MSU CEM 141 FINAL EXAM
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
scientific question
can be answered by doing experiments, making observation, taking measurements, etc. in a replicable way
Lights acts as what?
Particle and wave.
scientific model
drawing, graph, diagram, equation. represent many chemical entities.
Wavelength
The distance (m) of waves from peak to peak. Short: x-ray (red), long: infrared (blue)
Short - higher energy
Long - lower energy
scientific theory
A well tested concept that explains a wide range of observations (explains why). changes with time. Explains the underlying cause of a range of phenomena
Frequency (V)
The number of wavefronts per second. Highest: x-ray
scientific law
A theory that has been tested by and is consistent with generations of data. a rule that describes a pattern in nature (explains what)
Velocity of Light
C = 3.00 X 10^8
= wavelength X frequency
scientific explanation
claim, evidence, reasoning
Amplitude
The intensity, height of peaks of waves. Highest: blue light
size of an atom
0.1 x 10^-9m
Energy of Wave (J)
Increases as frequency increases and as wavelength decreases. Highest: x-ray
Greek philosophers atomic theory
-first atomic theory
-elements: earth, fire, water, air
-constantly in motion
-made of mostly empty space
Range of Wavelengths
10^-16 - 10^8 = 24. Only a third are visible
Black Body Radiation
When a mass is heated it emits a type of EM radiation, at very high temps the mass becomes "white hot" because all wavelengths of visible light become equally intense
molecular structure of a substance determines ___
the observable properties
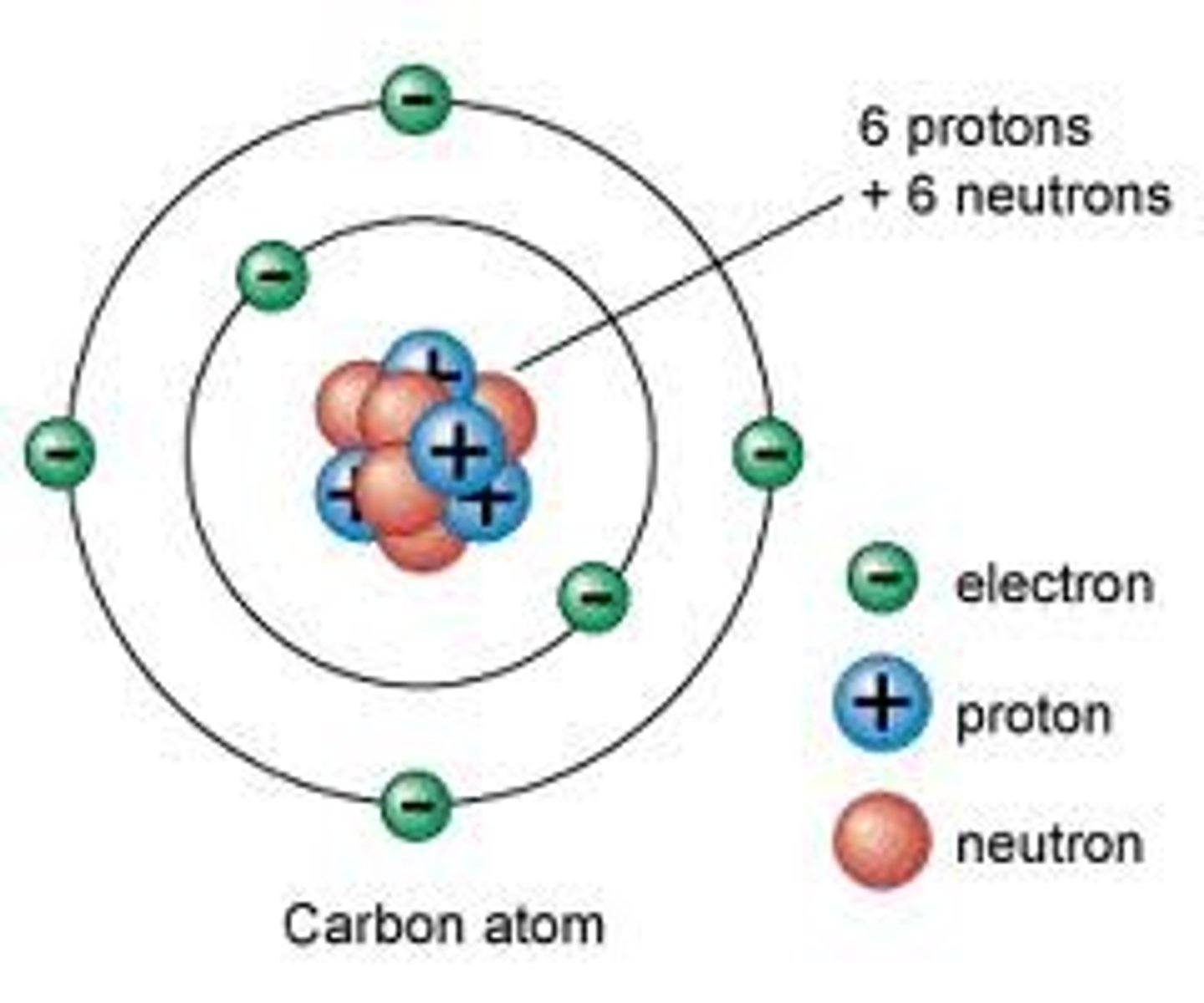
atom
smallest distinguishable part of an element
Photoelectric Effect
Metals emit electrons when electromagnetic radiation shines on the surface, light is transfers energy to the electrons at the metal's surface where it's transformed into KE that gives the electrons enough energy to leave the atom
Depends on frequency not intensity
how many atoms are naturally occurring?
91 naturally occurring elements
How many electrons are emitted if the light is below it's threshold frequency no matter the intensity?
None.
Dalton's atomic theory (1800s)
-elements composed of small, indivisible, indestructible, particles (atoms)
-all atoms of each element are identical (mass/properties)
-no subatomic particles
-compounds are formed by combos of atoms from 2+ elements
-chemical reactions occur from rearrangement of atoms
What increases the number of electrons to be emitted by the photoelectric effect?
Intensity.
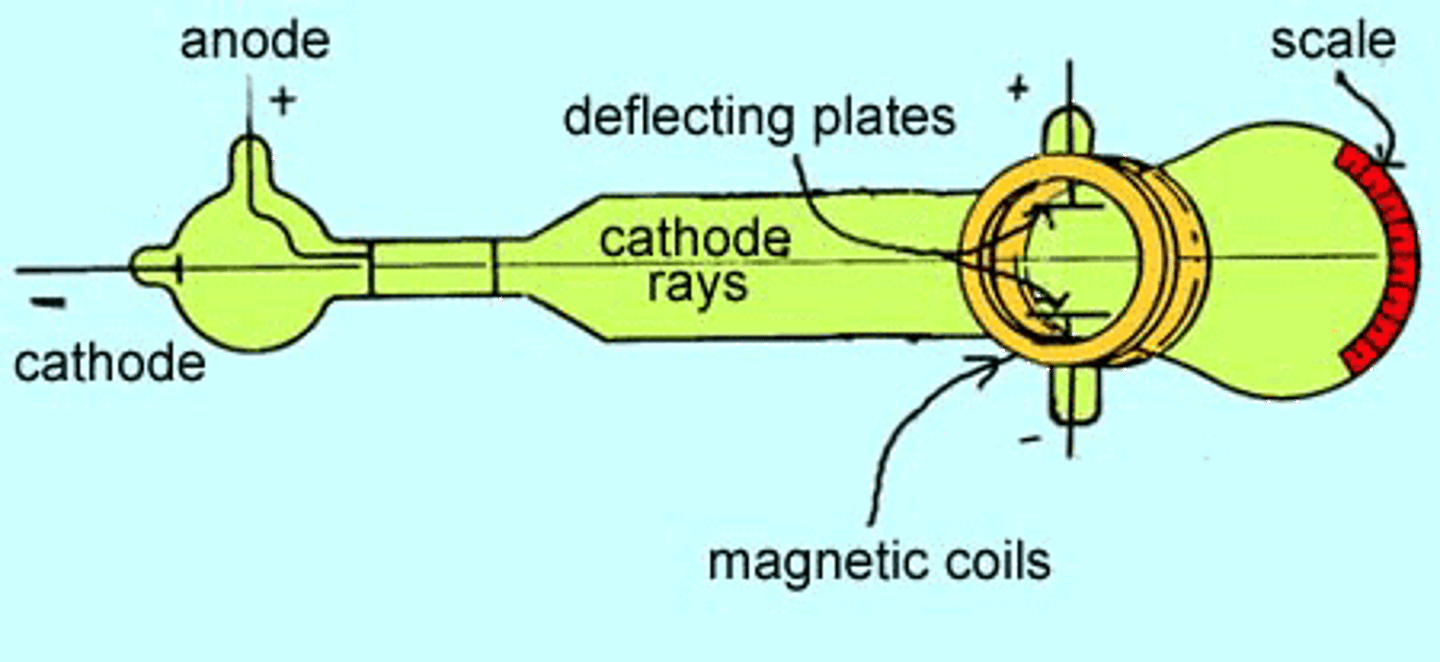
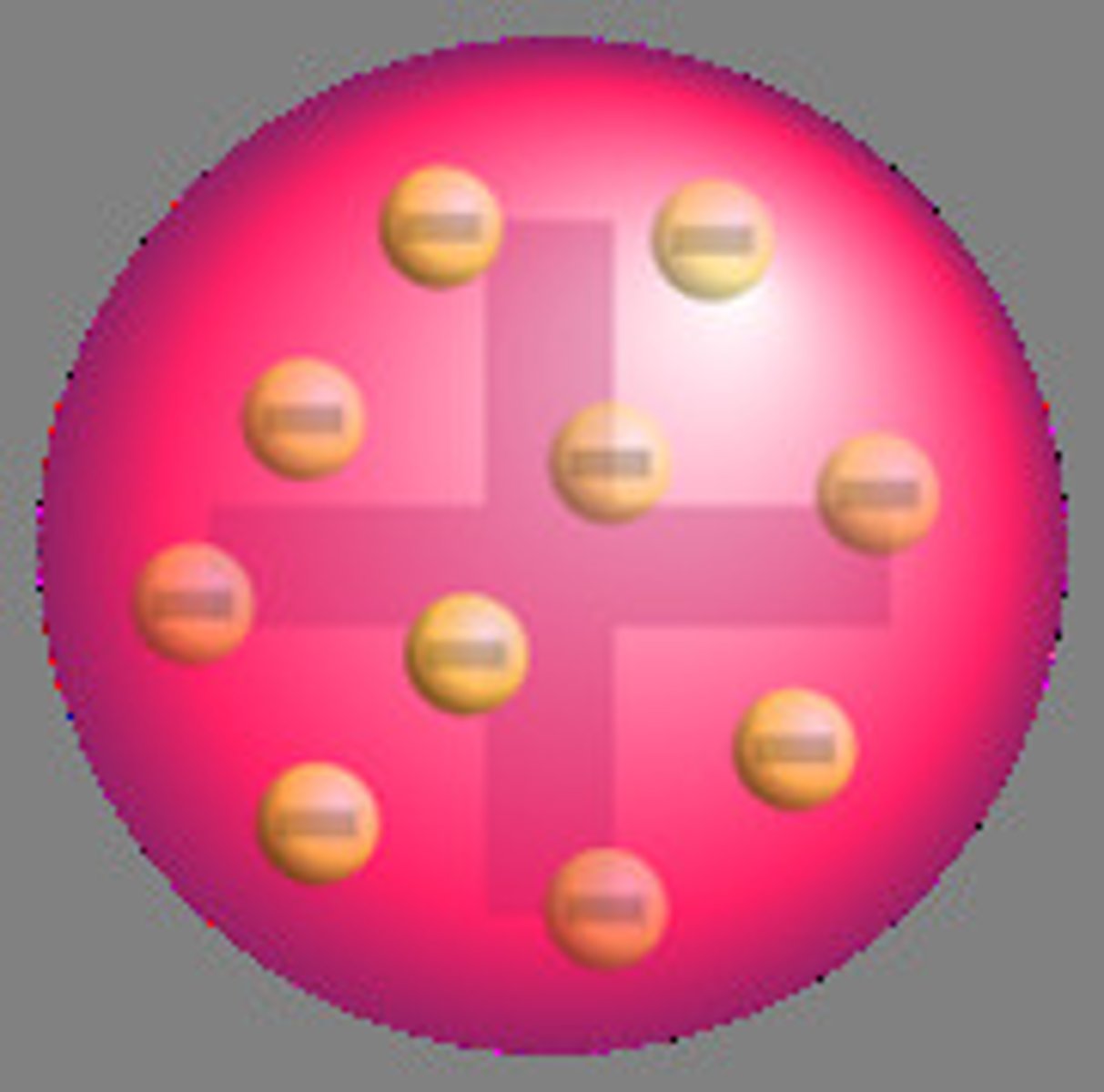
JJ Thomson
-first person to provide evidence of electron
-cathode ray tube
-plum pudding model
-particles carried electric charge
A particle that transfers light energy with a definable energy, emits one electron
energy of = h (6.626 x 10^-34 J)
Photon.
cathode ray tube
-JJ Thomson
-electron particles were emitted from cathodes
-particles carried electric charge
-ray was independent of the element it came from
-particles identical regardless of cathode
-proved all atoms contained electrons
Energy of light equation?
E = hV.
plum pudding model
-atoms contained electrons embedded in the middle
-JJ Thomson
h
Planck's constant, the energy of a photon.
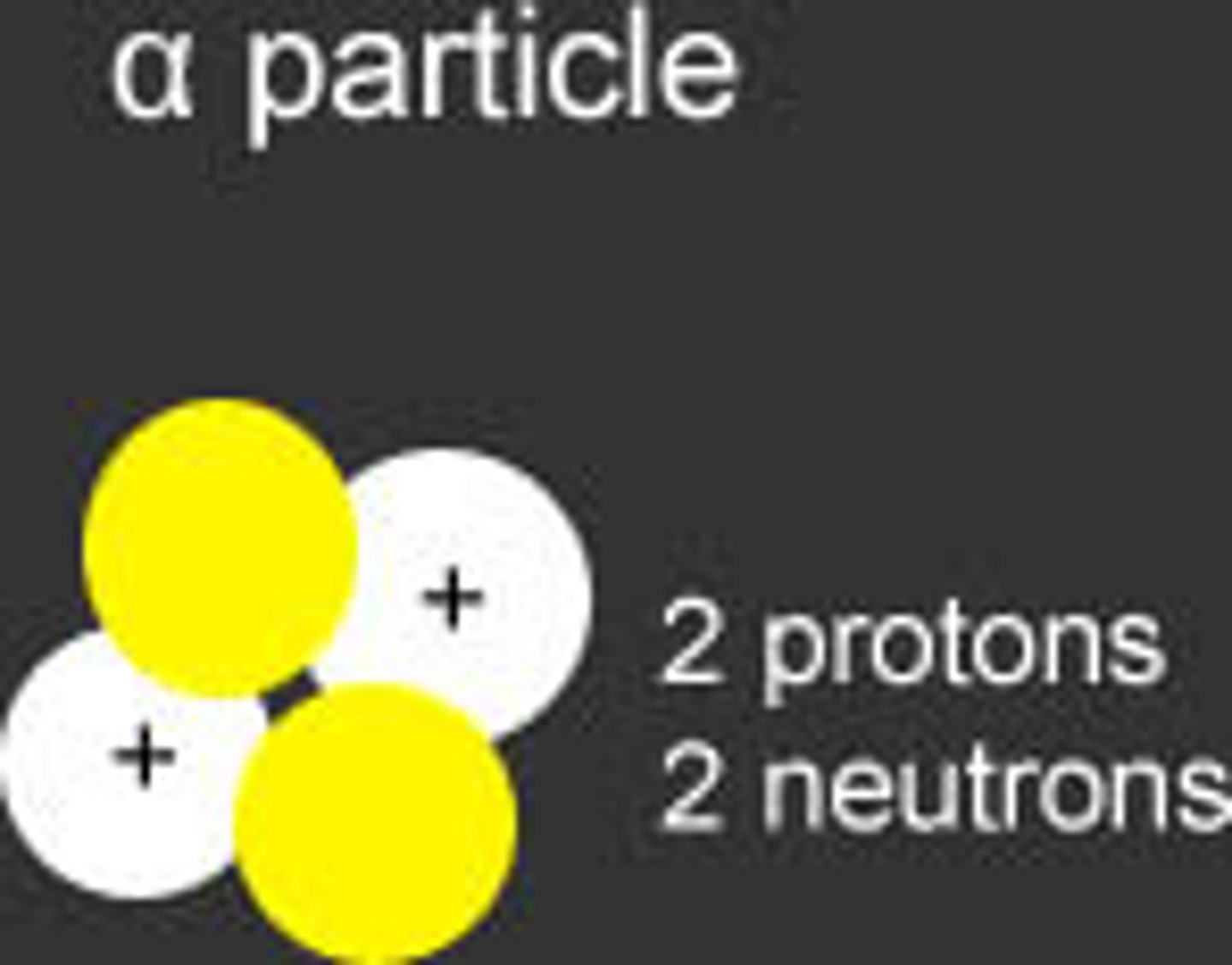
alpha particle
2 neutrons, 2 protons
What happens to the energy when there is a short wavelength?
High energy.
Light from the sun (white light) can be separated by a prism to create this, only a small part of the full EM spectrum?
Visible Spectrum.
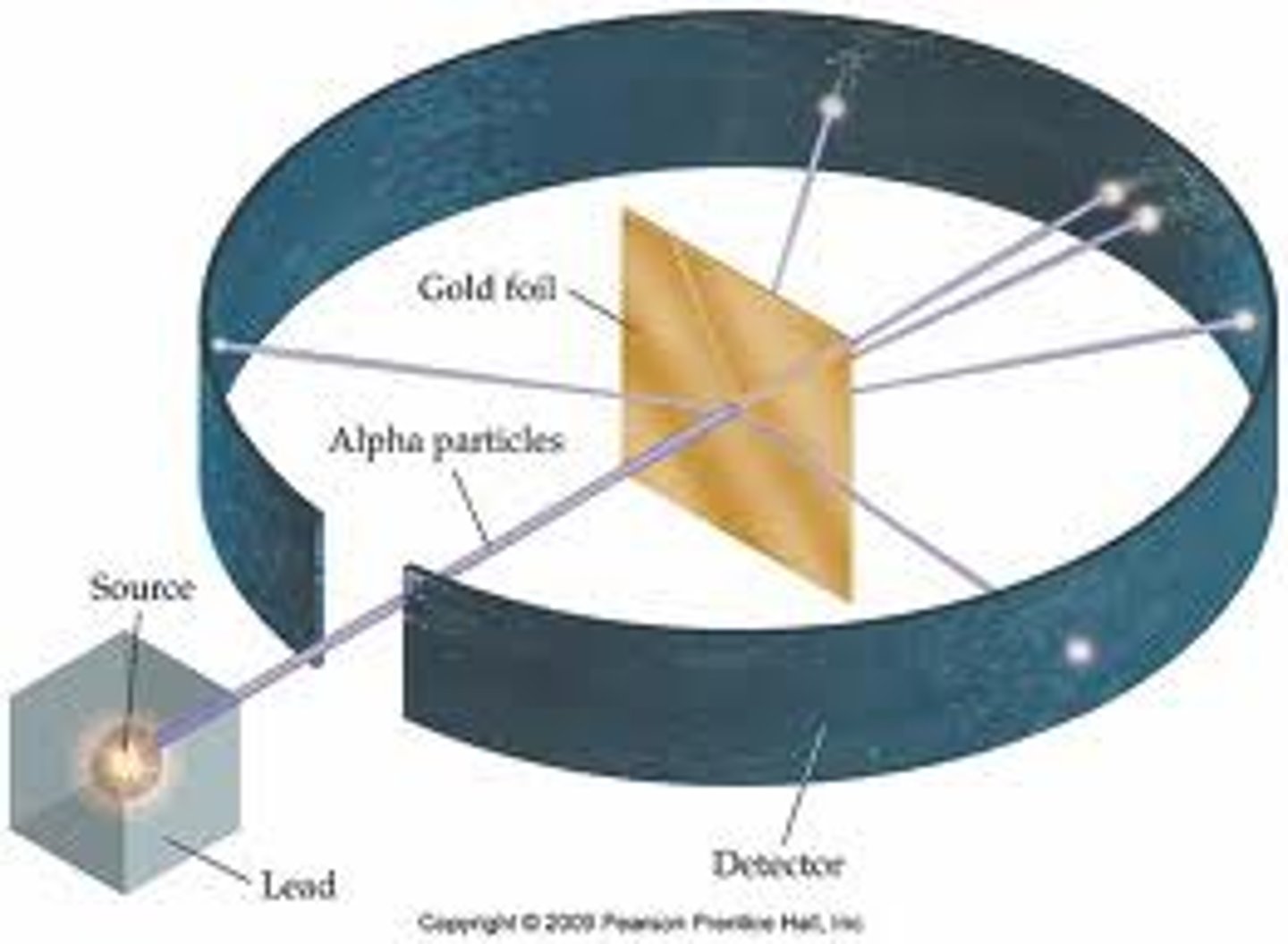
Rutherford
-gold foil experiment
-atoms mostly empty space
-small, dense, positively charged nucleus

Gold foil experiment
-most particles went straight through
-every once in awhile particles were deflected
-1/8000 particles bounced back
-led to model of atom; small, dense, positively charged nucleus
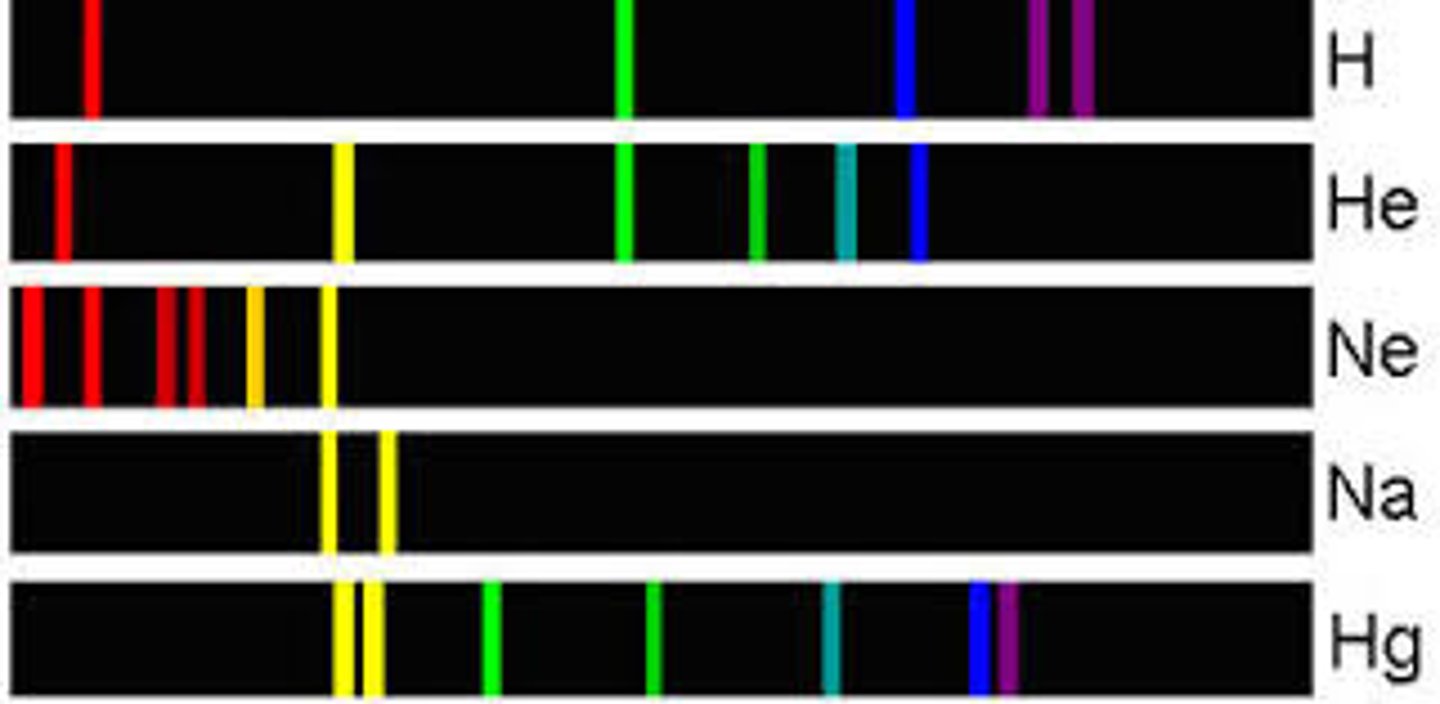
Atomic Emission Spectrum
Spectrum that emits photons, energy diagram: electron goes down energy levels.
neutrons
-discovered in 1932
-slightly heavier than protons
Atomic Absorption Spectrum
Spectrum that absorbs photons, energy diagram: electrons goes up in energy levels.
Current model of atom
-nucleus contains protons and neutrons
-cloud of electrons
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Principle states that we can't accurately measure both the position and the energy of a small particle (electron)
Bohr's model did - why its wrong.
charges of electrons, protons, neutrons
-electrons: -1, 1/3000 amu
-protons: +1, 1 amu
-neutrons: 0 charge, 1 amu
Schrodinger's Wave Equation
Treated electron as waves derived by mathematical descriptions of energies.
Psi = wave function of an electron
Psi^2 = probability of finding an electron.
force (types)
gravitational, electromagnetic, strong, weak
Atomic Orbitals
Regions of space where electrons with a particular quantized energy have a high probability of being found, described by quantum numbers.
gravitational force
attraction between objects that have mass. requires 2+ objects
Fg=Gm1m2/r^2
What are the quantum numbers?
n, l, ml, and ms.
electromagnetic force
attraction/repulsion between objects with electrical charge
Fe=Q1Q2/r^2
What does quantum number "n" mean?
Determines the energy of the electron and identifies its shell.
change in matter is accompanied by a change in_______
energy
What does quantum number "l" mean?
Identifies the type of orbital (s,p,d) and subshell
= 0 - n-1.
change in energy caused by a change in ______
forces
What does quantum number "ml" mean?
Specifies a particular orbital within a subshell
= -l - +l (2l + 1 possible values)
tells us how many s,p,d orbitals are found in each sub shell.
energy units
joule (kg/m^2s^2) and calories.
What does quantum number "ms" mean?
Describes the spin of the electron in each orbital
= +1/2 or -1/2
(only 2 e- in each orbital, each one has either + spin or - spin).
kinetic energy
Energy in motion
KE=1/2(mv^2)
Aufbau Principle
Principle that electrons occupy the lowest level orbitals first.
potential energy
-energy associated with the position of a system of objects in a field
-"stored energy"
Hund's Rule
Rule that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy singly until they have to pair up.
total energy
potential+kinetic
Core Electrons
Low in energy electrons that are close to the nucleus within the closed shell, doesn't participate in reactions.
energy
can be transferred or transformed
Valence Electrons
High in energy electrons that are outside of closed shell and determine reactivity.
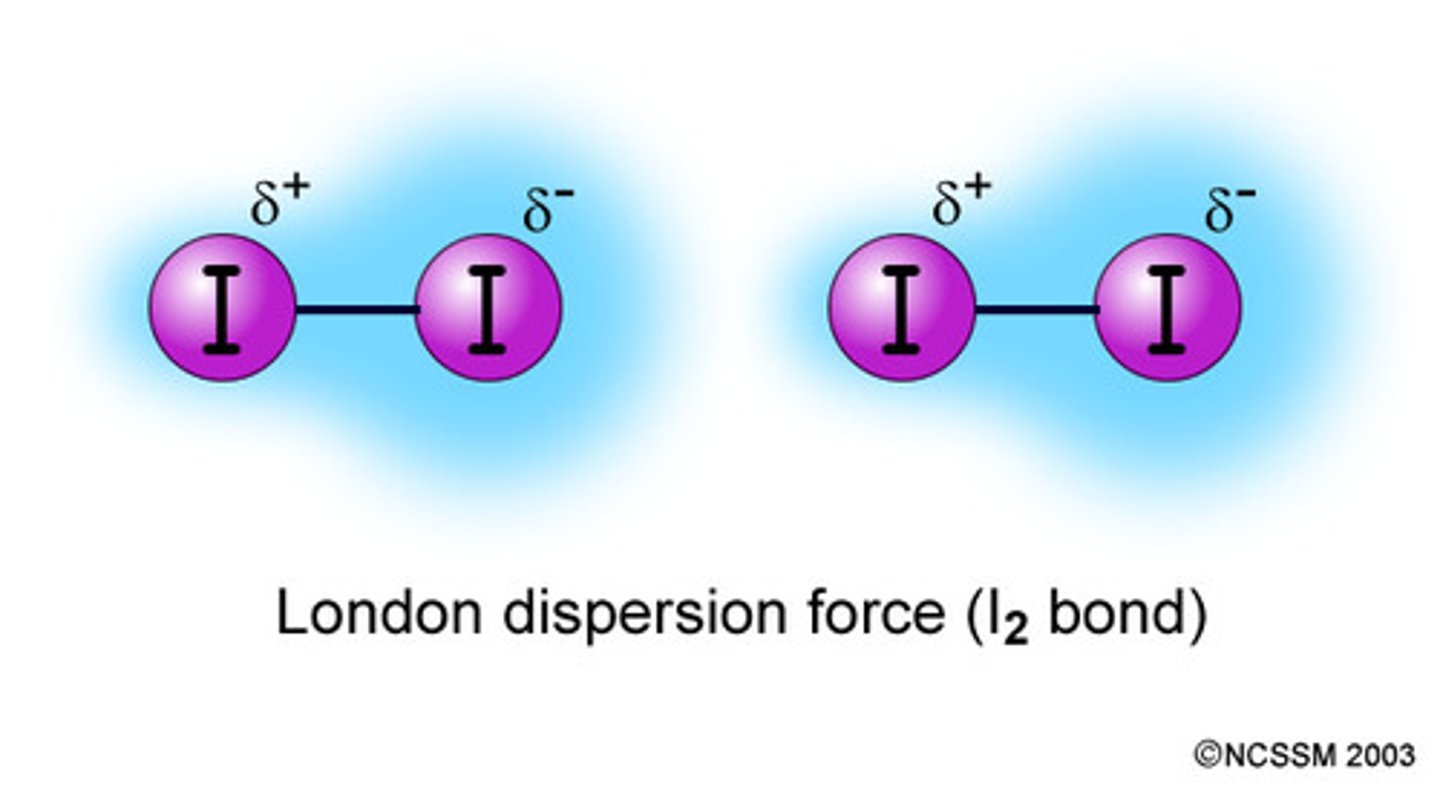
London dispersion forces
-caused by fluctuations of electron density in molecule
-causes atoms to stick together and attract
-present in all neutral atoms
Atomic Radius
Half the distance between two nuclei, increases down a group, decreases across a row
Depends on attraction of protons and electrons and repulsions of electrons
Represents state where forces between attraction and repulsion in an atom are equal.
to lose energy ...
add atoms because the energy will transfer
Effective Nuclear Charge
= Protons - Core Electrons
Increases across the row, decreases down the group (as atomic radius decreases)
How tight the electrons are being attracted to the nucleus.
why do atoms fly apart
when there are collisions. and there is more kinetic energy as the temperature increases
Ions
Atoms in which electrons have been added/removed.
when a single chemical bond is broken energy is _____
absorbed
Cations
Result of removing an electron, positively charged, smaller atomic radius.
Why are some London dispersion forces larger
because some atoms have more electrons so the electron cloud is easier to distort.
Anion
Result of adding an electron, negatively charged, larger atomic radius.
as the London dispersion forces increase the melting/boiling point ______
increases because there is a stronger reaction
Isoelectronic Series
Atoms with the same number of electrons but different number of protons, the attraction between electrons and protons increases as the charge of the nucleus increases.
Why do atoms attract each other?
because of the attractive electromagnetic forces between them
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase
Decreases down a group (removing an electron gets easier as atom gets bigger), increases across a row
Easier to remove a lone e- from a p orbital and the first paired e-.
attractions _____ the potential energy. repulsions _____ the potential energy
lower; raise
What sized atoms and what charge have higher ionization energies?
Small atoms & larger positive charge.
Big Bang
13.8 billion years ago, singular event in which matter was created.
Stable systems
when the attractive and repulsive forces are equal
How is the temperature of a phase change related to different elements?
the temperature of a phase change depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces. stronger force=higher temperature
What was created 1 picosecond after the Big Bang?
Leptons (quarks, electrons).
covalent bond
when two H atoms approach they are attracted stronger than two He atoms.
What two things formed 1 microsecond after the big bang by matter expanding and cooling?
Protons and Neutrons.
All neutral atoms and molecules ____ each other
attract
What formed a few minutes after the big bang? (H+,D+,He2+,Li3+)
Nuclei.
Energy is _____ to the surroundings when atoms attract each other
released
Everything in the universe is moving away from us with ____ speed.
Increasing
The distance between two atoms in a system are most stable when____
the potential energy is at a minimum
Doppler Effect
Frequency increases, creating a higher pitch when moving toward
Frequency decreases, creating a lower pitch when away.
what causes the attractive forces between two atoms
the electron clouds of the atoms fluctuate randomly causing a dipole that induces a dipole in the other atoms which causes them to attract to each other
Red Shift
Because the universe is expanding, frequency of things decreases the farther away they are (wavelength increases).
what causes a phase change (liquid -> gas)
as more molecules get more energy, they overcome the electrostatic forces of attraction and the molecules can escape into the gas phase. energy transferred through collisions, increasing the KE
Chemical Reactions
Reaction that involves the rearrangements of valence electrons, the element does not change.
Nuclear Reactions
Reaction that involves the nucleus, often results in change of element, accompanied by mass changes.
Rutherford scientific explanation (claim, evidence, reasoning)
claim- atoms are mostly empty space with a small dense nucleus
evidence- most alpha particles went straight through, few were deflected
reasoning- positively charged alpha particles were deflected by the repulsive interaction with the positive nucleus; since only a few were deflected the nucleus must take up a small area
Who discovered the electron and why was it discovered first?
JJ Thomson. The electrons are on the outside of the atom and carry a charge, so it's easiest to detect. They can be removed.
Nuclear Fusion
Adding two small/light nuclei together to create more stable element, releases energy, occurs in stars
Ex: Hydrogen burning and helium burning.
Current evidence for atoms
graphite AFM (atomic force microscopy) and STM (scanning tunnel microscopy)
Nuclear Fission
The fragmentation of heavy nuclei to form light, more stable nuclei, releases energy
Can become a chain reaction.
Thomson atomic theory (claim, evidence, reasoning)
claim- atoms have a sub structure and contain electrons embedded in the structure of the atom
evidence- electrons were ejected from the cathode regardless of what metal the cathode was made of
reasoning- particles are emitted regardless of the nature of the cathode, the must be part of the sub structure of the atom.
Radioactive Decay
Nucleus emits/captures particles of energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. a, b, y.