Module 3 Prerecorded Lecture Notes
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Shapes and morphology of bacteria
Cocci - round/spherical
Bacilli - rod shaped
Spirochaetes - spiral shped
Other shapes:
filamentous
curved
square
pleomorphic
Different arrangements of bacteria
Clusters (staphylo-)
Chains (strepto-)
Pairs (diplo-)
Tetrads (micro-)
Nomenclature of bacteria
Genus name + Species name
Genus = group with similar overall characteristics
Species = subgroup with same biochemical characteristics
Ex,, Staphylococcus Aureus
Staphylococcus = GENUS
Aureus = SPECIES
Process of gram staining
Crystal Violet is used once bacteria is fixated and stains all bacteria purple
Crystal violet is removed as much as possible using decolourizing agent (usually alcohol iodine)
Bacteria then stained with Safranin (counterstain) which turns gram (-) bacteria pink and keep gram (+) bacteria purple
Why do Gram (+) stay purple and gram (-) go pink
Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain due to their thick peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall
Gram-negative bacteria lose the stain (bc of no thick cell wall) and take up the safranin counterstain, appearing pink.
What are the three things needed to grow bacteria in a lab
Equipment
Media
Colony isolation
What are the “equipment” that are used to grow specific bacteria
Agar plate
Deep agar tube - for anaerobic bacteria
Broth - for initial bacterial growth
Agar slant
Different Media used when growing bacteria
Undefined media
Chemically defined media
Functional media
Physical nature media
Undefined media
used to grow ALL species of bacteria in a host sample (not selective)
Chemically defined media
media with know chemical components that will select for a specific bacteria
Functional media
once targeted bacteria is identified, nutrients and other functional measures will be added to ensure selected bacteria growth and death to other bacteria
Physical nature media
media that can vary in its physical properties to selectively grow a bacteria
Isolated Colonies
extraction of specific colony of bacteria which enables future research and test
Aerobes
bacteria that use oxygen
Anearobes
bacteria that die in the presence of oxygen and thrive in CO2 environment
*Anaerobes are very prevalent in the oral cavity
Aerotolerant
thrive in CO2 environment, but are not affected by O2 environment
Microaerophiles
only can grow in low concentration O2 environments
Ways of quantifying bacterial growth
Cell counting
Serial dilution and plating
Optical density of culture
qPCR
Cell counting
counting cells using a gridded slide to estimate the size of the entire colony
Serial dilution and plating
continue diluting solution until there are few enough bacteria to count - then extrapolate to find the colonies in units/ml
Optical density of culture
use spectrophotometer at 600nm to determine number of cells in a liquid culture by measuring light absorption.
qPCR
indirect measurement that provides the quantity of DNA or RNA in a sample by amplifying it through polymerase chain reaction and fluorescent light
Traditional methods of identifying bacterial species
Identify bacteria based on:
morphology
gram stain
standard biochemical testing
Novel ways of identifying bacteria
PCR: makes primers and detect bacteria by scanning the 16S subunit of ribosomal RNA
MALDI-TOF: “Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight” - uses spectrophotometry to measure time of flight of a particular protein
still need to have an idea for what bacteria you are looking for to do this technique
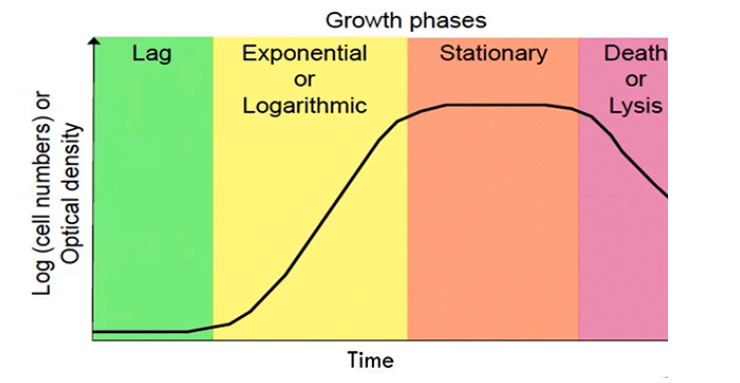
Features of the Bacterial Growth Curve
Lag Phase
Exponential/Logarithmic phase
Stationary phase
Death/Lysis phase
Lag phase
Few cells present, bacteria is looking for nutrients and is adapting to their environment
Exponential/Logarithmic phase
Nutrients are found and bacteria begin to rapidly grow and divide at exponential rate
Stationary phase
Number of cells growing = number of cells dying
due to nutrient competition and toxic byproducts (metabolic waste toxins) that restrict further growth
Death/Lysis phase
More dying bacterial cells due to a loss of nutrients and increase toxins in environment
Disease-causing Gram (+) bacteria
Streptococcus Mutans
S. Sanguinis
S. Oralis
S. Mitis
S. Gordonii
S. Parasanguinis
S. Salivarius
S. Anginosus
Most Students Often Memorize GRAM POSITIVE Species Accurately (MSOMGPSA)
Disease-causing Gram (-) bacteria
fusobacterium nucleatum
porphyromonas gingivalis
tannerella forsynthia
aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
treponema denticola (Spirochaetes)
Funky NEGATIVE Pirate Teach Amazing Tricks (FNPTAT)
Streptococci bacteria traits
Gram (+)
cocci shape
major genus of bacteria found in mouth
some can lyse red blood cells
Streptococci related to poor oral health
S. gordonii
S. salivarius
S. sanguis
Streptococci related to dental caries
S. pyogens
S. mutans
Bacteria that causes Gingivitis and Periodontis
Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas ginigivalis
mainly responsible for chronic gingivitis and periodontitis
Fusobacterium nucleatum
Prevotella intermedia
Selenomonas sputigena
Bacteria that cause juvenile periodontitis
Microaerophile Bacteria:
actinobacillus actinomycentemcomitans
Biofilm
matrix-encased community of microbes, held together by polymers and fibrils, that accumulates at tooth enamel surface
plaque = example of biofilm
biofilm allows ease of nutrient transfer between bacteria and protection from host immune response
Stages of microbial colonization of the oral cavity
Adhesion
Early colonizers
Late colonizers
mature plaque
Adhesion
Pellicles are salivary glycoproteins that are found on teeth after brushing
Bacterial surfaces contain glucose binding proteins which facilitate the bacteria binding to the tooth surface
What forces must the bacteria overcome to adhere to the tooth
Salivary forces (movement of saliva)
Shear forces (mouth movements)
Types of bacterial bonding to teeth
Initially,
Non-specific/low affinity bonding
quite weak and easily broken (ionic bonds, hydrophobic bonds, H-bonds, Van der Waals forces)
Later,
Specific/high affinity bonding
bacteria use their own proteins to bind to each other and to the teeth
Early and Late Colonizers
Early colonizer bacteria attach to pellicle, usually strepto bacteria
Examples
S. mitis
S. gordonni
S. sanguinis
S. oralis
Bacteria then aggregate using coadhesion to join biofilm
Examples
propionibacterium
haemophilus
actinomyces species
Late colonizers will continue to attach to the biofilm
Examples
fusobacterium nucleatum
prevotella intermedia
haemophilus prarainfluenzae
Mature Plaque
Plaque is now surrounded by matrix and combines with host DNA and polymers to make plaque ‘sticky’
morphology appears as ‘corn cob’, ‘test tube brushes’, or ‘hedgehogs’
Mature plaque is self sustainable and can break off into separate colonies
Growth of plaque is influenced by prevalence of salivary glycoproteins and diet
Aerobic bacteria (outer layer) → microaerophiles (middle) → anaerobes (inner layer of plaque)
*O2, nutrients, and pH decrease as you move from exterior to interior of the plaque
Beneficial bacteria-bacteria interactions (Veillonella with Streptococci)
Streptcocci produce lactate, which the Veillonella will consume
will reduce acidity of the mouth
Beneficial bacteria-bacteria interactions (S. gordonii with P. gingivalis and F. nucleatum)
S. gordonii will facilitate redox reactions that make the oral environment more anaerobic → increased growth of anaerobic bacteria like P. gingivalis and F. nucleatum.
Beneficial bacteria-bacteria interactions (F. nucleatum with P. gingivalis and T. forsythia)
Interaction reduces oxygen levels and increases pH → makes it easier for harmful anaerobic bacteria to thrive
Beneficial bacteria-bacteria interactions (P. gingivalis with T. forsythia, T. denticola, and P. intermedia)
Metabolize succinate and incorporate heme groups → increase in survival of pathogenic bacteria
Calculus
Calcium phosphate deposits within the biofilm that hardens and must be removed by a professional
accentuated by individuals with increased levels of Ca in saliva
Bacteria found on the tongue
prevotella
Veillonella
actinomyces
Bacteria found on the hard palate
prevotella
veillonella
actinomyces
gemella
Bacteria found in the bacterial mucosa
prevotella
veillonella
actinomyces
gemella
streptococcus
Bacteria found in the throat, tonsils, and saliva
prevotella
veillonella
actinomyces
gemella
streptococcus
Advantages for bacteria living in a biofilm
Antimicrobial resistance - biofilm will block antibiotics from entering the matrix
Food sharing - bacteria can exchange nutrients and metabolites with one another
Communication - cells can coordinate gene expression and virulence
Competence - transfer of DNA between bacteria to tolerate new environments
Disadvantages for bacteria living in a biofilm
Slow diffusion - matrix slows metabolism, nutrients are restricted to the deepest parts of the biofilm
Concentrating chemicals - chemicals are hard to remove from biofilm therefore bacteriotoxins can build up
Bacteriocins - release of proteins that kill other bacteria in the biofilm
Oral ecology
microorganisms and their interactions between each other and with their environment
Specific Plaque Hypothesis (SPH)
Walter J. Loesche (1976) - only specific cariogenic bacteria like S. mutans and lactobacilli are responsible for dental caries
relies on culture based techniques and microscopy to identify and target specific pathogens
Non-specific Plaque Hypothesis (NSPH)
Walter Loesche (1976)
initially stated that caries formed from the quantity of plaque accumulation rather than specific bacteria (as argued in SPH)
abandoned this and revised the NSPH in 1986 to suggest quantity and bacterial virulence cause caries and advocates for mechanical removal to prevent disease
Ecological Plaque Hypothesis (EPH)
Proposed by Marsh (1994)
integrates elements of SPH and NSPH
suggests that dysbiosis (imbalance of oral microflora) = disease
changes in pH, oxygen, and nutrient availability contribute to the disease
suggests using sugar alternatives to remove risk factors for disease
Keystone Pathogen Hypothesis (KPH)
Hajishengallis et al. (2012)
proposes that certain pathogens, known as keystone pathogens, can disrupt the host's microbial community balance, leading to dysbiosis and disease, even in low abundance
Polymicrobial Synergy and Dysbiosis (PSD)
complements KPS
emphasizes that keystone pathogens interact with other polymicrobes that lead to dysbiosis and contribute to disease progression
Which hypothesis is considered to be the best right now
Ecological Plaque Hypothesis due to consideration of environmental factors
Summary of Plaque Hypotheses

Factors that cause changes in the oral microbiota
bidirectional dynamic relationship
Intrinsic host factors (saliva, oral pH, host immune response)
Extrinsic host factors (lifestyle, diet, oral hygiene, environment)
Caries process (caries ecological hypothesis)
extensions of EPH to include caries formation and factors; pH, nutrients, oxygen that are included in the caries process
What are the four stages of caries ecological hypothesis
Dynamic stability stage
Acidogenic stage
Aciduric Stage
Proteolytic Stage
Dynamic stability stage
occurs when non-mutans streptococci and actinomyces dominate the biofilm
acid begins being released and mouth pH decreases
generally, reversible cascade can return pH to normal
if bacteria left long enough, low pH will not be reversible
Acidogenic stage
increase non-mutans strep. and actinomyces as pH continues to decreases
early demineralization of enamel
Aciduric stage
as pH crashes, mutans bacteria emerge along with non-mutans aciduric bacteria (lactobacilli)
further demineralization of enamel
Proteolytic stage
responsible for caries in dentine and root
stage exists between acidogenic and aciduric stage
demineralizes organic matrix (collagen) in dentine and roots
activates salivary matrix metalloproteinases (MPP) and cathepsins to further demineralize dentine and root
Generalist carious bacteria
Non-mutans streptococci
can adapt to variety of conditions in the biofilm
contain their own adhesion proteins for binding to pellicle
produce polysaccharides (glucans and glycosidases) to reinforce plaque matrix and lower pH
Specialist carious bacteria
specifically produce water-insoluble glucans to recruit more bacteria
contributes to pH falling close to 4
What is the critical pH of the mouth
5.5
Bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates
Bacteria perform glycolysis via the Emben-Meyrhof-Parnas (EMP) pathway
Glucose → pyruvate (ATP and NADH produced)
Pyruvate → lactate (S. mutans and lactobacilli produced - decrease pH)
Glucose metabolism produces other acids:
acetic
lactic
formic
propionic
Types of salivary glands
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
Intrinsic salivary glands
numerous and small (500-1000 of them)
found in mucosa/submucosa of oral cavity, tongue, oropharynx, upper resp. tract
Function:
mucous-secreting
saliva
lubrication
digestion
Extrinsic salivary glands
three pairs that are larger and located outside the oral cavity
Parotid gland - serous secretion
Submandibular gland - mixed secretion
Sublingual gland - mucous secretion
Main type of intrinsic salivary gland and where it’s found
Von Ebner’s Gland (found on tongue)
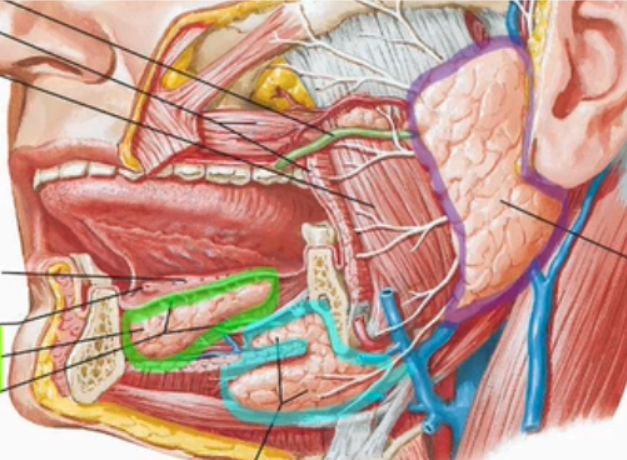
Label the extrinsic salivary glands
Sublingual Gland
Submandibular gland
Parotid gland
Describe the parotid gland
sits lateral to the ramus of the mandible and masseter
enclosed in parotid capsule
parotid capsule receives external carotid, retromandibular vein, facial nerve
parotid duct leaves gland superficial to the masseter and through the buccinator into the vestibule near the second molar (parotid papilla)
Innervation of the parotid gland
Parasympathetic: glossopharyngeal (CN IX) via the auriculotemporal nerve (a part of CN V3 that runs through the foramen ovale)
Sympathetic: external carotid plexus
Sensory: auriculotemporal nerve and greater auricular nerve (branch of the cervical plexus)
Describe the submandibular gland
medial to the body of the mandible
Has superficial and deep parts as it wraps around the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle
extraoral lobe sits below the mylohyoid muscles and the intraoral lobe wraps around the mylohyoid
duct opens into the sublingual papilla as it travels into the oral cavity
Innervation of the submandibular gland
Parasympathetic: chorda tympani (branch of the facial nerve CN VII)
Sympathetic: external carotid plexus
Sensory: lingual nerve (mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve CN V3)
**Sublingual is the same
Describe the sublingual gland
located between oral mucosa of the floor of mouth and the mylohyoid in the sublingual fossa
opens directly in the oral cavity proper via 8-10 ducts in the sublingual fold of the alveolar sulcus
Functions of saliva
wound healing
buffer
teeth mineralization
food digestion
lubrication
anti-viral/antibacterial/antifungal
Composition of saliva
mostly water
high K+ and HCO3-
low Na+ and Cl-
digestive enzymes (salivary amylase, lingual lipase)
mucin
lysozyme
IgA antibodies
What are the components that saliva is categorized into
Water and Electrolytes
Proteins
Small organic molecules
Hormones
Saliva components (1a: Water)
98-99% of saliva
makes saliva hypotonic
aids in lubrication
cleansing teeth and oral cavity
taste
remineralization via dissolved Ca and other minerals
Saliva Components (1b: Electrolytes)
osmolarity: Na, K, Cl, HCO3
Buffering of pH between 5.75-7.05 (HCO3 and HPO4)
remineralization: Ca, F
Salivary Components (2a salivary glycoproteins - i. Mucin)
tissue coating; branches of oligosaccharides that play a role in forming the pellicle
lubrication
Salivary Components (2a salivary glycoproteins - i. Proline-rich proteins)
40% of protein in saliva
high affinity for hydroxyapatite
lines tooth surface and allow bacteria to bind to tooth surface
also has negative charge that recruits bacteria
slows down loss of dissolved Ca and PO4 ions
Salivary Components (2a salivary glycoproteins - i. Alpha-amylase)
makes up 40-50% of all salivary proteins
80% of amylase is produced in the parotid glands
encoded by gene ‘Amyl’ on chromosome 1
is an endoglyco-hydrolase
digests starch into maltose
only active at low pH
Salivary Components (2a salivary glycoproteins - i. Lingual Lipase)
secreted by von ebner’s glands (in the tongue)
digests fat
breaks down medium-long-chain triglycerides
digests milk fat in newborns
highly hydrophobic and enter fat globules
Salivary Components (2b anti-microbial proteins - i. Lactoferrin)
a transferrin family protein that transfers to the cell
found in milk
binds to free iron in saliva and deprives bacteria of iron need for growth
Salivary Components (2b anti-microbial proteins - i. Lysozyme)
damages bacteria by degrading peptidoglycan cell wall (effective against gram +)
part of innate immune sys
derived from:
major/minor salivary glands
phagocytic cells
gingival crevicular fluid (GCF)
Salivary Components (2b anti-microbial proteins - i. Growth factors)
epidermal growth factors (EGF)
transforming growth factors alpha/beta (TGF-a, TGF-b)
fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I, IGF-II)
nerve growth factor (NGF)
Function:
interact with oral epithelium for;
wound healing
regulation of epithelial growth
epithelial lining homeostasis
Exocrine Glands
glands that release secretions via a duct directly to the surface
Endocrine glands
release secretions (generally hormones) into extracellular space (usually the bloodstream)
Structure of salivary glands
Secretory acinar cells
serous, mixed, mucous
lined by myoepithelial cells which contract to release secretions into collecting ducts
Intercalated ducts
transitional cells between the excretory ducts and the acinar cells
Striated ducts
Main secretory ducts
empties into excretory duct
Main excretory ducts
empties into oral cavity
Stages of the formation of saliva
Primary secretion
Secondary secretion (ductal secretion)
Primary secretion
Na-K-ATPase and Na-K-Cl symporter is establish due to conc. gradient in acini lumens
Na + water travels into lumen via conc. gradient
moves through leaky tight junctions between acini cells