10 - Anatomical variations of importance in endodontics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
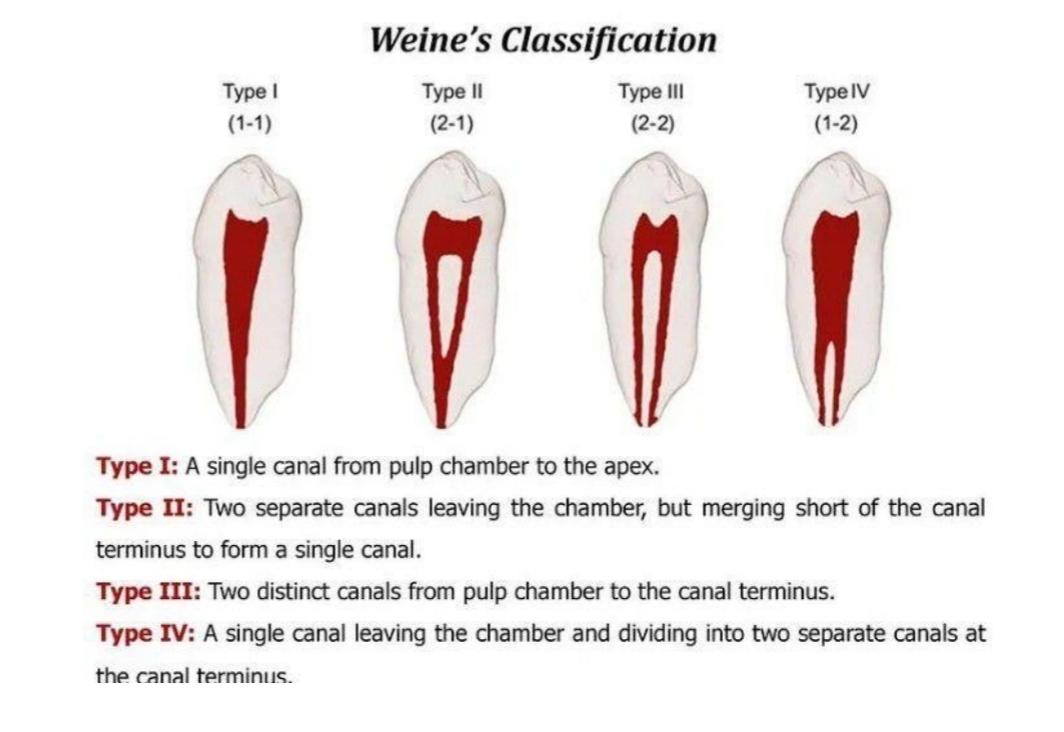
What are the 2 different types of root canal morphlogy classification
Weine's
Vertucci's
Weine’s classification
With endo of maxillary central incisor, what may prevent direct access, and what can make access difficult?
Lingual shoulder
Calcific metamorphosis
What is calcific metamorphosis and what appearance can it give the crown?
Tooth’s trauma response - canal partially/completely filled with hard tissue
Yellow discoloration of crown
What are dilacerations?
Sharp bend in root - from trauma or bony interference during root formtation
What cases require extra attention?
Wide open apex (blunderbuss teeth)
Calcific metamorphosis
Dilacerations
What is the first cause of failure in root canal treatment of upper incisors?
Apical curvature in root (disto-palatal direction). In lateral incisor.
Files straigten canal and leave apical 3rd uninstrumented

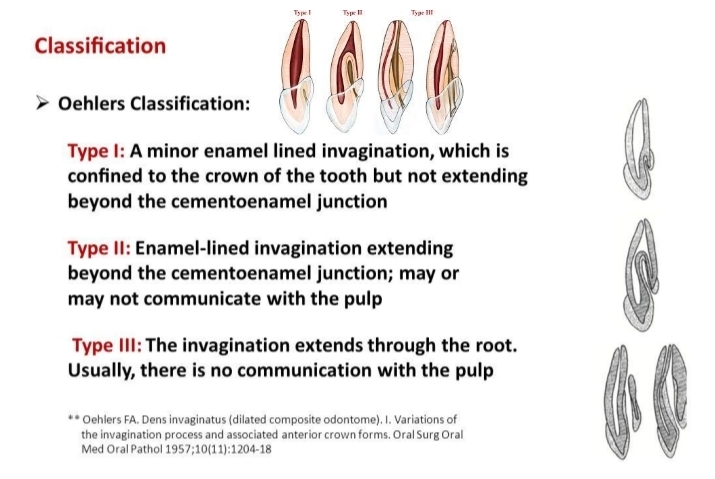
What is dens in dente?
Invagination of enamel (enamel lined cavity in crown or root).
On xray looks like tooth within tooth
Mainly in maxillary lateral incisors
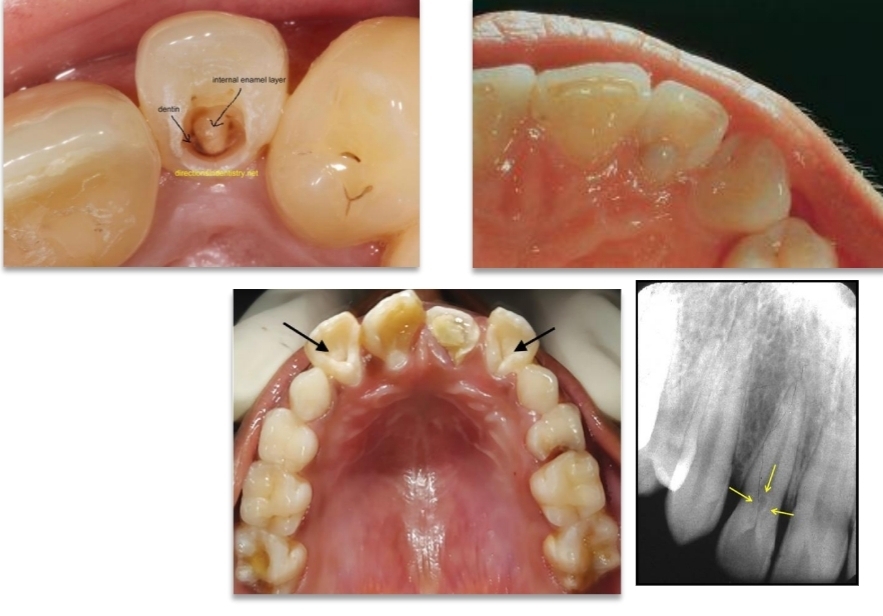
Dens invaginatus (den in dente) Oehlers classification
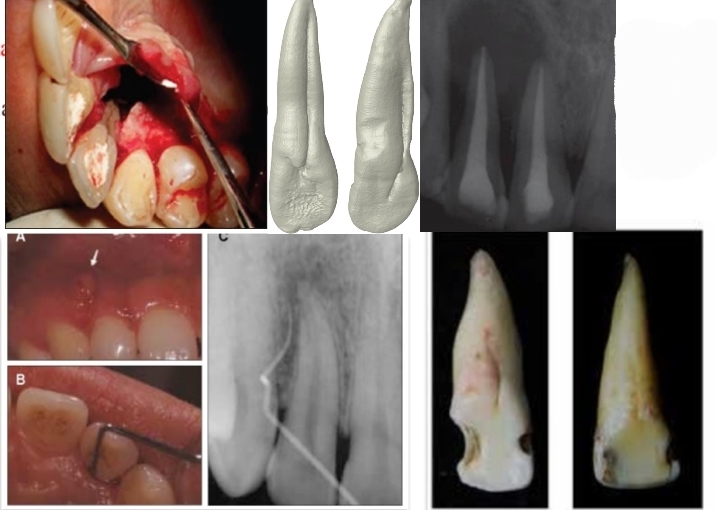
Why is Palatal groove a major cause of rct failure? Where is it found and what is its origin
Creates large permanent and irreparable periodontal bag - extraction needed
Is a developmental groove mainly found in maxillary lateral incisor lingual surface
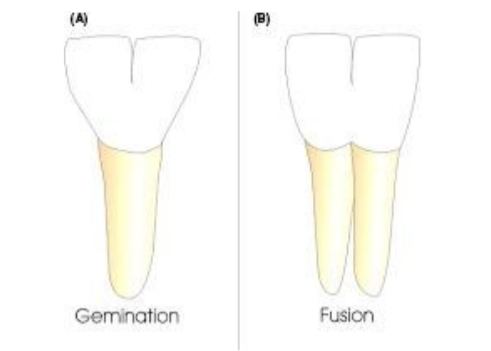
Describe what Gemination and fusion are, and in what teeth do they occur?
Mandibular anteriors (also maxillary)
Fusion - 2 tooth germs forming one large tooth.
Gemination - When one tooth bud tries to divide. mainly primary teeth. usually disfigured from enamel irregularities
differentiate between the 2 - fusion causes reduced number of teeth
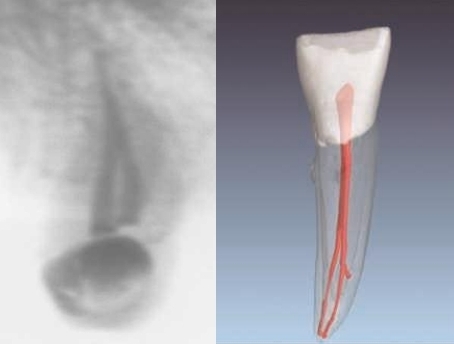
How may the pulpal space of fused teeth appear?
Separated pulpal space
One pulp chamer and 2 canals
Large bifid crown with one pulpal space
How long may it take for high radiolucency cases take to resolve after RTC?
Up to 2- years
If minimal bone formation after a few months - successful treatment
What are the 4 signs of Celsos inflammation?
Pain, Heat, Redness, Swelling
Anomalies of Maxillary canine (longest tooth) and mandibular canine in rare cases?
Maxillary - 2 roots
Mandibular - more than one canal and root
Anomalies of Maxillary and Mandibular first premolars?
Maxillary - 3 root canals
Mandibular - Bi/trifurcations of roots/canals
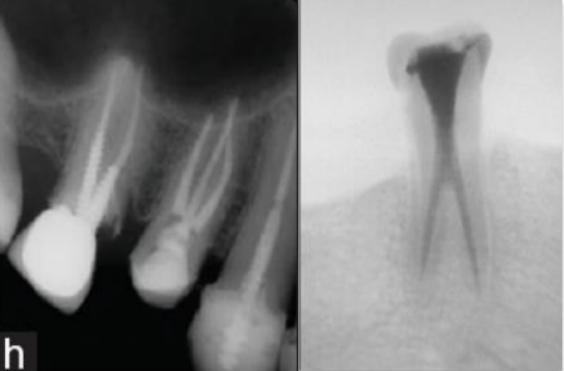
Anomalies of Maxillary and Mandibular 2nd premolars?
Maxillary - 3 roots
Mandibular - 2 roots
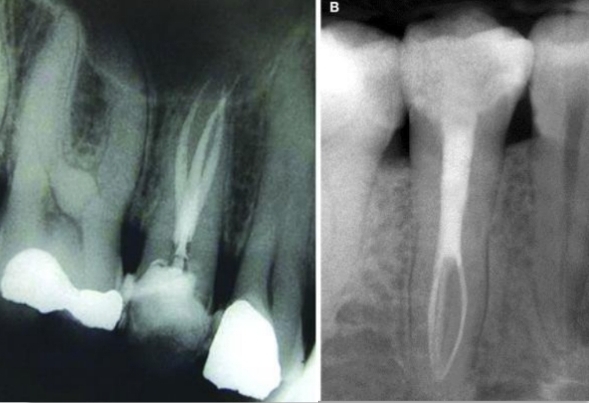
Anomalies of Maxillary first molar?
Single root and canal
2 distal canals
2 palatal roots
3 MB caals
8 canals
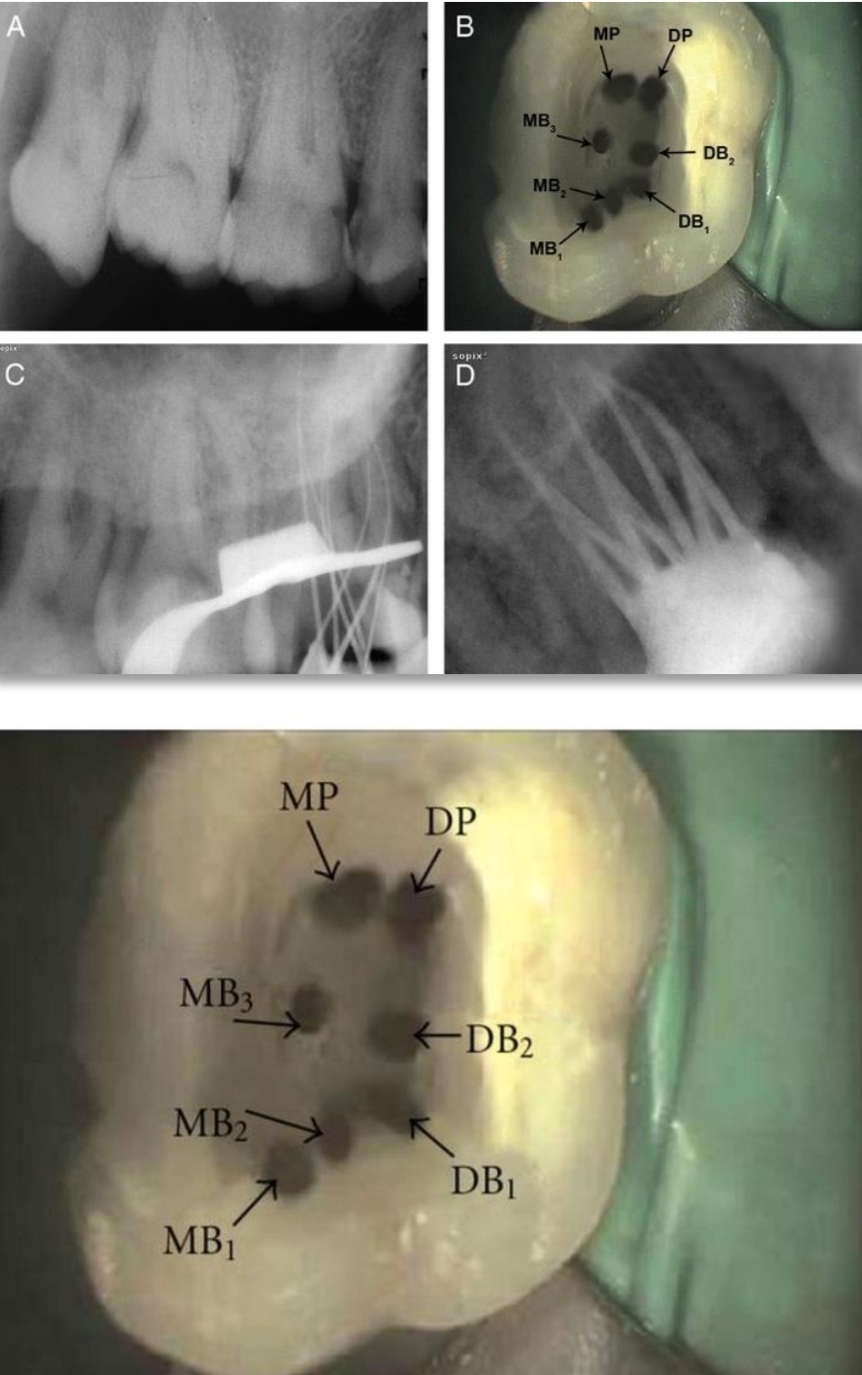
Anomalies of Maxillary 2nd molar?
Two most frequent:
One root and canal
Pulp stones
other:
5 roots and 5 canals
3 MB canals
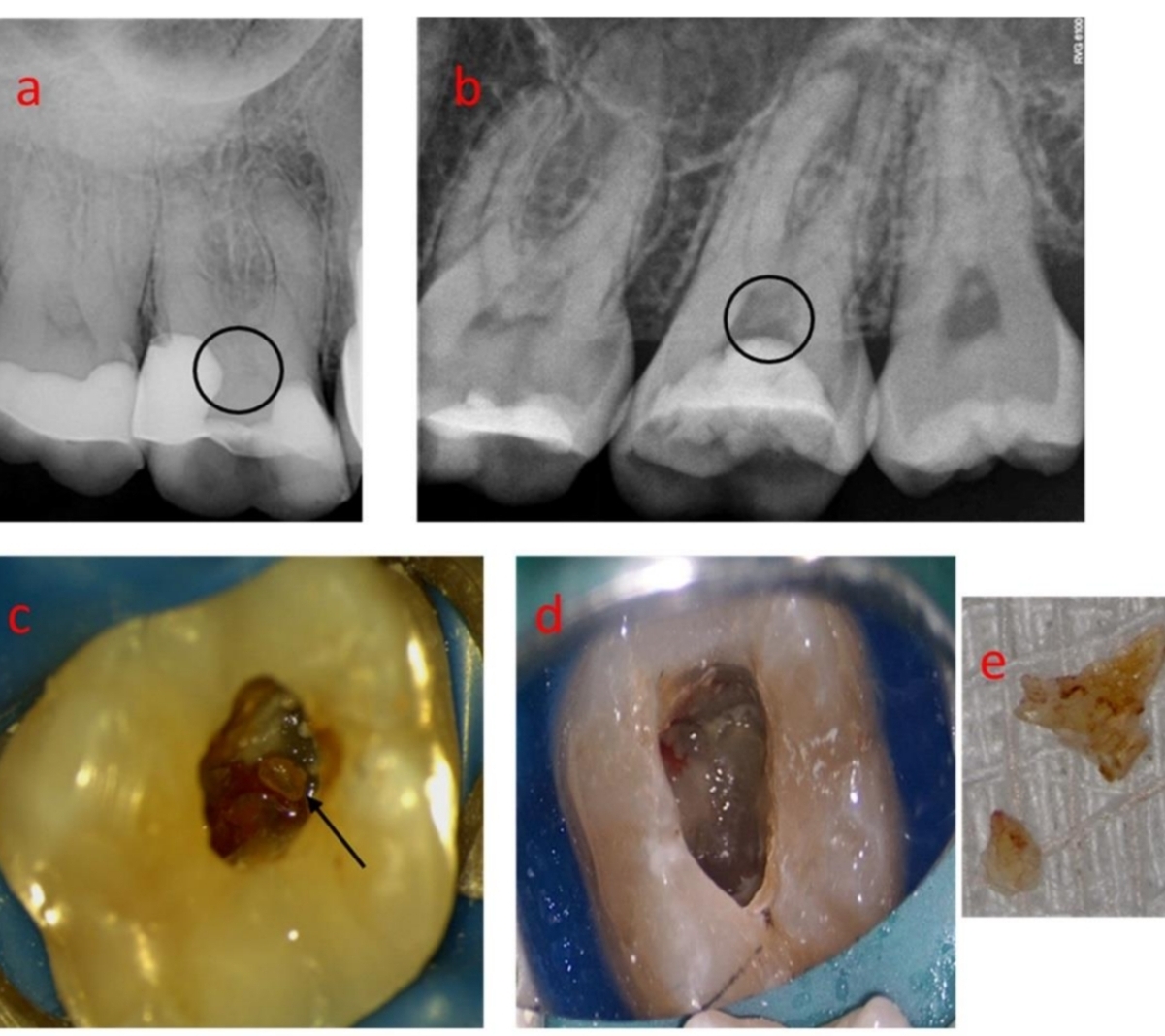
In what tooth are anomalies common rather than exceptions?
Maxillary 3rd molars
Complex anatomy common in mandibular 3rd molars
Bayonet root image. From trauma. Can lead to necrotic pulp from intrapulp pressure increase
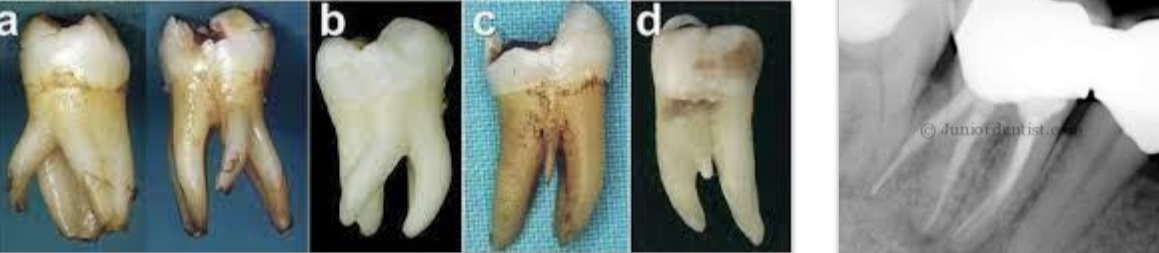
Mandibular first molar anomalies?
3 roots
3rd root called Radix entomolaris
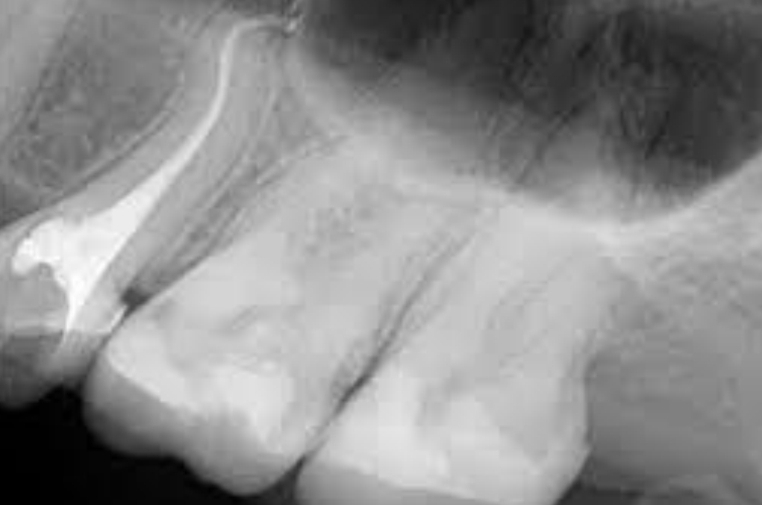
Mandibular second molar anomalies?
3rd root
One conical root with one conical canal
C shaped canal
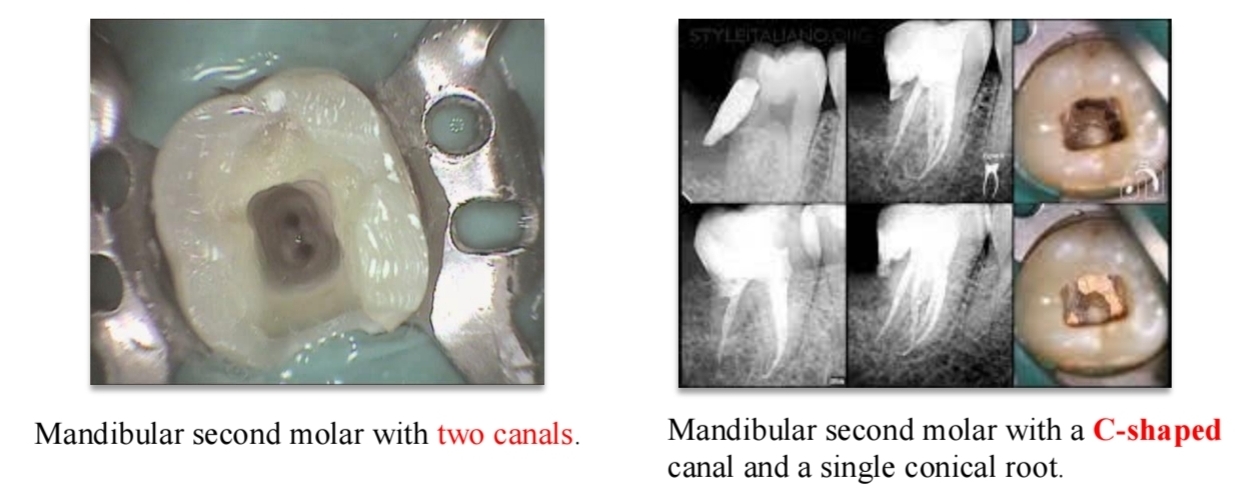
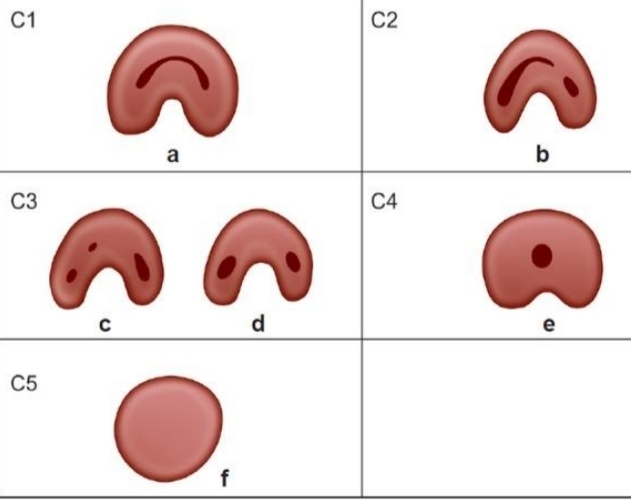
Melton’s method for classifying C shaped canal (mandibular molars)?
C1 - uninterrupted C
C2 - semicolon shape
C3a - 2 seperate canals
C3b - 3 seperate canals
C4 - One round or oval canal