A&P Chapter 4 Histology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
tissues
groups of cells similar in structure and function
four types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve
epithelial tissue
lines things and produce glands
cellularity
composed almost entirely of cells
polarity
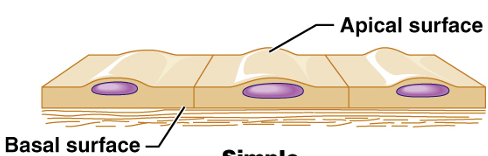
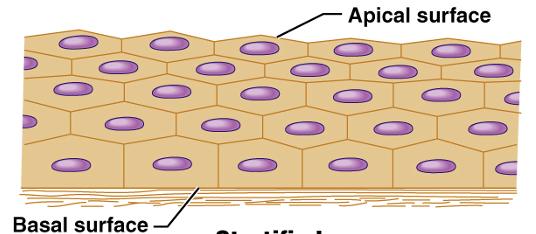
apical and basal surfaces
special contacts
form continuous sheets held together by tight junction and desmosomes
basal layer
bottom layer ; connective tissue
apical layer
top layer which will probably be touching nothing
supported by connective tissue
reticular and basal laminae
avascular but innervated
contains no blood vessels but supplied by nerve fibers
regenerative
rapidly replaces lost cells by division
simple epithelial tissue
stratified epithelial tissue
squamous epithelial

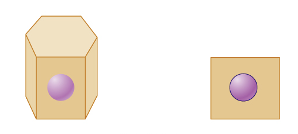
cuboidal epithelia
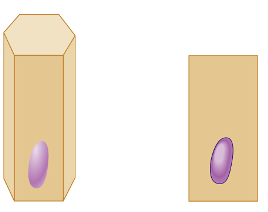
columnar epithelial
simple squamous
single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
function of simple squamous epithelia
allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important ; lubricating substances in serosae
location of simple squamous epithelial
kidney glomeruli, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and serosae
simple cuboidal epithelial
single layer of cubelike cells with large, spherical central nuclei
simple cuboidal function
secretion and absorption
simple cuboidal location
kidney tubules ; ducts and secretory portion of small glands ; ovary surface
simple columnar epithelial
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei; some cells bear cilia; layer may contain mucus-secreting unicellular glands (goblet cells)
simple columnar epithelial function
absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus by ciliary action
simple columnar epithelium location
nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract, gallbladder, and excretory ducts of some glands, ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus
cilia
help move substance through internal passageways