CHEM 43A Final
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What is PPE?
lab coat
safety goggles
closed toe shoes
socks
long pants
hair pulled back
What is RAMP?
R- recognize hazards
A- assess risk of hazards
M- minimize risk
P- prepare for risks
Why do we use boiling chips?
Danger of boiling is large bubble that spontaneously bursts so boiling chips serve as nucleation site for bubbles to form
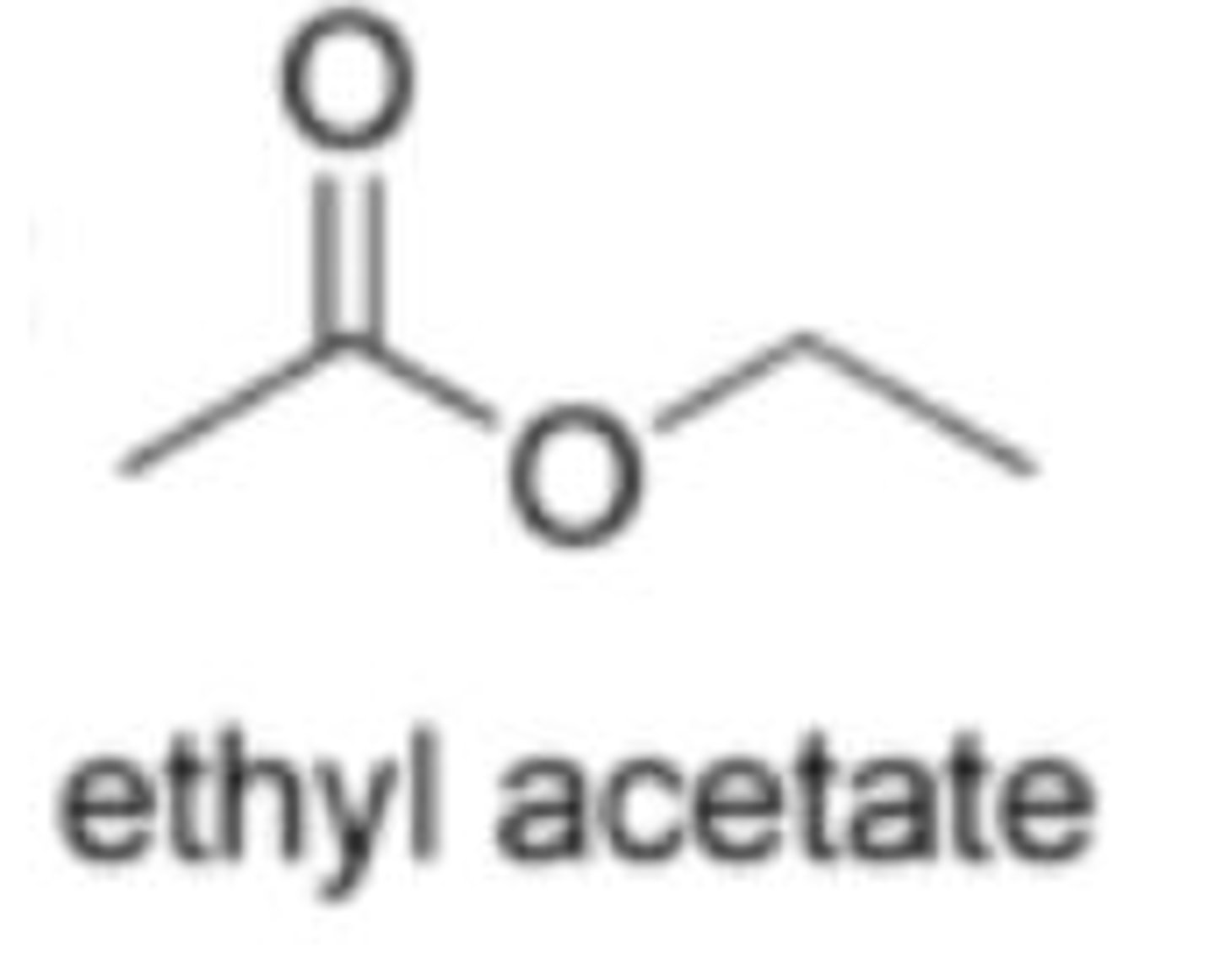
ethyl acetate
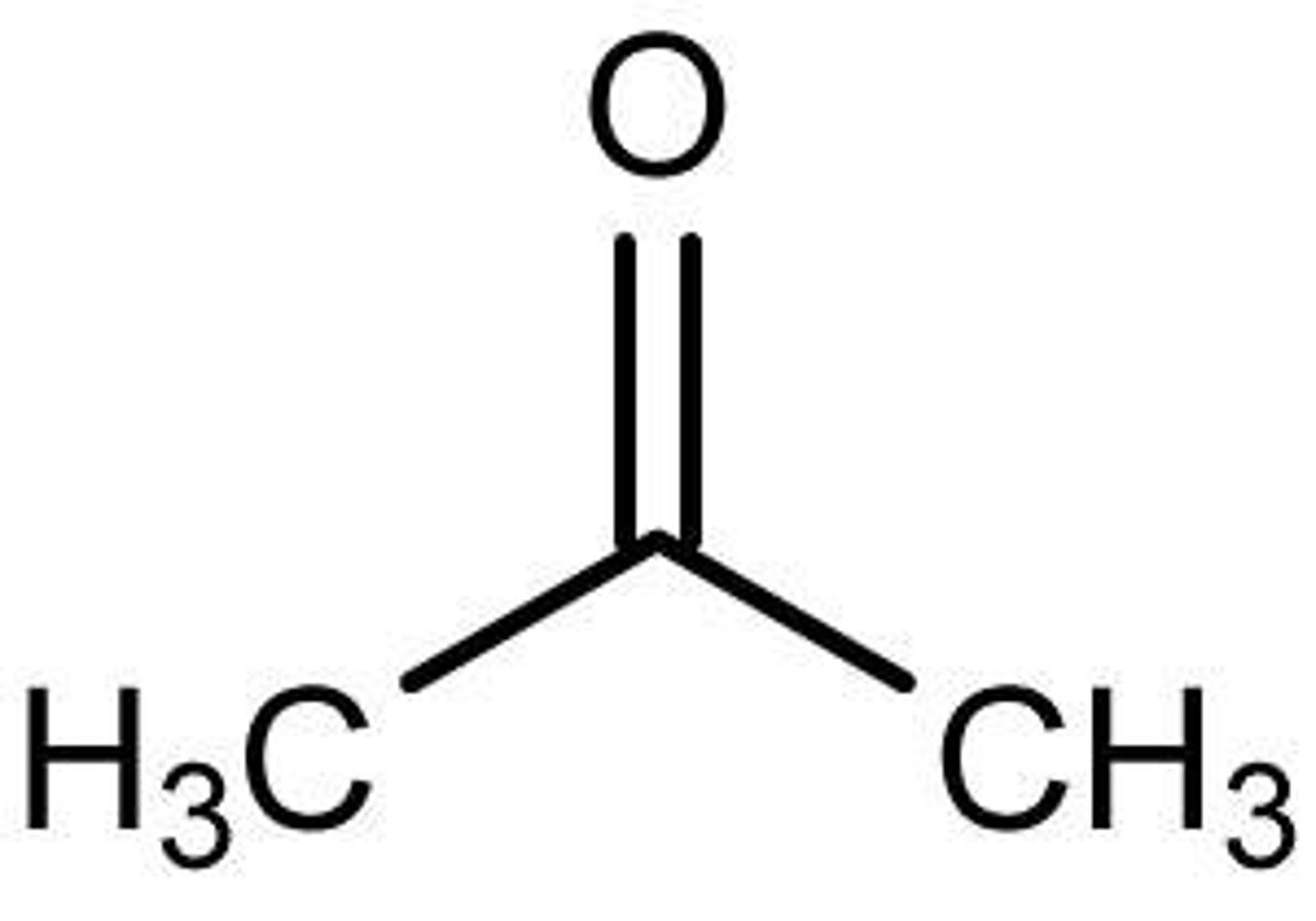
acetone
How is miscibility decided?
If it's in water, it will be miscible if it's 4-5 carbons and has a functional group to H bond with
like dissolves like (organic dissolves organic)
water and butanol
benzene and dichloromethane
acetone and water
MTBE and dichloromethane
strong acids/bases are inorganic solvents
E0
Why are cotton plugs used in pipettes?
To transfer liquids without solid contaminants from entering
The cotton is at the neck of the pipette and the solid/liquid mixture is added to the top of pipette
E0
What is melting point?
Temperature at which a solid transitions to a liquid
-characteristic chemical property
E0
How do impurities affect melting point?
Impurities will lower and broaden the melting point into a melting range
E0
What do mixed melting points do?
Confidently identifies an unknown compound
-if unknown and known are the same, the mixture is pure and you will see a sharp melting point
-if impure, melting point range will be lower and broader
E0
Why do we calibrate?
it is common for thermometers to be inaccurate; difference between literature mp value and observed mp is correction factor
correction factor accounts for accuracy
E0
Given molecular structures, estimate relative melting points based on intermolecular interactions?
The more polar interactions, the stronger a compound so higher melting point
highest: benzamide (CONH2)
nitrobenzene (NO2)
lowest: toluene (hydrocarbon
E0
Why do organic chemists weigh liquid reagents when accuracy is important?
mass is generally more precise/accurate and reliable
E0
Graduated cylinders and pipettes are not particularly accurate nor are your measurements precise. Explain how this affects the reliability of your data (i.e. the observed density of water)?
Data and calculations are not very price or reliable
E1
What is crystallization?
A technique where a solid compound is dissolved into a solvent and then slowly reformed into crystalline form
hot solvent is used so the compound dissolves
E1
What happens to a compound after being dissolved in a hot solvent?
Upon cooling, the solubility of the compound in the solvent should decrease
the solution becomes supersaturated and crystals form
E1
What is recrystallization?
Recrystallization is used as a purification technique that takes advantage of differences in solubility between desired compound and impurities
E1
What happens during recrystallization?
After dissolution, insoluble impurities can be filtered from the hot solution
After recrystallization, crystals are recovered by hot gravity filtration and soluble impurities remain in the cold solution
E1
What are the key steps to successful purification by recrystallization?
Dissolution
Decolorizing
Hot Filtration
Crystallization
Recovery
E1
Explain dissolution?
-dissolve compound in minimum solvent just below boiling point
-if compound concentration is too low, cooling will not yield a supersaturated solution and compound will not crystalize
E1
What is crystal formation dependent on? How to maximize recovery?
concentration of solute, temperature of solvent, and cooling rate
if solution cools too quickly, crystals are unstable and rapidly precipitate with impurities
Once crystals have formed, solution is often placed in ice bath to maximize recovery
E1
What is the ideal solvent?
If solute is very soluble in solvent, it may never crystallize
E1
How can crystal nucleation be induced?
-addition of previously obtained crystals
-scratching side of flask
-increase concentration by reheating solution to remove excess solvent by evaporation
E1
What is macroscale and microscale isolation?
vacuum filtration
centrifuge and craig tube
E1
What should you do if you don't recover any crystals after the recrystallization? (Where'd the compound go?)
boil solvent
check funnel
scratch glass
add seed crystal
E1
Why is it important to slowly cool the hot solution of dissolved compound? What might happen if you cool the solution too quickly?
slower cooling= higher purity
faster may trap impurity
E1
What are the characteristics of a good recrystallization solvent?
solute is soluble in hot solvent
solute is insoluble in cooler solvent
E1
Was your recrystallized compound pure? How do you know?
Width of melting point range indicates purity
E2
What is liquid liquid extraction?
Separation method based upon differential solubility of components in a mixture between 2 immiscible solvents (different partition coefficients)
distribution/partition coefficient (K) is the ratio of the solubility of the component in the 2 solvents (g/ml in organic/ g/ml in water)
E2
What are the steps of liq-liquid extraction?
dissolution
mixing
separation
drying an organic solution
isolation and recovery
E2
What is dissolution?
Mixture is dissolved in an organic solvent and then added to aqueous solution (water or MTBE)
organic solvent must not be miscible with water/MTBE or else they won't separate
denser layer forms on bottom (most dense- naoh, hcl, water, mtbe- least dense)
components of mixture partiion between layers based on their K values in each
E2
Why is brine used in extraction?
vigorous shaking can lead to emulsions, which make good separation difficult
brine (salt water) reduces emulsions by removing dissolved water
E2
Why is organic solvent washed?
Organic solvent will always have small amount of water so brine is used to removed dissolved water
solid drying agent is then used to adsorb any last traces of water
E2
What are good drying agents?
MgSO4 (Faster, more effective) of Na2SO4 (removes more water but is slower)
When water is absent, excess drying agent will float freely in solution and look like a slow globe
E2
How is isolation and recovery done?
Desire compound id isolated by filtering solution to removing drying agents and then removing the solvent via evaporation
extraction is a separation technique but not purification (use distillation or recrystallization)
E2
What were the insoluble compounds in tea?
cellulose
removed in the first solid-liquid extraction with hot water; water soluble components are extracted into the water but the tea leaves stay behind
E2
What were the water soluble compounds?
proteins and pigments- these are soluble in water but not methylene chloride
saponins- amphiphiles that increase solubility of organic molecules in water in the form of emulsions; broken up with brine since it increases the polarity of water and reduces solubility of organic molecules
tannins-bitter taste of tea; soluble in methylene chloride so aqueous base like CaCO3 of NaCO3 is used to form water soluble gallic acid salts and glucose
(base catalyzed hydrolysis of tannins)
E2
How is caffeine purified?
-with sublimation
-sublimation is going from solid to vapor state and depositing back to solid crystalline without passing through liquid phase
-done at low pressures
E2
Determine how many extractions are needed to recover more than 90% of compound?
Kd= [organic]/[water]
Let's say Kd is 1.5, it means 60% organic and 40% aqueous
now take 40% aqueous and you get 60% of 40%=24%
Now take 16% aqueous and you get 60% of 16=9.6%
60 + 24 + 9.6 = 93.6 %
E2
If there's 55 mg caffeine, how much can be extracted If there's 40 ml tea/water and Kd is 7.2?
What if Kd is 2?
40mg
20 mg
E2
Why was sodium carbonate added to tea?
hydrolysis of tannins with base
E2
How to tell if something is soluble in water?
4-5 carbons and a polar functional group will h bond
E3
What are pKas you should know?
5- carboxylic acid
10- phenol (benzene ring with OH)
15- alcohol
E3
How can acidic organic compounds be converted to water soluble anions?
Use inorganic bases like NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate) or NaOH
carboxylic acid is sparingly soluble in acidic and neutral aqueous solution but very soluble in basic aqueous solution
E3
How can basic organic compounds be converted to water soluble anions?
use inorganic acids like HCl for extraction/removal of basic organic substances from organic phase
E3
How do you recover an organic compound?
To recover the organic compound, aqueous solution containing the charged ionic compound is treated with acid or base to reverse the acid/base reaction and extracted back into a new portion of organic solvent (MTBE)
E3
Describe the steps to isolate an amine.
--unknown in MTBE--
1. Add HCL to unknown
This forms MTBE layer and HCl aqueous layer (containing amine)
2. Drain aqueous HCL layer
3. Add NaOH to neutralize until it's basic
4. Add MTBE and extract the basic aqueous solution
5. Wash with brine and dry with MgSO4
E3
Which layer is top and bottom?
aqueous- bottom organic- top
E3
How do you recove rthe carboxylic acid?
1. Add NaOH to unknown mixture sans amine, creating an MTBE mixture and NAOH layer (this has the CA)
2. Wash NaOH layer with MTBE and discard organic layer
3. Neutralize with HCl until it is acidic
4. Extract with MTBE, wash the combined organics with brine and dry with MgSO4
E3
How do you isolate the neutral compound?
1. Add MTBE to original MTBE solution
2. Add water
3. Remove aqueous layer and extract aqueous layer
4. Add brine and MgSO4 to organic layer
E3
How were the acids, bases, and neutrals identified?
Melting point determination
E3
Did you recover 100% of starting compound?
Some compounds might not have been in the organic layer when needed and still in aqueous
E3
Were recovered products pure?
Determine based on melting point ranges
E3
How could mass recovered been decreased or increased?
Decrease: not enough acid/base was added neutralize
when heating off the solvent, compound evaporated as well
Increase:
MgSO4 wasn't properly filtered out
compound didn't try completely so water still stuck to compound
E4
how does capillary action work?
water has attraction to surface and leads to solvent going up because it's being pushed from the sides to attract to the surfaces
E4
Why have the filter paper?
It saturates the chamber so that solvent from the TLC doesn't evaporate
E4
What does chromatography separate based on?
Intermolecular interactions between the compound
E4
What is the mobile phase and stationary phase?
mobile- solvent
stationary- silica gel
E4
What is the difference between liquid and gas chromatography?
liquid- solid stationary phase and liquid mobile phase
gas- liquid stationary and gas mobile phase
E4
What is happening in liquid chromatography?
Silica gel and alumina (stationary phase) are highly polar
polar molecules withh strongly but reversibly interact and move slowly
nonpoalr compounds weakly interact and move down quickly
this causes compounds moving at difference rates, resulting in a physical separation
E4
How does solvent polarity affect rate?
Polar solvents reversibly interact with polar surfaces of the stationary phase, causing polar compounds to travel faster and farther and nonpolar compounds to go faster-er
if less polar, Rf will decrease
E4
Rank functional groups and solvents by polarity.
functional groups:
carboxylic acid
alcohol, amine, thiol
aldehyde, ketone, thiols
halogenated hydrocarbons
unsaturated hydrocarbons
saturated hydrocarbons
solvent:
water
methanol/ethanol
acetone
ehtyl acetate
diethyl ether
dichloromethane
toluene
hexane
E4
What's the difference between TLC and column chromatography?
TLC:
stationary phase is fixed in a thin layer to a plate (glass, plastic, aluminum) and placed in solvent reservoir
solvent moves up stationary phase via capillary action
column: stationary phase is packed into a tube and mobile phase is passed over stationary phase using gravity or pressure
E4
Why does spot size in TLC matter?
Too big: covers up other spots, overloads plate/smears
Too small: can't measure accurately, giving incorrect Rf
E4
What happens to Rf if you left TLC plate in chamber for too long?
Spots keep moving up the plate, become diffuse, or both, leading to inaccurately high Rfs and possibly disordering spots
E4
Why do ortho and para have different Rfs?
ortho is less polar bc it's dipole moments cancel out slightly and intramolecular H bonding reduces plate interactions, resulting in higher Rf than para
E5
What is distillation?
Separation and purification technique that relies on differences in boiling points (and vapor pressure) to separate components in a liquid mixture
E5
How does distillation work?
Mixture of miscible liquids is heated and begins to boils
Vapors contain a greater percentage of the more volatile components (lower boiling point/higher vapor pressure)
the vapor is then cooled and condensed into a separate flask
resultant liquid now contains an increased percentage of the more volatile compound and a decreased percentage of the less volatile compound
has to be repeated numerous times, each time increasing the purify the collected liquid
E5
How does fractional distillation work?
Technique to do a large number of simple distillations in a single continuous operation
fractionating column has an extensive surface area that induces vapors to condense before the collection flask
cooled condensate falls down the fractionating column where it encounters hot vapors rising up
hot vapors transfer heat to the condensate so that liquid components return to the gas phase according to their boiling points and vapor is more enriched in more volatile component
E5
What is gas chromatography?
analytical technique that uses a gas as the mobile phase
solution containing the compounds is injected to the instrument, where the sample is rapidly heated under reduced pressure to vaporize everything
retention time: similar to Rf
E5
Explain why the observed starting vapor temperature in the simple distillation should be above the boiling point of hexane.
vapors contain mixture of hexane and heptane
E5
Explain how fractionating column works to improve separation in a fractional distillation.
Enrichment of more volatile component due to more vaporization/condensation cycles (many simple distillations) with increased theoretical plates (increased surface area)
E6
What is esterification?
Formation of an ester using alcohol and carboxylic acid (reversible and under equilibrium)
Use Le Chatelier's principle to push reaction forward by using large excess of alcohol as solvent
catalyst: sulphuric acid
E6
What is boiling point determination?
boiling point of pure liquid is temperature at which vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure
E6
What is IR?
organic molecules absorb infrared light when the wavelength (and energy) corresponds to specific molecular vibrations and rotations
inverted peaks are shown at wavelengths of lights which are absorbed
E6
What is refluxing?
Most organic reactions don't occur quickly at room temperature and require a period of heating without loss of reagents
refluxing means boiling a solution while continually condensing the vapor by cooling it and returning the liquid to the reaction flask
condenser is used as means of cooling the vapor so that it condenses and flows back into the reaction flask
What are key IR regions?
finger print- until 1400
region 1: 1400-1800 (double bond)
region 2: 1800- 2500 (triple bond)
region 3: 2500-end (single bond)
c=o: 1700
broad swoop: OH
amine= fangs
broad but with fangs= COOH
What is Jones Oxidation?
reagent- chromic acid (from CrO3 and H2SO4)
primary, secondary, and aldehydes turn red/orange to blue/green
R-OH + CrO3/H2SO4/H2O --> Cr2(SO4)3 + R(C=O)(OH/R)
What is Lucas?
reagent- anhydrous Zinc Chloride and HCl
secondary (slow) tertiary (fast) alcohols go from clear solution to cloudy with 2 layers
R(OH) + ZnCl2 + Hcl --> H2O + R-Cl (RR-Cl)
What is DNP test?
reagent- 2,3 dintrophenyl hydrazine
aldehydes and ketones form red/orange precipitate in clear orange solution
What is Tollens test?
reagent- AgNO3 and NH4OH
aldehydes form silver mirror from clear solution
What is the derivative for alcohols and aldehydes/ketones?
alcohols-
ester formation with 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride and pyridine
aldehydes/ketones:
1. hydrazone formation with 2,3 dinitrophenylhydrazine and HC:
2. semicarbazone formation with semicarbazide hydrochloride and sodium acetate