Lecture 5 - primary and secondary structure
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
how is a peptide bond formed
condensation of alpha-carboxyl of one amino acid with the alpha-amino of another
which direction is the polypeptide read
n terminus to c terminus
residues
the amino acids that compose of the peptide chains
backbone
repeating N-Cα-C unit of the peptide chain
secondary structure
regions of regularly repeating conformations of the peptide chain
alpha helices
beta strands
conformation of a protein
functional 3d structure
native conformation
polypeptide chain folds into a single stable shape
what is the native conformation determined by and what does it determine
determined by the sequence of amino acids
determines biological function
3 representations of protein structure
space-filling model
cartoon ribbon model - shows secondary structure
substrate-binding site view
what factors contribute to protein structure
allowable bond rotations around the backbone of the polypeptide
weak non-covalent bond interactions between backbone and sidechain groups
peptide bond properties
lone pair on amide nitrogen
electronegative oxygen will accept the double bond electrons
creates intermediate bond length
double bond character
why does C-N peptide bond have double bond character
resonance
peptide bond and rotation
nitrogen cant rotate
peptide group
6 atoms in the same plane
half of one amino acid and half of another
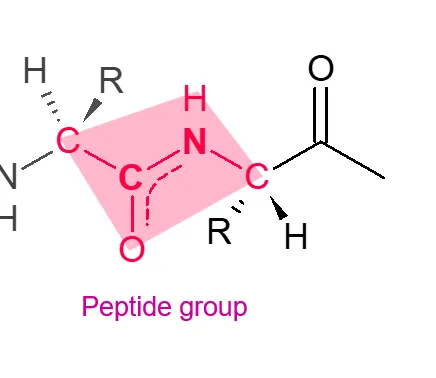
trans conformation of peptide group
Cα opposite sides
cis conformation of peptide group
C α same side
which conformation of the peptide group is more favourable and why
trans conformation
cis conformation has steric interference of alpha-carbon side chains
where is there bond rotation in peptide group
N-Cα phi bonds
Cα-V psi bonds
rotation of N-Cα bond (phi) in proline
restricted
due to ring structure
properties of secondary structures
alpha helix
beta strands beta sheets
loops and turns favoured by allowable phi and psi bonds
and stabilising hydrogen bonds
alpha helix structure
right handed
backbone turns clockwise
all side chains point outwards
helix is stabilised by hydrogen bonds
each C=O forms a hydrogen bond with an amide hydrogen of residue n+4
hydrogen bonding in alpha helix
each C=O forms a hydrogen bond with an amide hydrogen of residue n+4
pitch of alpha helix
vertical distance between turns
0.54nm in length
rise in helix
each residue advances by 0.15nm along the axis of the helix
how many acids per turn in alpha helix
3.6
amphipathic alpha helix
hydrophobic residues
hydrophillic residues
amino acids that do not accommodate alpha helix
proline
glycine
what amino acids are loops made of
hydrophillic amino acids
loops are generally in aqueous environments
domain
3d globular protein subunit
connects polypeptide chains together
turns
loops containing less than or equal to 5 amino acid residues
which direction does beta sheet arrow point to
direction of c terminal residue