DAT Integumentary System Study Guide - Key Terms & Definitions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis?
1. stratum corneum
2. stratum lucidum
3. stratum granulosum
4. stratum spinosum
5. stratum basale
Camilla Likes Good Soft Bread
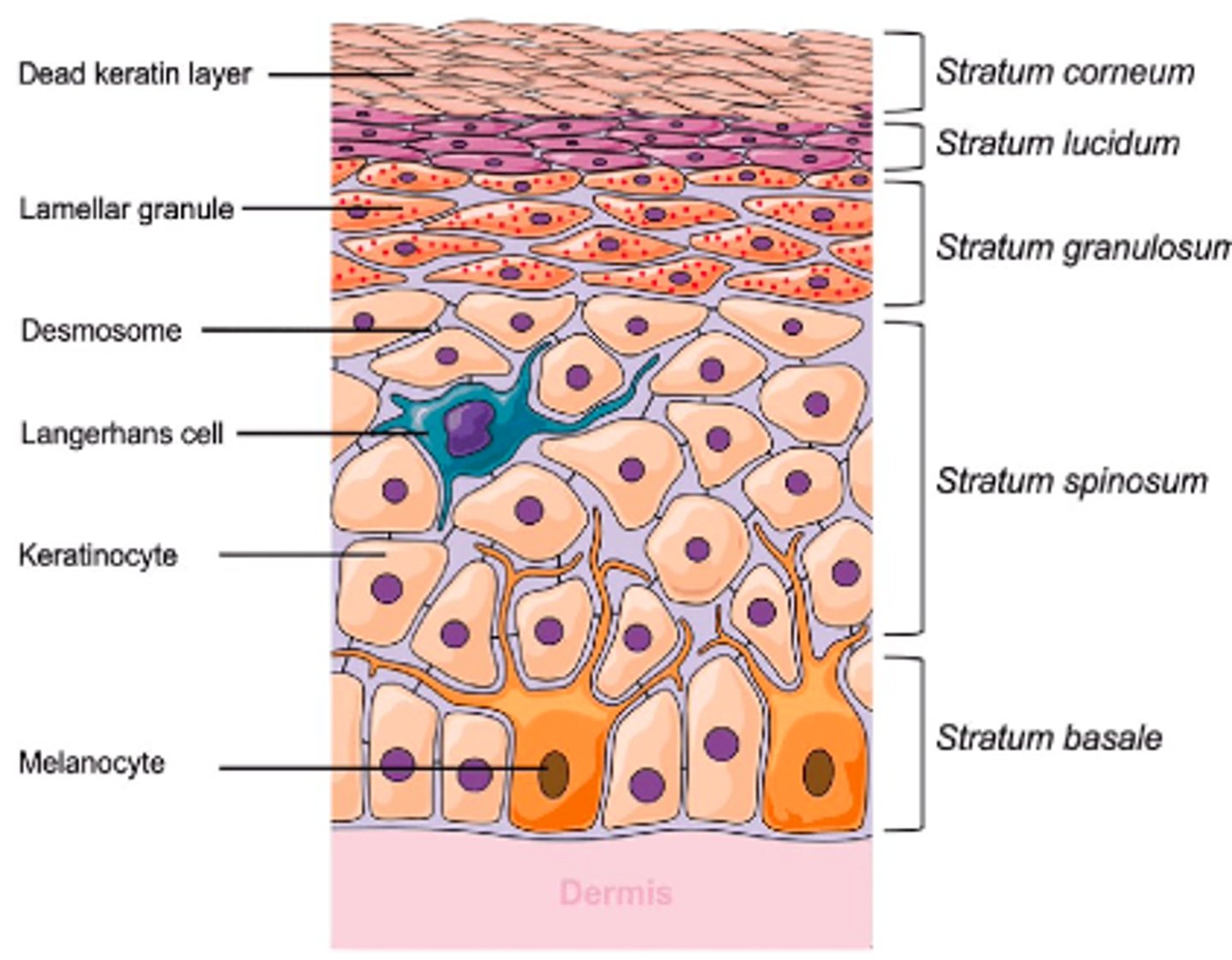
Outermost hydrophobic layer
corneum
3 multiple choice options
Only present in palms of hands & soles of feet
lucidum
3 multiple choice options
Skin cells lose organelles here, begin dying, and are filled with keratin
granulosum
3 multiple choice options
Provides skin strength/flexibility
Held together by desmosomes
spinosum
3 multiple choice options
Deepest layer of the epidermis where new skin cells are formed
basale
3 multiple choice options
Which layer of the skin is avascular?
epidermis
which layer of skin is highly vascularized?
dermis
what are the 2 individual layers of the dermis
1. Papillary Region
2. Reticular Region
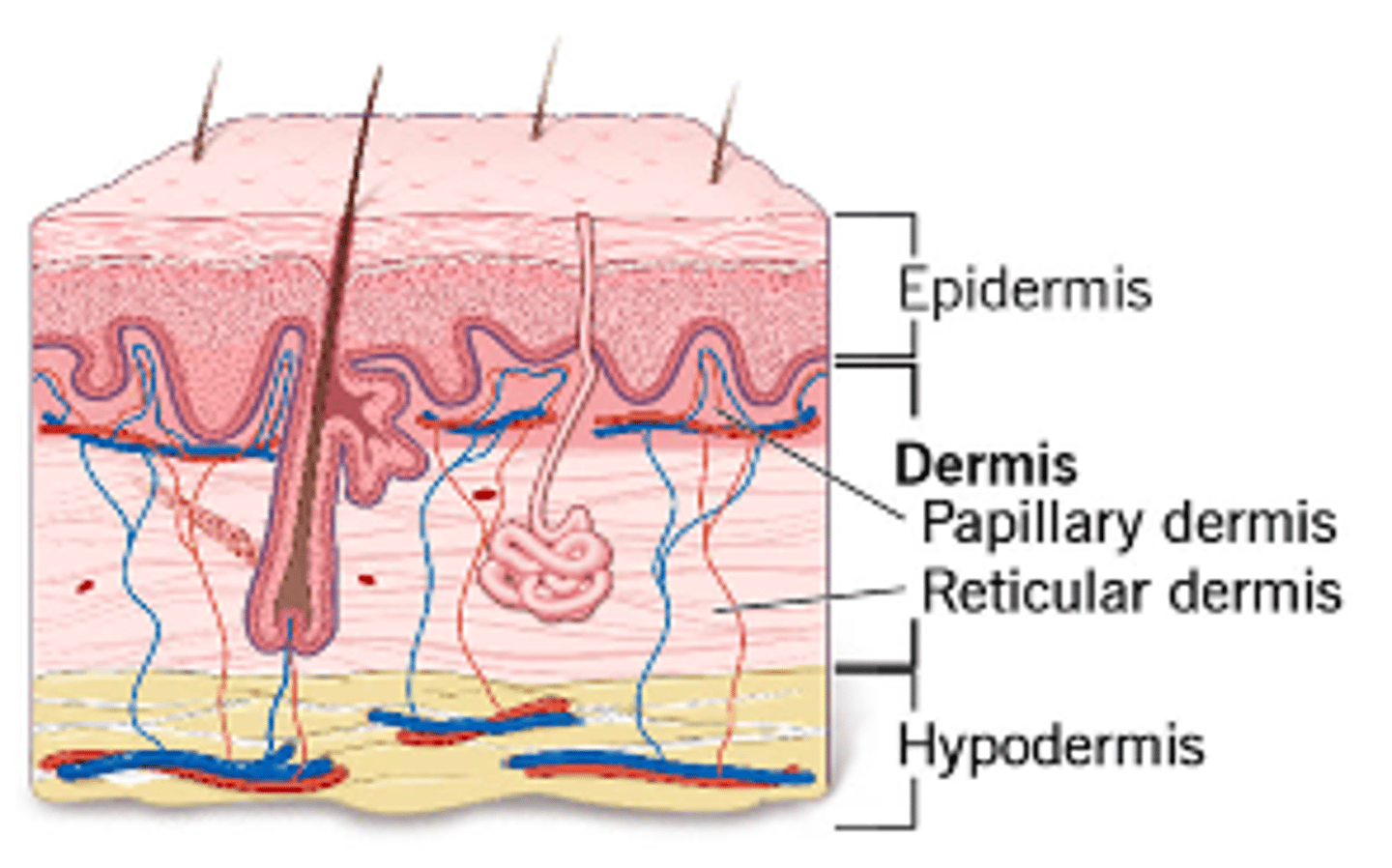
Vascular network within upward projecting papillae
papillary region
2 multiple choice options
what do papillae do?
supply nutrients to epidermis and regulate temperature
Papillae contain ____ _____ which are sensory touch receptors
Meisner's corpuscles
Region with dense connective tissue, collagen & elastic fibers; packed with glands, sweat gland ducts, fat, and hair follicles
reticular region
2 multiple choice options
Consists of areolar & adipose tissue
Contains pressure sensing nerve ending & passage for blood vessels
hypodermis region
2 multiple choice options
what is the function of the hypodermis region
fat storage, heat insulation, shock absorption
what are the 4 epidermal cells?
keratinocytes, melanocytes, merkel cells, langerhans cells
Transfers skin pigment melanin to keratinocytes
melanocytes
3 multiple choice options
Attach to sensory neurons and functions in touch sensations
merkel cells
3 multiple choice options
Produce keratin
Help waterproof
keratinocytes
3 multiple choice options
Interact with immune cells
langerhans cells
3 multiple choice options
What are the 6 functions of the skin?
1. thermoregulation
2. environmental sensory input
3. vitamin D synthesis
4. protection
5. immunity
6. excretion
how does the skin aid in thermoregulation?
Capillaries dilate to release heat & constrict to preserve heat
Sweat releases onto skin and evaporates to cool us down
What are goosebumps?
occurs when cold, elevates hairs to trap heat

how is the skin able to synthesize vitamin D
UV radiation activates skin molecules
what are the 2 kinds of sweat glands?
eccrine and apocrine
Opens directly to skin
located on majority of the skin.
Regulates temperature through perspiration and urea elimination
eccrine glands
2 multiple choice options
Opens to hair follicles; more viscous secretions.
Located: armpits, pubic region, nipples
apocrine glands
2 multiple choice options
Connected to hair follicles
Secrete oil (sebum) that discourage microbial growth
sebaceous glands
2 multiple choice options
Found in ear canal & produce
a wax-like material that acts as a barrier to entrance
ceruminous glands
3 multiple choice options
Column of keratinized cells held tightly together
Unique to the skin of mammals
hair