UNCW BIO 246 Final (Ch. 16 - 21)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
1
New cards
diagnosis
the identification of a disease or other condition
2
New cards
ON TEST... FOR EACH DISEASE....
- name the disease
- name the microbe(s)
- identify type of microbe (virus, bacteria, yeast, etc.)
- recognize symptoms
- identify mode(s) of transmission
- describe prevention and/or treatment
- compare & contrast to similar disease
- name the microbe(s)
- identify type of microbe (virus, bacteria, yeast, etc.)
- recognize symptoms
- identify mode(s) of transmission
- describe prevention and/or treatment
- compare & contrast to similar disease
3
New cards
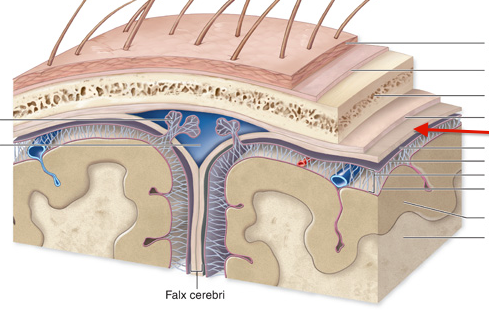
Place the tissue layers in order from superficial to deep:
1. epidermis
2. dermis
3. subcutaneous layer
4. muscle
2. dermis
3. subcutaneous layer
4. muscle
4
New cards
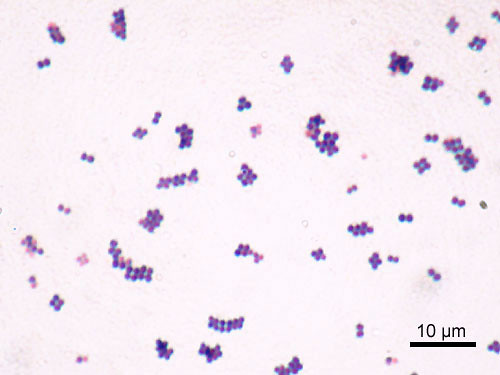
Staphylococcus aureus ( S. aureus)
- infections of skin, blood, and bone
- ex: pneumonia, food poisoning, meningitis
- carriage: 30-50%
- gram POSITIVE cocci in CLUSTERS
- catalase = positive
- produces exotoxins, exoenzymes, superantigens, coagulase
- more resistant to antibiotics; HA-MRSA, CA-MRSA, VRSA
- ex: pneumonia, food poisoning, meningitis
- carriage: 30-50%
- gram POSITIVE cocci in CLUSTERS
- catalase = positive
- produces exotoxins, exoenzymes, superantigens, coagulase
- more resistant to antibiotics; HA-MRSA, CA-MRSA, VRSA
5
New cards
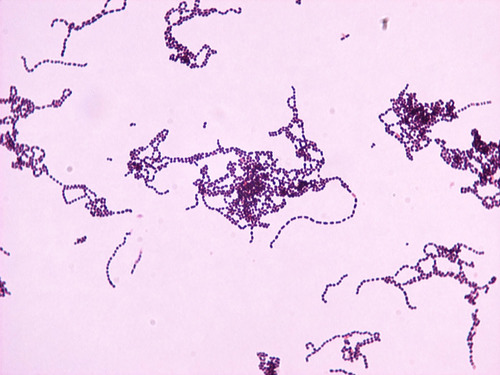
Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes)
- infections of skin and blood
- ex: pharyngitis, pneumonia, scarlet & rheumatic fever
- carriage = 10-20%
- gram POSITIVE cocci in CHAINS
- catalase = negative
- produces exotoxins, exoenzymes, superantigens
- not very resistant; can still use beta-lactams
- ex: pharyngitis, pneumonia, scarlet & rheumatic fever
- carriage = 10-20%
- gram POSITIVE cocci in CHAINS
- catalase = negative
- produces exotoxins, exoenzymes, superantigens
- not very resistant; can still use beta-lactams
6
New cards
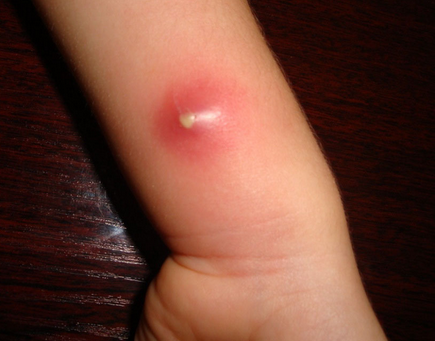
abscess
Collection of pus underneath the skin
7
New cards
CA-MRSA
community-associated MRSA infection
8
New cards
HA-MRSA
healthcare-associated MRSA infection
9
New cards
CA-MRSA often mistaken for "spider bite":
folliculitis, furuncle, or carbuncle
10
New cards
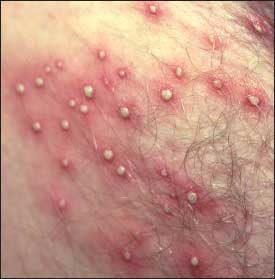
Folliculitis
inflammation of the hair follicles
- symptoms: rash (small red bumps or white headed pimples around hair follicles)
- symptoms: rash (small red bumps or white headed pimples around hair follicles)
11
New cards
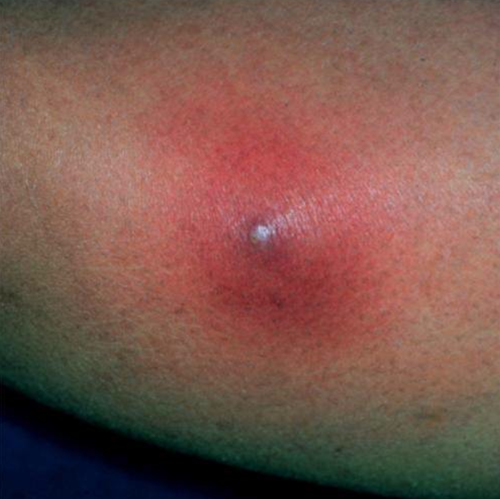
furuncle
boil; a painful nodule formed in the skin by inflammation originating in a hair follicle
- caused by staphylococcosis
- caused by staphylococcosis
12
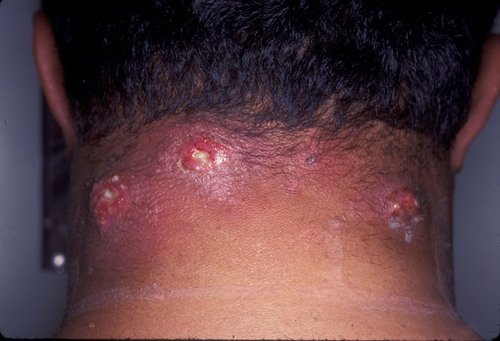
New cards
carbuncle
a cluster of connected furuncles (boils)
13
New cards
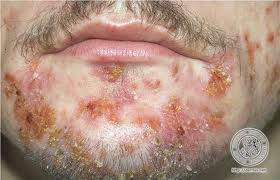
Impetigo
superficial skin infection characterized by pustules and caused by either staph or strep
- SYMPTOMS: pustules, skin peeling, yellowish crusts
- SPREAD BY: direct or indirect contact
- TREATMENT: topical mupirocin
- SYMPTOMS: pustules, skin peeling, yellowish crusts
- SPREAD BY: direct or indirect contact
- TREATMENT: topical mupirocin
14
New cards
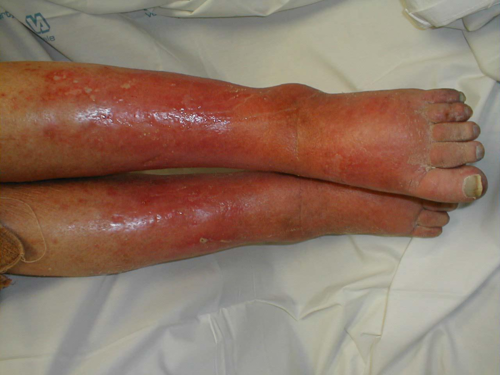
Cellulitis
infection of dermis and subcutaneous tissue caused by staph or strep resulting from parenteral (thru the skin) implantation
- lymphangitis or bacteremia can result
- TREATMENT: oral antibiotics for uncomplicated infections OR i.v. antibiotics & debridement for serious infections or immunocompromised
- lymphangitis or bacteremia can result
- TREATMENT: oral antibiotics for uncomplicated infections OR i.v. antibiotics & debridement for serious infections or immunocompromised
15
New cards
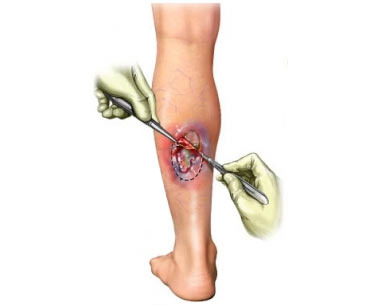
debridement
Removal of foreign matter or dead tissue from a wound
16
New cards
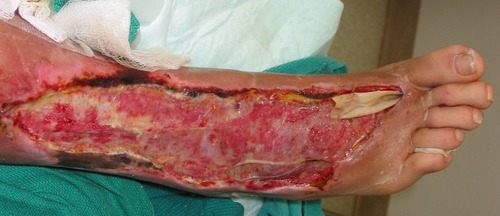
necrotizing fasciitis
flesh-eating disease characterized by massive, rapid tissue digestion caused by staph or strep
- bacteria introduced thru cuts, scrapes, etc.
- TREATMENT: treat aggressively w/ i.v. antibiotics, debridement, amputation
- bacteria introduced thru cuts, scrapes, etc.
- TREATMENT: treat aggressively w/ i.v. antibiotics, debridement, amputation
17
New cards
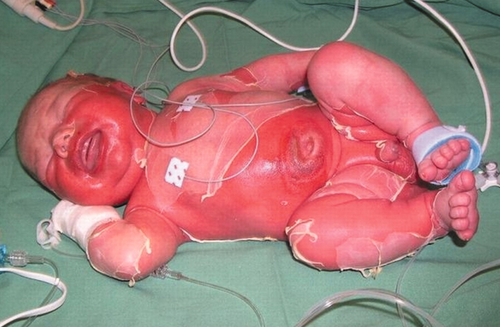
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)
STAPH infection, typically in NEWBORNS, characterized by widespread desquamation of epidermis
- looks like a burn
- 5% of S. aureus strains produce exfoliative toxins
- looks like a burn
- 5% of S. aureus strains produce exfoliative toxins
18
New cards
Meningitis symptoms
fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, photophobia
19
New cards
photophobia
aversion/sensitivity to light
20
New cards
CNS (central nervous system) illness
meningitis, listeriosis, poliomyelitis
21
New cards
Bacterial Meningitis
- most severe type
- neisseria meningitidis, streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae
- neisseria meningitidis, streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus influenzae
22
New cards
viral meningitis
- less severe
- no treatment
- no treatment
23
New cards
Fungal meningitis
- Cryptococcus
- opportunistic; immune compromised patients (AIDS)
- opportunistic; immune compromised patients (AIDS)
24
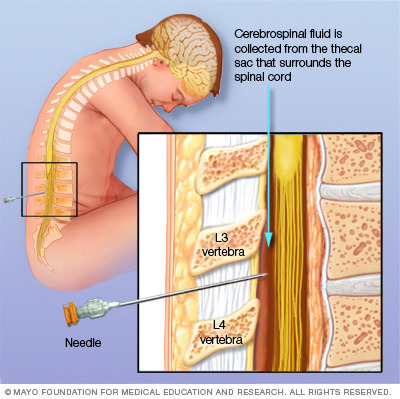
New cards
diagnosis for meningitis
lumbar puncture, CT, EEg ---> CSF (gram stain or culture)
25
New cards
Meningococcal meningitis
Neisseria meningitidis
- ENCAPSULATED gram NEGATIVE diplococcus
- 3-30% carriers
- college students
- MOST SERIOUS FORM... 15% mortality rate
- symptoms: coma clotting, convulsions, shock, cardiac failure, petechiae (rash)
- ENCAPSULATED gram NEGATIVE diplococcus
- 3-30% carriers
- college students
- MOST SERIOUS FORM... 15% mortality rate
- symptoms: coma clotting, convulsions, shock, cardiac failure, petechiae (rash)
26
New cards
Pneumococcal meningitis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
- ENCAPSULATED gram POSITIVE diplococcus
- 70% carriers
- ENCAPSULATED gram POSITIVE diplococcus
- 70% carriers
27
New cards
Haemophilus Meningitis
Haemophilus influenzae
- ENCAPSULATED gram NEGATIVE pleomorphic bacillus
- carriers common
- most common type in young kids before 1992 when Hib vaccine was introduced
- ENCAPSULATED gram NEGATIVE pleomorphic bacillus
- carriers common
- most common type in young kids before 1992 when Hib vaccine was introduced
28
New cards
preventing bacterial meningitis...
conjugate vaccines = capsule linked to protein antigen
- vaccines: ActHIB 1992, Prevnar 2000, Menactra 2004
- ActHIB and Prevnar are for INFANTS
- vaccines: ActHIB 1992, Prevnar 2000, Menactra 2004
- ActHIB and Prevnar are for INFANTS
29
New cards
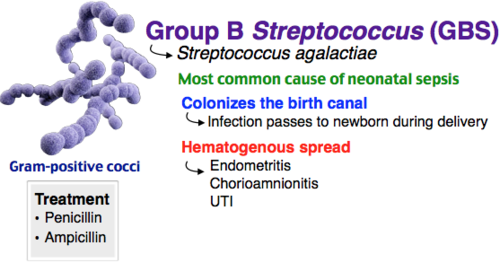
Neonatal meningitis
Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B strep)
- 10-30% women colonized in vagina
- vertical transmission during delivery
- 10-30% women colonized in vagina
- vertical transmission during delivery
30
New cards
septicemia
growth of bacteria in the blood
31
New cards
preventing neonatal meningitis...
pregnant women routinely screened at 35-37 weeks
- i.v. beta-lactam administered before delivery (prophylaxis)
- i.v. beta-lactam administered before delivery (prophylaxis)
32
New cards
Group B strep
Streptococcus agalactiae
33
New cards
Group A strep
Streptococcus pyogenes
34
New cards
Neonatal conjunctivitis
-present w/in 24 hrs of life: chemical conjunctivitis due to silver nitrate; resolves spont
-presents on 2nd day of life: gonococcal; most destructive; ceftriaxone
-presents day 5-14: chlamydia; oral erythromycin
-presents on 2nd day of life: gonococcal; most destructive; ceftriaxone
-presents day 5-14: chlamydia; oral erythromycin
35
New cards
West Nile Virus symptoms
fever, headache, brain swelling, impaired function, paralysis
36
New cards
West Nile Virus and encephalitis is caused by...
arthropod borne virus
- mosquito vector, bird reservoir
- mosquito vector, bird reservoir
37
New cards
Listeriosis
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Usually food-borne transmission
- Grows at refrigerator temperatures
- 4th leading cause of bacterial meningitis
- May cause miscarriage or stillbirth
- Usually food-borne transmission
- Grows at refrigerator temperatures
- 4th leading cause of bacterial meningitis
- May cause miscarriage or stillbirth
38
New cards
Desquamation
Shedding of epithelial elements; chiefly of the skin in scales or sheets
39
New cards
Measles (Rubeola)
- viral infection begins w/ non-specific symptoms (fever, sore throat, headache) (herd)
- KOPLIK'S SPOTS appear in mouth
- red MACULOPAPULAR EXANTHEM (rash) spreads from head to trunk & extremities
- 1 million kids die annually from measles
- pneumonia or encephalitis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
- VACCINE introduced in 1964
- KOPLIK'S SPOTS appear in mouth
- red MACULOPAPULAR EXANTHEM (rash) spreads from head to trunk & extremities
- 1 million kids die annually from measles
- pneumonia or encephalitis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
- VACCINE introduced in 1964
40
New cards
humans are the only reservoir for measles virus....
true
41
New cards
measles virus is extremely contagious via _________ transmission
respiratory
42
New cards
Chickenpox (Varicella Zoster)
- fever accompanies rash, MILD self-resolving rash
- CENTRIPITAL VESICULAR rash
- confined to face, scalp, trunk (doesn't spread to extremities)
- antiviral drug (ACYCLOVIR) given to at-risk patients
- humans are the only reservoir of varicella zoster (HHV-3)
- virus very contagious via respiratory transmission
- natural ACTIVE IMMUNITY after recovery
- CENTRIPITAL VESICULAR rash
- confined to face, scalp, trunk (doesn't spread to extremities)
- antiviral drug (ACYCLOVIR) given to at-risk patients
- humans are the only reservoir of varicella zoster (HHV-3)
- virus very contagious via respiratory transmission
- natural ACTIVE IMMUNITY after recovery
43
New cards
chickenpox vaccine
Varivax, 1995
44
New cards
Chickenpox and Shingles
- 10-20% latent infection of cranial or spinal nerves (shingles)
- postherpetic neuralgia
- 1.1 million cases in USA per year
- Zostavax vaccine 2006
- postherpetic neuralgia
- 1.1 million cases in USA per year
- Zostavax vaccine 2006
45
New cards
Reye's syndrome
Syndrome which is an acute encephalopathy (inflammation of the brain). Usually follows a viral illness & linked to intake of aspirin. Use acetaminophen (not aspirin) to reduce fever with child with a communicable disease (virus) to prevent this. (RISK OF CHICKENPOX)
46
New cards
Smallpox (Variola major)
- fever precedes CENTRIFUGAL PUSTULAR rash
- begins at head and trunk, but spreads to extremities
- can be mistaken for chickenpox early on
- 20-30% mortality rate
- RECOVERY = natural active immunity but scars/organ damage
- begins at head and trunk, but spreads to extremities
- can be mistaken for chickenpox early on
- 20-30% mortality rate
- RECOVERY = natural active immunity but scars/organ damage
47
New cards
smallpox pt. 2
- human reservoir for variola major and minor viruses
- mildly contagious via respiratory transmission (also fomites or direct contact)
- NO EFFECTIVE TREATMENT
- vaccine (Jenner 1798)
- mildly contagious via respiratory transmission (also fomites or direct contact)
- NO EFFECTIVE TREATMENT
- vaccine (Jenner 1798)
48
New cards
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasma gondii
- from cats
- from cats
49
New cards
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
progressive, incurable, neurologic disease caused by infectious prions (from cows)
50
New cards
Tetanus
- Clostridium tetani
- paralytic disease you get from PUNCTURE WOUNDS
- soil bacteria
- gram positive bacilli
- neurotoxin = tetanospasmin
- SPASTIC paralysis
- paralytic disease you get from PUNCTURE WOUNDS
- soil bacteria
- gram positive bacilli
- neurotoxin = tetanospasmin
- SPASTIC paralysis
51
New cards
preventing tetanus...
- wound cleaning
- TOXOID vaccine (DTaP)... 10 yr boosters
- passive immunization
- TOXOID vaccine (DTaP)... 10 yr boosters
- passive immunization
52
New cards
Botulism
- Clostridium botulinum
- food borne transmission
- "sausage", honey & infants
- neurotoxin = botulin
- FLACCID paralysis ("floppy baby syndrome")
- food borne transmission
- "sausage", honey & infants
- neurotoxin = botulin
- FLACCID paralysis ("floppy baby syndrome")
53
New cards
preventing botulism...
- food processing techniques & monitoring
- passive immunization
- Botox
- passive immunization
- Botox
54
New cards
tetanus and botulism
- BOTH PARALYTIC
- clostridium sp.
- soil bacteria
- gram positive bacilli
- endospores, anaerobic, neurotoxins
- clostridium sp.
- soil bacteria
- gram positive bacilli
- endospores, anaerobic, neurotoxins
55
New cards
poliomyelitis (polio)
inflammation of the gray matter of the spinal cord, leading to paralysis of the limbs and muscles of respiration
56
New cards
Meningicoccal meningitis is characterized by a skin rash called:
petichiae
57
New cards
The three major causes of bacterial meninigitis can be prevented with conjugate vaccines. By linking the bacterial ____________ to a protein antigen, the conjugate vaccine creates a T-dependent response and opsonizing antibodies to aid in bacterial phagocytosis.
capsule
58
New cards
Arthropod-Borne Diseases
-when a pathogen, such as a bacteria or virus, is transmitted from its reservoir (natural host) to a human via the arthropod vector(bug)
- also called ARBOVIRUS
- West Nile virus, Lyme disease, malaria, yellow fever, etc.
- also called ARBOVIRUS
- West Nile virus, Lyme disease, malaria, yellow fever, etc.
59
New cards
most common arthropod vectors...
fleas, ticks, flies, mosquitoes, lice
60
New cards
Tetanus and botulism have all of the following in common:
- bacterial neurotoxins
- paralysis
- passive immunization
- endospores
- paralysis
- passive immunization
- endospores
61
New cards
Pregnant women are tested for ________ before they deliver. Women testing positive can be prophylactically treated with antibiotic so that they do not spread this pathogen to the newborn during delivery.
Streptococcus agalactiae
62
New cards
Match the disease with the description.
A. botulism
B. tetanus
C. poliomyelitis
D. listeriosis
E. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
A. botulism
B. tetanus
C. poliomyelitis
D. listeriosis
E. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- A. bacterial neurotoxin causes FLACCID paralysis
- B. bacterial neurotoxin causes SPASTIC paralysis
- C. virus spread by fecal-oral route causes paralysis in 1% of those infected
- D. intracellular bacterium spread by contaminated food causes meningitis
- E. prion causes brain damage or spongiform encephalopathy
- B. bacterial neurotoxin causes SPASTIC paralysis
- C. virus spread by fecal-oral route causes paralysis in 1% of those infected
- D. intracellular bacterium spread by contaminated food causes meningitis
- E. prion causes brain damage or spongiform encephalopathy
63
New cards
Match the barrier defense w/ its example:
1. Chemical Barrier
2. Biological Barrier
3. Physical Barrier
4. Mechanical Barrier
1. Chemical Barrier
2. Biological Barrier
3. Physical Barrier
4. Mechanical Barrier
1. salt & acid in secretions such as sweat & sebum
2. competition by normal flora skin bacteria
3. keratinized cells of the stratum corneum
4. shedding of dead cells from the stratum corneum
2. competition by normal flora skin bacteria
3. keratinized cells of the stratum corneum
4. shedding of dead cells from the stratum corneum
64
New cards
endocarditis
infection and inflammation of heart valves
65
New cards
speticemia
blood infection
66
New cards
acute endocarditis
- Staphylococcus aureus (sometimes S. pyogenes or S. pneumoniae)
- enter bloodstream via parenteral route
- colonization of normal heart valves (coagulase)
- fibrin-platelet vegetations (biofilm) (coagulase)
- enter bloodstream via parenteral route
- colonization of normal heart valves (coagulase)
- fibrin-platelet vegetations (biofilm) (coagulase)
67
New cards
parenteral route
deposited directly into tissues when barriers are penetrated
- ex: needles
- ex: needles
68
New cards
acute endocarditis SYMPTOMS:
fever, abnormal heartbeat, high fatality rate, bacteremia, embolism
69
New cards
acute endocarditis TREATMENT:
- high-level antibiotics in bloodstream
- surgical debridement of valves (extreme cases)
- surgical debridement of valves (extreme cases)
70
New cards
subacute endocarditis
- oral streptococci
- minor mucosal injuries; possibly from dental procedures
- risk factors for colonization: prior heart valve damage OR congenital malformations
- TREATMENT: prophylactic antibiotics
- minor mucosal injuries; possibly from dental procedures
- risk factors for colonization: prior heart valve damage OR congenital malformations
- TREATMENT: prophylactic antibiotics
71
New cards
Which example would not be an appropriate use of antibiotic prophylaxis?
A. prevent subacute endocarditis by giving antibiotics to person with heart valve defect before undergoing dental procedure
B. prevent neonatal conjunctivitis by giving antibiotic eye drops to a newborn whose mother might have chlamydia
C. prevent neonatal meningitis by giving antibiotics to a mother who carries group B strep so she will not pass it on to her newborn
D. prevent infant botulism by giving antibiotics to a 6 month old child before eating raw honey
A. prevent subacute endocarditis by giving antibiotics to person with heart valve defect before undergoing dental procedure
B. prevent neonatal conjunctivitis by giving antibiotic eye drops to a newborn whose mother might have chlamydia
C. prevent neonatal meningitis by giving antibiotics to a mother who carries group B strep so she will not pass it on to her newborn
D. prevent infant botulism by giving antibiotics to a 6 month old child before eating raw honey
correct answer: D
72
New cards
Lyme disease
- 1970s Connecticut
- arthritis
- SYMPTOMS: fever, headache, fatigue
- PATHOGEN: borrelia burgdorferi (gram neg spirochete)
- TICK vector
- DEER & MICE reservoir
- 70% of cases present w/ erythema migrans (bulls eye rash)
- arthritis
- SYMPTOMS: fever, headache, fatigue
- PATHOGEN: borrelia burgdorferi (gram neg spirochete)
- TICK vector
- DEER & MICE reservoir
- 70% of cases present w/ erythema migrans (bulls eye rash)
73
New cards
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
- PATHOGEN: Rickettsia rickettsii (gram neg, coccobacillus)
- SYMPTOMS: early measles-like rash, fever, attacks cardiovascular & nervous systems
- TICK vector
- RODENT & SMALL MAMMAL reservoirs
- SYMPTOMS: early measles-like rash, fever, attacks cardiovascular & nervous systems
- TICK vector
- RODENT & SMALL MAMMAL reservoirs
74
New cards
Which is a differential symptom for Lyme disease?
bull's eye rash
75
New cards
AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome)
- before it was AIDS it was called: "gay cancer", GRID (gay-related immune disorder), 4H disease (homosexual, heroin user, hemophiliac, Haitian)
- got an official name in 1982
- HIV is transmitted via blood & bodily fluids
- cause (HIV- human immunodeficiency virus) was identified in 1983
- TODAY: more than 30 million infected worldwide, 1-2 million cases in USA, 40,000 new infections yearly (Africa and Asia), 1.8 million deaths in 2010
- direct contact, vehicle, #7 STD in USA
- got an official name in 1982
- HIV is transmitted via blood & bodily fluids
- cause (HIV- human immunodeficiency virus) was identified in 1983
- TODAY: more than 30 million infected worldwide, 1-2 million cases in USA, 40,000 new infections yearly (Africa and Asia), 1.8 million deaths in 2010
- direct contact, vehicle, #7 STD in USA
76
New cards
Ryan White
- A hemophiliac that died of AIDS at the age of 18
- contracted HIV via blood transfusion in 1984 (13 y/o)
- was refused admittance into Indiana school in 1985
- died in 1990 of respiratory infection
- contracted HIV via blood transfusion in 1984 (13 y/o)
- was refused admittance into Indiana school in 1985
- died in 1990 of respiratory infection
77
New cards
HIV can be transmitted by all the following routes EXCEPT:
a. biological vector
b. direct contact
c. vehicle
d. vertical
a. biological vector
b. direct contact
c. vehicle
d. vertical
CORRECT ANSWER: biological vector
78
New cards
CD4 is the host receptor for HIV. Therefore, the virus specifically infects and destroys __________, which leads to immune deficiency (AIDS).
helper T lymphocytes
79
New cards
Ottis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
- streptococcus pneumoniae OR haemophilus influenzae
- primarily children
- effusion (too much fluid)
- TUBES for DRAINAGE
- 25% antibiotics prescribed to humans (biofilms & resistance)
- Prevnar & Hib conjugated vaccines
- primarily children
- effusion (too much fluid)
- TUBES for DRAINAGE
- 25% antibiotics prescribed to humans (biofilms & resistance)
- Prevnar & Hib conjugated vaccines
80
New cards
In addition to otitis media, both Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are also known to cause:
meningitis
81
New cards
Strep Throat
- streptococcal pharyngitis
- pharyngitis (sore throat) are usually caused by cold viruses
- 30% of sore throat cases are caused by streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat)
- 15-20% carriers in pharynx (endogenous)
- SYMPTOMS: inflamed pharynx & tonsils, fever, nausea, white pus nodules, headache
- COMPLICATIONS: scarlet fever, rheumatic fever, toxic shock, etc.
- TREATMENT: beta-lactam antibiotic
- pharyngitis (sore throat) are usually caused by cold viruses
- 30% of sore throat cases are caused by streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat)
- 15-20% carriers in pharynx (endogenous)
- SYMPTOMS: inflamed pharynx & tonsils, fever, nausea, white pus nodules, headache
- COMPLICATIONS: scarlet fever, rheumatic fever, toxic shock, etc.
- TREATMENT: beta-lactam antibiotic
82
New cards
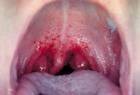
scarlet fever
erythrogenic toxin from bacteriophage, sandpaper-like rash, strawberry tongue
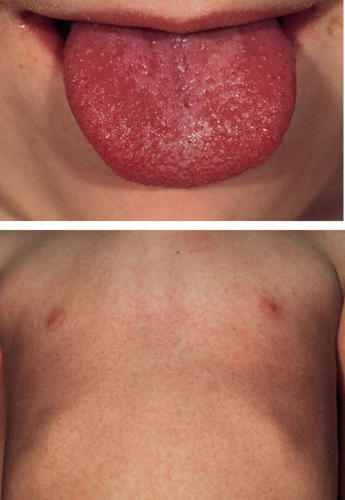
83
New cards
rheumatic fever
- autoimmune disease that is caused when the host produces cross-reactive antibodies to Streptococcus pyogenes that also bind to heart and joint tissues to trigger inflammation
- heart and joints
- heart and joints
84
New cards
Pertussis (whooping cough)
1. catarrhal stage: bordatella pertussis, filamentous hemagglutinin, COLD-LIKE symptoms
2. paroxysmal stage: tracheal cytotoxin, severe coughing, antibiotic treatment, pertussis toxin/endotoxin
3. convalescent phase: damaged cilia (secondary infections)
2. paroxysmal stage: tracheal cytotoxin, severe coughing, antibiotic treatment, pertussis toxin/endotoxin
3. convalescent phase: damaged cilia (secondary infections)
85
New cards
Pertussis treatment
wP "whole cell" vaccine (1930s) produced some adverse reactions so it was replaced by aP "acellular" vaccine (mid 1990s)
86
New cards
Which virulence factor of Bordatella pertussis is directly responsible for the "whooping cough" symptoms during the paroxysmal stage of the disease?
tracheal cytotoxin
87
New cards
Influenza (Flu virus)
- transmitted via respiratory secretions (direct/indirect)
- prolonged cold-like symptoms w/ fever, aches, chills, and fatigue
- less than 30,000 deaths in US per year (very young or old ppl)
- ENVELOPED RNA VIRUS
- hemagglutinin (H) and neuramindase (N)
- neuramindase inhibitors
- TREATMENT: tamiflu and relenza
- new vaccine yearly bc antigenic drift (they accumulate mutations in H gene during RNA synthesis
- prolonged cold-like symptoms w/ fever, aches, chills, and fatigue
- less than 30,000 deaths in US per year (very young or old ppl)
- ENVELOPED RNA VIRUS
- hemagglutinin (H) and neuramindase (N)
- neuramindase inhibitors
- TREATMENT: tamiflu and relenza
- new vaccine yearly bc antigenic drift (they accumulate mutations in H gene during RNA synthesis
88
New cards
antigenic shift in influenza
mixing of 8 gene segments of different flu strains (co-infection)
- pandemic flu
- pandemic flu
89
New cards
Antigenic shift vs drift
*Shift*: major genetic changes result in *pandemics*
*Drift*: minor genetic mutations result in *epidemics*
*Drift*: minor genetic mutations result in *epidemics*
90
New cards
Tuberculosis (TB)
infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; lungs usually are involved, but any organ in the body may be affected
- intracellular acid-fast bacillus (wax mycelia acid)
- respiratory droplets (ID = 10)
- intracellular acid-fast bacillus (wax mycelia acid)
- respiratory droplets (ID = 10)
91
New cards
Stages of Tuberculosis
primary: PPD skin test for exposure to Mtb
92
New cards
What is the most important method of treatment for a patient with diarrheal illness?
hydration
93
New cards
bacterial vaginosis
Caused by Gardnerella vaginalis
94
New cards
Chlamydia
A bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs of both males and females
- most women are asymptomatic for this intracellular bacterial infection
- can cause infertility if not treated
- most women are asymptomatic for this intracellular bacterial infection
- can cause infertility if not treated
95
New cards
genital herpes
a virus that causes latent infection can cause recurrent painful vesicles
96
New cards
Genital Warts (HPV)
human papilloma virus infection produces skin nodules that may lead to cancer
97
New cards
Candida albicans
- fungus (yeast)
- vaginitis
- opportunistic
- vaginitis
- opportunistic
98
New cards
Gardnerella vaginalis
- bacterium (BV)
- opportunistic
- vaginosis
- opportunistic
- vaginosis
99
New cards
Trichonomas vaginalis
- protozoan (parasite)
- #2 STD (increased risk of HIV)
- vaginitis
- #2 STD (increased risk of HIV)
- vaginitis
100
New cards
STD...
symptoms of Disease = you have symptoms