C6- The rate and extent of chemical change
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the rate of a chemical reaction?
How fast the reactants are changed into products
How can you find the speed of a reaction?
-record the amount of product formed over time
-record the amount of reactant used up over time
What do steeper graphs of rate of reaction represent?
faster rates of reaction
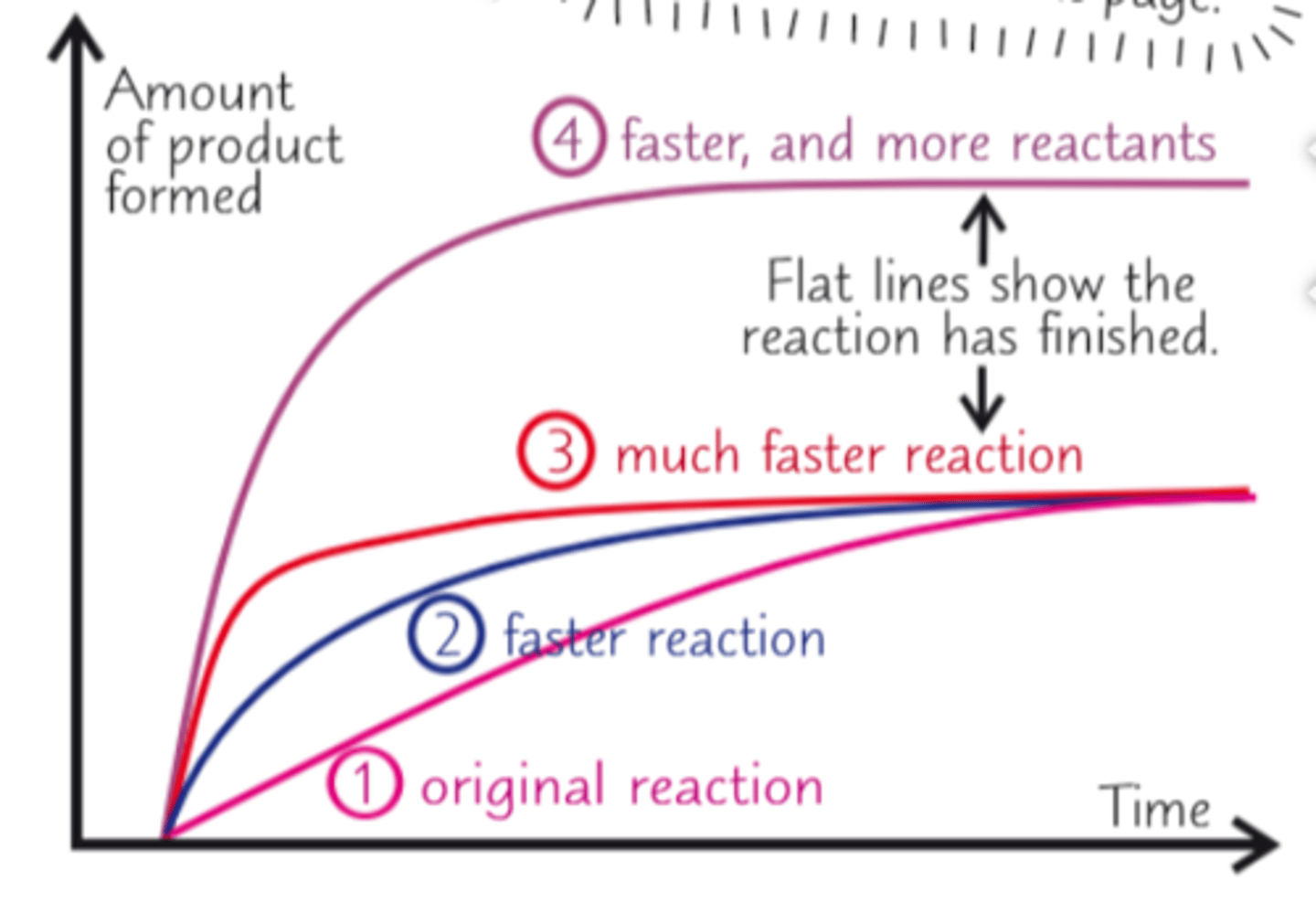
How is a finished reaction presented on a rate of reaction graph?
with a straight line (reactants are used up)
What does the rate of a chemical reaction depend on?
-the collision frequency of the reacting particles (more collisions=faster reaction)
-the energy transferred during a collision
What is the activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy needed for the particles to react (used for breaking bonds
What are the 4 things the rate of reaction depends on?
-temperature
-concentration of a solution/pressure of the gas
-surface area
-the presence/absence of a catalyst
What happens when the temperature is increased?
-the particles move faster
-they collide more frequently (so more succesful collisions)
-the faster they move the more energy they have, so more collisions have enough activation energy
What happens when you increase the concentration/pressure?
-collisions between particles are more frequent (less space)
-leads to more succesful collisions
What happens when you increase the surface area?
-for the same volume of a solid, the particles around it have more area to work on
-leads to more collisions (+more succesful collisions)
What happens when you introduce a catalyst?
-decrease the activation energy needed for the reaction
-provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
What is a catalyst?
-speeds up a reaction
-isn't used up
What are enzymes?
biological catalysts
How do you calculate rate of reaction?

How can you measure a reaction with changing turbidity?
-observe a mark through the solution
-measure how long it takes for it to disappear from vision
(although subjective-people don't agree when the mark disappears)
What is turbidity?
cloudiness
What are three ways of measuring rate of reaction?
-percipitation/colour change
-change in mass
-the volume of gas given off
How do you measure ROR with change in mass?
-usually gas given off
-quicker the reading on the balance drops, faster the reaction
-most accurate of the 3 methods
How do you measure ROR with the volume of gas given off?
-use a gas syringe
-the more gas given off during a certain time interval, the faster the reaction
-fairly accurate
What do magnesium and hydrochloric acid react to produce?
hydrogen gas
How can you investigate the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction with Mg and HCl?
-add a set volume of dilute HCl to a connicle flask and carefully place on a mass balance
-add some magnesium ribbon to the acid and quickly plug the flask with cotton wool
-start the stop watch and record the mass on the balance at regular intervals
-plot the results in a table and work out the mass lost for each reading
-plot a graph of time and loss of mass
-repeat with more concentrated acid solutions (keep other variables the same)
How can you investigate the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction with sodium thiosulphate and HCl?
-add a set volume of dilute sodium thiosulphate to a conicle flask
-place the flask on a piece of paper with a black cross drawn on it
-Add dilute HCl to the flask and start the stopwatch
-time how long it takes to go cloudy.
-repeat the reaction with solutions of either reactant at different concentrations (only 1 at a time) (other variables kept the same)
What do sodium thiosulphate and HCl react to produce?
a cloudy yellow percipitate of sulphur
How do you find the mean rate of reaction?
overall change in y value (where the line goes flat) DIVIDED BY total time
How do you find the rate of reaction at a certain point?
-draw a tangent on the point you are investigating
-pick 2 point that are easy to read
-calculate the gradient with change in y DIVIDED BY change in x
What happens in a reversible reaction when the reactants react?
-reactants concentrations falls
-so forward reaction slows down
-but more and more products are formed
-so the products concentration rises
-and the backwards reaction speed up
What will eventually happen in a reverisble reaction?
-the forward reaction will go at the exact same rate as the backwards one
-so the system is at equilibrium
What happens when a system reaches equilibrium?
-both reactions are still happening
-but there is no overall effect (it's a dynamic equilibrium)
-the concentration of reactant and products have reached a balance and won't change
-only occurs in a closed system
-does NOT mean the amounts of reactants/products are equal
What is a closed system?
none of the reactants/products can escape and nothing else can get in
What is the concentration if the equilibrium lies to the right?
the concentration of products is greater than the reactants
What is the concentration if the equilibrium lies to the left?
the concentration of the reactants is greater than the products
What does the position of equilibrium depend on?
-the temperature
-the pressure (only in gases)
-the concentrations
What is an example of a reversible reaction?
hydrated copper sulphate ⇌ anhydrous copper sulphate+ water
What is Le Chatelier's principle?
-the idea that if you change the condition of a reversible reaction at equilibrium, the system will try to counteract that change
-it can be used to predict the effect of any changes you make to a reaction system
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you decrease the temperature?
-the equilibrium will move in the exothermic direction to produce more heat
-you will get more products for the exothermic reaction
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you increase the temperature?
-the equilibrium will move in the endothermic direction to try to decrease the heat
-you will get more products for the endothermic reaction
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you increase the pressure?
If it is a gas:
-the equilibrium tries to reduce it
-moves in the direction with fewer molecules of gas
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you decrease the pressure?
It it is a gas:
-the equilibrium tries to increase it
-moves in the direction with more molecules of gas
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you increase the concentration of the reactants?
tries to decrease it by making more products
LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE what happens if you decrease the concentration of the reactants?
tries to increase it by making more reactants