AVS 472 Cumulative Exam Practice
1/677
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
678 Terms
testis
primary sex organ
scrotum
thermosensor, radiator, protective sac
tunica dartos
contract testis inwards, smooth muscle, testosterone dependent
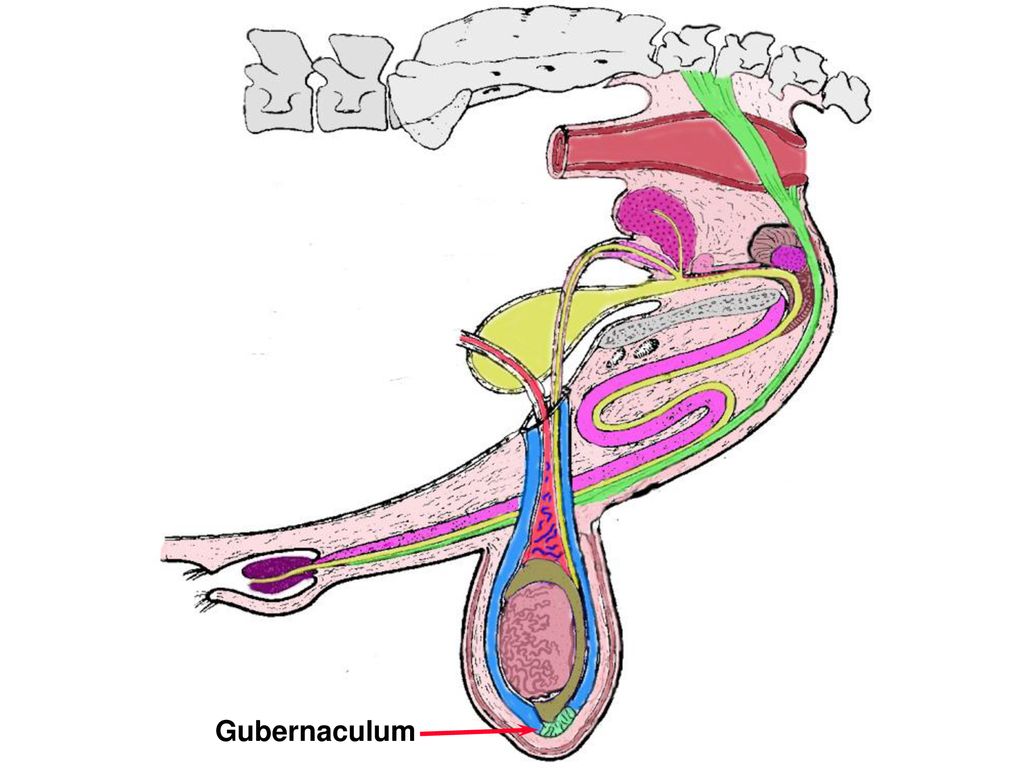
gubernaculum
wad of gum shaped, keeps the testis from spinning on its axis, shrinks as they get older
smooth muscle
doesn’t fatigue
skeletal muscle
does fatigue
cross section
cut through the middle, caudal cranial
longitudinal section
cuts in half, dorsal ventral
space between two tunics
open into the body cavity (peritoneal cavity)
tunica albuginea
encases testis
mediastinum
sperm converge to get to tubules
seminiferous tubules
ramen noodle shaped in testis
caput epididymis
head of the epididymus
corpus epididymis
body of the epididymus
cauda epididymus
bottom/tail of the epididymus, sperm is stored here
retes testis
in mediastinum, connects seminiferous tubules
vas Efferent
water reabsorption
number of ejactulates in caudal epididymus
5-7
spermatic cord functions
vascular, lymphatic and nerves; heat exchanger; houses cremaster muscle
cremaster muscle
fight or flight, skeletal muscle
pampiniform plexus
intertwining of blood vessels, counter current exchange of temp and testosterone, and arterial pulse
testosterone concentration unit
ng T/ml
testis arterial pulse
variation is much smaller than what is in systemic circulation
coppers gland
pre-ejaculate, fluid secreting, cleanses urethra
sigmoid flexure
s-shaped, when engorged in blood = straightens which pushes out penis
retractor penis muscle
retracts penis after erection
blood rich sections of bull penis
corpus spongiosum and corpus cavernous
corpus cavernous
more blood rich than corpus spongiosum
movement of sperm
testis > epididymus > tail of epididymus > accessory sex glands > penis
how is the horses testis oriented
horizontal
ram is missing what structure
body of the prostate
boar has a large what
ejaculate and cowpers gland (low concentration of sperm)
horses lack what structure
disseminate prostate
dogs are lacking what
ampulla, seminal vesicles, disseminate prostate or cowpers gland (highly concentrated sperm with little fluid)
what structures is a cat lacking
seminal vesicles and disseminate prostate
what is unique to a cat repro?
fishhooks on tip of penis
what type of penis does a stallion have
muscular-vascular
what type of penis does a bull have
fibroelastic
fibroelastic penis
only gain length and not width
muscular vascular penis
gains length and width
Sertoli cell are also called
nurse cells
Sertoli cells respond to
FSH
leydig cells respond to
LH and produce testosterone
Sertoli cells produce
E2 and inhibin
myoid cell
smooth muscle cell
spermatogonium
stem cells, closest to the basement membrane (one divides - one leaves, one stays, infinite divisions)
pre-sertoli cells secrete
AMH (antimollerian hormone aka female repro tract)
ABP
androgen binding protein
structure unique to only canines
bulbs glandis (sexes become tied)
all species have
retractor muscle
sigmoid flexure is only present in species that have
fibroelastic penis
large glans =
no sigmoid flexure
how long does it take for spermatogenesis cycle to occur
2 months (roughly 60 days)
sperm is not fertile until
reaching the vaginia
spermatocytogenesis
mitotic divisions of spermatogonia
hormone blood concentration first peak
GnRH (medium peak)
hormone blood concentration second peak
LH (highest peak)
hormone blood concentration hump between first peak and second
FSH (lowest peak)
LH causes a high peak of
testosterone slightly after the peak
how many pulses are there in 12 hours
4 pulses
importance of pulsatile secretion of LH
high t2 for spermatogenesis, leydig would become refractory to high LH concentrations, excess t2 thought to suppress Sertoli cells
testosterone synthesis (in leydig cell)
cAMP 2nd messenger system
sequence of spermatogenesis
proliferation > meiosis > differeniation
phase 1: proliferation
mitotic division (spermatogenesis) near the basement membrane
phase 2: meiosis
DNA replication and crossing over
phase 3: differentiation
(spermatogenesis) develops head, flagellum, and principal piece near lumen of tubule
flagellum
tail of the sperm
growth of sperm
spermatogonia > primary spermatocytes > secondary spermatocyte > spermatozoa
spermiation
releasing the spermatozoa from the certoli cells
number of mitotic division
are species dependent (between 2 and 6 which produces 4 to 64 daughter cells)
cytoplasmic bridges form
between the daughter cells
degenerating spermatogonia
apoptosis as high as 75%
things that can impact apoptosis of germ cells
normal, season, disease, trauma or heat, hormone levels
stem cell renewal
keeps spermatogenesis going indefinitely and replenish testis in case of injury, trauma, or high heat
proliferation occurs in the
basal compartment (near basement membrane)
meiosis and differentaition occurs in the
adluminal compartment
three types of spermatogonia
A, I, B
meiotic phase results in
4 haploid daughter cells
number of phases of meiosis
2 phases
four phases of differentiation
Golgi, cap, acrosomal, maturation
Golgi Phase
formation of acrosomic vesicle, migration of centrioles
Cap phase
asrcosome development continues, flagellum elongates
Acrosomal phase
acrosome manchette elongation
manchette
a series of microtubules, associated with nuclear elongation
Maturation Phase
manchette disappears, mitochondria migrates, dense fibers form
how does the sperm tail move?
ATP from middle section
spermiation
sprem finishing development and being released
cytoplasmic droplet
freshly released sperm have this, it moves down the tail as they sperm migrates and eventually falls off
cytoplasmic droplet on sperm indicate what?
an overworked male
stages of spermatogenesis
specific cellular associations within a small segment of the seminiferous tubule
stages differ in
duration (amount of time)
A’gonia present in
every stage of spermatogenesis
Which stage takes the longest?
stage 1 (4.09 days)
which stage takes the shortest amount of time?
stage 5 (0.22 days)
bull spermatogenesis length
13.5 days (one cycle)
number of stages in bull spermatogenesis
8 stages
the duration of the cycle differs
between species
number of cycles in bull spermatogenesis
4.5 cycles
typically 4.5 cycles are required
for A1 spermatogenia to become mature spermatozoa
single cycle day length for ram
10.4 days