HAP Connective Tissues + Muscle and Nervous Tissues + Tissue Membranes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Areolar (Loose Connective) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: fibroblasts (versatile) + adipocytes (cushion) + WBC (immunity)
-Matrix: collagen (not much…for strength) + elastic fibers (resilience) + reticular (soft)
-High in polysaccharides to make loose (ground tissue)
Function:
- Diffusion and movement (binds skin and muscle)
VERY VASCULAR
Adipose (Loose Connective) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: adipocyte
-Matrix: elastic, reticular, and collagen fibers
-EASY TO HEAL CUZ VERY VASCULAR
Function:
- has triglycerides for expanding/shrinking and storage of lipids (born with set amount of adipocytes)
Tendons and Ligaments (Dense Regular) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: fibroblasts (versatile)
-Matrix: collagen fibers (strength/thickness)
- Has stacked fibers
Function:
- Tendon: muscle to bone
- Ligament: bone to bone
- STRONG IN ONE DIRECTION ONLY
- HARD
- A LITTLE VASCULAR
Reticular Tissue (Dense Irregular) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: fibroblasts
-Matrix: collagen and elastic fibers
-thick polysaccharides for ground tissue
Function:
- support, protection, and flexibility
-MOVEMENT IN MANY DIRECTIONS (strong fibers)
- SOFT
- NOT VERY VASCULAR
-(ex.) fascia: connects skin to muscle (can tangle → roll out)
3 Types of Cartilage (Connective Tissue) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: chondrocytes
-Matrix: collagen, proteoglycan (protein chains), and polysaccharides (thickness)
Function:
-covering ends of bone
-AVASCULAR (slower healing)
-does diffusion for healing/nutrients
1. Hyaline Cartilage: covers bone, flexible/strong, lots of collagen
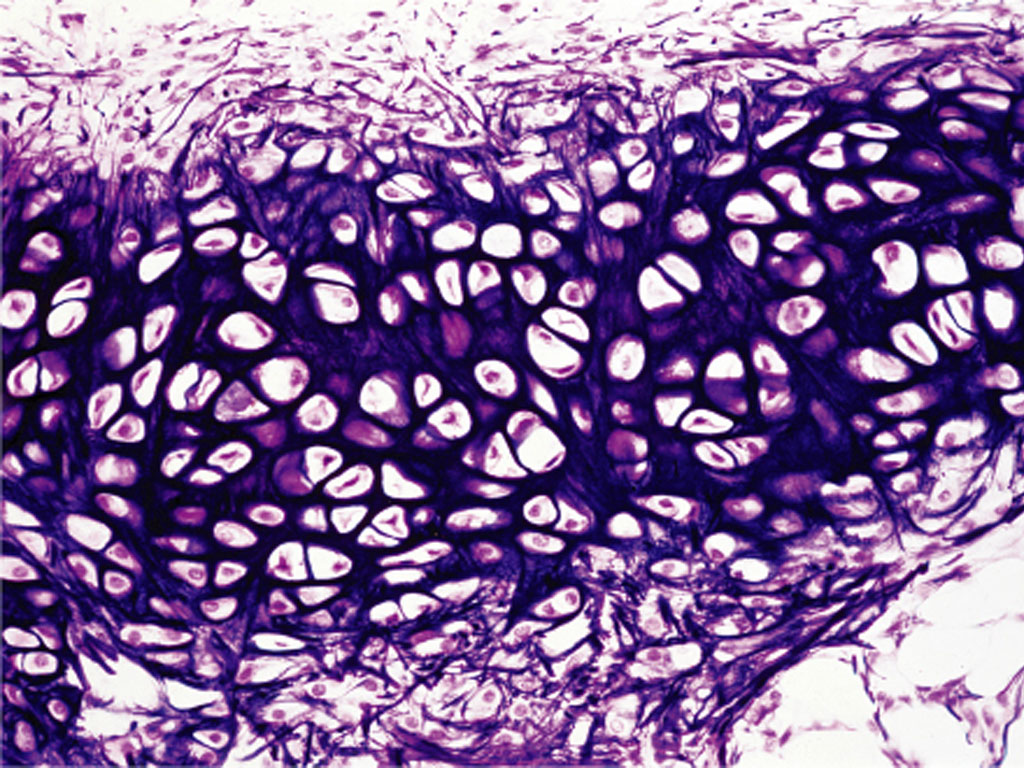
2. Fibrocartilage: intervertebral disks, has collagen for strength, and is the least flexible
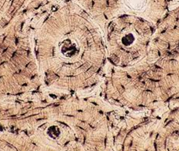
3. Elastic Cartilage: fibers that stretch, support/shape, has collagen (ex. ears)
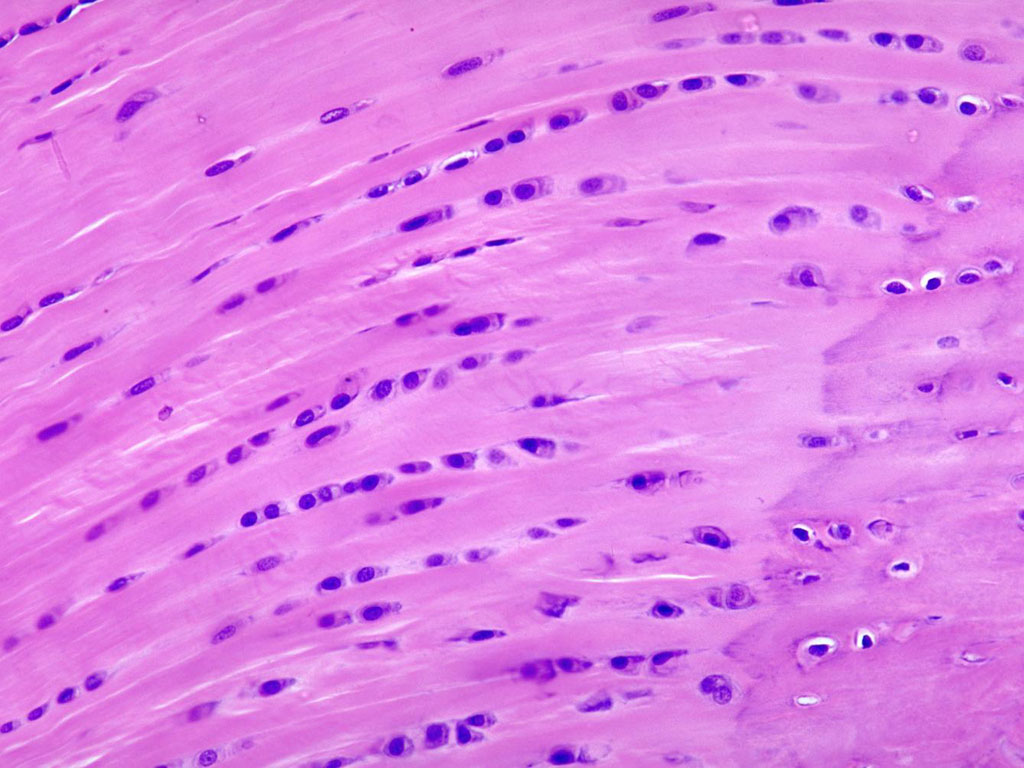
Bone (Connective Tissue) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: osteocyte
-Matrix: collagen fibers for strength and calcium phosphate for hardening
-CENTRAL CANAL HAS BLOOD AND NERVES
Function:
-VERY VASCULAR → QUICK HEALING
-Lacunae: small cavities in the bones (osteocytes in it)
-Central Canal: has blood and nerves for quick healing
Blood (Connective Tissue) → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
-Cells: red blood cells for transportation of O2 and CO2, which blood cells for fighting disease, and platelets for blood clotting
-Matrix: plasma
Function:
-transportation (RBC)
-protection (P’s)
-immunity (WBC)
Skeletal Muscle Tissue → structure, function, location
Structure:
-Cells: striations and MULTINUCLEATED
Function:
- VOLUNTARY AND STRIATED
Location:
- between bones, entrance points on body
Cardiac Muscle Tissue → structure, function, location
Structure:
-Cells: intercalated disks that connect muscle tissue to contract
-have gap junctions and desmosomes (adhesion)
-ONE NUCLEUS (balanced) and MITOCHONDRIA
Function:
- INVOLUNTARY AND NON STRATIFIED/BRANCHED
-contractions (pumping blood)
Location:
-in the heart (myocardium)
Smooth Muscle Tissue → structure, function, location
Structure: (weak ish)
-Vasoconstriction: the narrowing of blood vessels (decreased blood flow)
-Vasodilation: the widening of blood vessels (increased blood flow)
Function:
- INVOLUNTARY AND NON STRATIFIED
- peristalsis: a series of involuntary, wave-like muscle CONTRACTIONS that move food through the digestive tract, or other tubular organs
-CONTRACTS involuntary organs, moving them
Location:
-bladder and uterus
-arteries and veins
Nervous Tissue → structure, cell, matrix, function
Structure:
- Neuron: amitotic (doesn’t do mitosis)
- Neuroglia: mitotic (does mitosis) and the glue that holds this tissue together
Function:
-irritability: detects and responds
-conductivity: transmits electricity
-specialized to receive and send electrical impulses
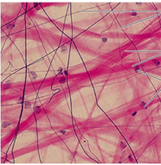
Areolar
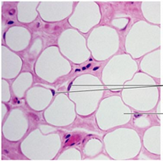
Adipose
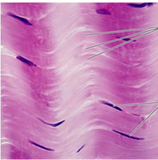
Tendons (muscle to bone) and Ligaments (bone to bone)
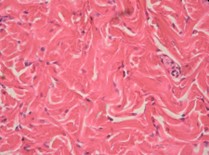
Reticular
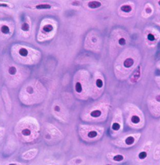
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Bone
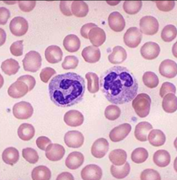
Blood
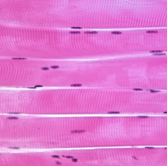
Skeletal Muscle
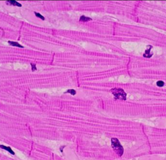
Cardiac Muscle
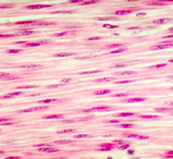
Smooth Muscle
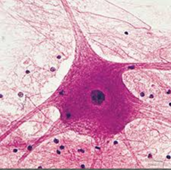
Nervous Tissue
What is a tissue membrane?
-a combination of tissues, epithelial and connective, that cover or line parts of your body
Synovial Membrane (name type of tissue, location in body, and function)
Type of Tissue:
- connective: areolar
Location in the body:
- lines the joints (shoulder, elbow, knee)
Function:
- lubricates the joints
Mucous Membrane (name type of tissue, location in body, and function)
Types of Tissues:
- connective: areolar
-epithelial: simple columnar and simple squamous
Location in the body:
- internal surfaces
- wet areas
- digestive and respiratory systems
Function:
- diffusion, protection, secretion, or absorption
Serous Membrane (name type of tissue, location in body, the function, and types of layers)
Types of Tissues:
- connective: areolar
-epithelial: simple squamous
Location in the body/Function:
- covers organs, NOT open to the outside
-Pericardium(around the heart
-Pleura (around the lungs)
-peritoneum (abdominal cavity)
Layers:
1. Visceral Layer (covers/actually touches the heart)
2. Serous Fluid (decreases friction)
3. Parietal Layer (lines/outside)
Cutaneous Membrane (name type of tissue, location in body, and function)
Types of Tissues:
- connective: areolar and adipose
- epithelial: stratified squamous
Location in the body:
- skin (covers exposed surfaces)
-dry areas
Function:
- protection
Name the Tissue Membrane: Provide smooth surfaces and secretes lubricating fluid between bones
Synovial
Name the Tissue Membrane: Functions in absorption and secretion in moist membranes
Mucous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Function to reduce friction around a beating heard
Serous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Serves as protection from external stress and water loss
Cutaneous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Lines cavities surrounding joints
Synovial
Name the Tissue Membrane: Peritoneum (around internal organs), pleura (around lungs), and pericardium (around heart)
Serous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Makes up the skin
Cutaneous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Lines the digestive tract; stomach and small intestines (simple columnar)
Mucous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Stratified squamous epithelial and loose connective tissue (areolar and adipose)
Cutaneous
Name the Tissue Membrane: Only composed of connective tissue
Synovial