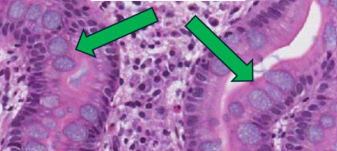
Basic types and properties of epithelial tissue at the microscopic level
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
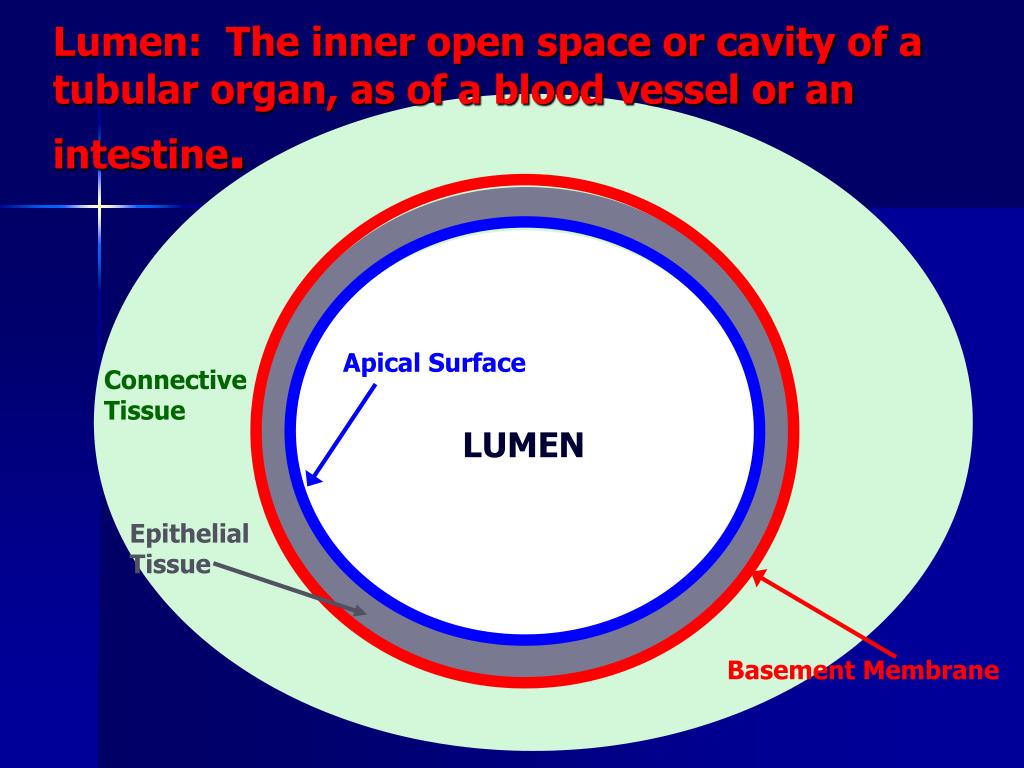
Lumen
The inner inside open space of a hollow organ/cavity or structure like intestines, blood vessels, or stomach
pic: also on the white surface that is outside of all the purple (its zoomed in)
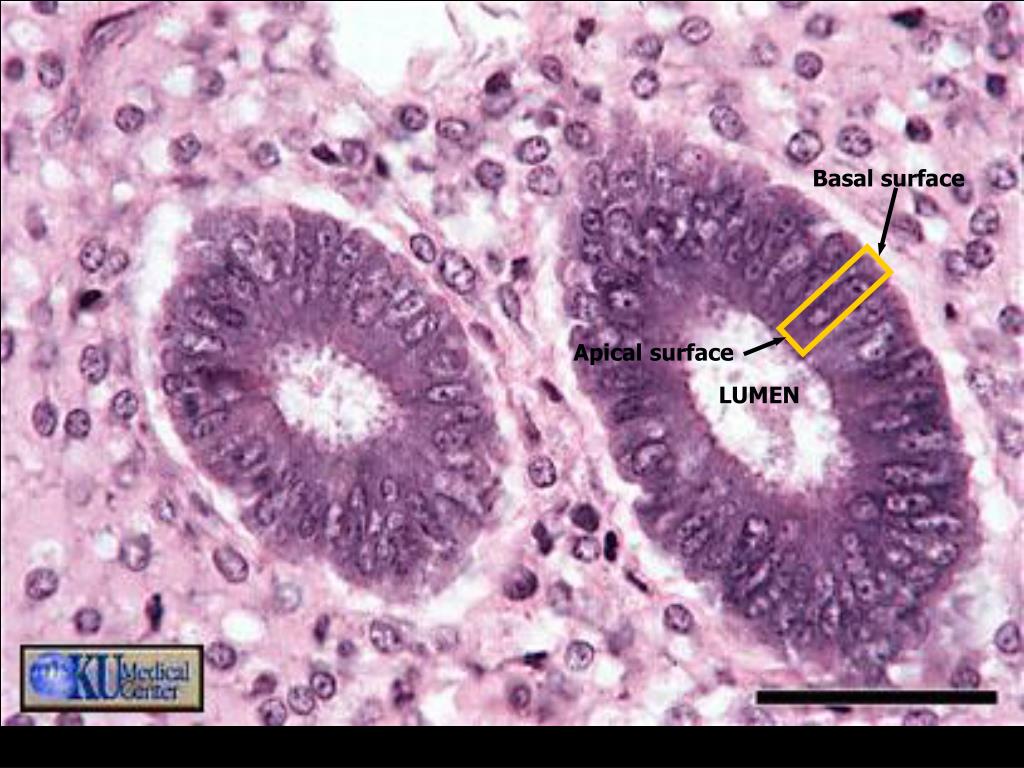
Apical surface
Top or exposed side of epithelial cells & it faces outside of the body (skin) or the inside space of an organ (intestines)
specialized for absorption, secretion and protecting underlying tissues

Apical surface: Microvilli
Extend from the surface of the certain cells particularly in the small intestine and increases the surface area of the cell, allowing for more efficient absorption of nutrients

Apical surface: Cilia
Extends from the apical surface and moves substances along the surface of the tissue

Basal surface
is attached to the basement membrane

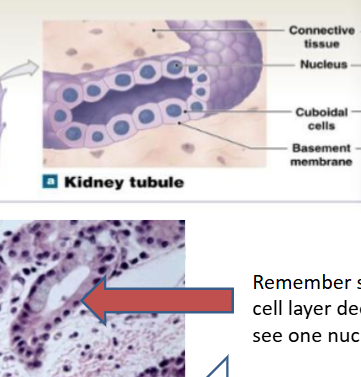
Simple squamous epithelium
1 layer squished, reduces friction, controls vessel permeability, and performs absorption and secretion
location: portions of kidney tubules which are thin sections of nephron loops
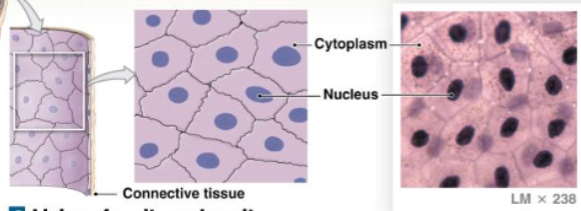
Simple cuboidal epithelium
It has limited protection, secretion, and absorption. 1 layer, cube shaped
locations: glands; thyroid gland, portions of kidney tubules
Simple columnar epithelium
1 layer and column shaped, it protects, secretion, absorption. TALL cells
locations: lining of stomach, gallbladder, etc

Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Protects, secretion, and moves mucus with cilia
Location: lining of nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi

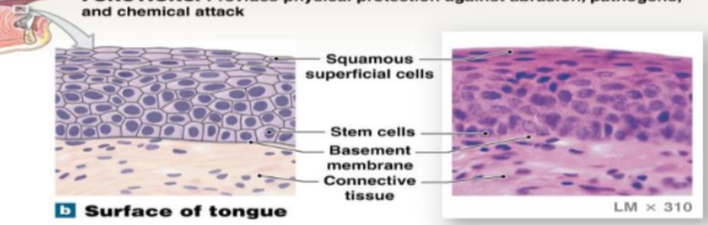
Stratified squamous epithelium: Keratinized
It contains keratin and is a protein that provides strength and waterproofing, acts as a protective barrier for underlying tissues from mechanical stress, dehydration, and microbial invasion/infection
location: epidermis of the skin, oral cavity-surface of tongue, and palms hands and sole of feet
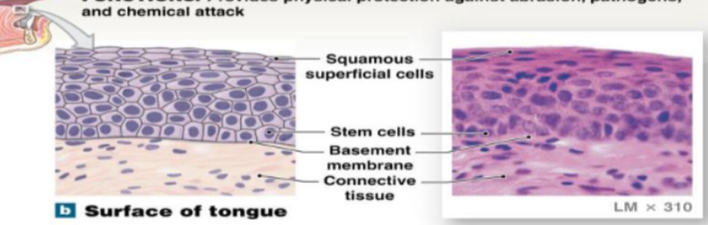
Stratified squamous epithelium: non-Keratinized
many layers and squished, it provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack and lacks keratin
locations: surface of skin; lining of mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, vagina
Transitional epithelium
It allows organs to stretch and expand when needed and returns to its normal shape, it protects underlying tissues from urine’s effects
Location: urinary system: lining of bladder
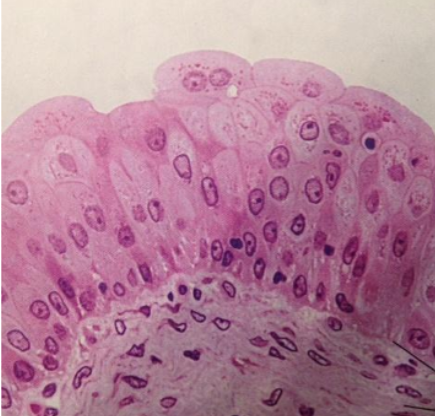
Goblet cell
Specialized epithelial cells that secrete mucins, which are key components of mucus, unicellular glands, protecting and lubricating the epithelial surfaces.
Location: in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts