Lectures 20-21: Regulation of Adaptive Immunity
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Immunological Tolerance
unresponsiveness to self antigens
Immature lymphocytes become tolerant to an antigen if they _____
Encounter it early in fetal life
What are the two types of T cell tolerance mechanisms?
1. Central tolerance
2. Peripheral tolerance
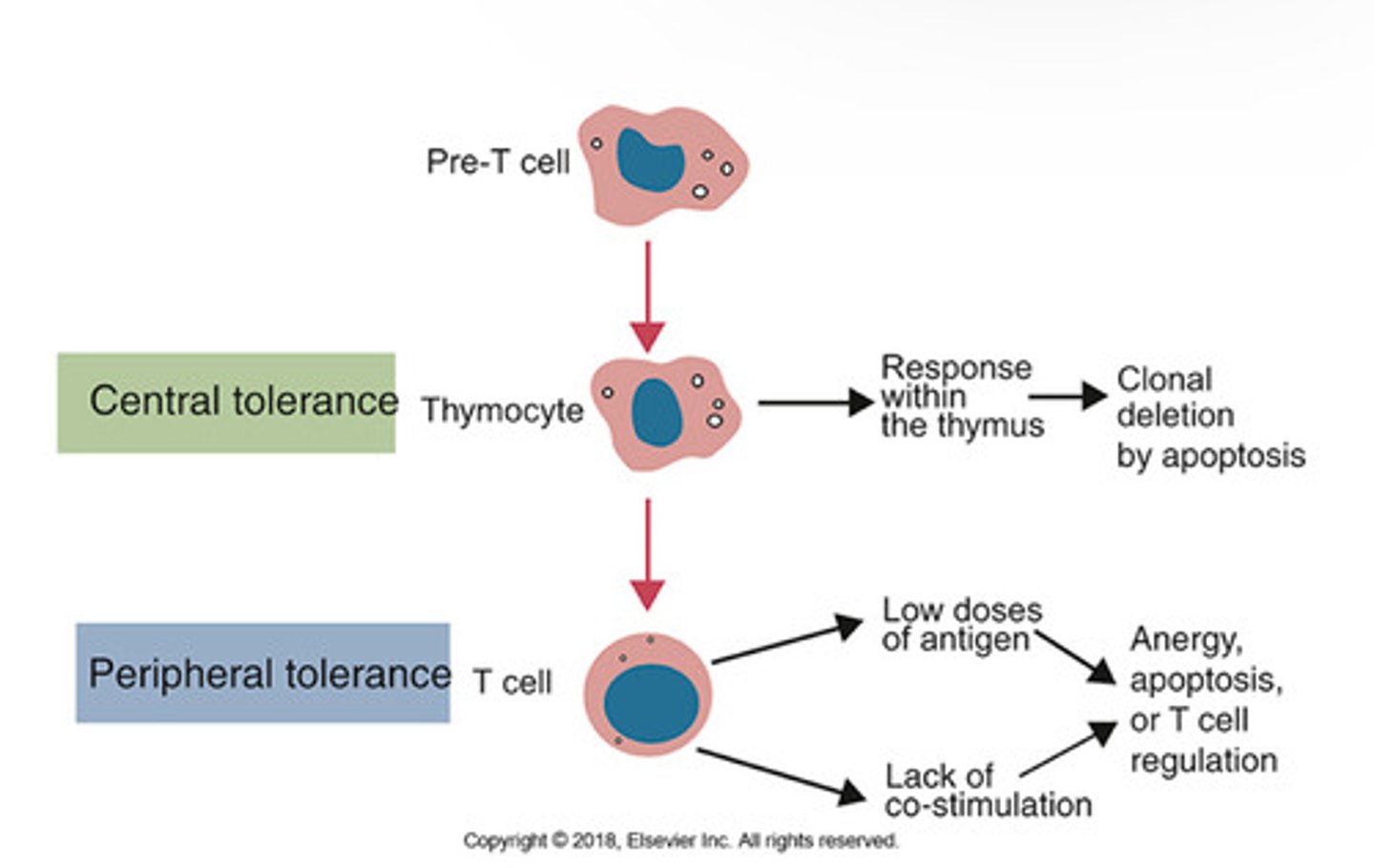
Describe Central and Peripheral Tolerance.
What is AIRE?
autoimmune regulator, transcrptional factor
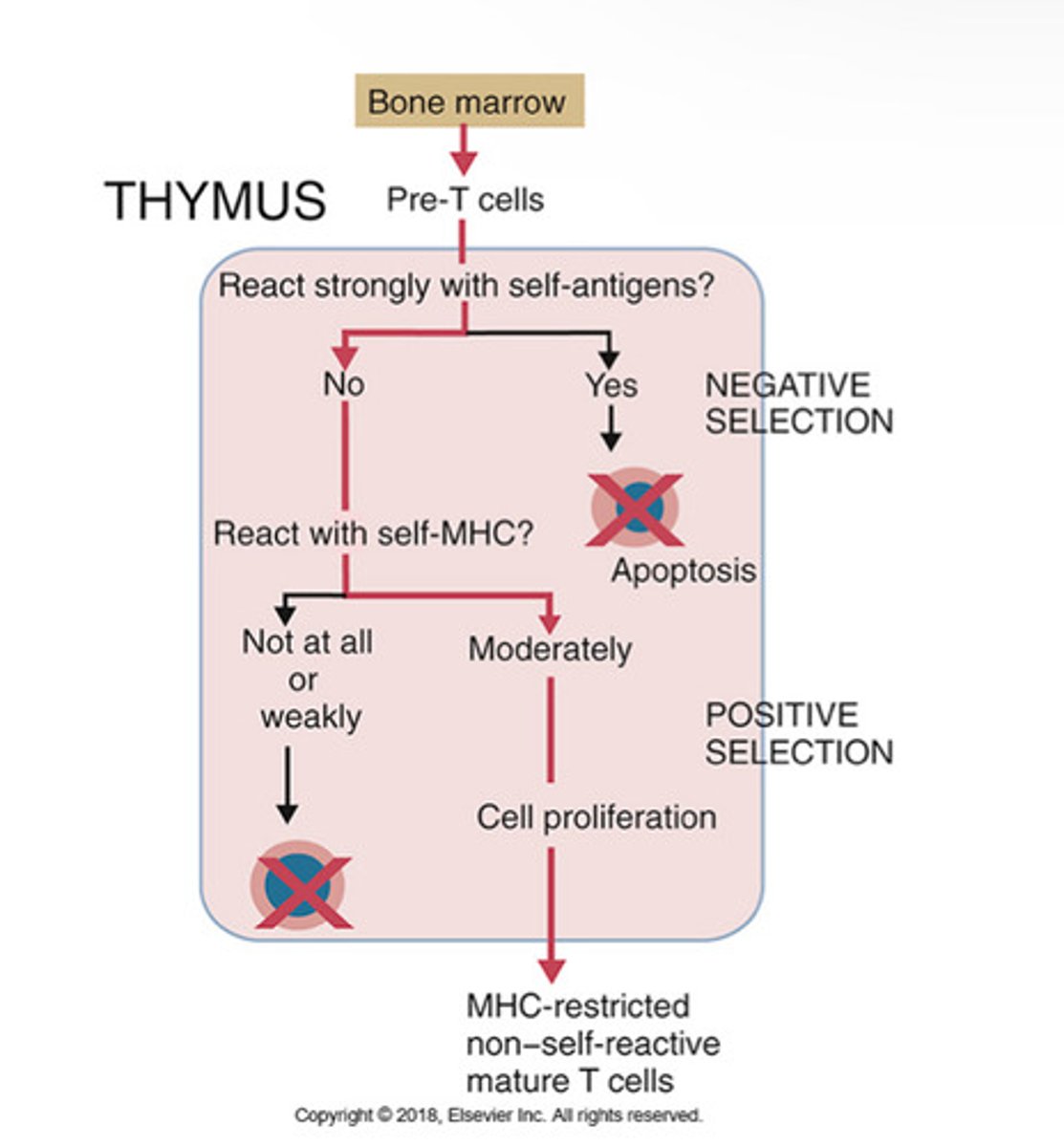
Central T cell tolerance in the thymus:
Negative Selection: if T cell does not react strongly to self, it is kept. If it does react strongly to self, apoptosis happens.
Postive Selection: if T cell reacts with self-MHC, it goes onto cell proliferation. If it doesnt react, apoptosis happens.
Outcome: MHC-restricted non-self reactive mature T cells
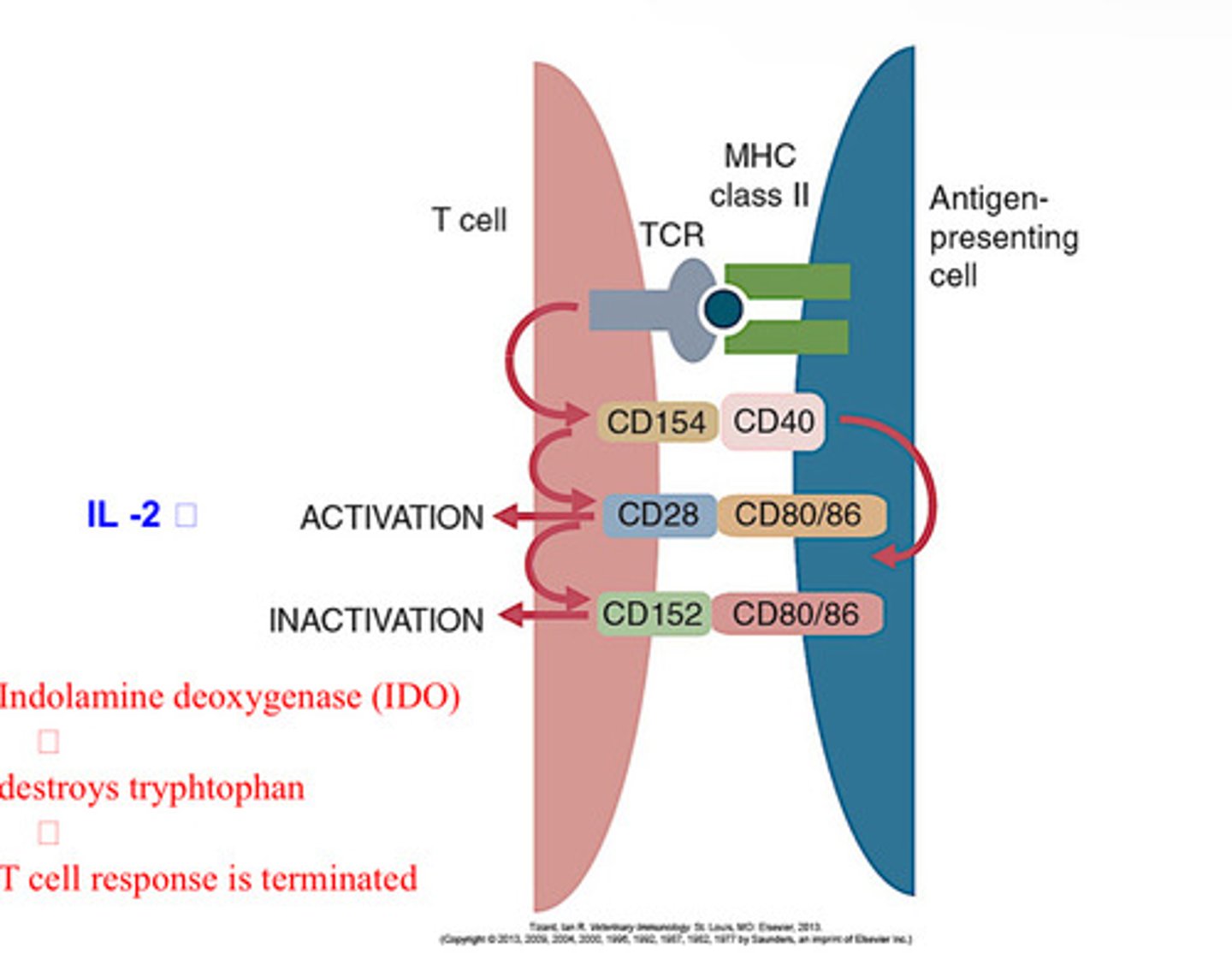
Lack of co-stimulation leads to ______.
Peripheral T cell tolerance
Anergy
Long-lived functional inactivation that occurs when these cells recognize antigens without adequate lveles of co-stimulators that are needed for full T cell activation
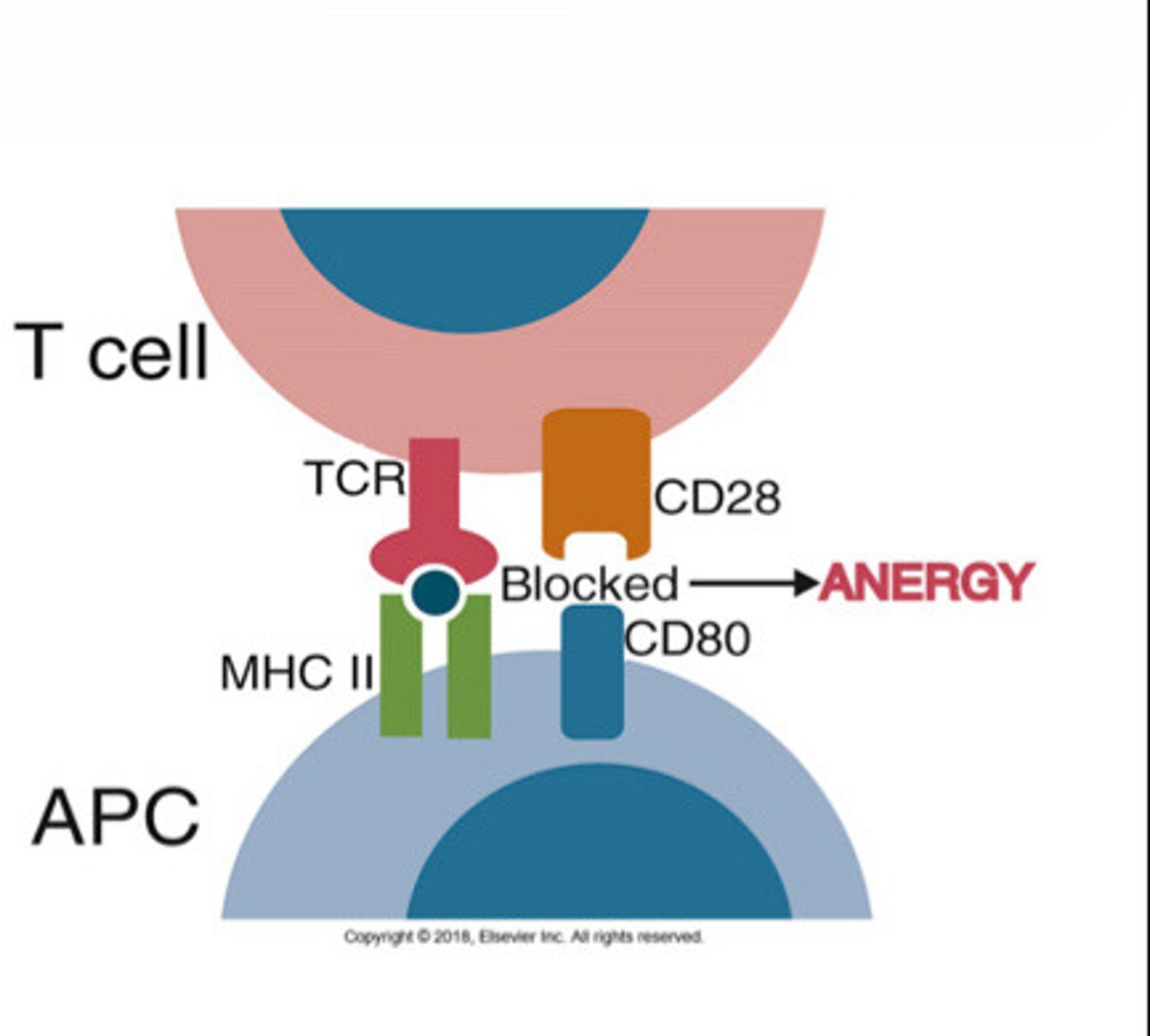
The absence of co-stimulatory molecules on APCs results in T cell _____.
Anergy
What is the function of T reg cells?
-suppress other effector T cells
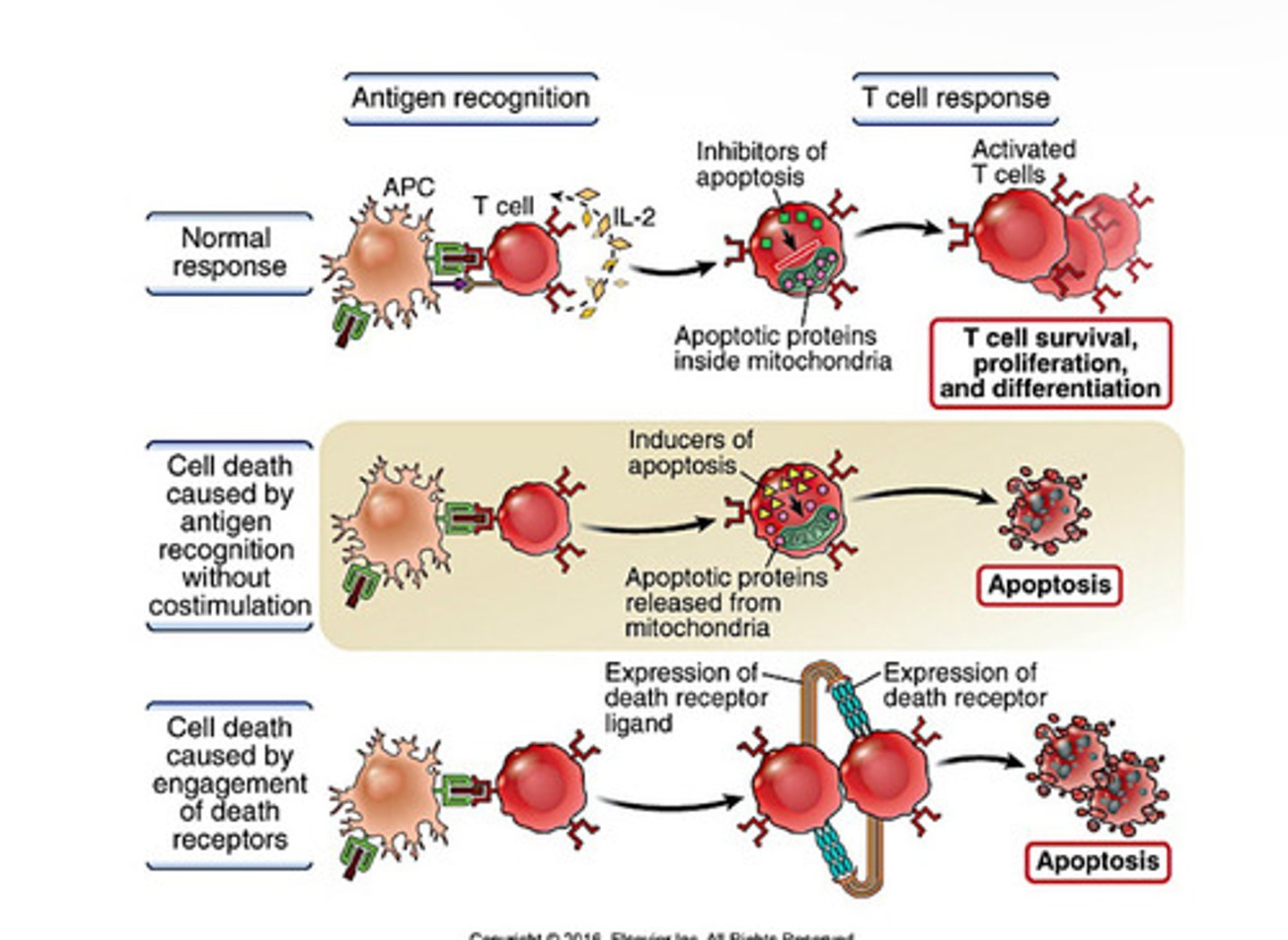
Mechanisms of Apoptosis of T cells
Tolerogenic vs Immunogenic Antigens
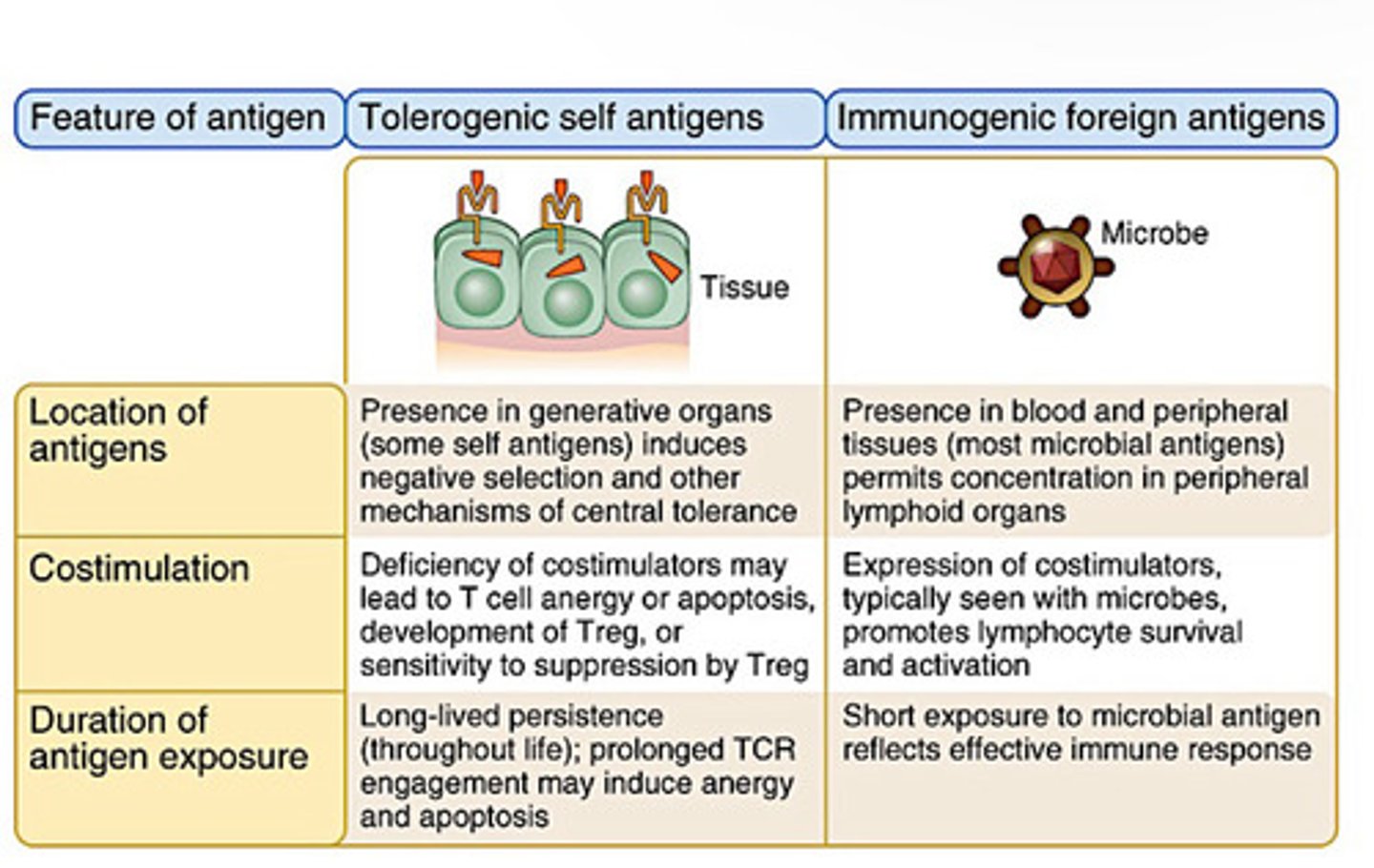
Central B cell tolerance
-immature B cells that recognize self antigens in the bone marrow with high affinity either change their specificity or are deleted
-recognize with low affinity become anergic
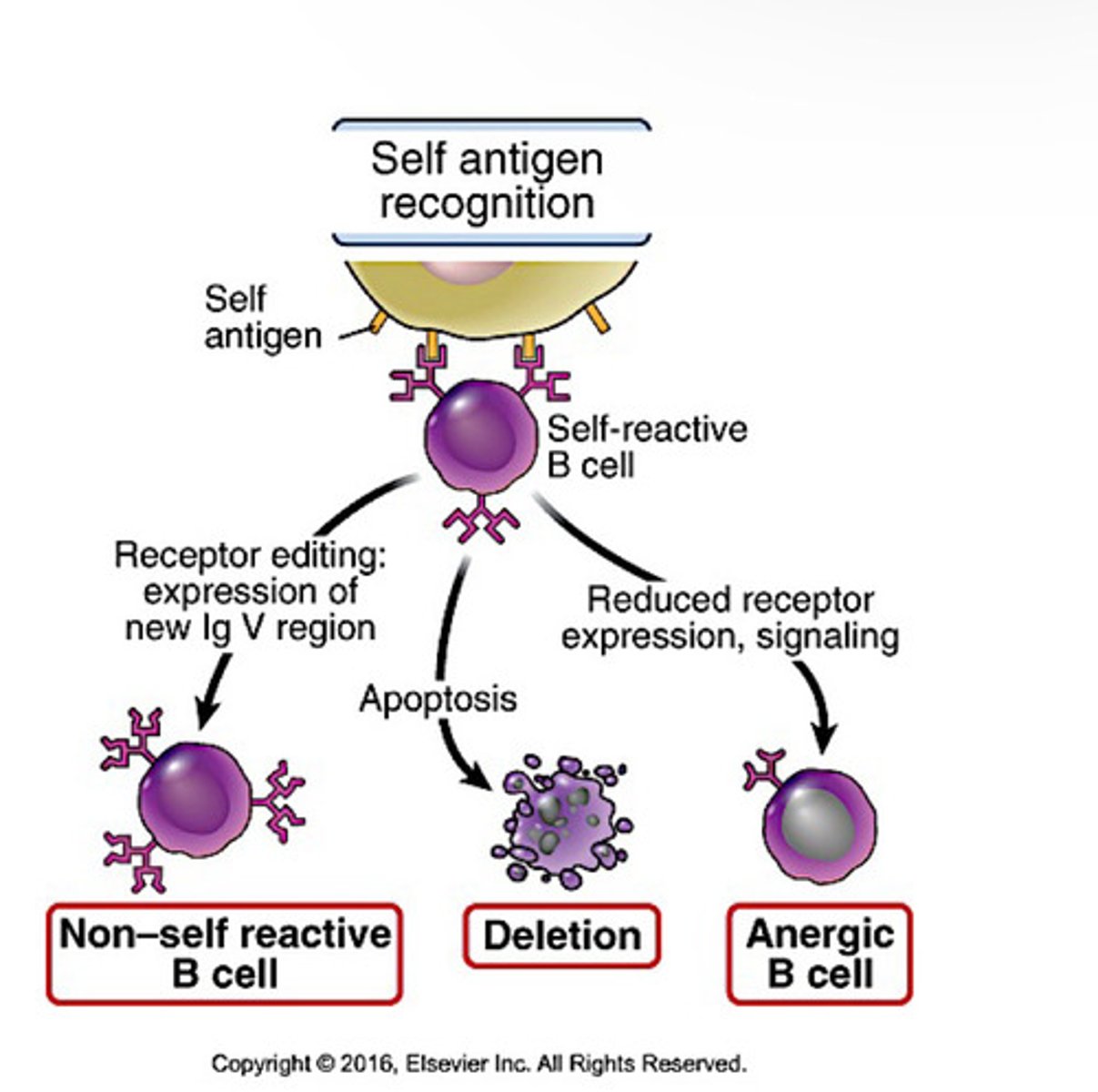
Peripheral B cell tolerance
-mature B cells that recognize self in peripheral tissues in the absence of T cells become anergic or die by apoptosis
-no Th cell help because T cells specific to self are deleted
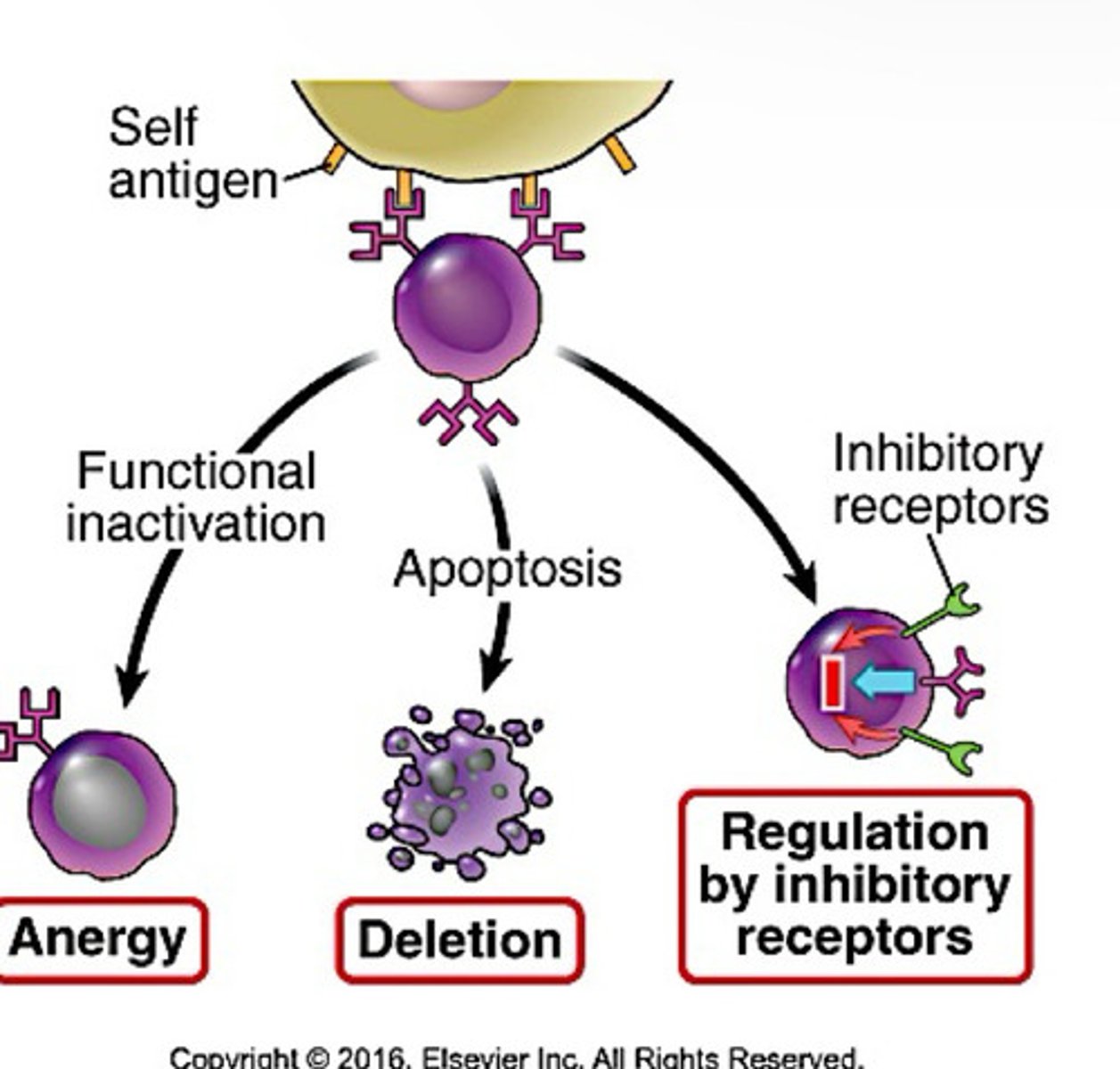
Inhibitory Receptors on B Cells
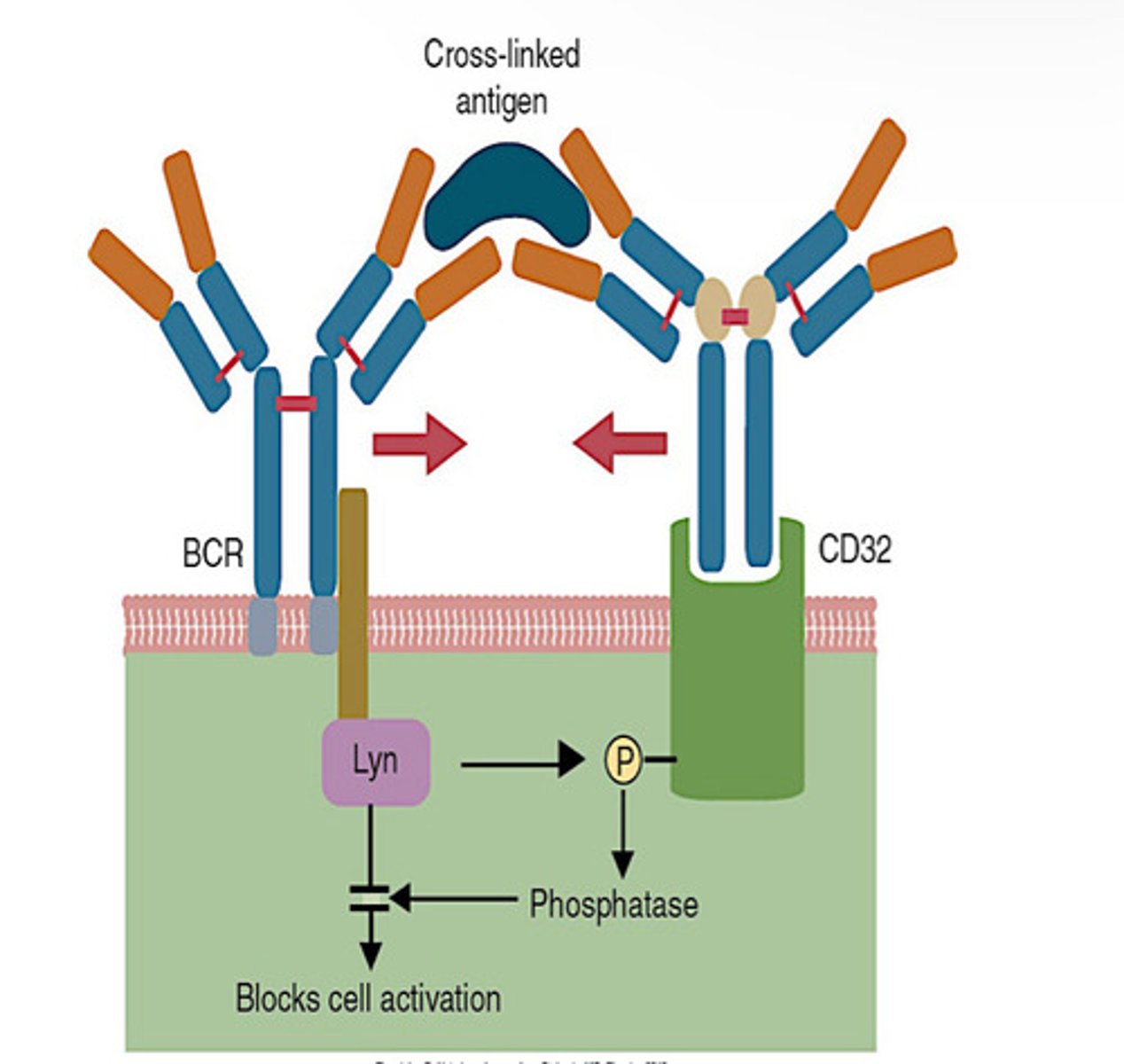
Inhibitory Receptor on T Cells
IL-2
-Secreted by all T cells
-Stimulates growth of helper, cytotoxic, and regulatory T cells, and NK cells
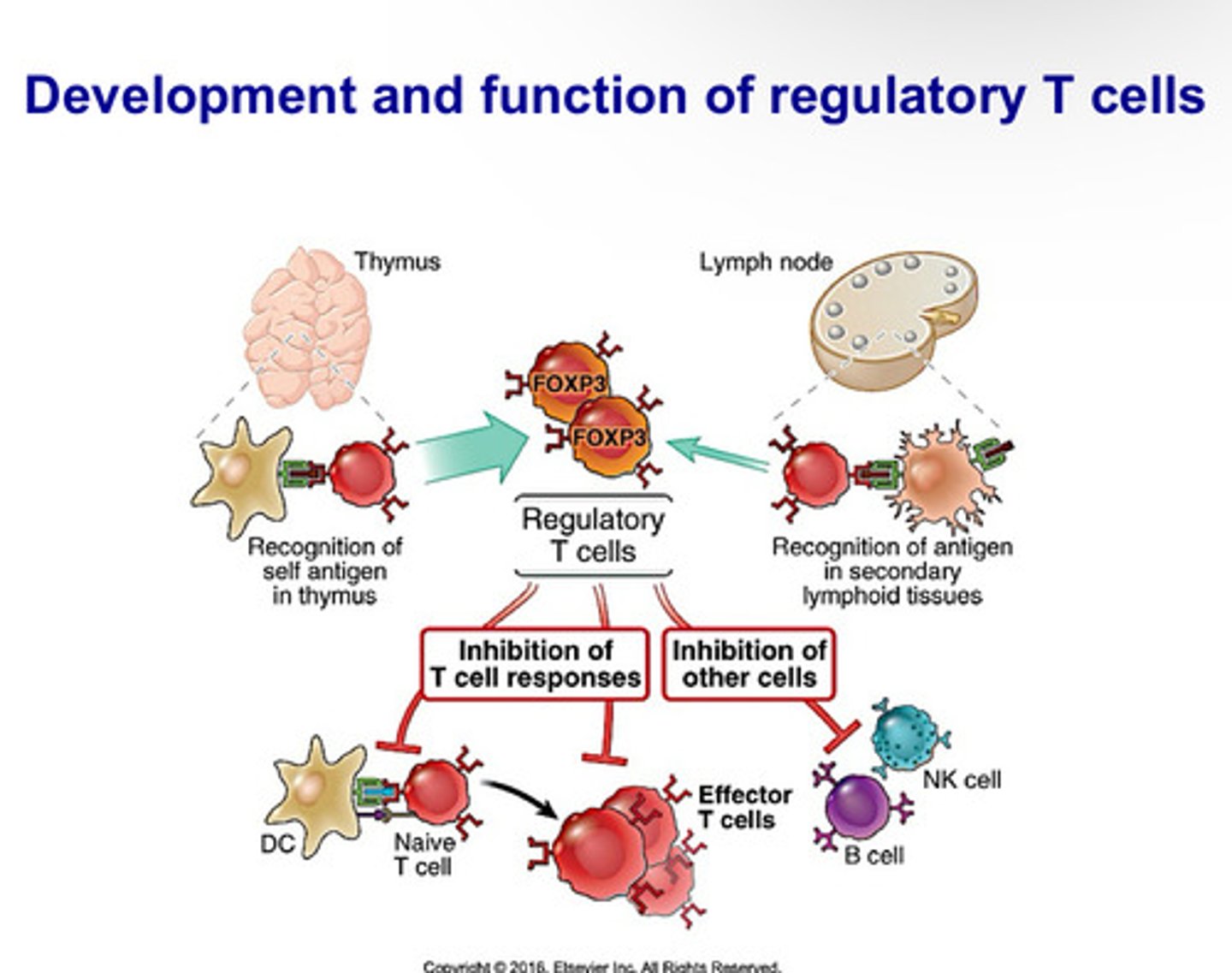
Treg cells
-regulate immune system and maintain balance between peripheral tolerance and immunity
-multiorgan autoimmune disease is a result if none
-some develop naturally, some are induced by cytokines
-express CD4 and CD25
-al activated T cells express CD25, but T regs are the only ones that express it when naive
-use FoxP3
What are the two things Tregs express?
CD4 and CD25
What transcriptional factor does T reg cells use?
FoxP3
Natural T reg Cells
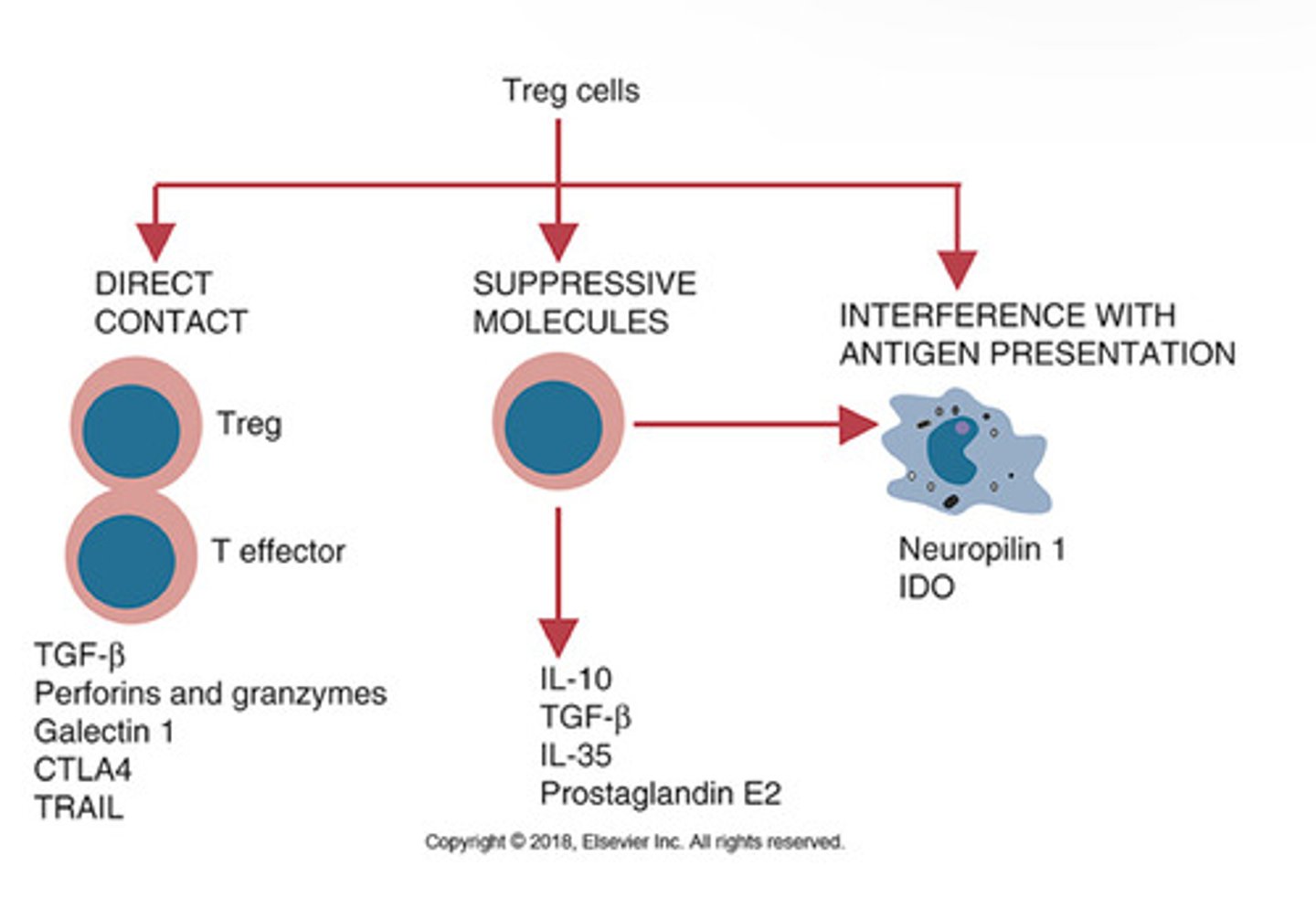
Originate in thymus. Act by direct cell to cell contact and delivery of immunosuppressive molecules through gap junctions, membrane bound suppressive cytokines, production of cytotoxic granzymes and perforins, or by CTLA-4 reverse signaling through CD80
Induced T reg Cells
Produced in secondary lymphoid organsm especially in intestine. Act by using immunosuppressive molecules
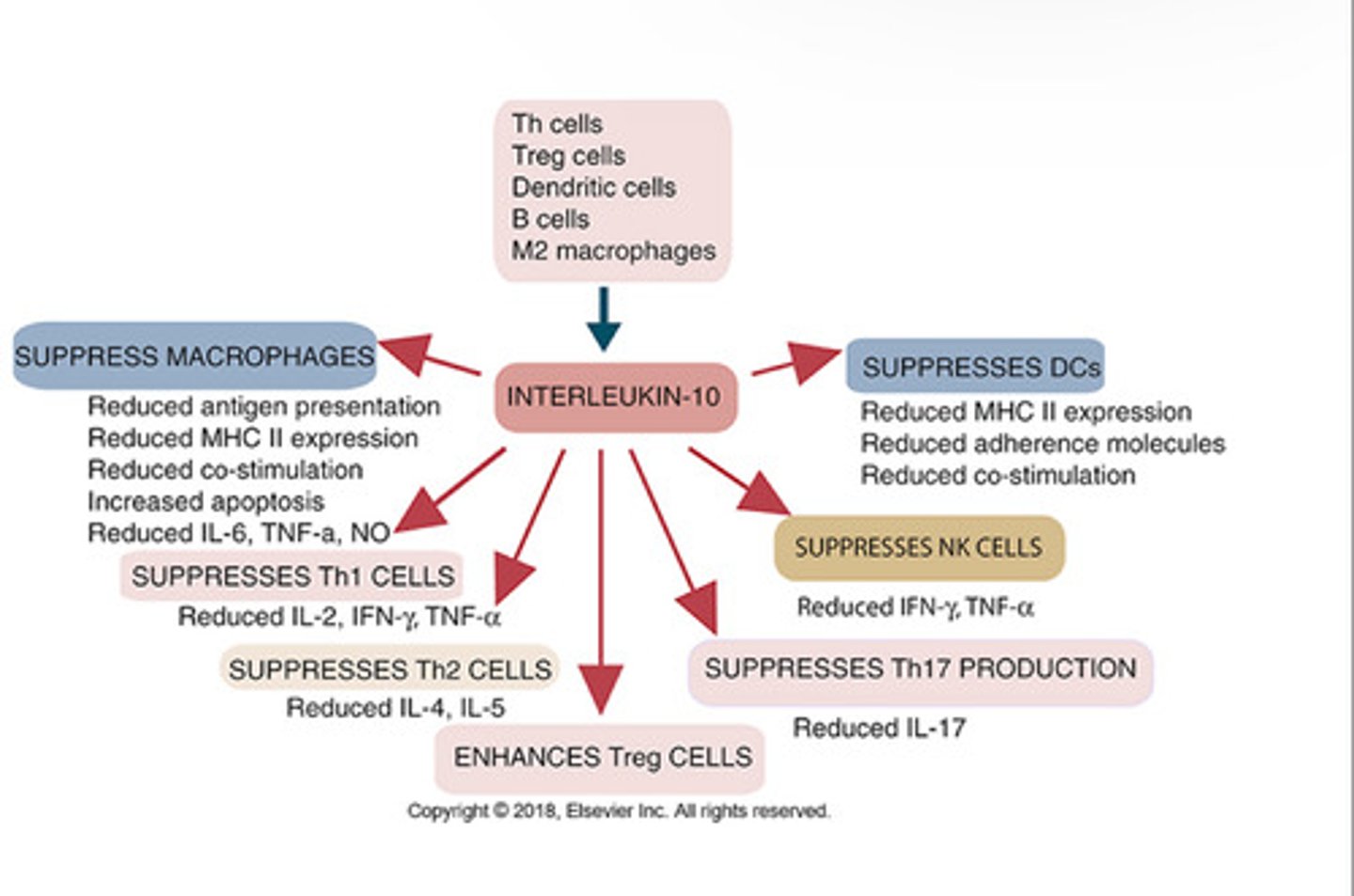
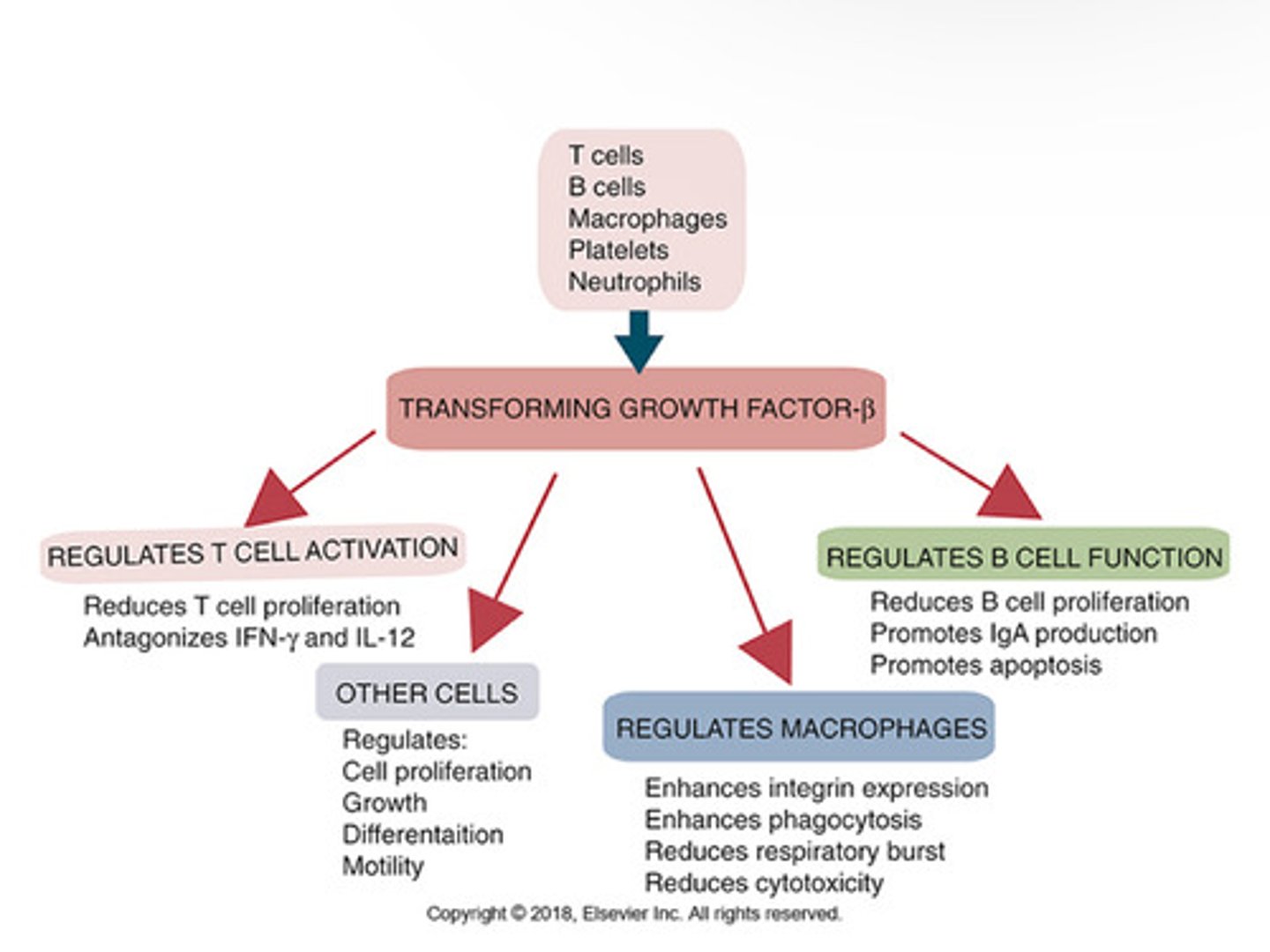
IL-10 and TGF-beta have ______ on innate and adaptive immune repsponses.
IL-10 _____ TCR-indiced intracellular signaling. It inhibits macrophage actication and inflammatory cytokine secretion. They also block APC function, T helper cell proliferation, and IL-2 production. Lacks _____.
Downregulates, IL-2
TGF-beta _____ macrophage and NK cell activation; blocks proliferation of T cells. Also blocks IL- production, downreglates Ig synthesis, and interferes with stimulatory effects of IL-2 on T and B cells.
Inhibits
Mechanisms of T reg suppression
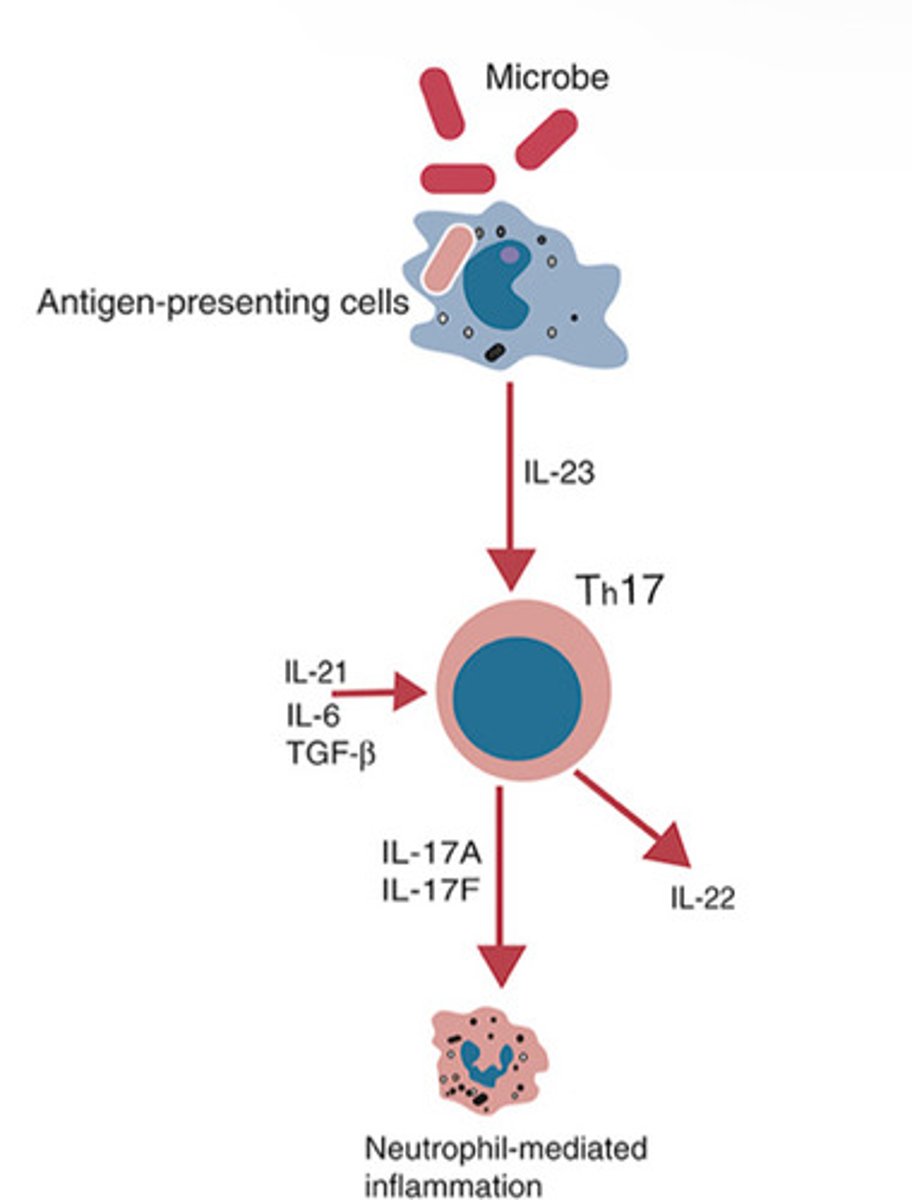
How are Th17 cells produced?
Th0 interaction with IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-21
Origin and Properties of IL-10
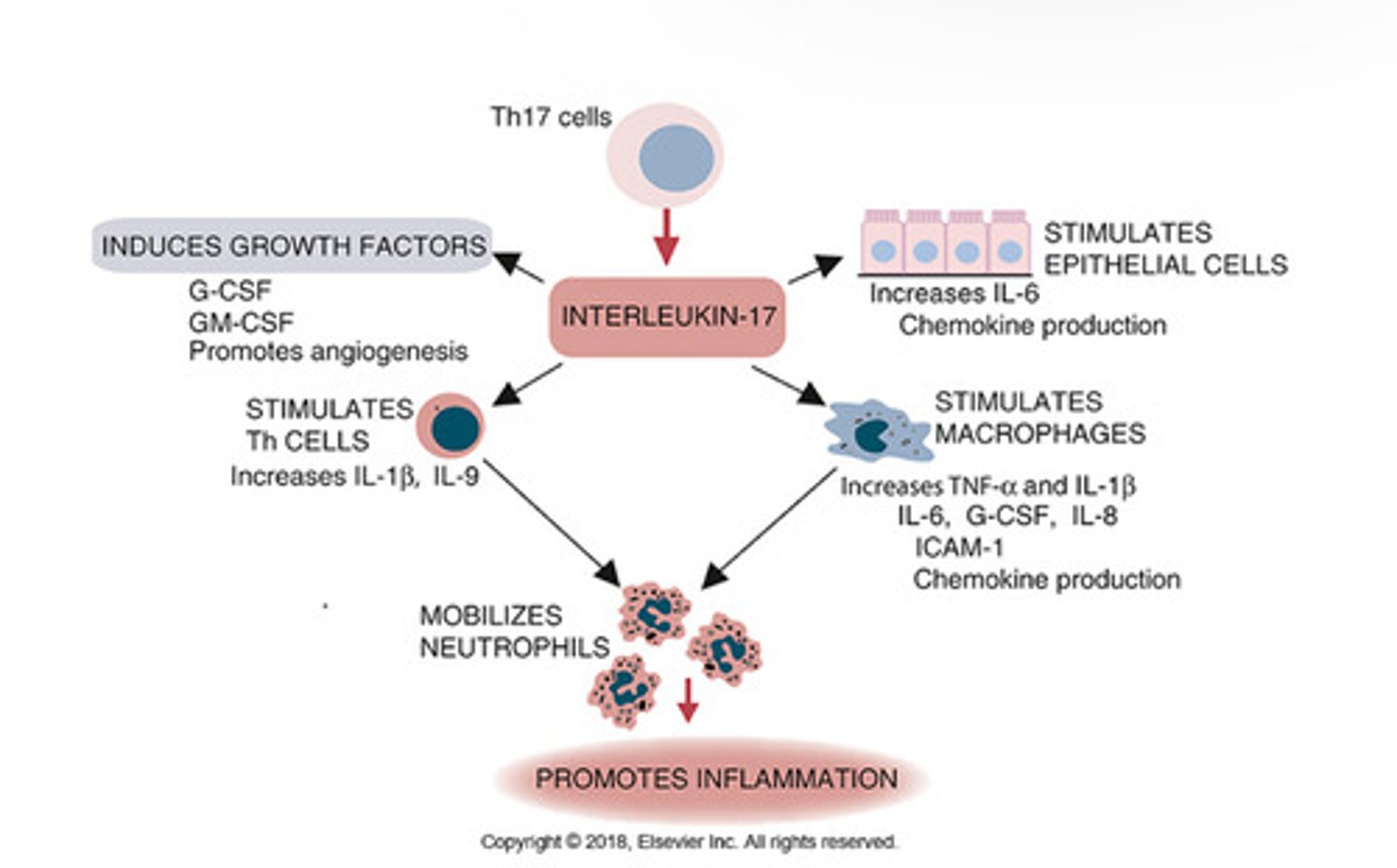
IL-17
-Stimulation of acute inflammation
-increased cytokine production in macrophages and endothelial cells
-Associated with allergic responses and a crucial cytokine in Th17 CD4+ T cell response.
Origin and Properties of TGF-beta
Immune deviation
A phenomenon in which an adaptive response that has the potential to cause direct or indirect tissue damage is converted to a less harmful response
How is immune deviation caused?
Bias towards the differntation of specific type of effector T helper cell following the activation of a naive T cell
Example of Immune Deviation:
Eye tissues are senstive to TH1 responses; factors within the microenvironment of the eye direct TH2 responses
immune privelege sites
Regions naturally less subject to immune responses than most areas of the body
What are the immune privileged sites?
CNS, brain, eyes, and testes
Why does immune privilege exist?
collateral damage accompanying typical immune responses would irreplaceably damage these highly sensitive tissues
intestinal microflora
microorganisms that inhabit the large intestine
Innate and adaptive leukocytes in a healthy gut ______ mount aggressive inflammatory responses against the intestinal microbiotia.
Do not
What is critical for maintaing overall gut immune homeostasis and oral tolerance to food antigens?
Commensal bacteria
What does the gut microbiota affect?
DCs and reg T cells
DCs that interact with certain species of commensal bacteria are
Tolerogenic and differentate TH0 cells to T reg cells; results in anti-inflammatory microenvironment in healthy gut
T cells must be made tolerant to self-antigens.
This may be accomplished through central tolerance whereby self-reactive T cells are killed.
Alternatively, it may be achieved through peripheral tolerance whereby these T cells are
"turned off" by inappropriate signaling.
B cells are much harder to tolerize than T cells.
They are generally regulated by peripheral mechanisms and by the absence of T cell help.
Antigens stimulate immune responses, although very low or very high doses of antigen may cause
tolerance.
Antibodies tend to regulate antibody production through negative feedback mechanisms. This can prevent the successful vaccination of newborn
animals as a result of maternal immunity.
Immune responses may also be controlled by the activities of regulatory T cells (Treg cells). These Treg cells secrete cytokines such as IL-10 and
TGF-β.
Another T cell subset, Th17 cells, regulates inflammation by secreting a cytokine called
interleukin-17 (IL-17).