Chapter 19, Lesson 5: Blood Flow, Heart Sounds, and the Cardiac Cycle
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 19, Lesson 5 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Cardiac cycle
The complete contraction and relaxation of all four chambers of the heart
Pressure
The principal cause of blood flow
Resistance
The opposition to blood flow
Pressure gradient
Required for blood flow from high to low; higher volumes mean lower pressure and vice versa
Valvular insufficiency (incompetence)
Any failure of a valve to prevent reflux, or the backward flow of blood
Valvular stenosis
Where the cusps of the heart are stiffened and constricted by scar tissue; regurgitation is heard as a murmur
Mitral valve prolapse
Insufficiency in which one or both mitral valve cusps bulge into the atria during ventricular contraction
Auscultation
Listening to sounds made by the body
First heart sound (S1)
The closure of the AV valves’ sound causing the movements of the heart wall (a “lubb”)
Second heart sound (S2)
The closure of semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic) and movements of the heart wall
Third heart sound (S3)
Rarely heard in people over 30; may indicate enlarged or failing heart
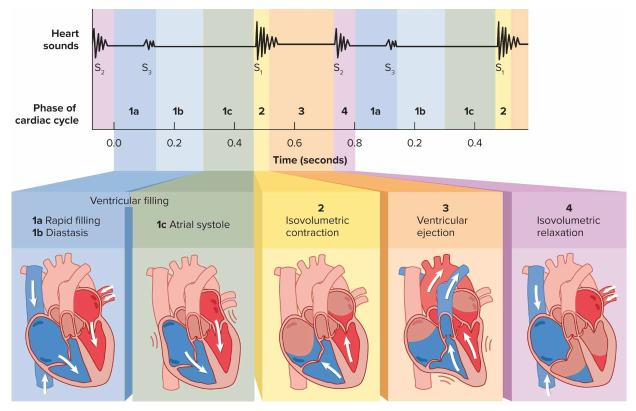
Cardiac cycle phases
Ventricular filling
Isovolumetric contraction
Ventricular ejection
Isovolumetric relaxation
Ventricular filling
The first step in the cardiac cycle where ventricles expand and blood flows into the ventricles from the atria
Isovolumetric contraction
The second step in the cardiac cycle where atria repolarize, ventricles depolarize, and S1 occurs with the QRS complex
Ventricular ejection
The third step in the cardiac cycle where semilunar valves open and ejection occurs, causing the T wave later on
Isovolumetric relaxation
The fourth step in the cardiac cycle where semilunar valves close and S2 occurs; sets up AV valves to refill and restart cycle
Congestive heart failure (CHF)
The failure of either ventricle to eject blood effectively; left failure can result in a pulmonary edema and right failure can cause a general edema