cell bio lab 1
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
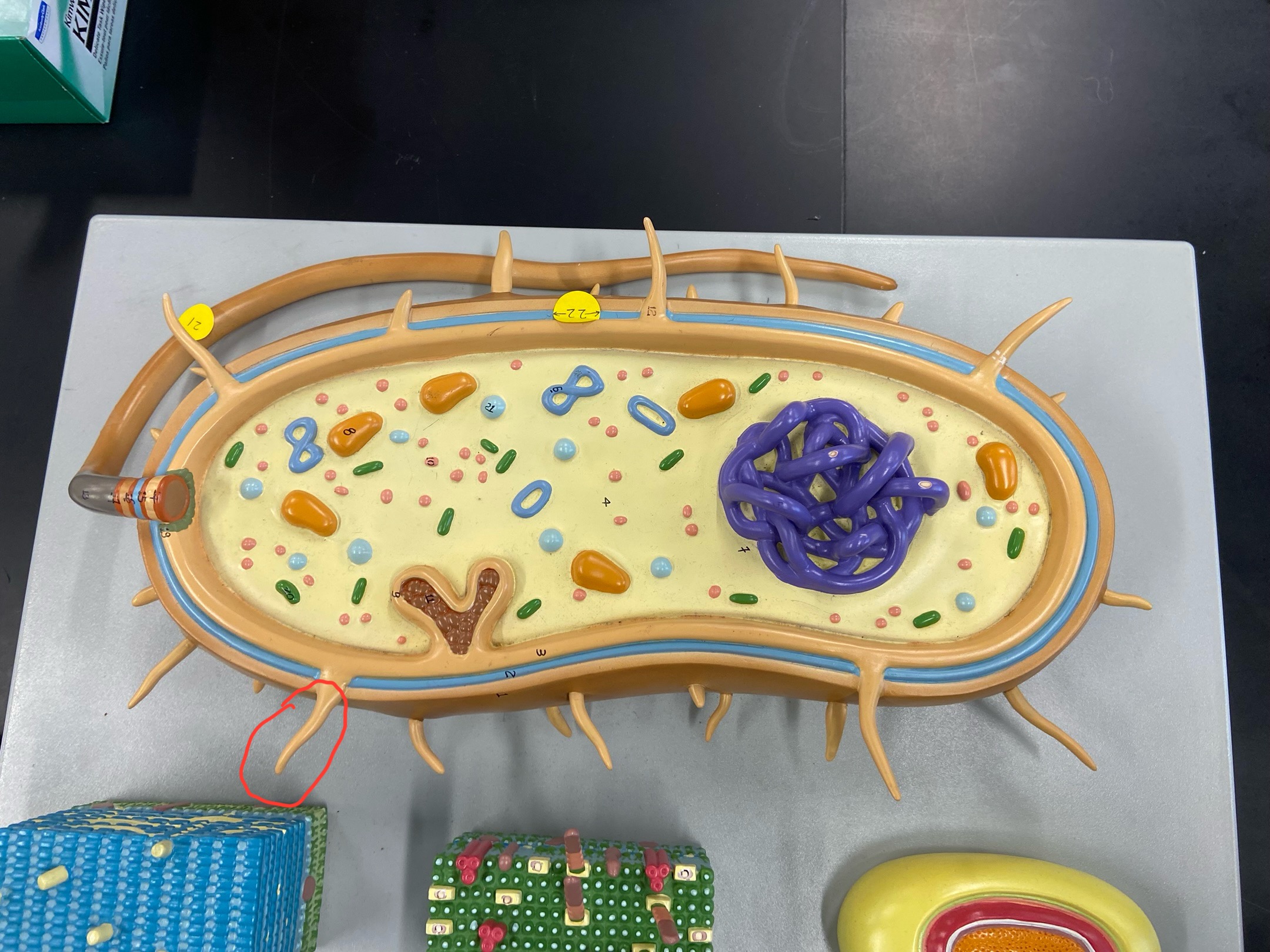
Fimbria
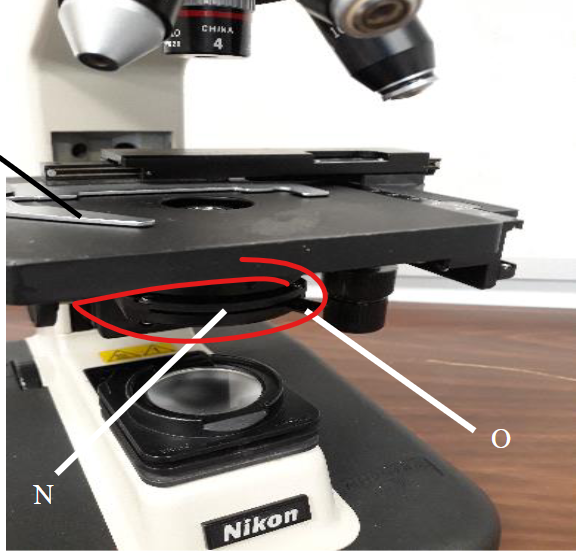

condenser lens
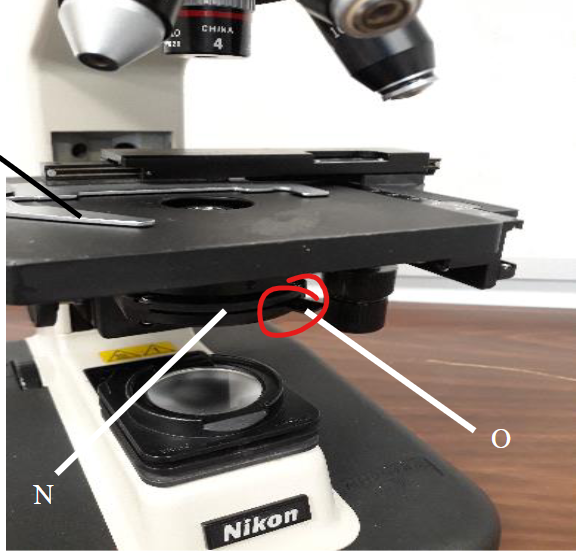

diaphragm
scanning power
ocular lens magnification: 10x
object lenes magnification: 4x
total 40x
low power
ocular lens magnification: 10x
object lenes magnification: 10x
total 100x
high power
ocular lens magnification: 10x
object lenes magnification: 40x
total 400x
oil immersion
ocular lens magnification: 10x
object lenes magnification: 100x
total 1000x
property “e” demonstrated
inversion
property “colored thread” demonstrated
depth
light microscope
light bounce off
electron microscope
pass through
why Robert Hooke important in cell biology?
saw a cell wall in a cork and coined the term "cell"
electron microscope invented?
1930s
Transmisson electron microscope
Embedded in resin and thinner sections
It shows the internal cellular structure
Scanning Electron Microscope
Covered in thin layer of gold or other metal
Shows surface detail and structure
4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
DAPI = blue
Tetramethylrhodamine
TRITC = bright orange
Allophycocyanin
APC = Red
Green fluorescent protein
GFP = Green
unique about the dyes used in fluorescent microcopy?
The dyes absorb light at one wavelength and give off light at a different wavelength
light microscope invented?
1600s
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek the first to do?
observed living microscopic organisms
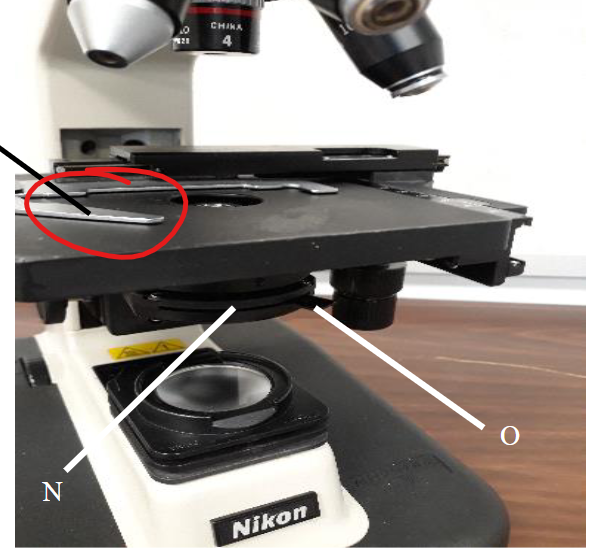

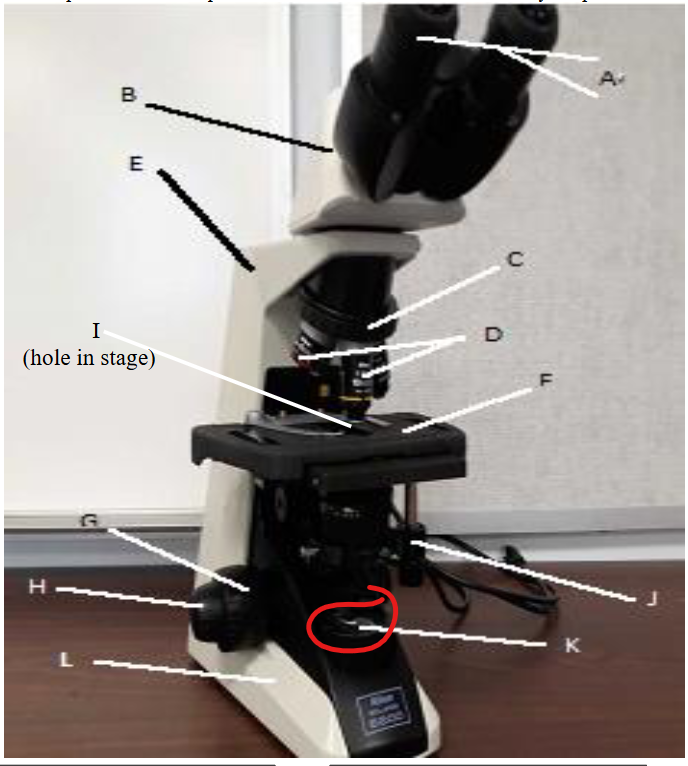
stage clip
lamp
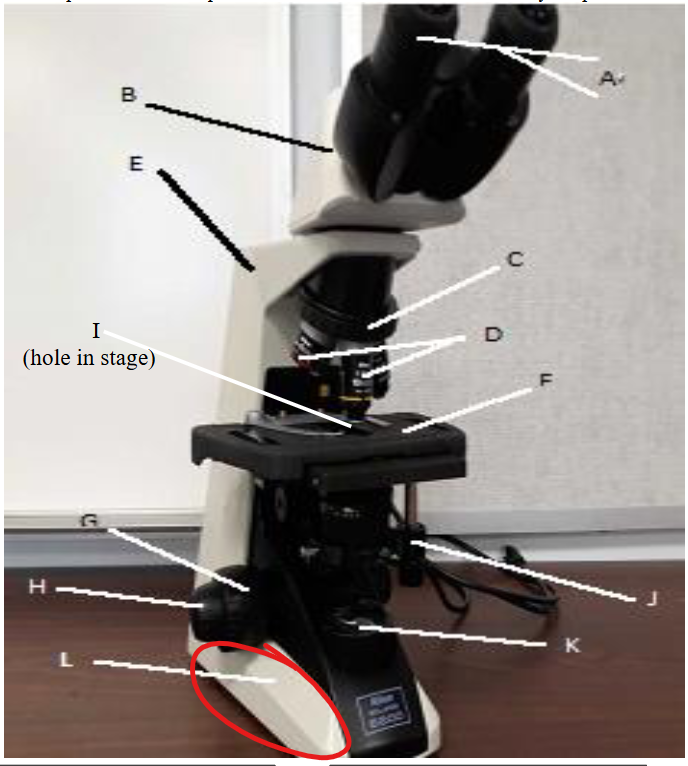
base
fine focus knob
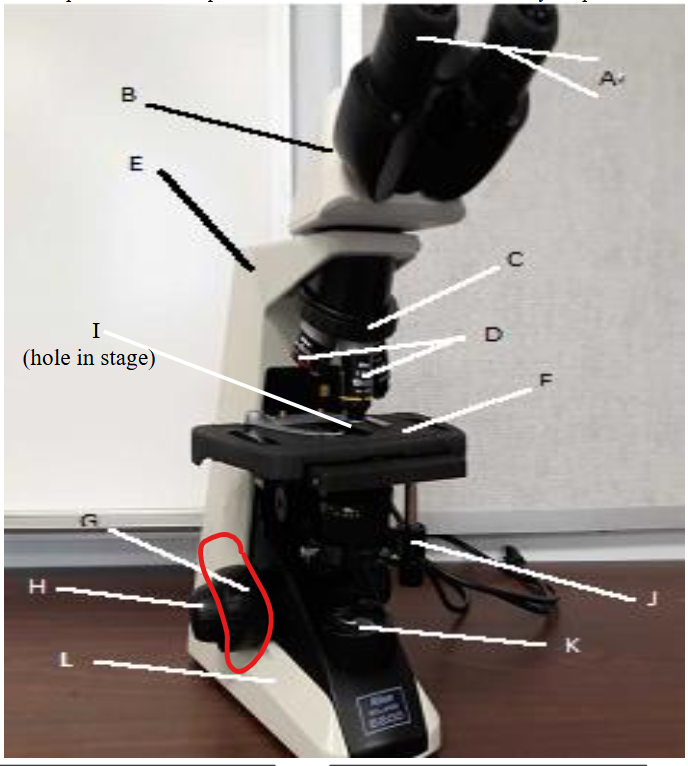
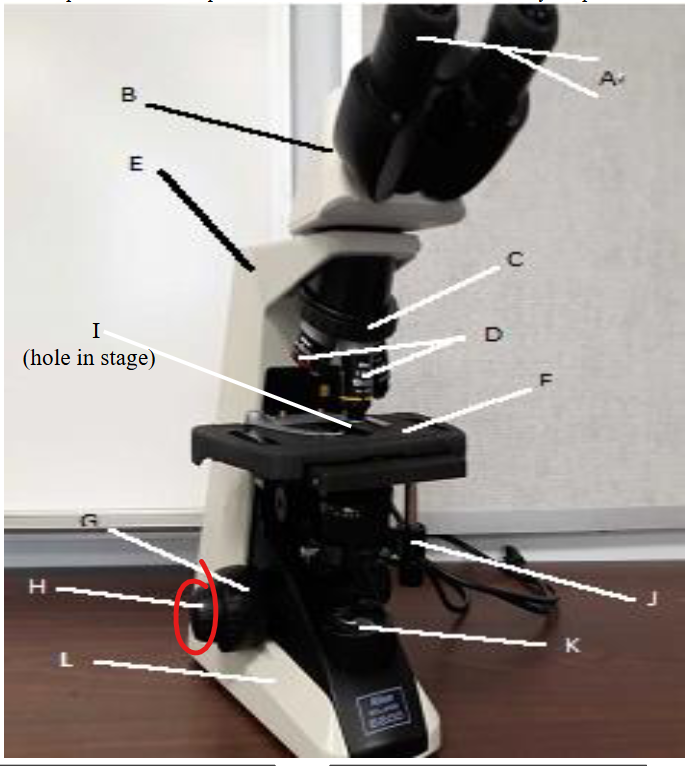
coarse focus knob
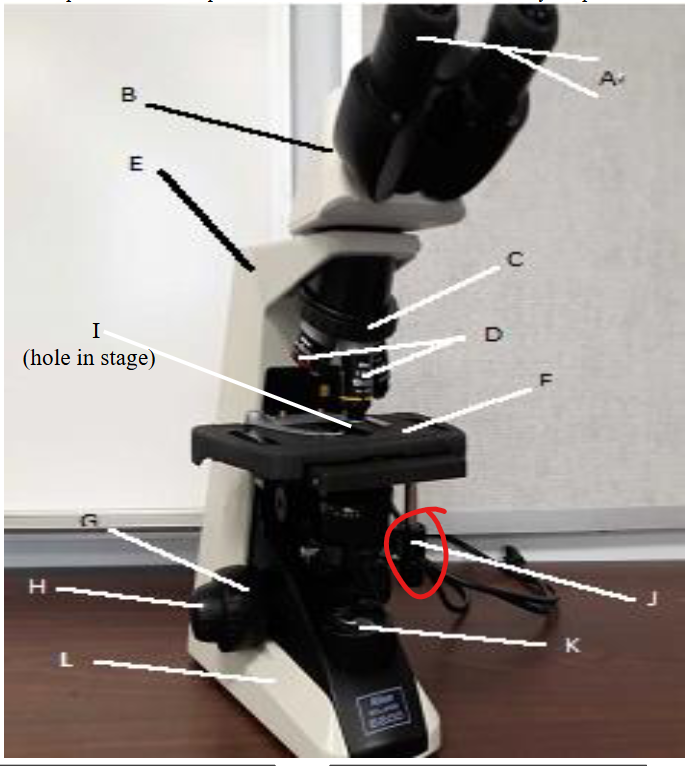
mechanical stage knobs
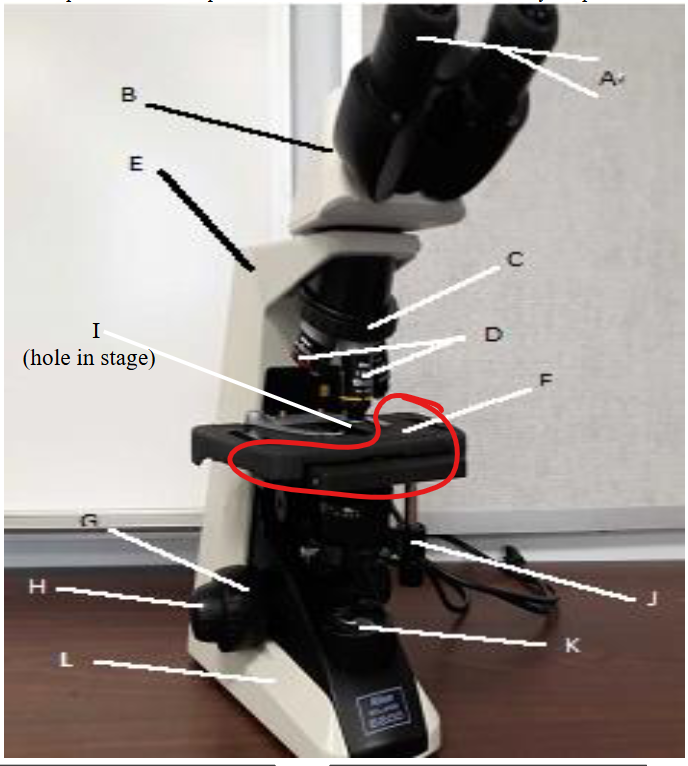
stage
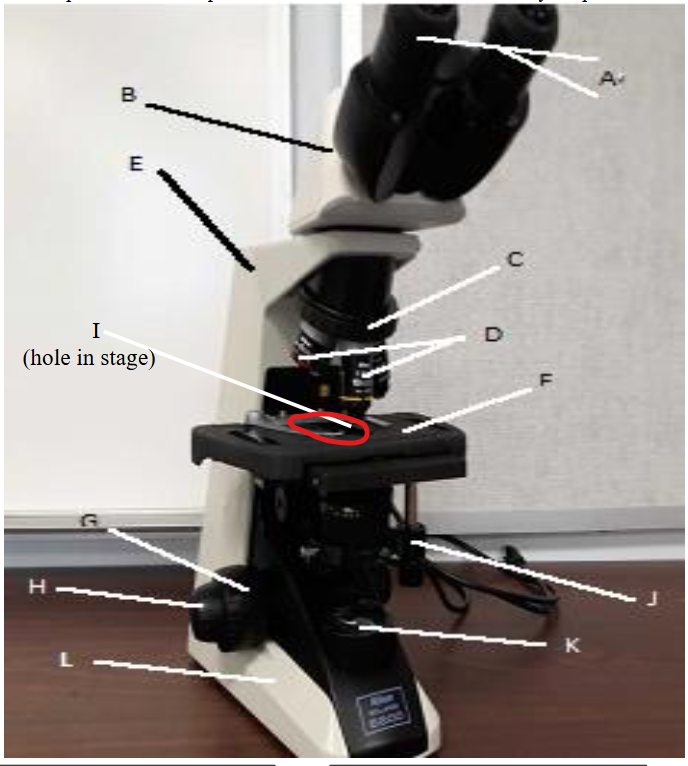
aperture
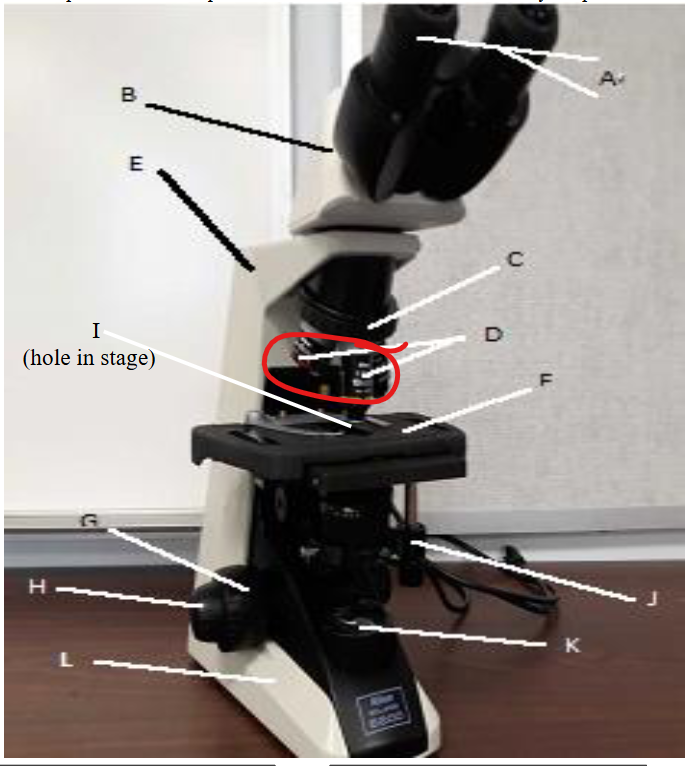
objective lens
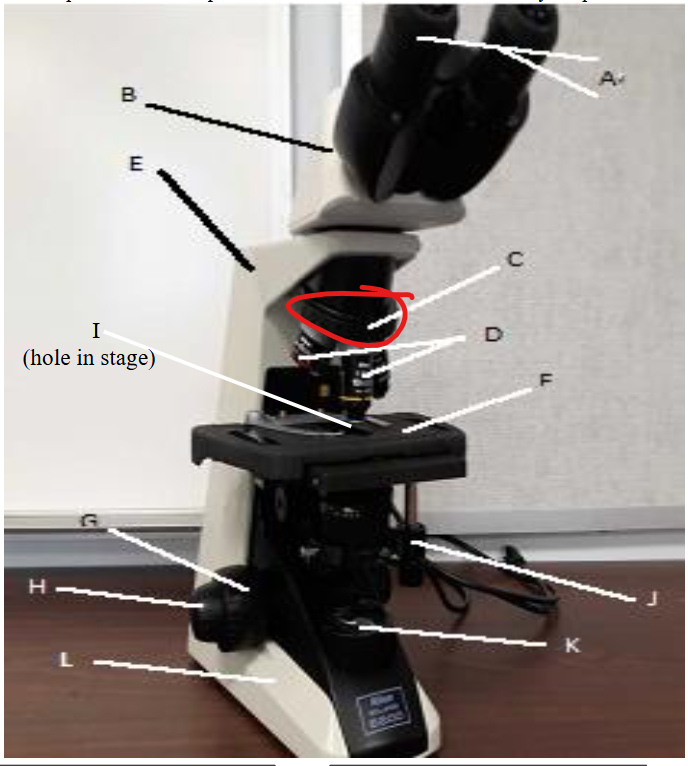
nose peice
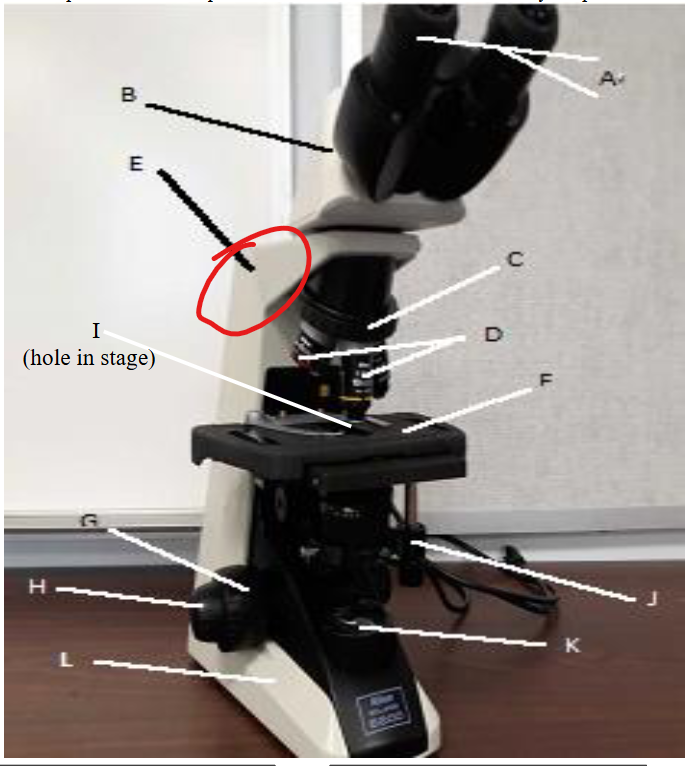
arm
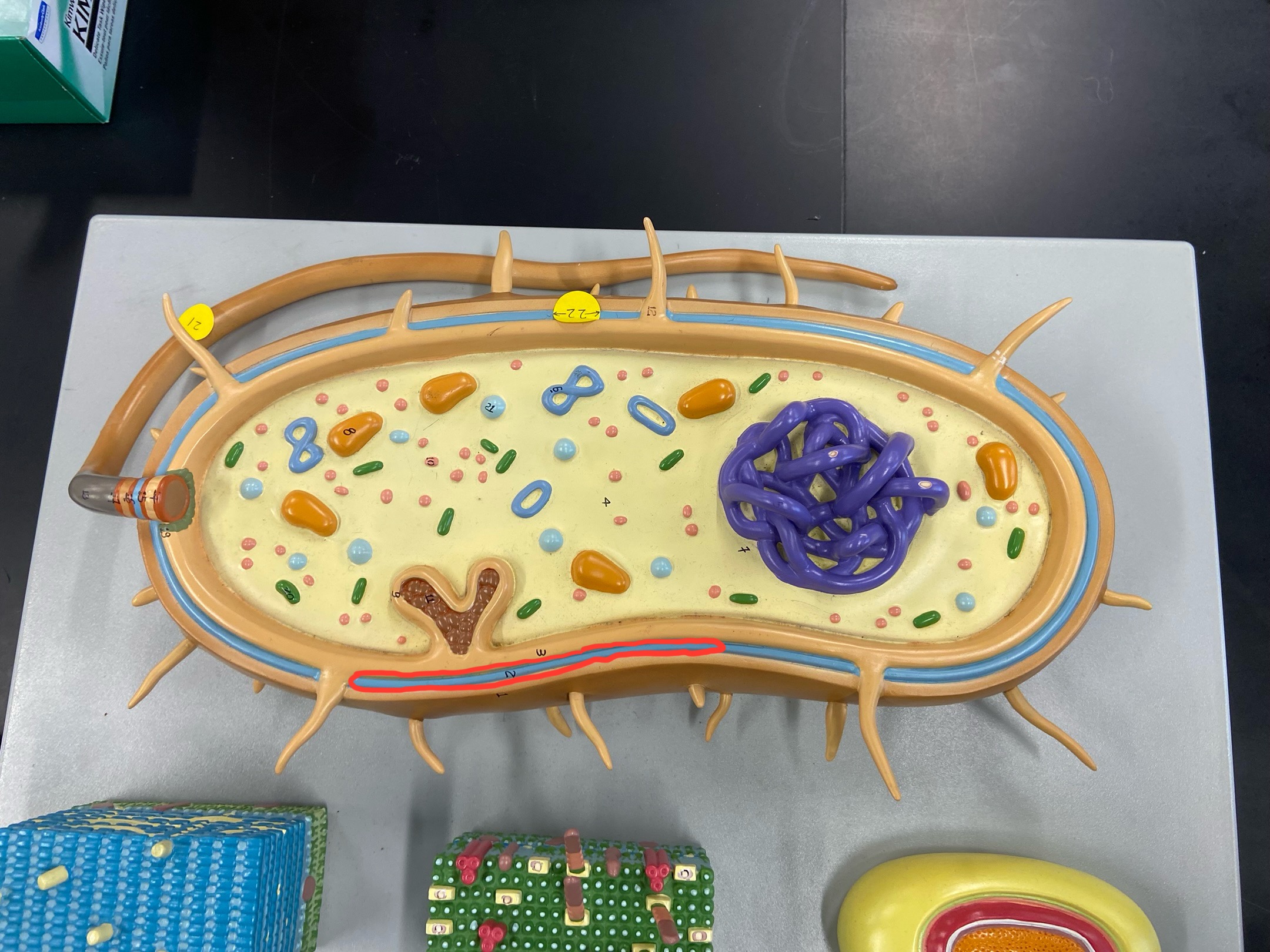
Cell wall
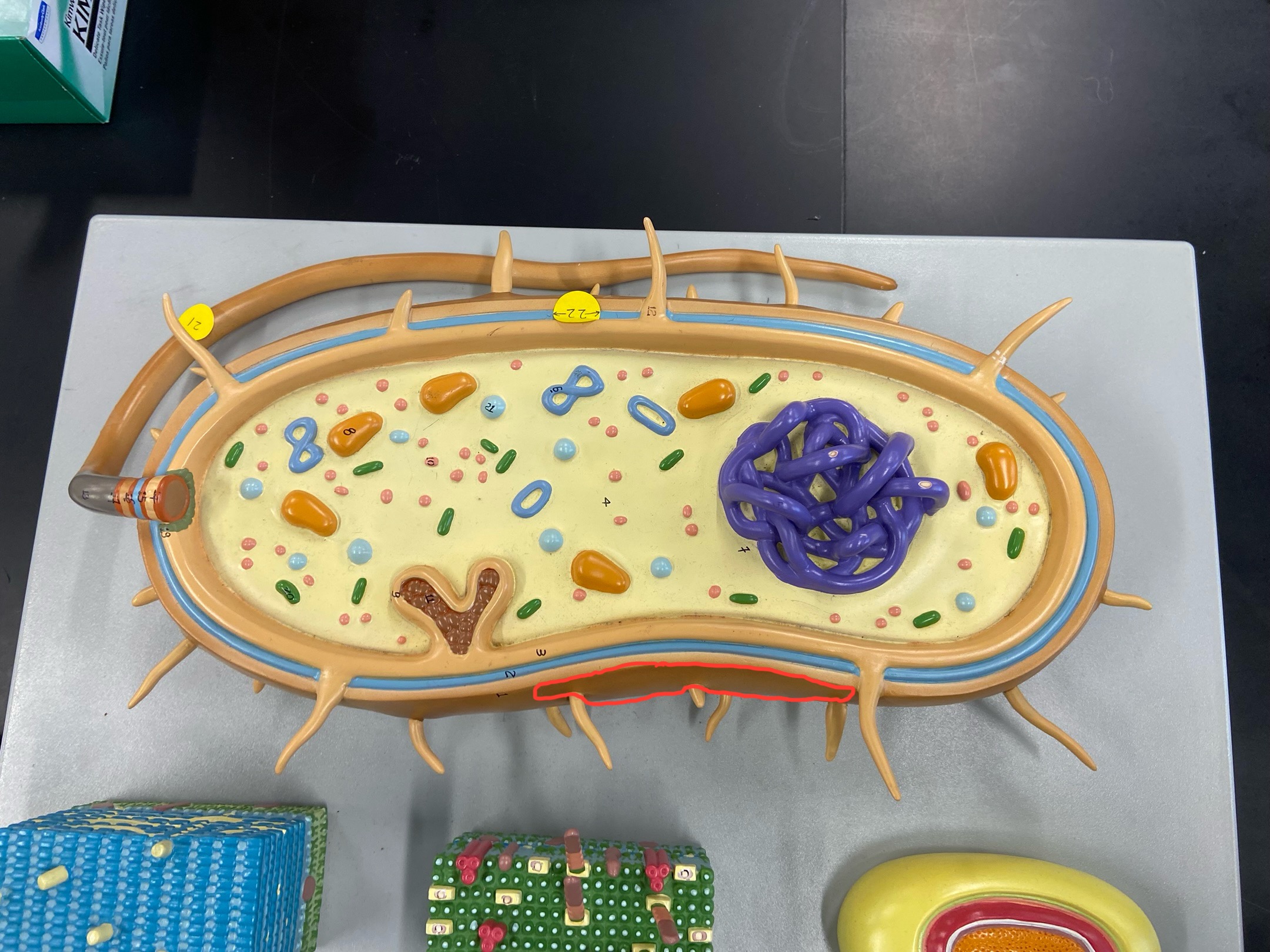
Outer membrane
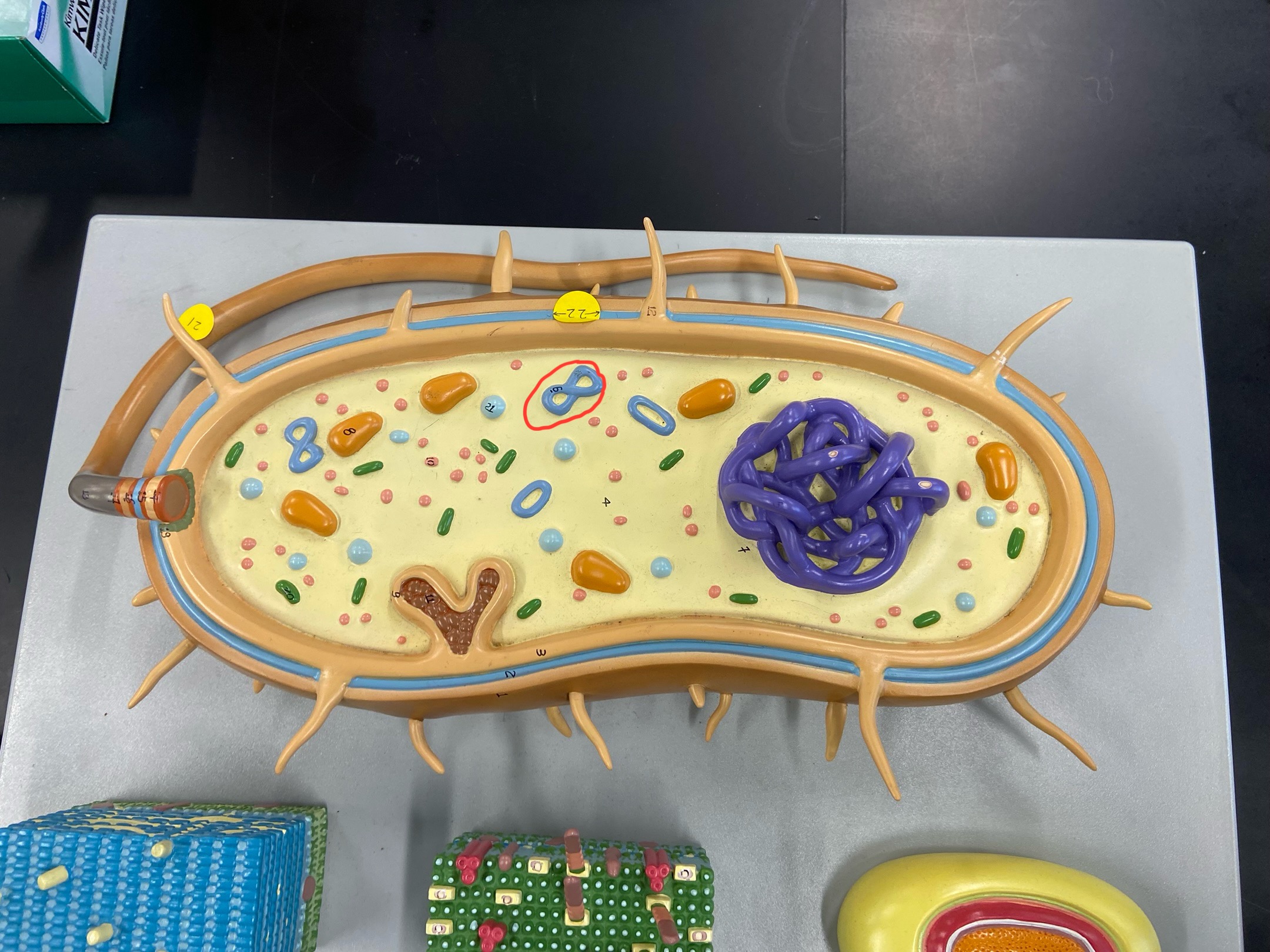
Plasmid
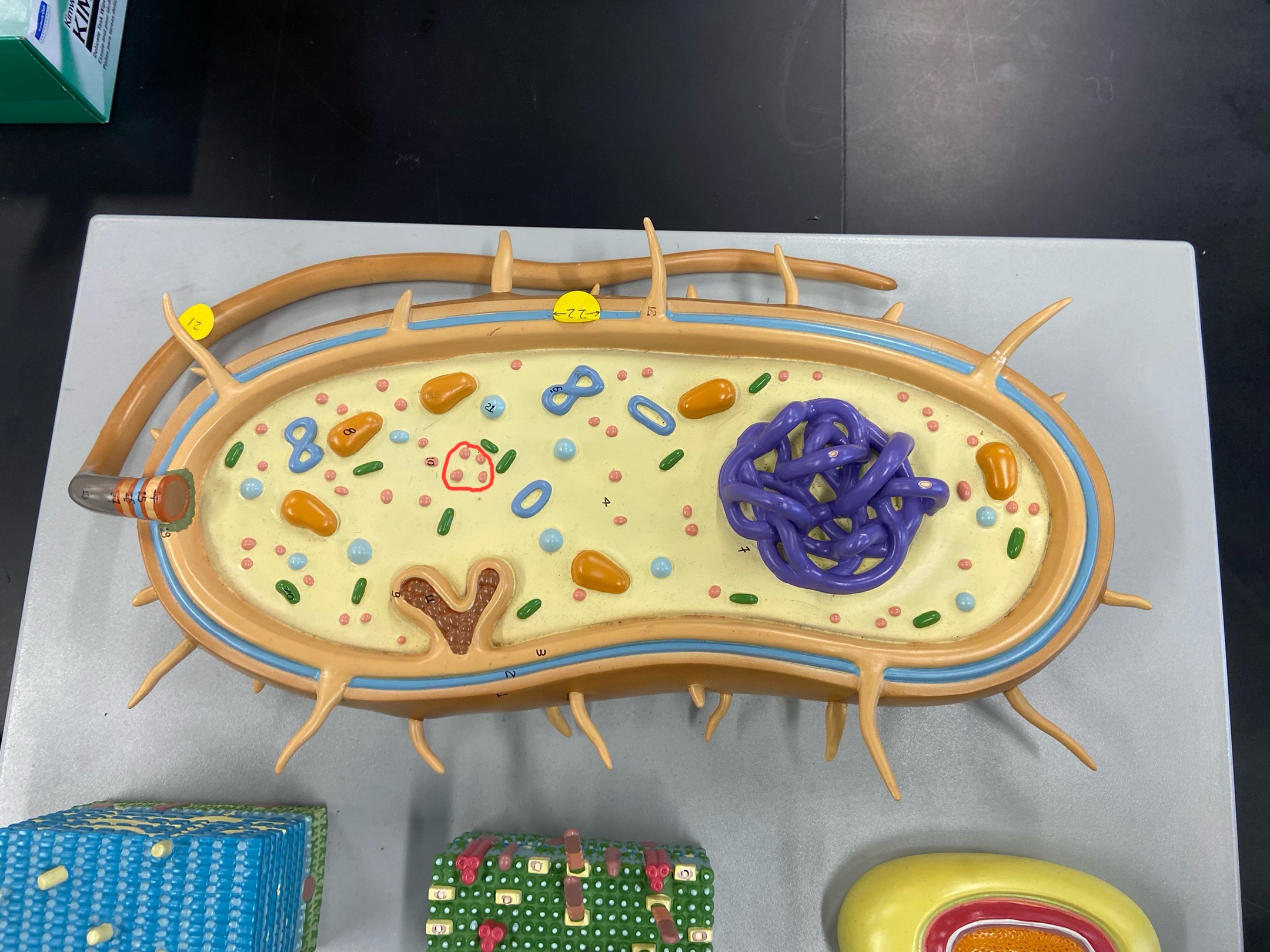

Ribosomes
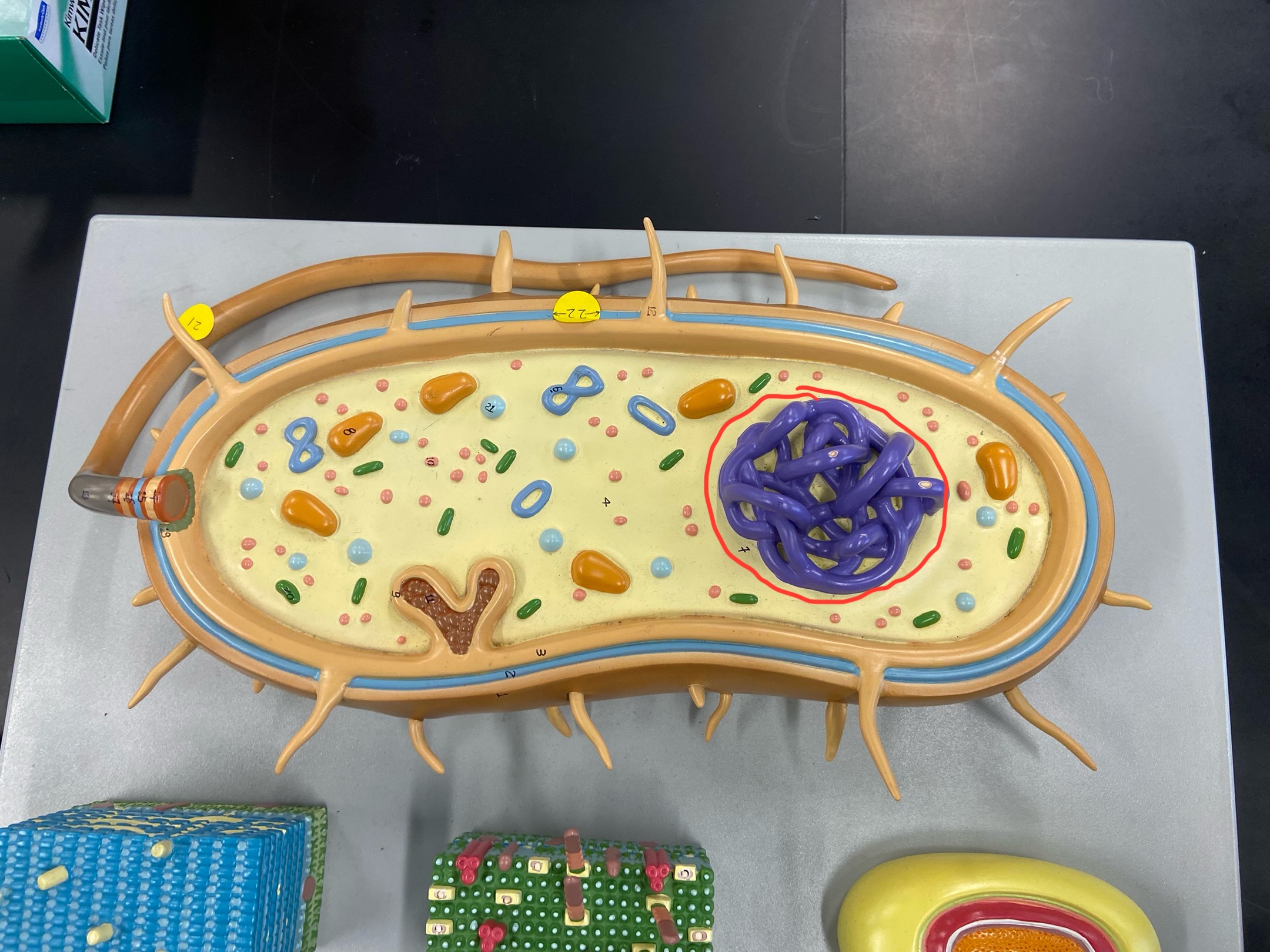
DNA
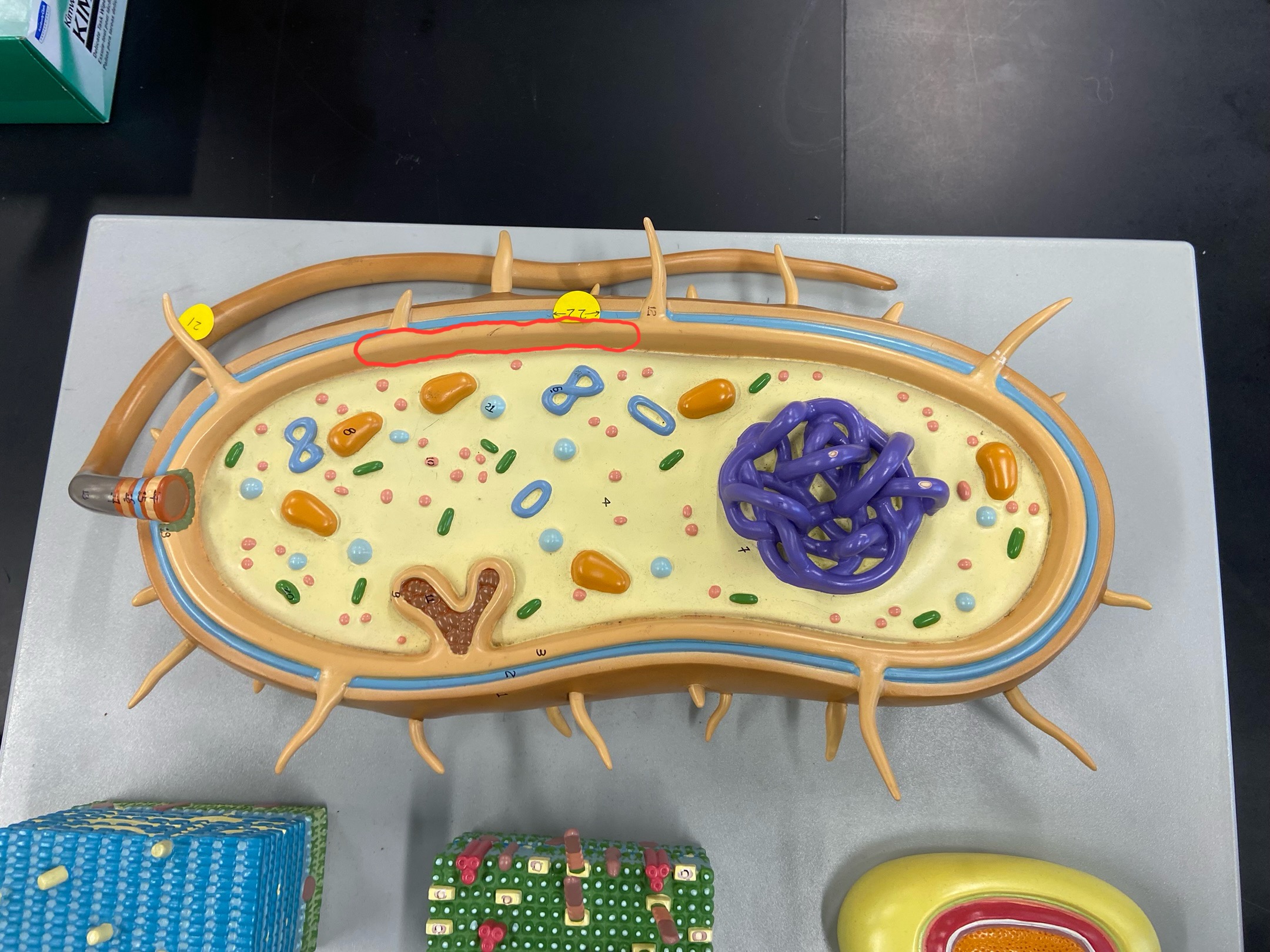
Cytoplasmic membrane
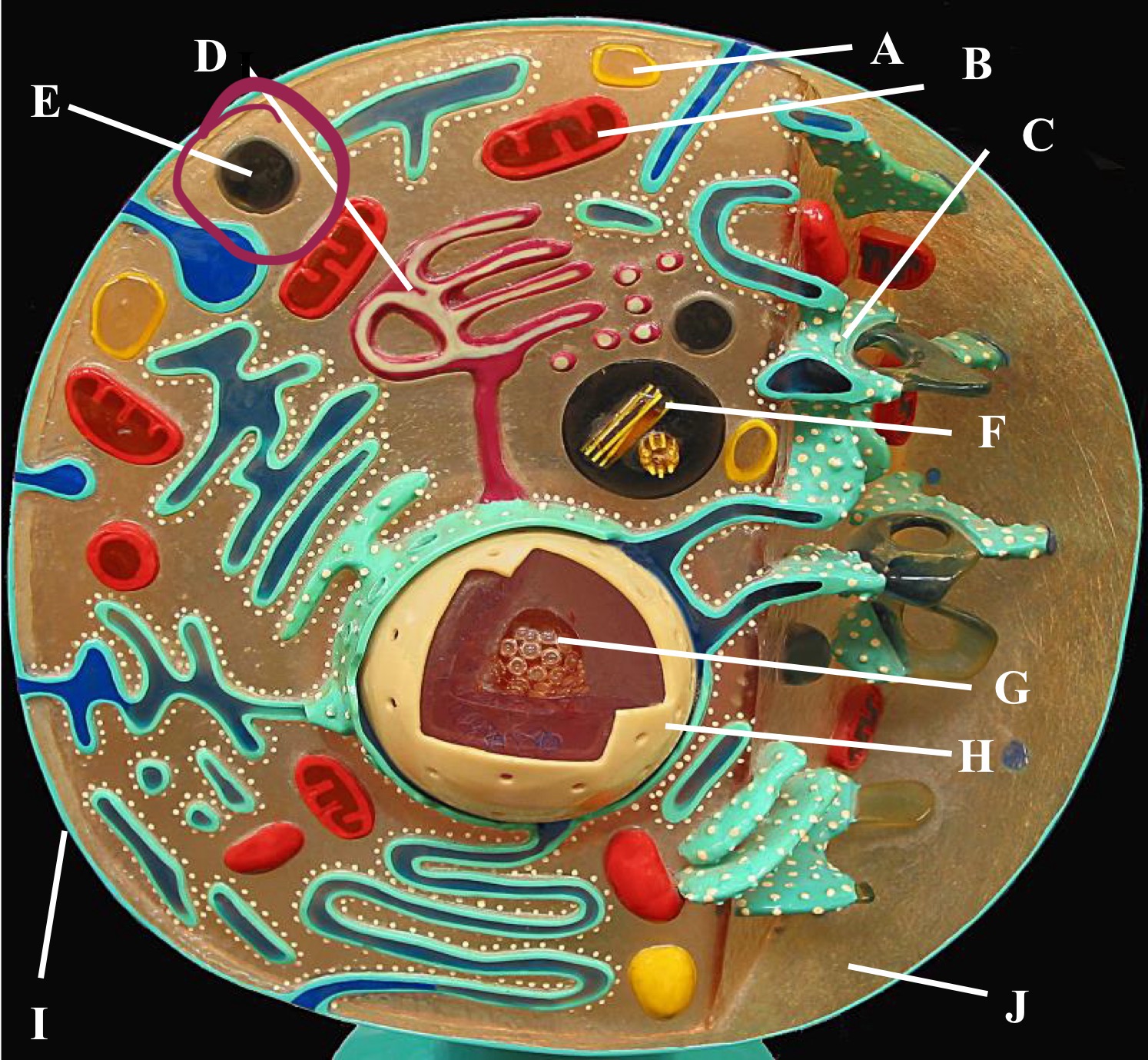
Preoxisome
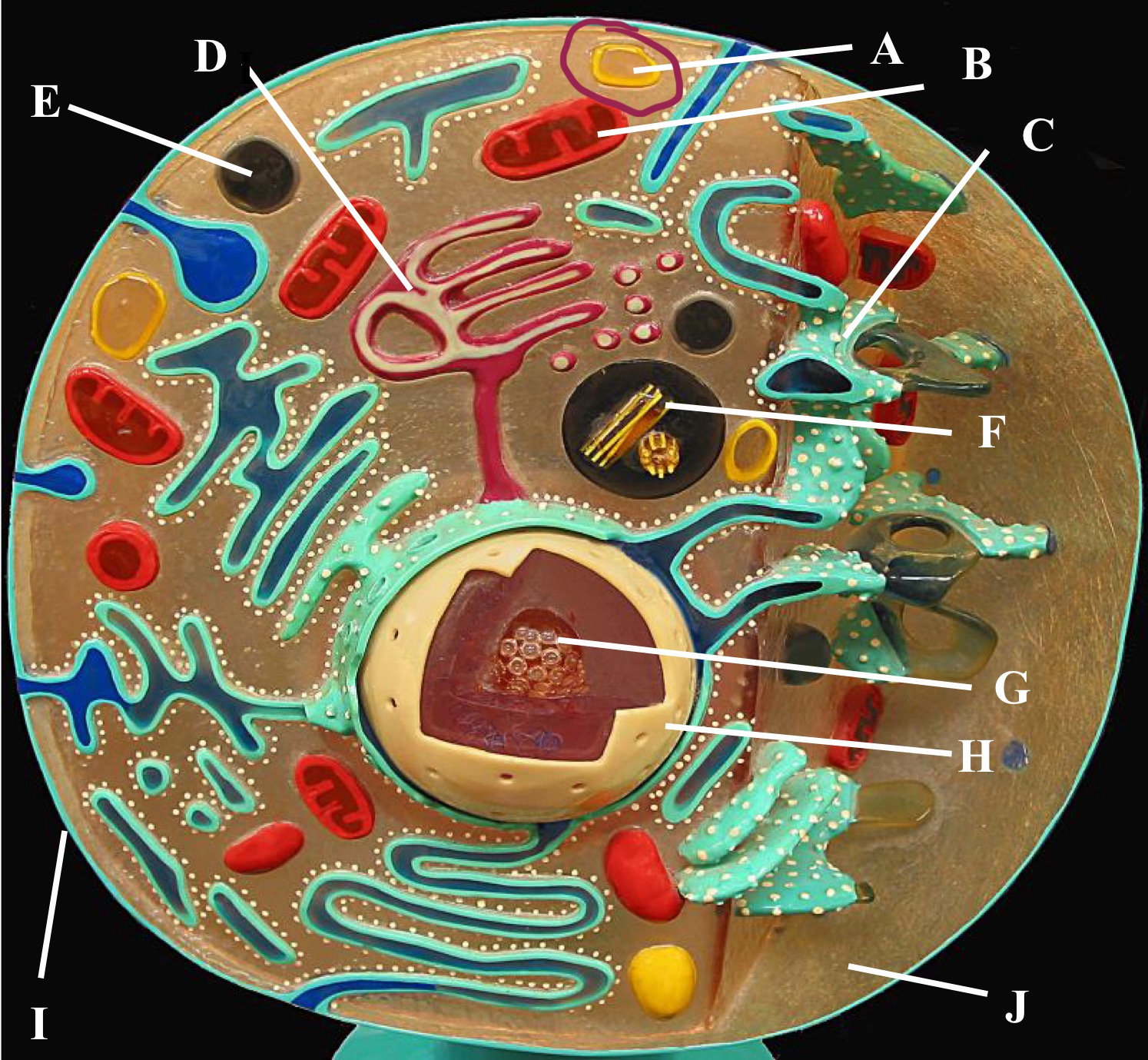
Lysosome
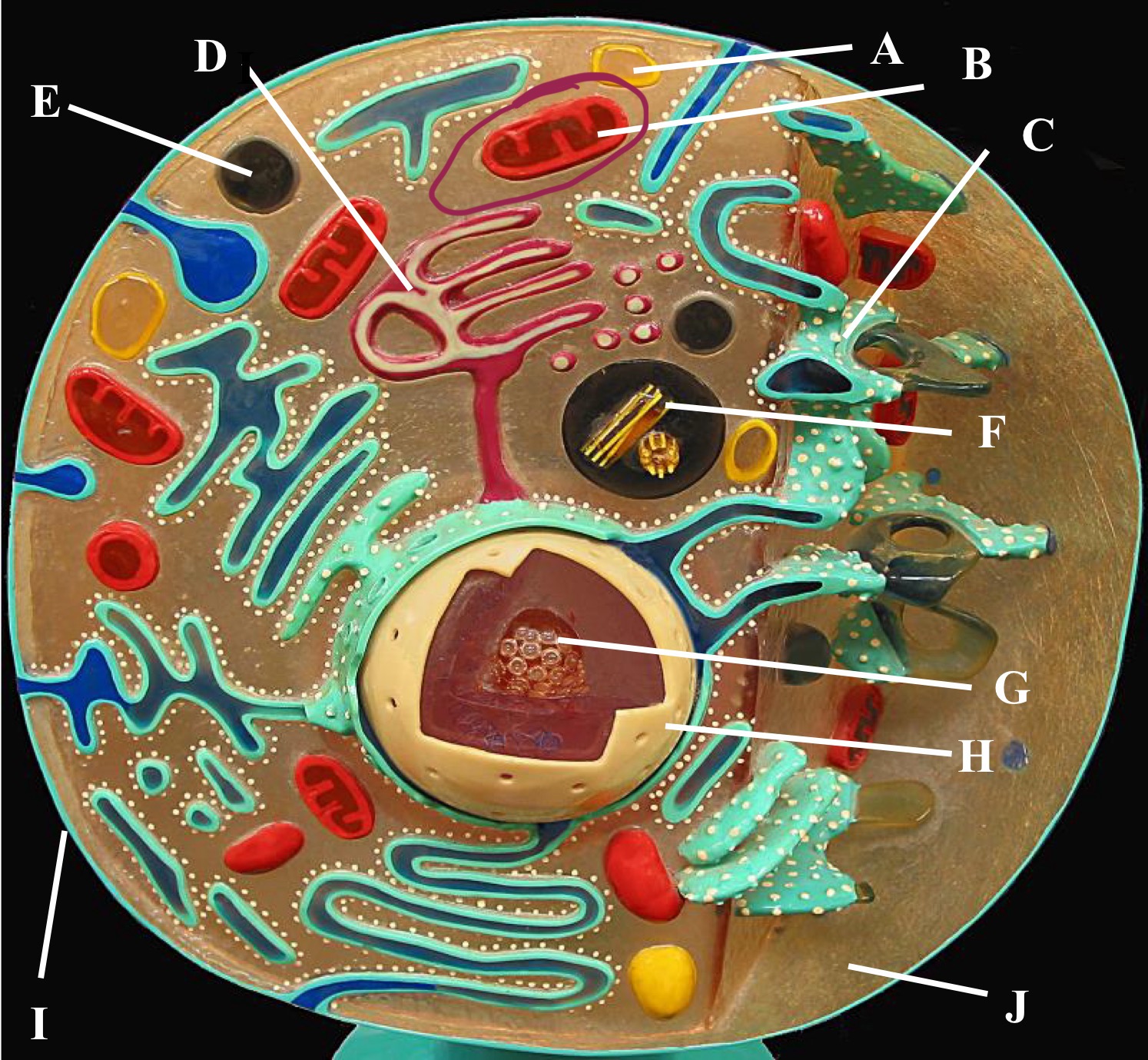
Mitochondria
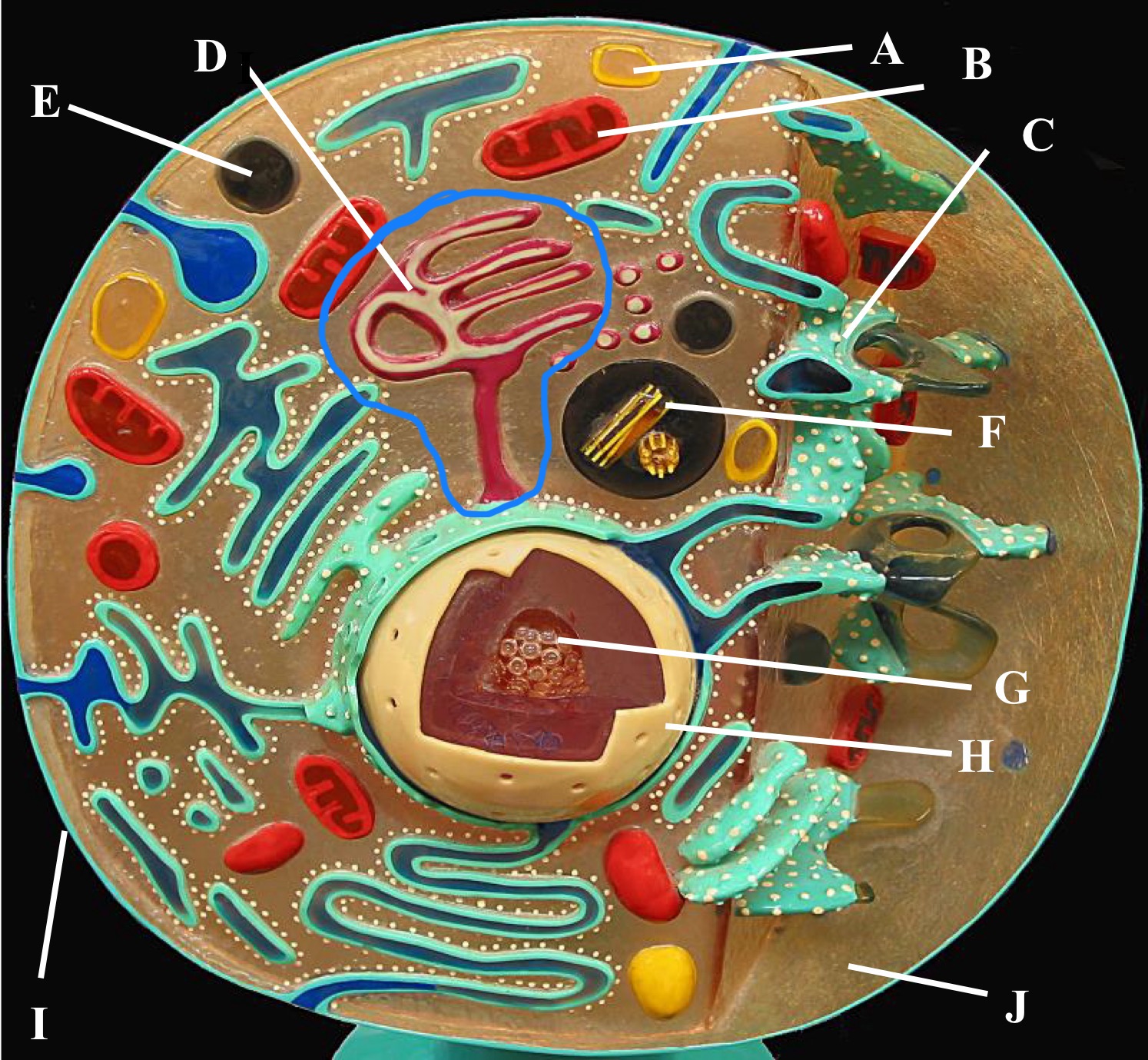
Golgi body
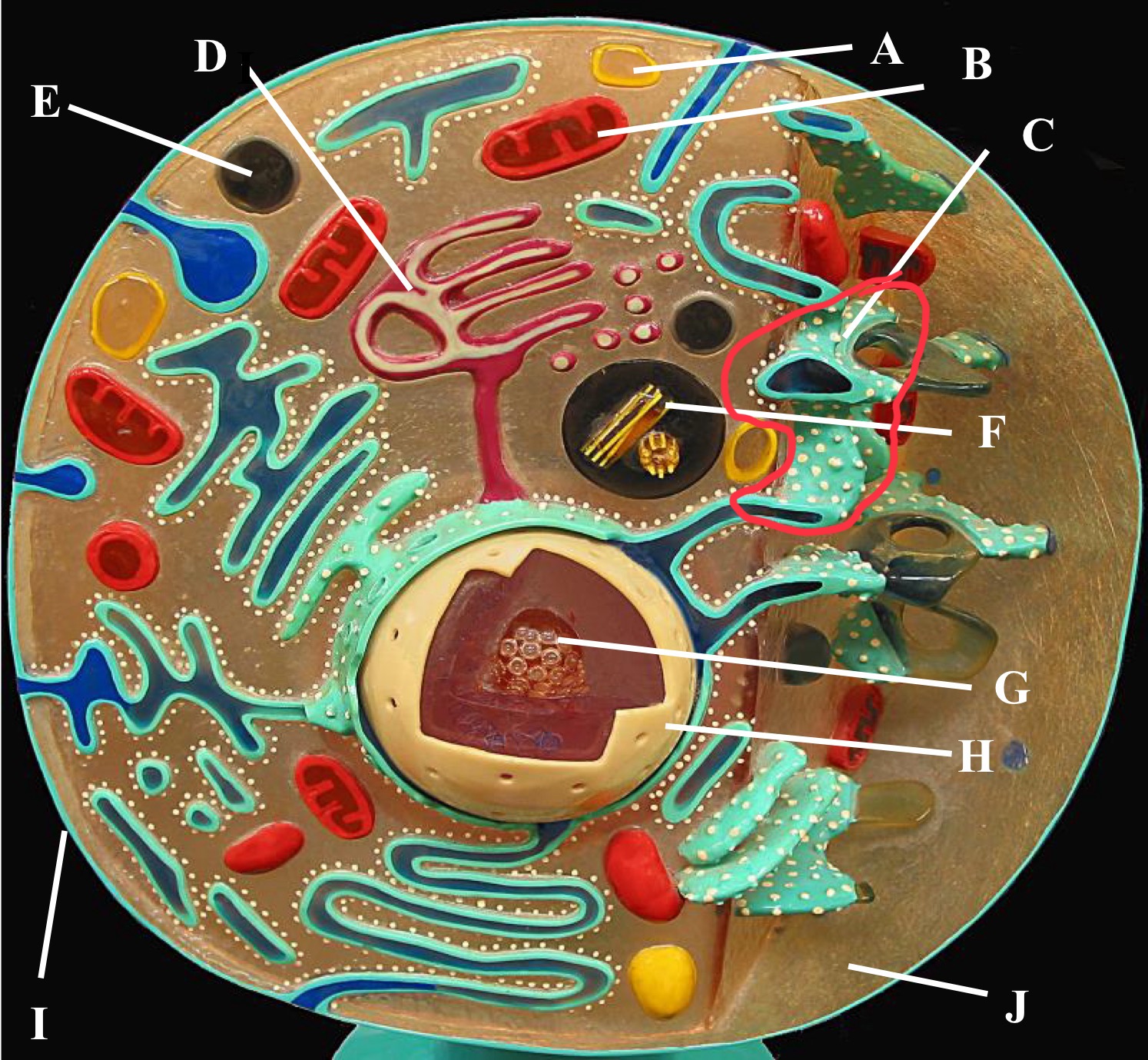
Rough Er
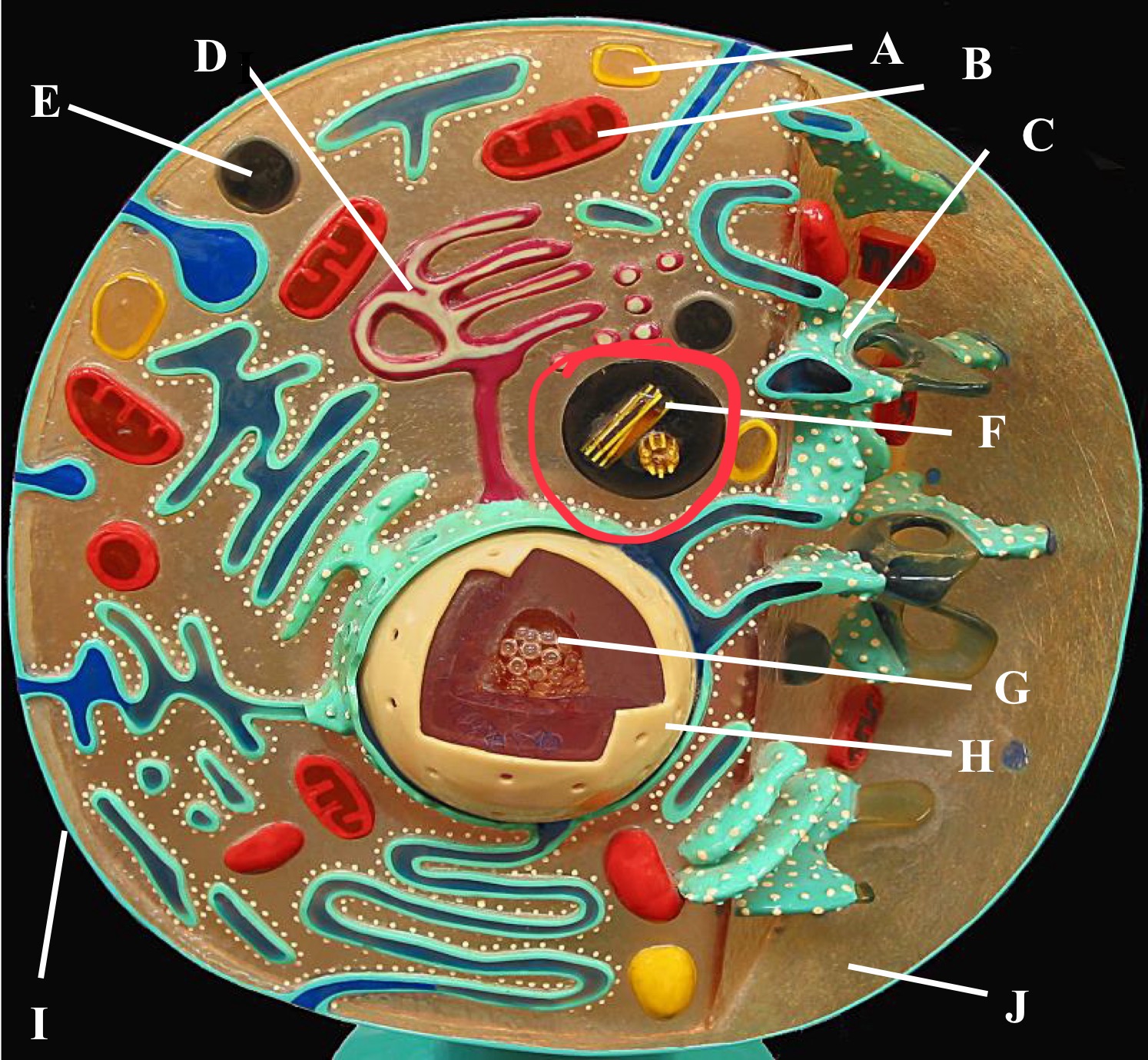
Centrioles
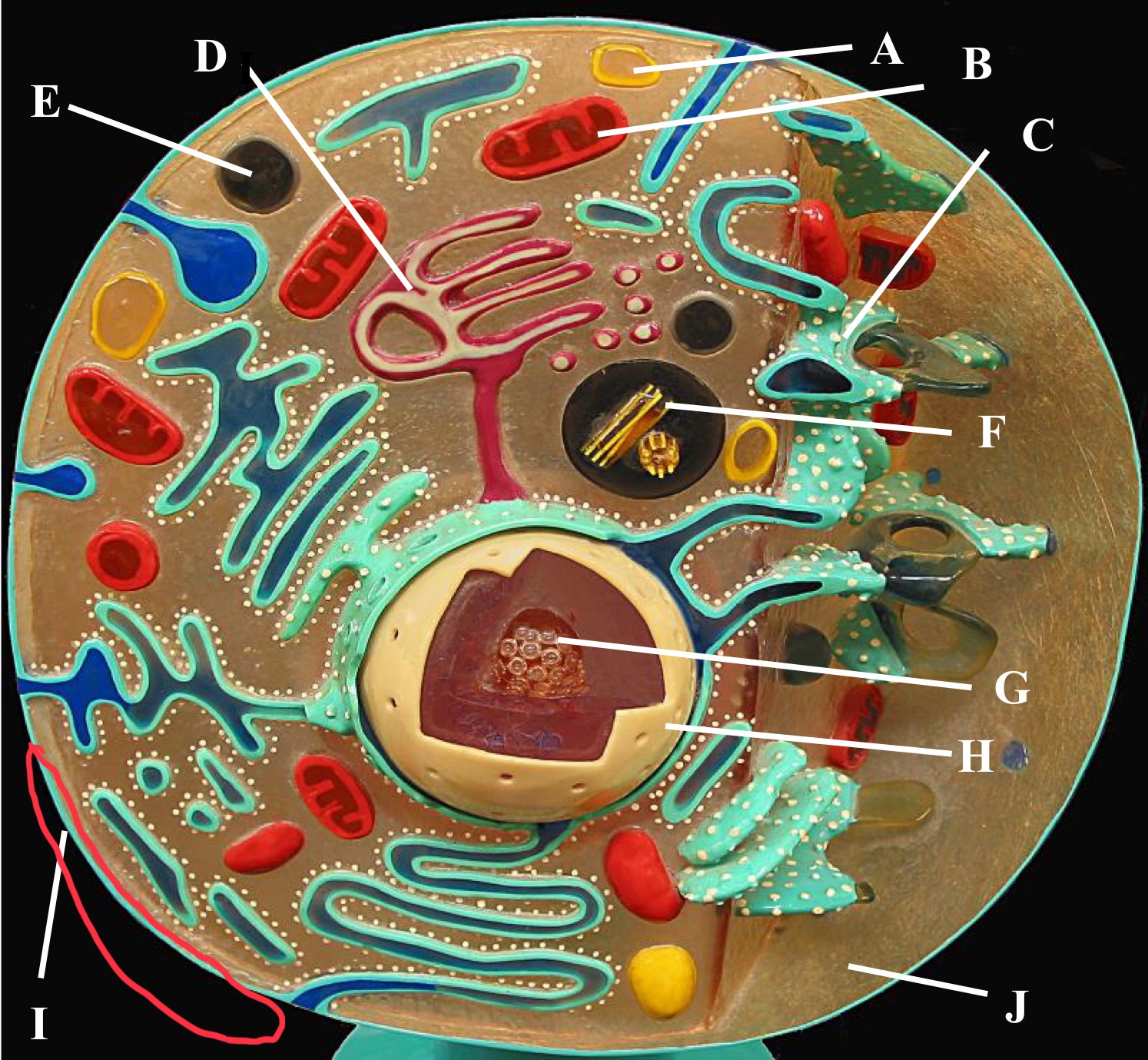
Plasma membrane
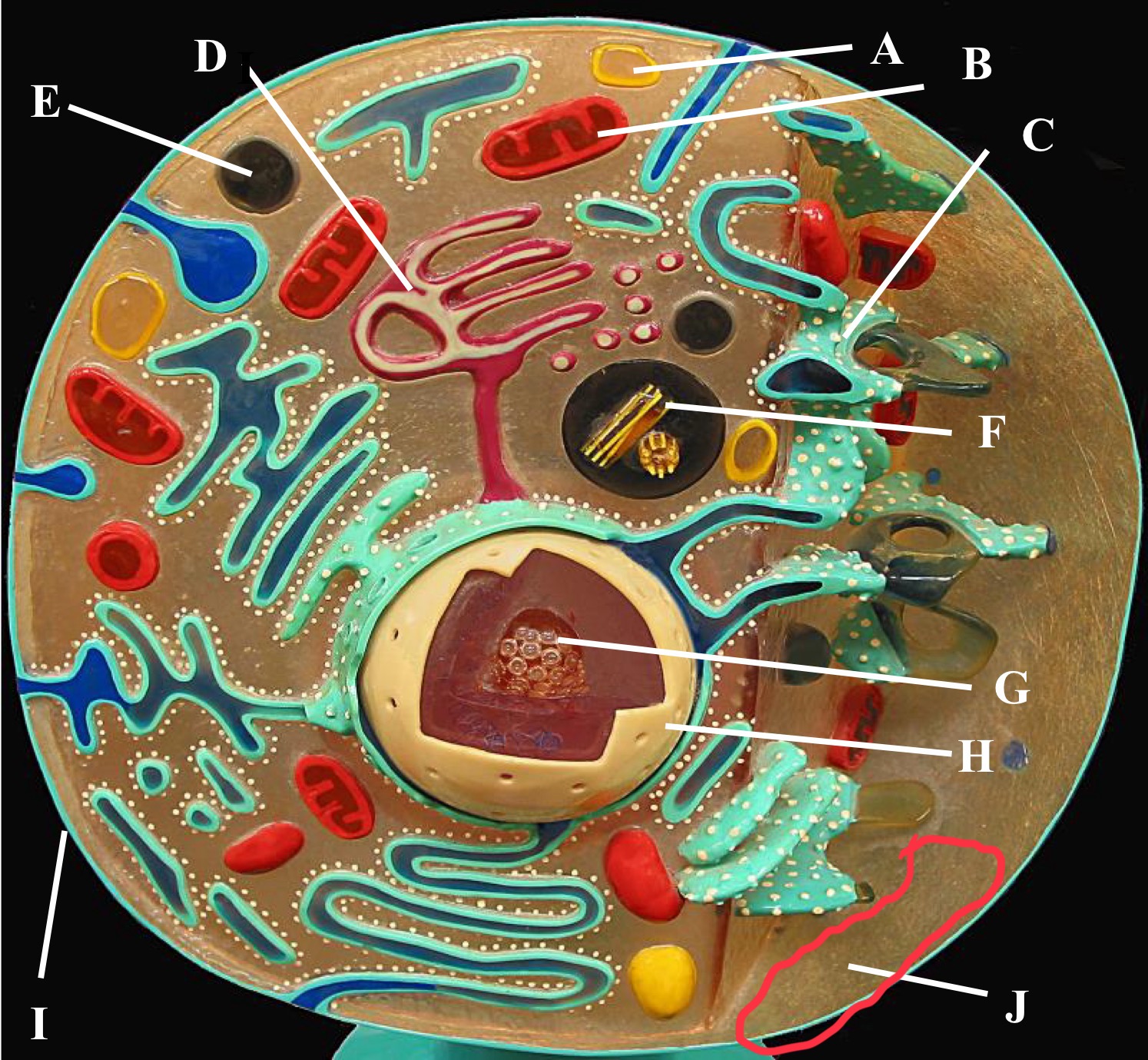
Cytoplasm
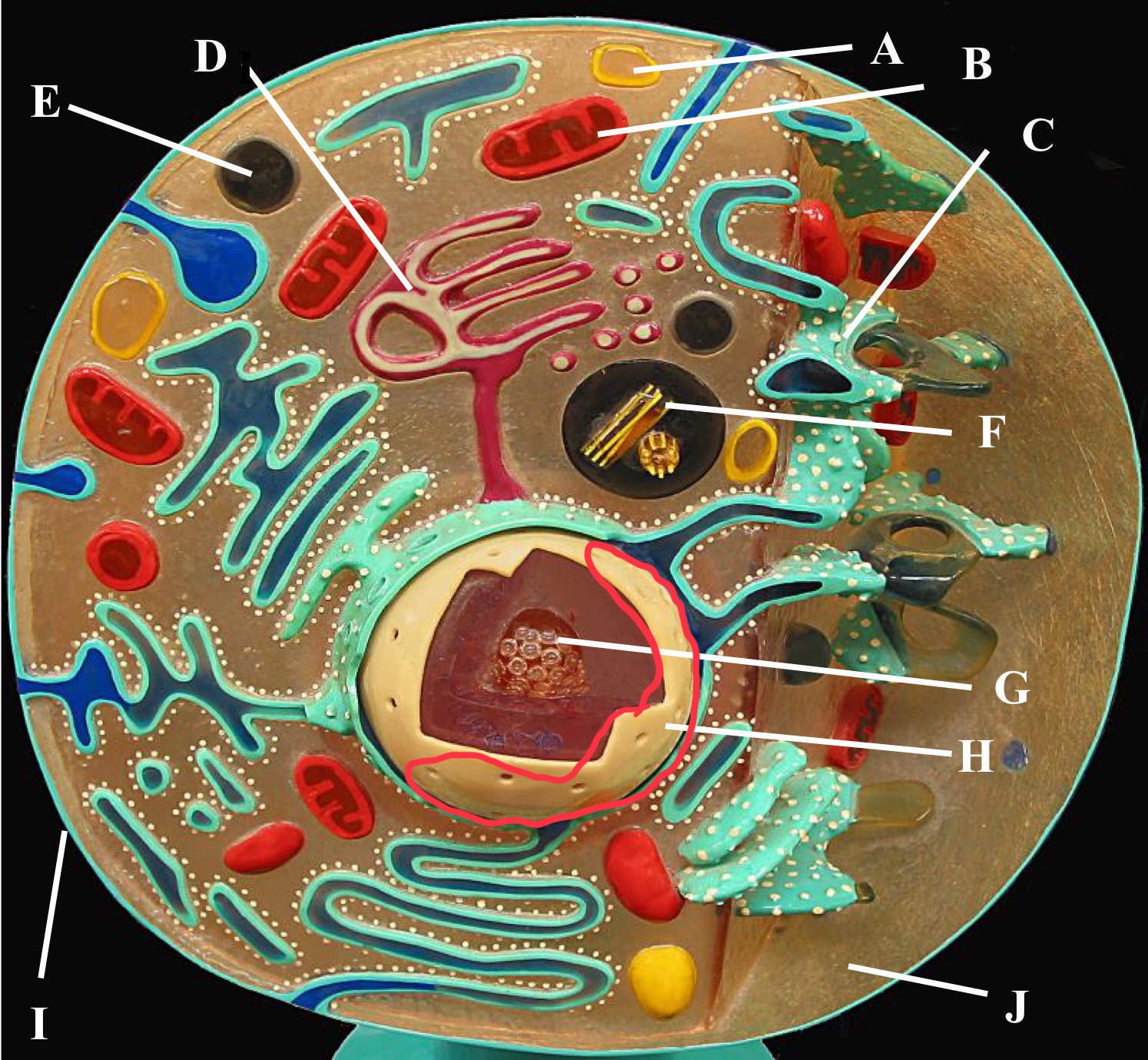
Nucleus
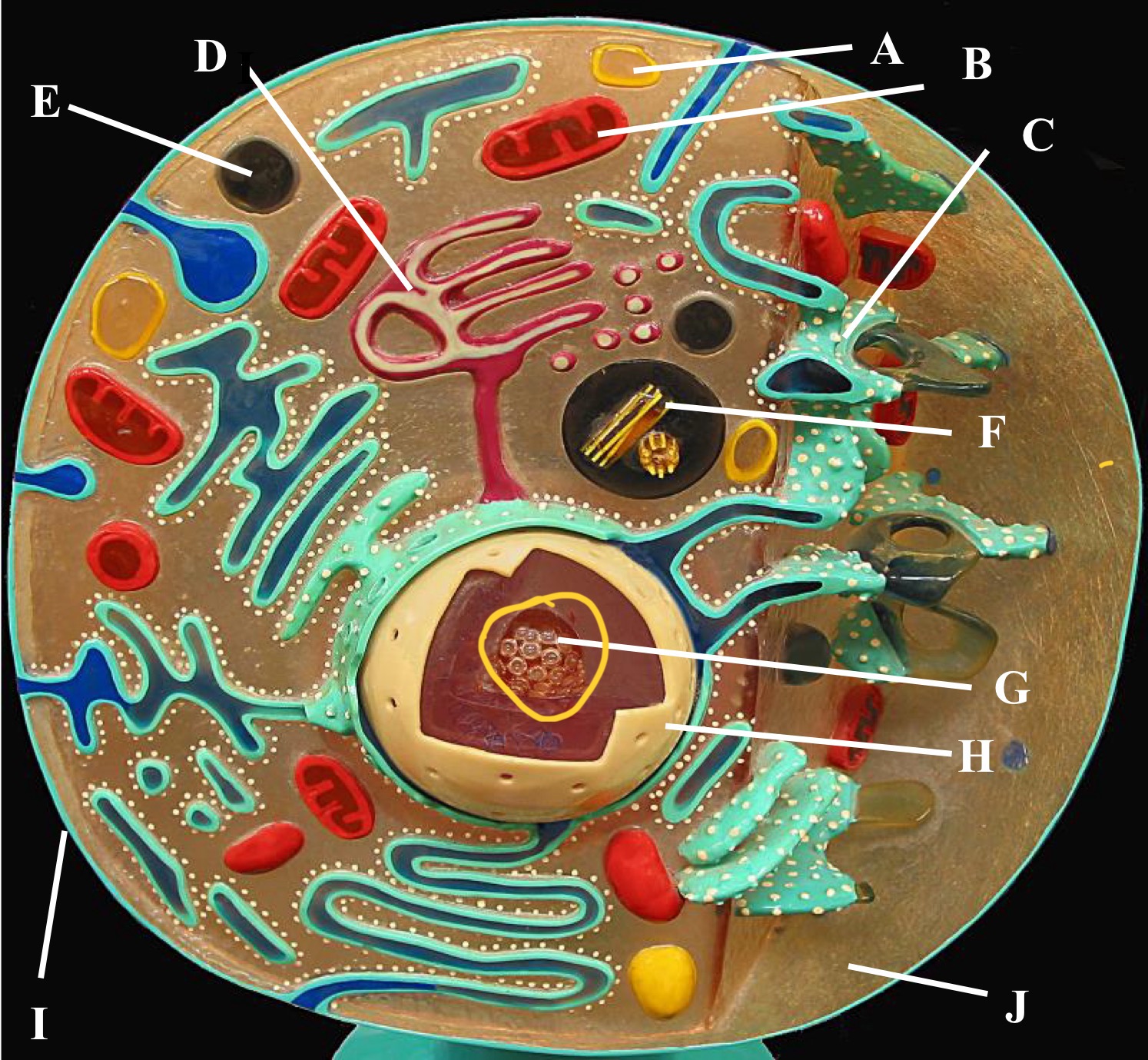
Nucleolus
Nucleus function
Store cell DNA
Control gene expression
Mediate DNA replication
Rough Er function
Modify, fold , and synthesize proteins
Insert, secrete into membranes or delivery
Smooth Er function
Synthesize lipids and steroids (cholesterol and sex hormones)
Has a role in carbohydrate metabolism
Mitochondria function
Generate cell energy or ATP
by cellular respiration
Plasma membrane function
Acts as a barrier
Control what enters and exits
Provide structural support
Communicate with receptors and markers
Have cell processing with endocytosis and exocytosis
Chloroplast function
Photosynthesis
Turn light energy into glucose using chlorophyll
Golgi Apparatus (function)
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids from ER
deliver outside the cell or inside
Peroxisomes (function)
breakdown fatty acids and toxic substances
synthesis essential lipids manage reactive oxygen species
Centrioles (function)
organize microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system
Nucleolus (function)
produce and assemble the cell's ribosome
Lysosome function
digest and recycle cells
use hydrolytic enzymes to break down waste products, cellular debris, and foreign materials
Cell Wall function (plants and fungi only)
structural support & maintaining the cell's shape
3 most common bacterial cell shapes
rod, round, spiral
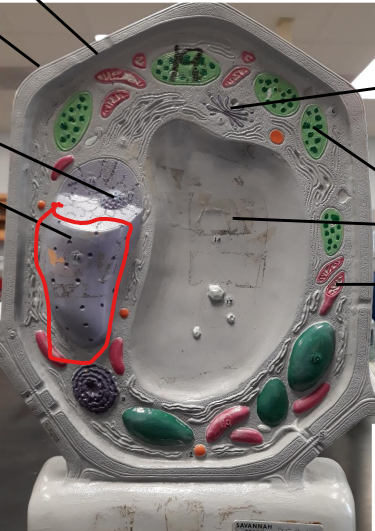
Nucleus

Nucleolus
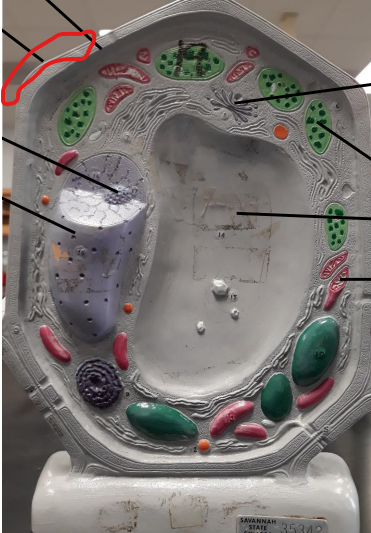
Cell Wall

Plasma membrane

Golgi Body
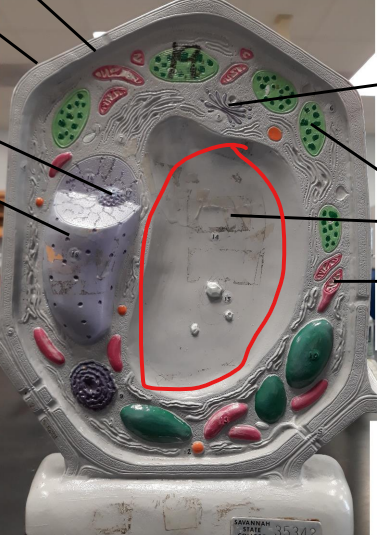
Central Vacuole

Chloroplast

Mitochondria
substance found in the cell walls of bacteria is important in Gram-staining?
peptidoglycan
two dyes used in the Gram-Staining process
crystal violet
safranin
Gram-positive
purple
Gram-negative
pink-red
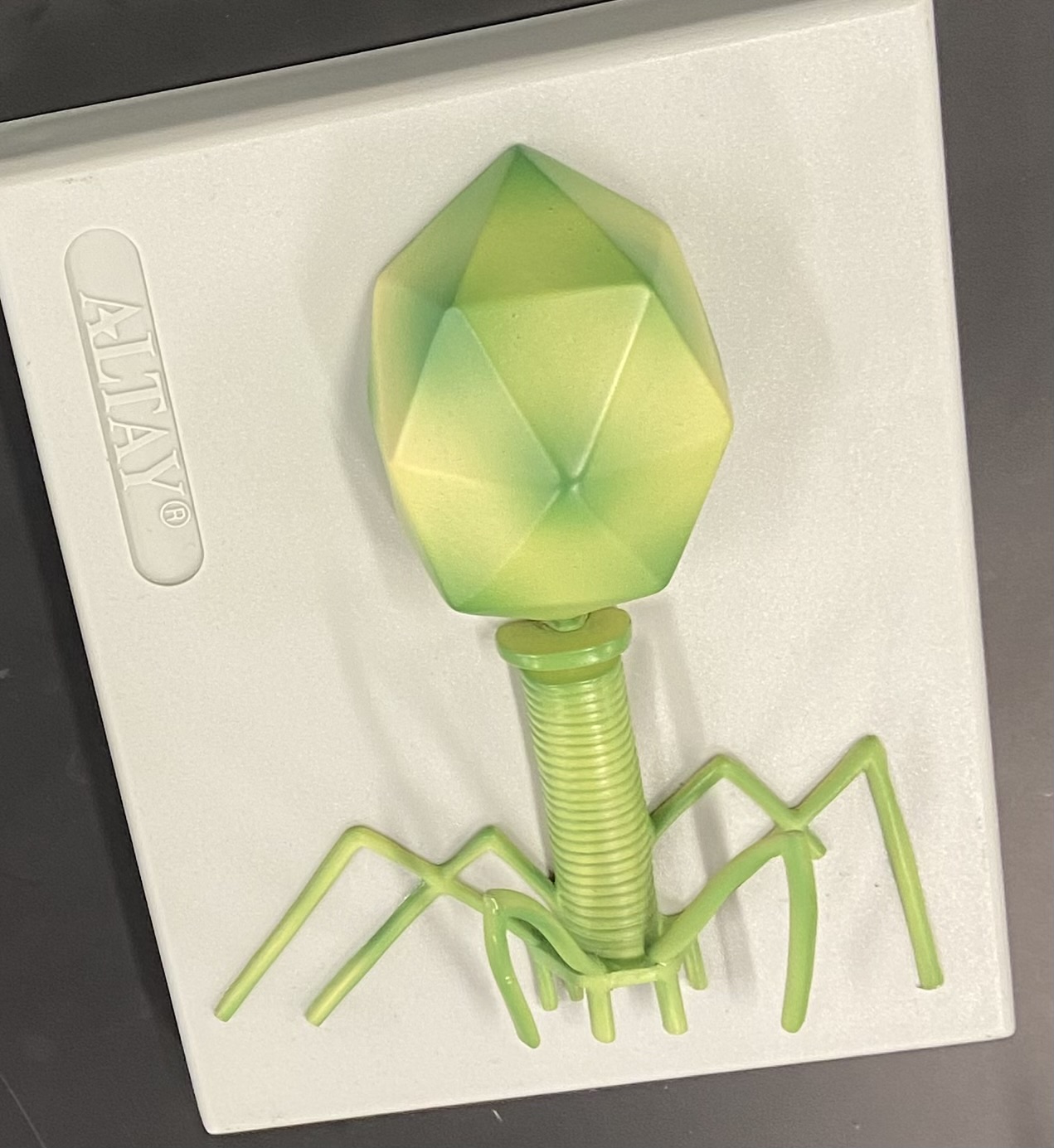

T4 phage
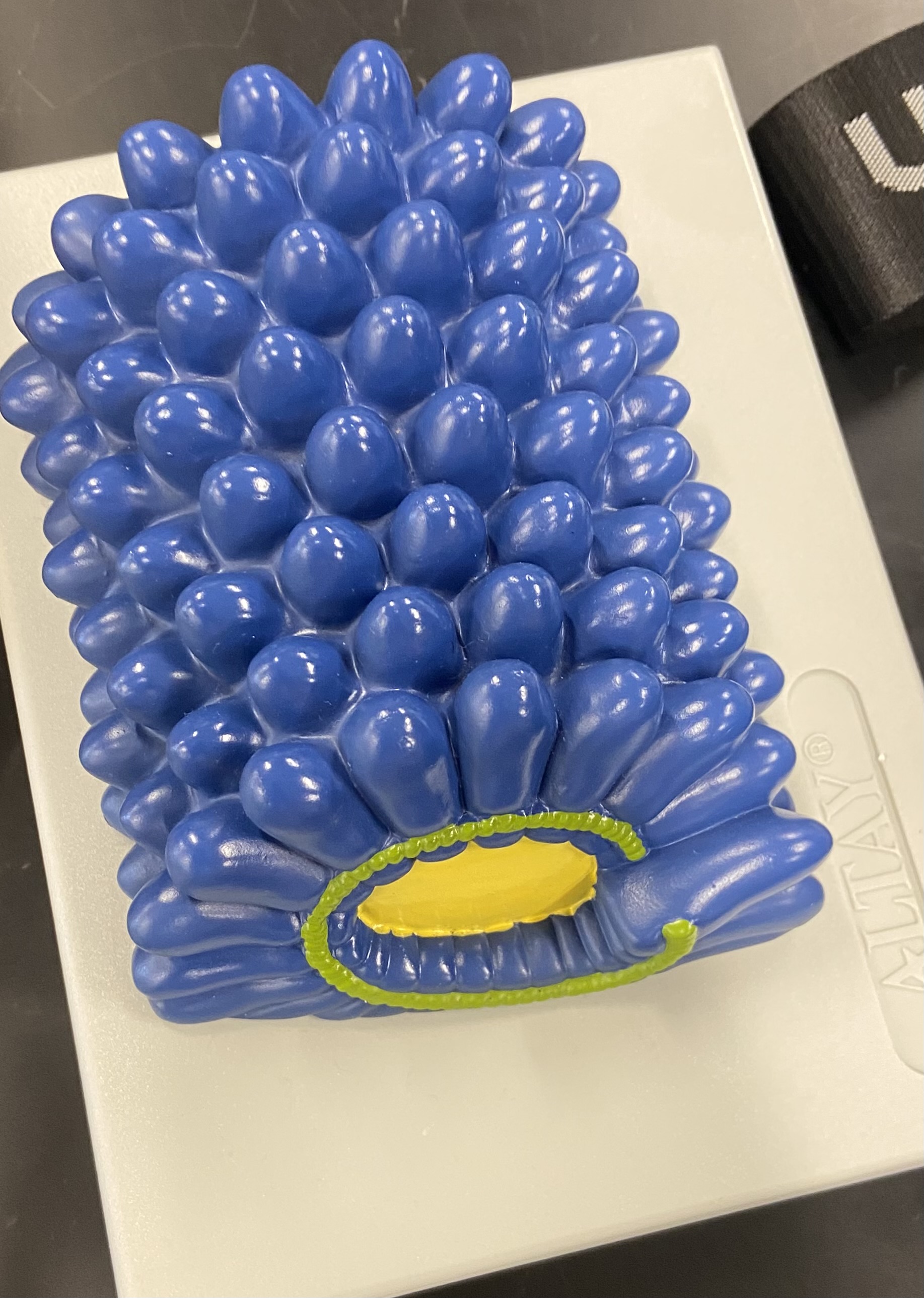

Tobacco mosaic virus
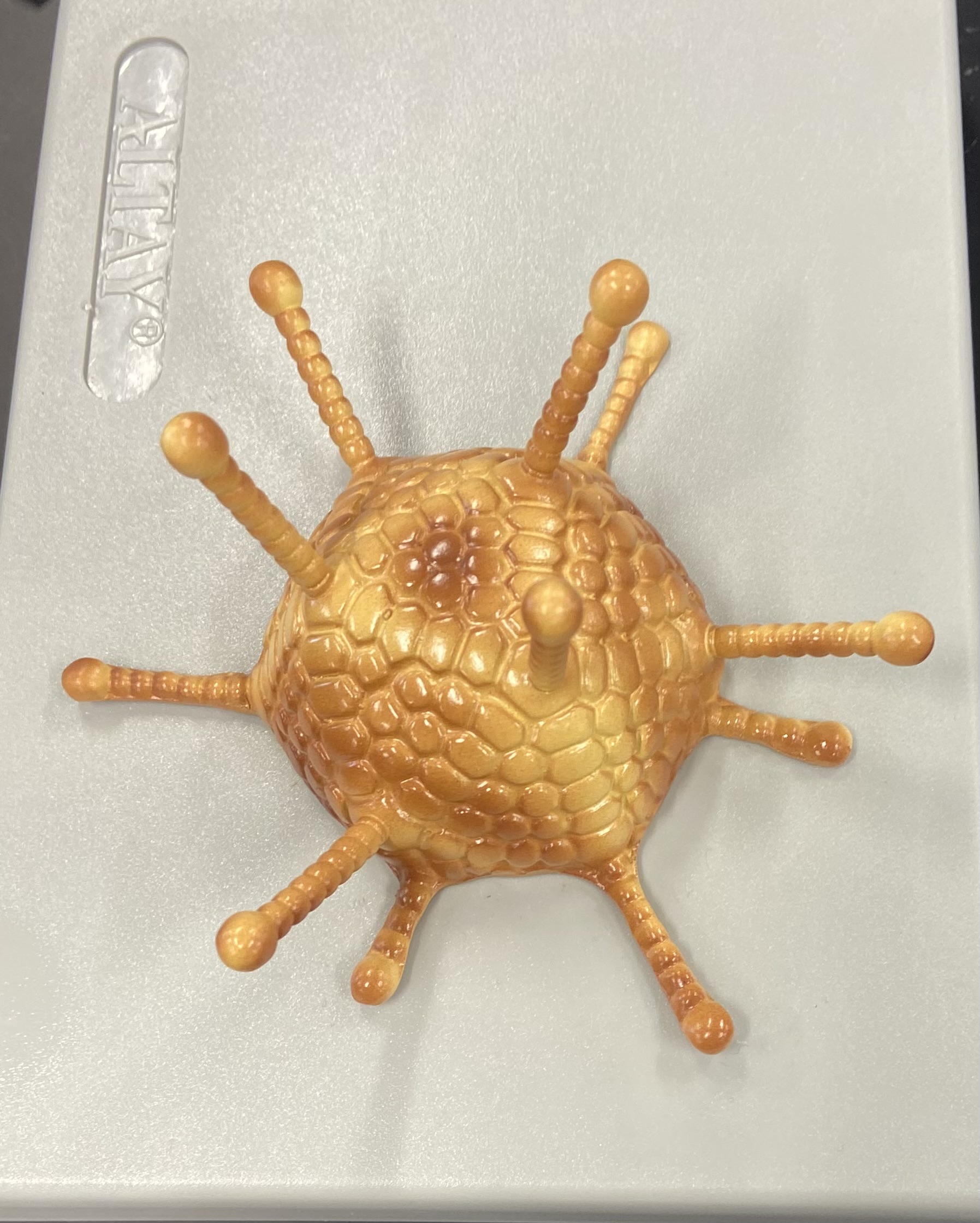

Adenovirus
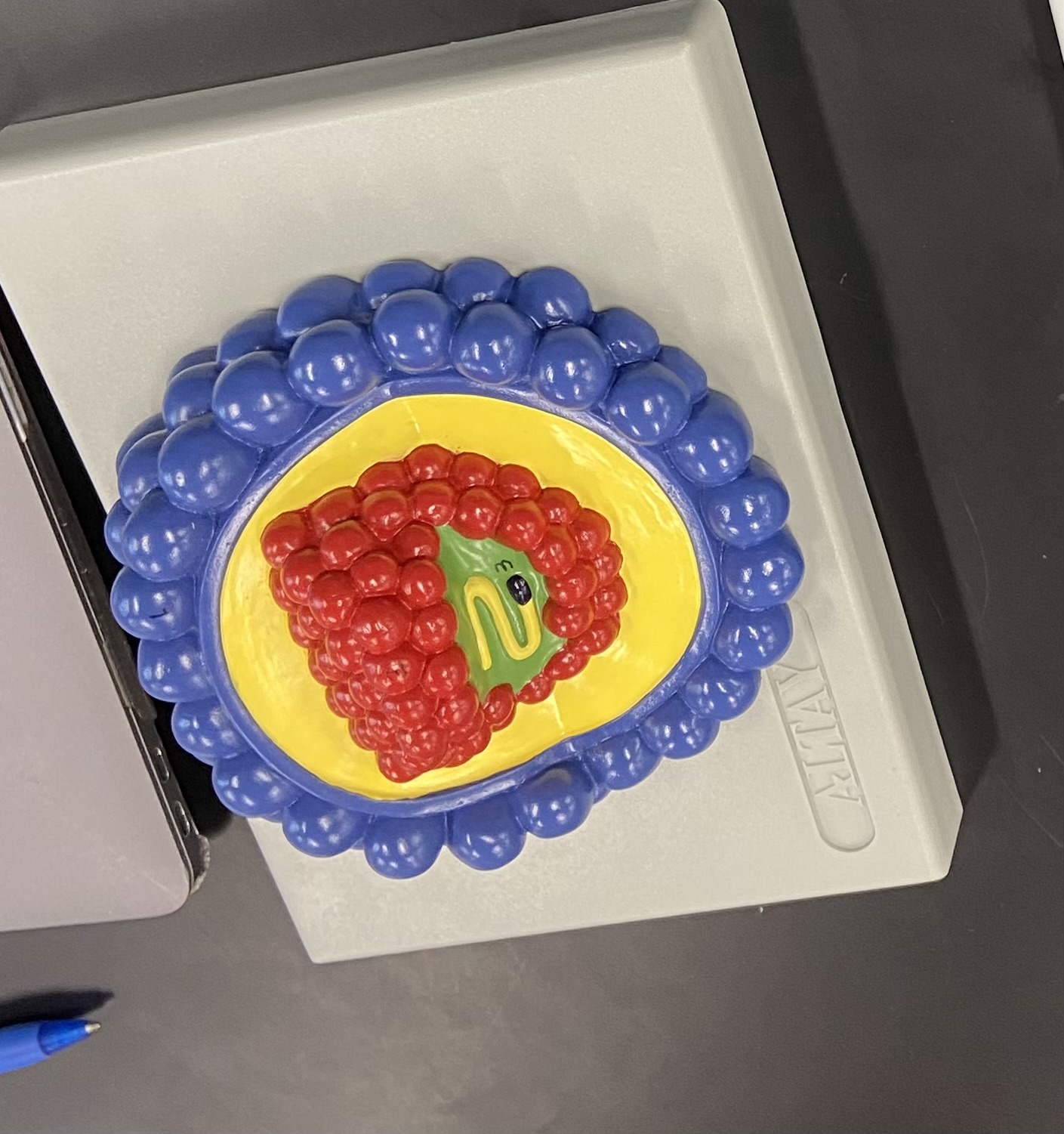
HIV
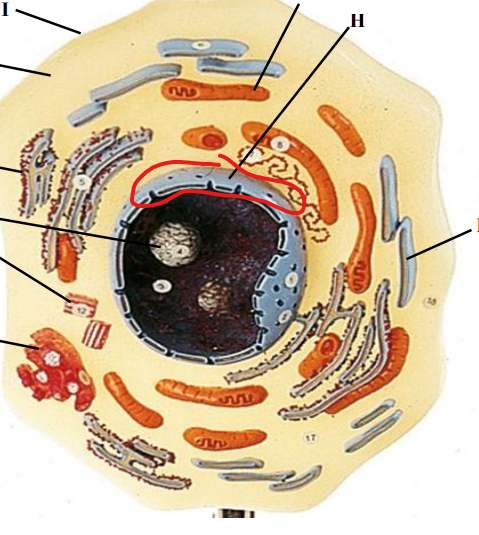
Nucleus
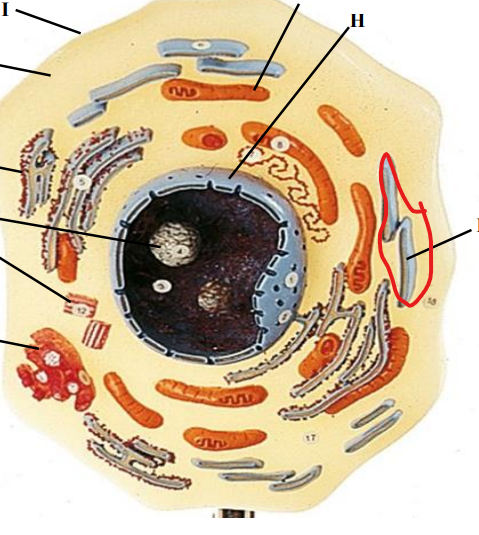
Smooth ER
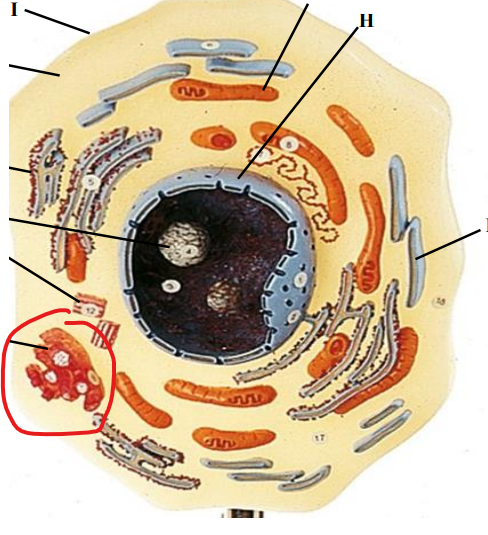
Golgi Body
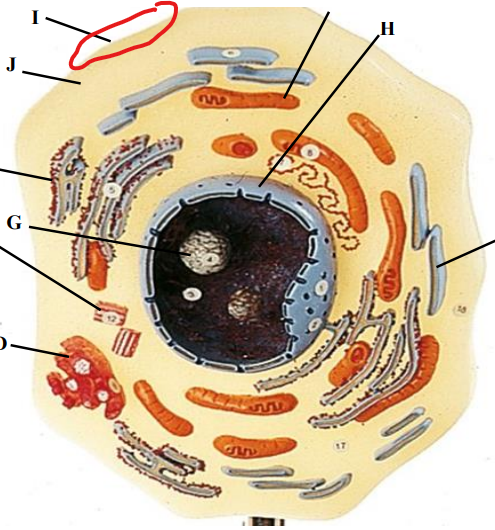
Plasma membrane
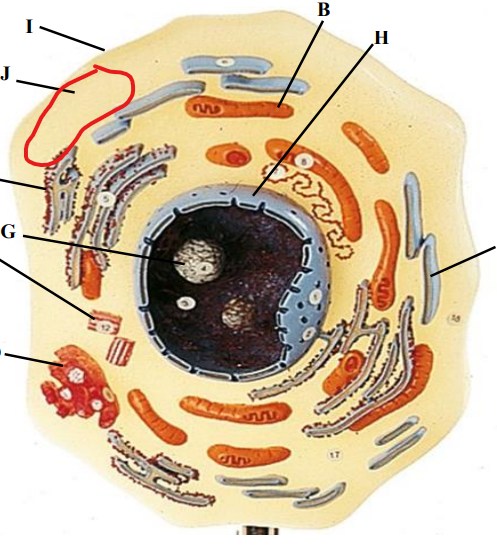
Cytoplasm
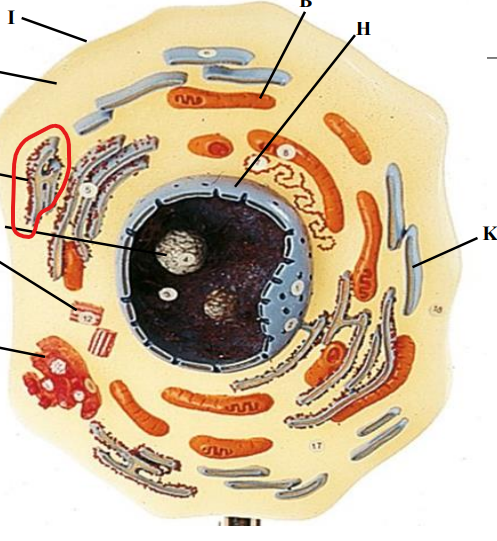
Rough ER
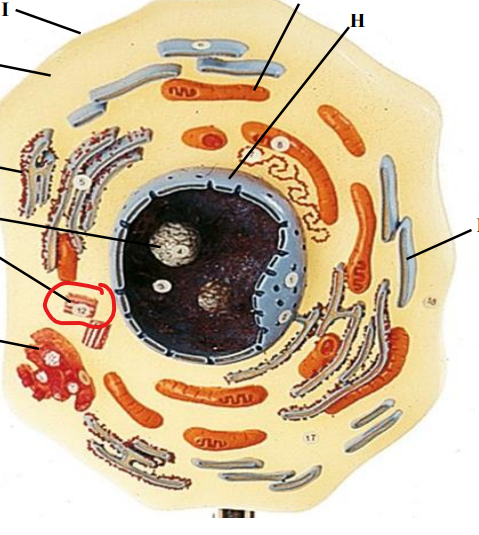
Centrioles
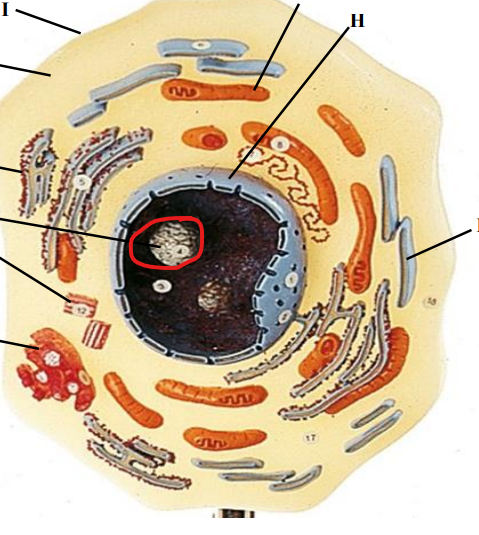
Nucleolus