosome seperates, the cell seals off, Final phase of mitosis.
Centrosome
A structure in animal cells containing centrioles from which the spindle fibers develop.
Spindle fibers
help pull apart the cell during replication and are made up of microtubules
Microtubules
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tubelike structure; part of the cytoskeleton
Cleavage furrow
The first sign of cleavage in an animal cell; a shallow groove in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate.
Cell plate
A double membrane across the midline of a dividing plant cell, between which the new cell wall forms during cytokinesis.
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
Meiosis I
The first division of a two-stage process of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in cells with half the number of chromosome sets as the original cell.
Meiosis II
The second phase of meiosis consisting of chromatids separating, along with the two diploid cells splitting in two
Gametes
reproductive cells, such as sperms and eggs
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
Bivalent
a pair of homologous chromosomes
Crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
Tetrad
structure containing 4 chromatids that forms during meiosis
Independent assortment
Independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes during meiosis
Zygote
A fertilized egg
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Synapsis
the pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
Chiasma
the site of crossing over during meiosis
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
Oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum
Polar body
a small cell containing little cytoplasm that is produced along with the oocyte and later discarded
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes.
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
Down syndrome
Trisomy 21
Barr body
Inactivated X chromosome
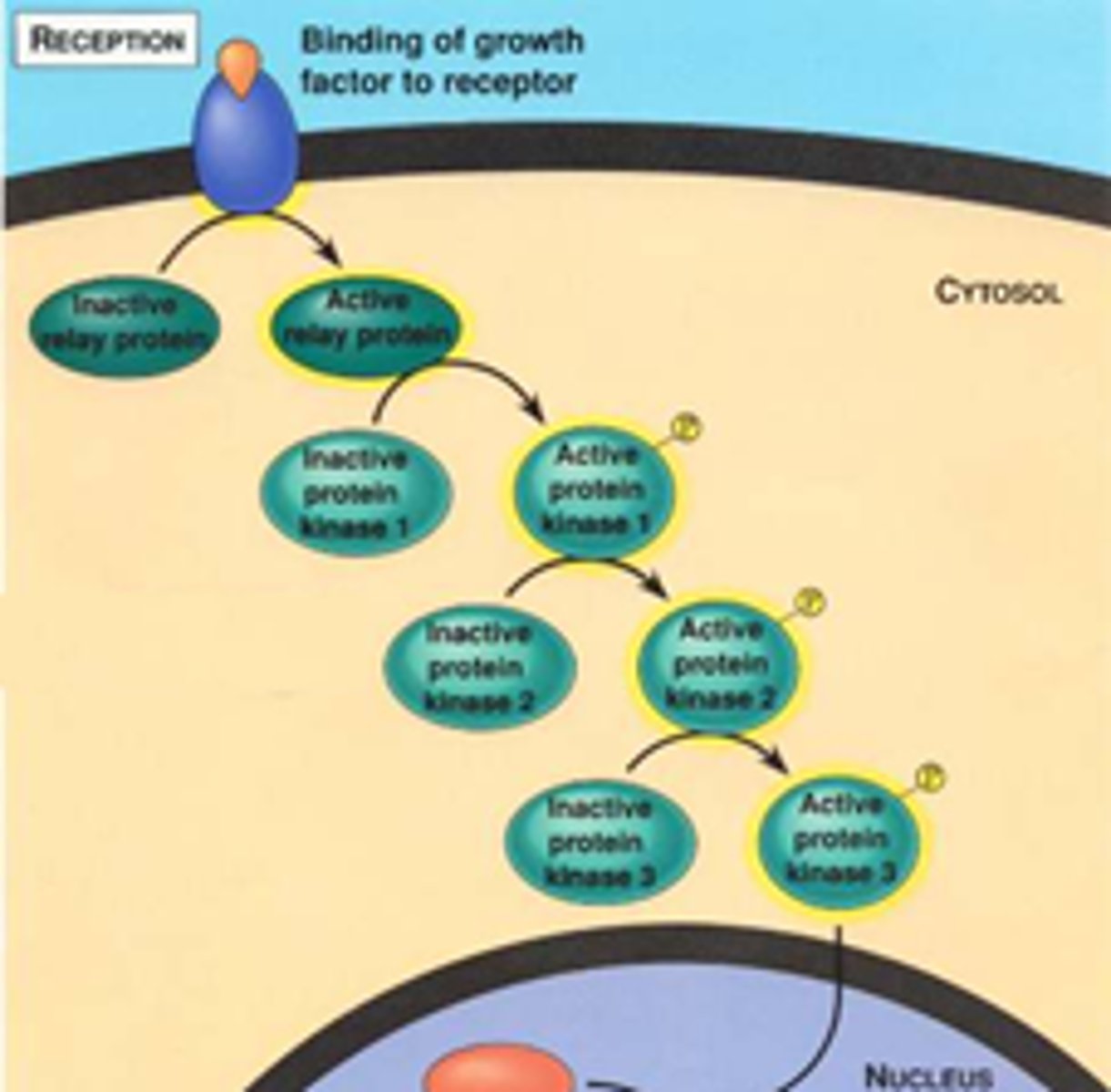
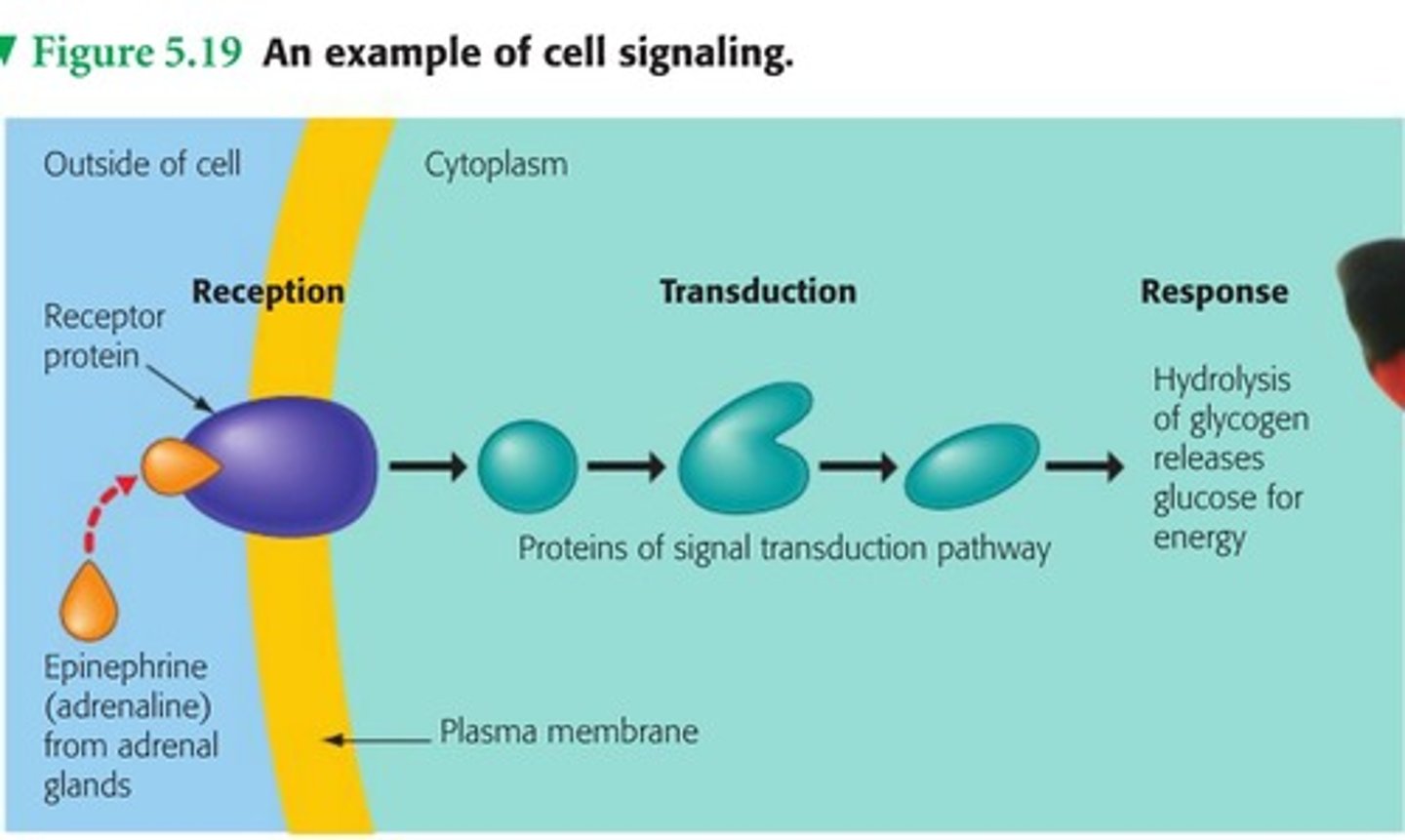
Cell signaling
The process of cell-to-cell communication mediated by signaling molecules and membrane receptors. Composed of three steps:
1) reception
2) transduciton
3) response
reception
The target cell's detection of a signal molecule coming from outside the cell.
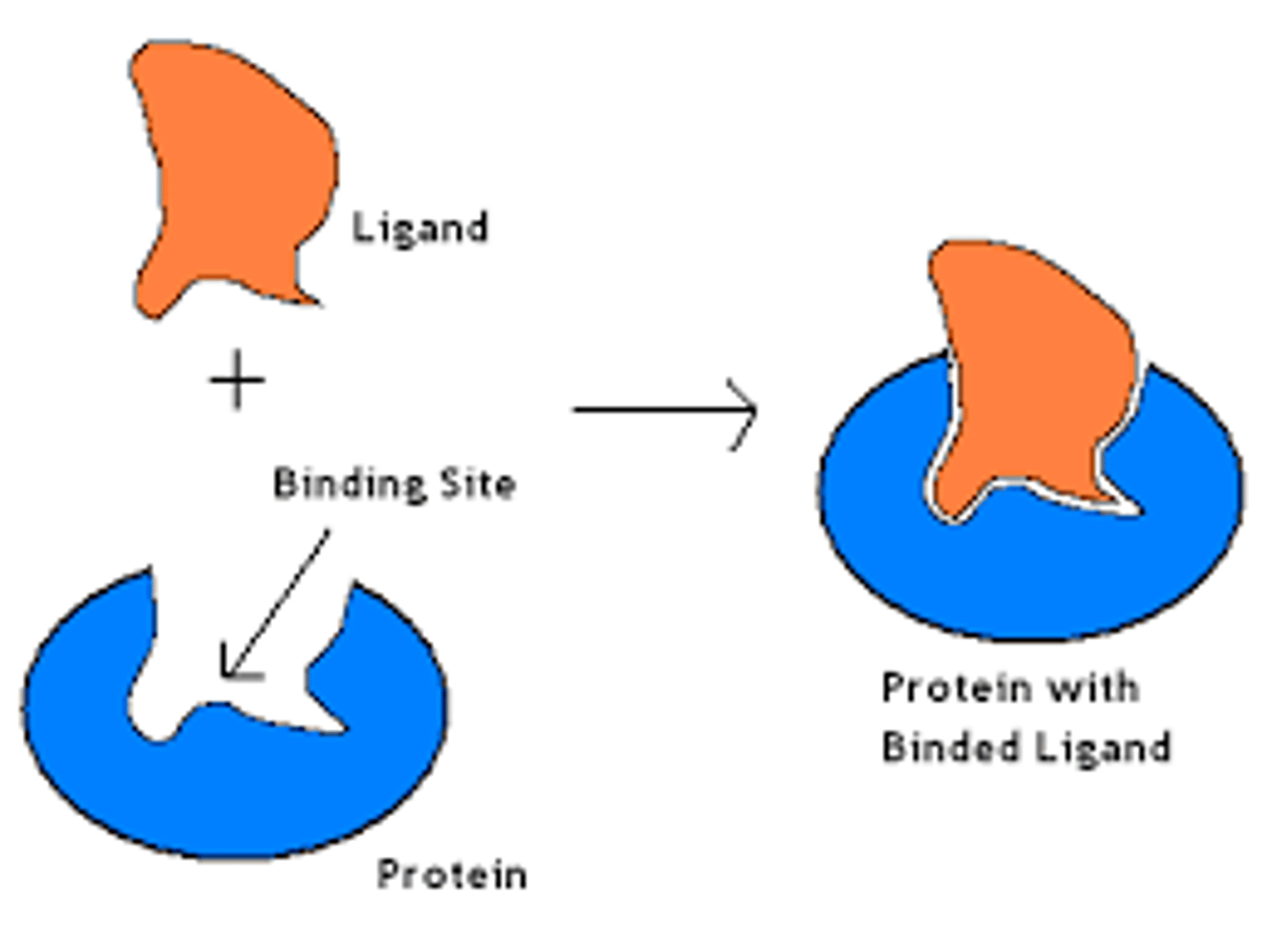
receptor
protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
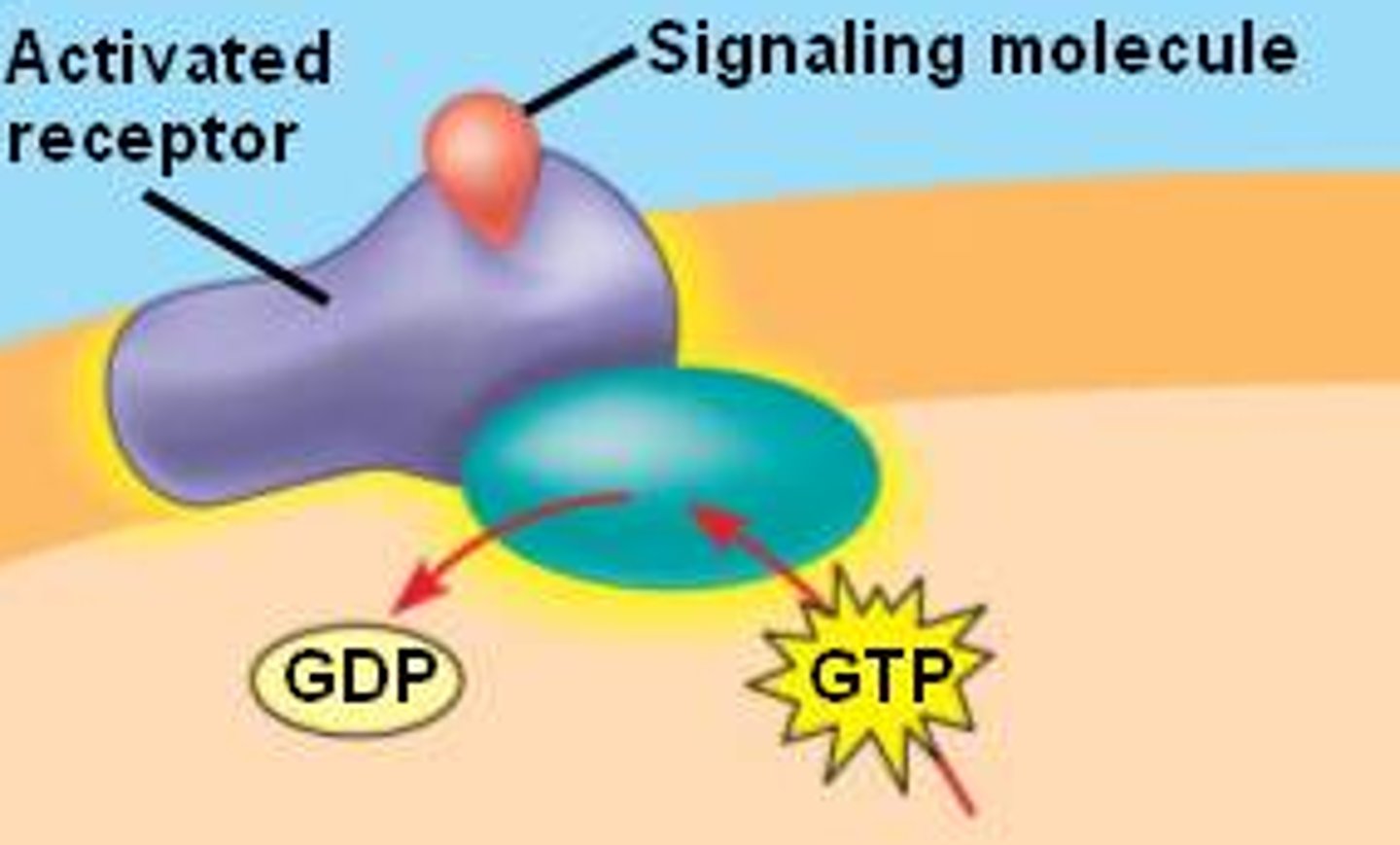
transduction
the signaling molecules binds to the receptor and changes it shape, causing the receptor to change its function
cAMP
a second messenger produced in GPCR signaling
response
In cellular communication, the change in a specific cellular activity brought about by a transduced signal from outside the cell.
phosphorylation
The transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a molecule.
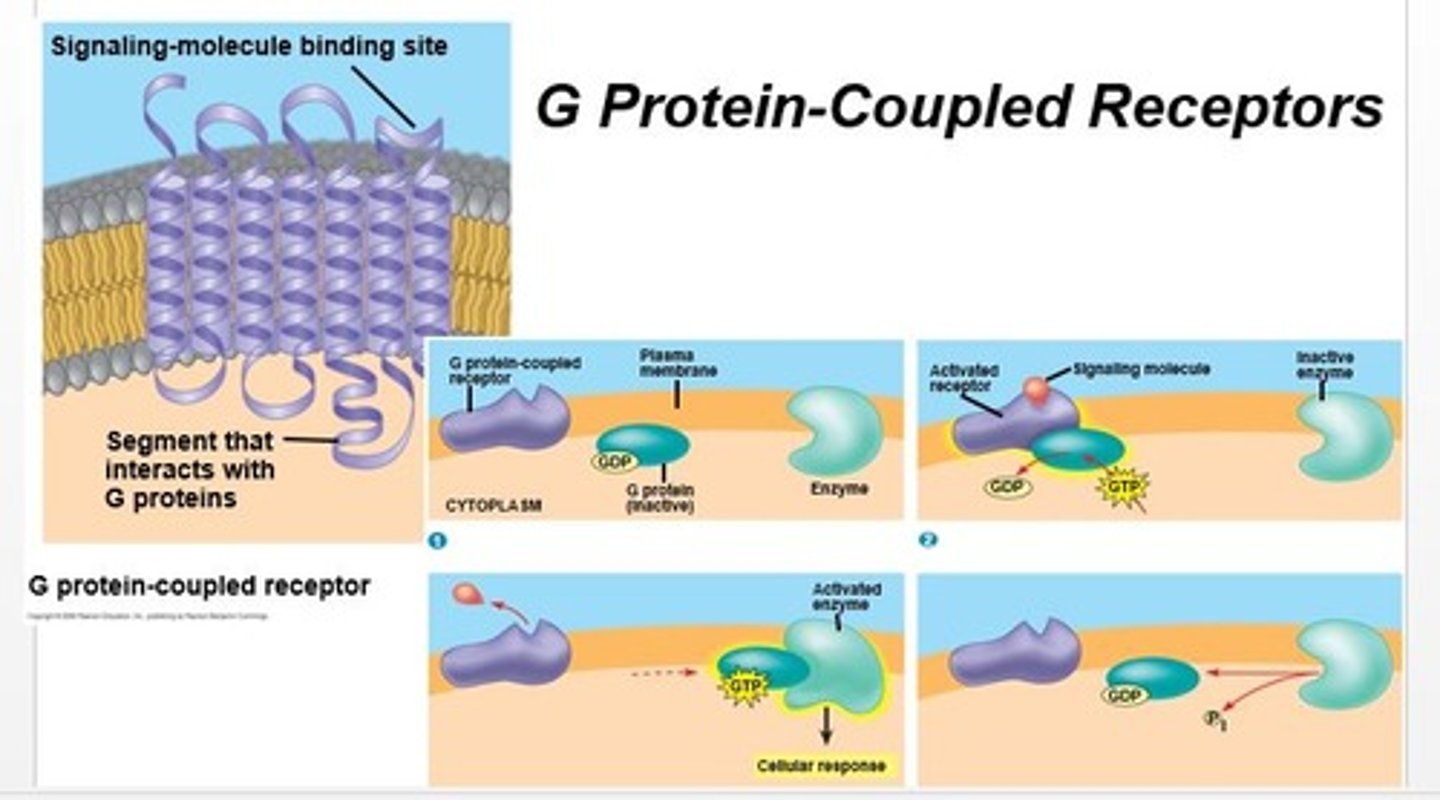
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
a large family of proteins that function as receptors; they provide a mechanism for molecules outside a cell to influence the inner workings of the cell.
Fun fact: these are Dr. Hathaway's favorite proteins :)
Signaling cascade
Series of events, starting with the binding of a ligand to a receptor. This sequence of events ultimately results in a change in cellular behavior
second messenger
a molecule that is generated when a specific substance attaches to a receptor on the outside of a cell membrane, which produces a change in cellular function
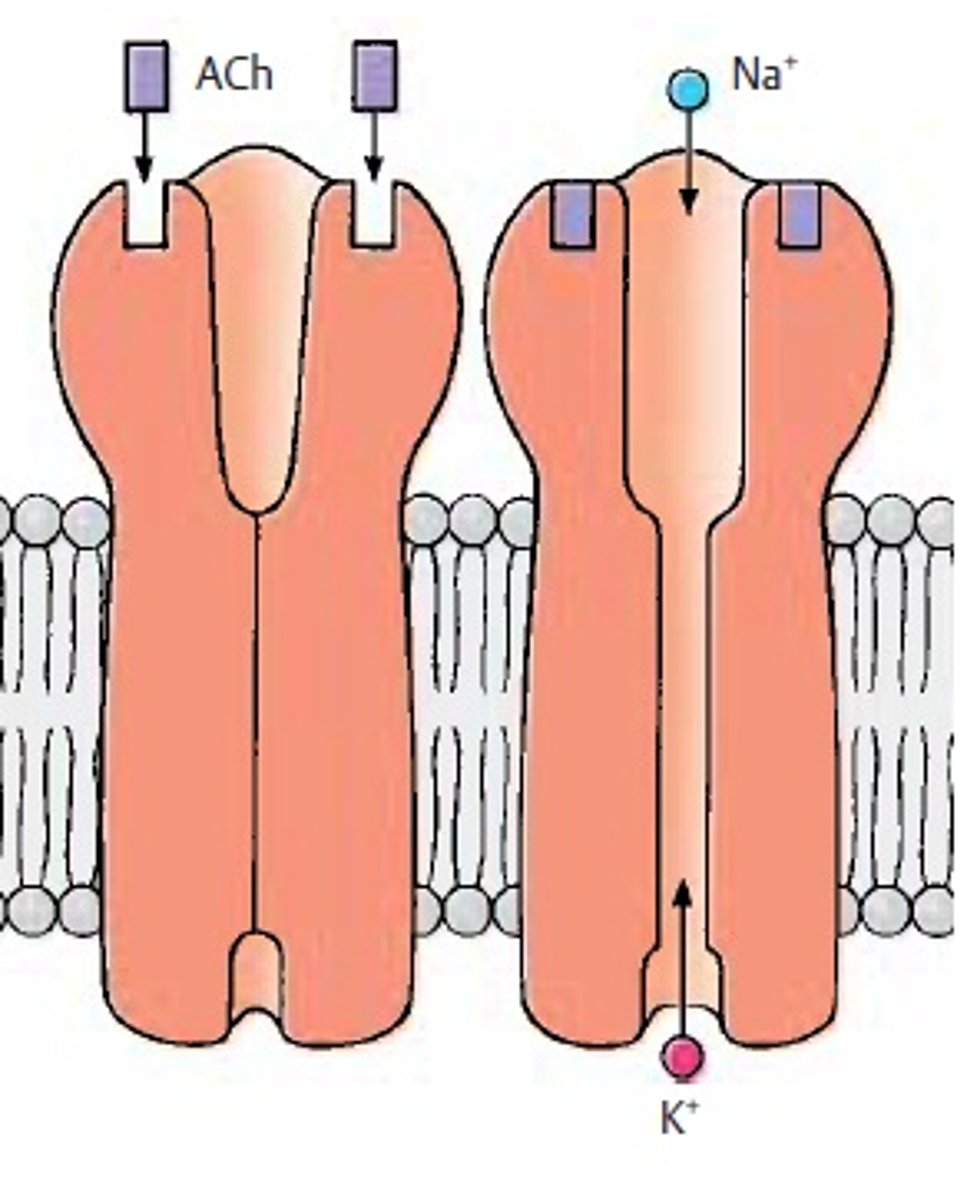
ligand-gated ion channel
Type of membrane receptor that has a region that can act as a "gate" when the receptor changes shape. When the receptors are activated they open and allow ions to cross the cell membrane.
apoptosis
programmed cell death involving a cascade of specific cellular events leading to death and destruction of the cell
gene expression
process by which certain genes are turned "on" or "off"