OMIS 340
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Supply chain
Network of orgs and activities
Produces and delivers products or services
Also called the value chain
Supply chain management (SCM)
Strategic coordination across the supply chain
Integrates supply and demand decisions
Focuses on end to end performance
Logistics
Manages forward and reverse flows
Goods, services, information, and cash
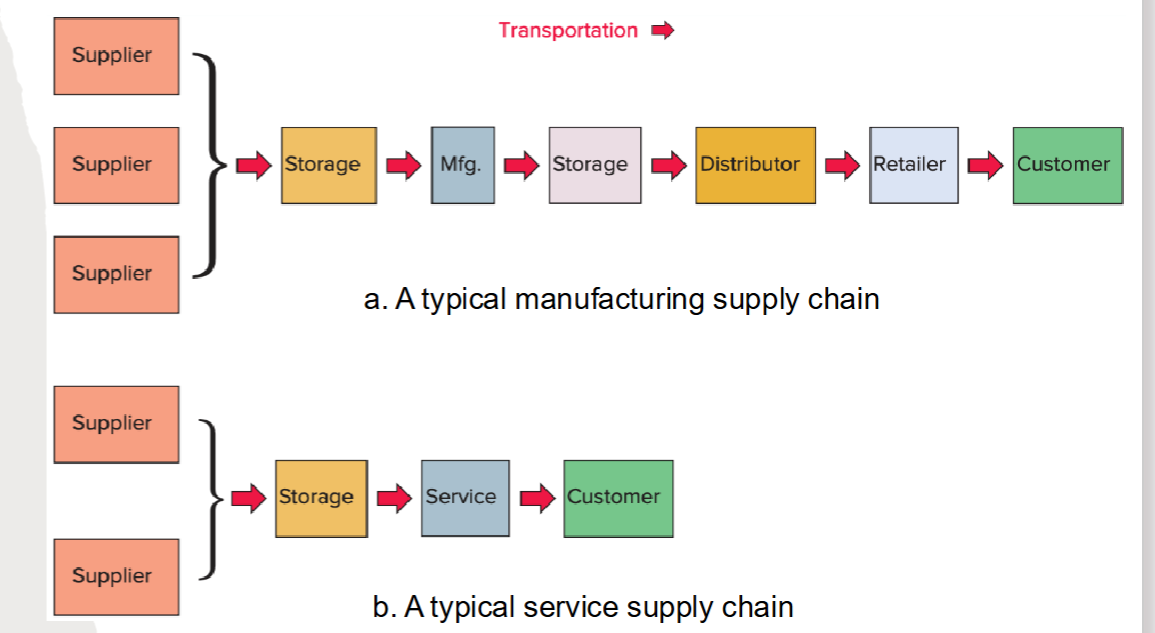
Typical Service Supply Chain
Goal of SCM
Match supply and demand efficiently and effectively
Key SCM Focus Areas
Outsourcing decisions
Procurement & supplier management
Customer relationship management
Rapid problem identification & response
Supply chain flows
Product & service flow -> goods, services, returns
Information flow -> forecasts, orders, tracking
Financial flow -> payments, credit terms, ownership
Benefits of Outsourcing
Lower labor operating costs
Docs on core competencies
Convert fixed costs to variable costs
Accessible supplier expertise
Free up capital
Support global expansion
Share selected risks with suppliers
Risks of outsourcing
Longer lead times and reduced flexibility
Higher transportation costs
Loss of control and business knowledge
Quality and productivity issues
Cultural and communication barriers
Intellectual property concerns
Increased coordination effort
Operations
That part of a business organization that is responsible for producing goods and/or services.
Operations management
The management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services.
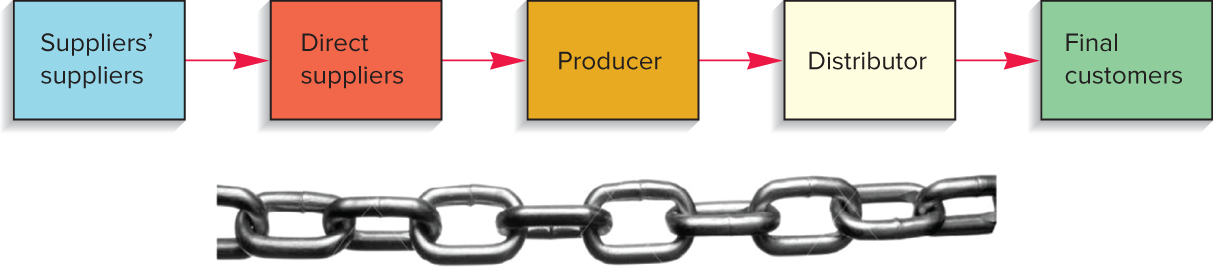
Supply chain
A sequence of organizations—their facilities, functions, and activities—that are involved in producing and delivering a product or service.
Supply chain steps image
Types of analytics
Descriptive analytics - Analytics that involves summarizing data.
Diagnostic analytics - Analytics that relates to answering the question of why something happened.
Predictive analytics- Analytics that focuses on what will happen.
Prescriptive analytics - Analytics that involves analyzing data to determine how to influence a desired change.
Key issues in business operations today:
Economic conditions
Innovating
Quality problems
Risk management
Cybersecurity
Competing in a global economy
Common Supply Chain Risks (DIRQ?!)
Disruptions
Information risks
Risk management
Quality failures
Resiliency
ability of a business to recover form an event that negatively impacts the supply chain
Disruptions
Natural disasters
supplier failures
Quality failures
Recalls, liability, reputational damage
Information risks
Loss of sensitive or proprietary data
Risk management
Identify and assess risks
Evaluate likelihood and impact
Develop response strategies
Risk avoidance
Risk reduction
Risk sharing
Keys to effective risk management
Know your suppliers
Improve supply chain visibility
Develop rapid response capability
What makes a supply chain global?
Design, sourcing, and production span multiple countries.
Manufacturing and services often outsourced for cost advantages
Products sold in global markets
Key complexities
Cultural and language differences
Currency fluctuations
Political and economic instability
Longer lead times and higher transportation costs
Greater need for trust and coordination among partners
How do natural disasters (such as hurricane helene) impact supply chains? (QUIZ QUESTION)
transportation difficulties
can’t access facilities/ they are damaged
relied heavily on a single critical source with few readily available alternatives
What could be done during a goods shortage? (ex: IV bags) (QUIZ QUESTION)
outsource from other facilities (diversify sourcing)
don’t rely heavily on a single critical source with few readily available alternatives
restore the main facility via:
gov support
increased production from other manufacturers
reducing demand through conservation
reduced hoarding
sharing across facilities
What could be done for quartz shortage (good that was inaccessible due to the mines being clogged from the hurricane and could not have been prevented) (QUIZ QUESTION)
no immediate replacement supply
Short term: focus on restarting operations quickly
Long term: substitute materials, alternative sources.
Key lessons manufacturers and retailers learned about the supply chain disruption from pandemic (QUIZ QUESTION)
companies become more flexible diversifying suppliers
diversify their routes to manage delays
moving away from cheapest only sourcing (quality)
relaxing overly lean inventory policy
increasing lead times and order quantity
ordering earlier
using alternative ports when needed
What are the benefits of regionalization, nearshoring, and reshoring? (QUIZ QUESTION)
prevent delays
save costs
reduce external disruptions
reduce transportation/ shipping costs for longer travel
keeps issues localized (not global)
reduces the impact of pandemic related disruptions
reduces pandemic related disruptions
What are the negatives of regionalization, nearshoring, and reshoring? (QUIZ QUESTION)
it can be more expensive
is typically cheaper to outsource
unrealistic for smaller businesses to participate in bc its too expensive
can take months to yrs to reorganize supply chain operations
must weigh benefits between higher costs and different risks against original benefits
significant investment to restructure supply chains
underlying causes of the drug shortages? (QUIZ QUESTION)
not meeting FDA requirements
not enough manufacturers producing each generic drug
need for lowest price = limited transparency
poor quality can halt production
difficulty obtaining ingredients
seasonal demand
disease spread
drug life cycles
healthcare trends
How can reshoring help with drug shortages (QUIZ QUESTION)
helps reinstall reliability into the supply chain
no more issues w/ international distributors, financial strains, manufacturer shutdowns
increased quality
better transparency for parties involved
3 SCM decisions
Strategic - (Long term, direction setting)
Tactical - (Midterm, planning focused)
Operational - (short term, execution focused)
Strategic planning
(Long term, direction setting)
Supply chain strategy alignment
Network configuration
IT
Product And service design
Capacity planning
Strategic partnerships
Distribution strategy
Risk and uncertainty management
Tactical planning
(Midterm, planning focused)
Forecasting
Sourcing
Operations planning
Inventory planning
Transportation planning
Collaboration
Operational planning
(short term, execution focused)
Scheduling
Receiving and transforming
Order fulfillment
Inventory control
Shipping
Information sharing
Day to day control
Procurement -
Responsible for obtaining materials, parts, and services
Supports production and service delivery
Goals of procurement
ensure right quality
Ensure right timing
Align purchasing with operation technology
The purchasing cycle
receive requisition
Select supplier
Place order
Monitor order
Receive goods/ services
Centralized purchasing
uses one main team for all buying, focusing on cost savings, standardization, and control
Lower price through volume consolidation
Better supplier service
Better handling of specialized items
Decentralized purchasing
empowers individual departments, branches, or teams to manage their own procurement needs directly, rather than relying on a central, corporate purchasing office
Departments understand needs better
fast er response time
Flexibility with local suppliers
Supplier management includes:
Selecting suppliers
Vendor analysis
Supplier audits
Supplier certification
Supplier relationship management
Key supplier evaluation tools
Vendor analysis
Price, quality, reputation, service
Supplier audits
production/ service capability
Quality and delivery performance
Supplier certification
Verifies supplier meets buyer requirements
Reduces need for incoming inspection
Types of supplier relationships
Short term
Competitive bidding
Minimal interaction
Medium term
Ongoing relationship
Long term
Highly cooperative
Often evolves into partnerships
Strategic partnering
long term collaboration for mutual benefit
ex:
Supplier holds inventory
Customer commits long term
Lower inventory costs and stable demand
Collaboration approaches CPFR
Collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment
Inventory velocity
speed at which inventory moves through the supply chain
Bullwhip effect
small changes in customer demand
Lead to larger demand swings upstream
Causes increasing inventory fluctuations across the supply chain
Main causes of the bullwhip effect
Forecast inaccuracies
Overreaction to stockouts
Order batching
Sales incentives and promotions
Quantity discounts
Product and service mix changes
Ways to reduce bullwhip effect
Strategic inventory buffering
Information sharing across the supply chain
Replenishment based on actual demand
Vendor managed inventory (VMI)
Supplier monitors inventory levels
Supplier replenishes inventory when levels are low
Reduces demand distortion and improves coordination
Bullwhip effect is fundamentally
an information problem not a demand problem
Order fulfillment
processes used to respond to customers
Order fulfillment strategies
Engineer to order (ETO) - product designed after order is received
Make to order (MTO)- production starts after order
Assemble to order (ATO) - final assembly after order
Make to stock (MTS) - products produced in advance and stocked
Remember
ETO -> MTO -> ATO -> MTS moves from high customization to high efficiency
Logistics manages the movement of:
Materials
Services
Cash
Information
Logistics activities
Movement within facilities
Incoming and outgoing shipments
Objectives of logistics activities
Getting goods to the right place at the right time
Movement within a facility
Flow of materials between:
Receiving
Storage
Work centers
Shipping
Incoming & outgoing shipments (traffic management)
Oversees shipment scheduling and routing
Considers:
Transportation costs
Government regulations
Organizational needs
Shipping delays or disruptions
Tracking goods with
RFID
Uses radio waves to identify and track items
Compared to barcodes
More information
No line of sight required
Multiple items read at once
Benefits of RFID
Greater supply chain visibility
Improved inventory management
Better quality control
Strong supplier and customer relationships
3rd Party Logistics (3PL)
Outsourcing logistics activities
Common services
Warehousing
Distribution
Benefits of 3PL
Logistics expertise
Advanced information systems
Lower shipping costs
Logistics is about
flow, visibility, and coordination. Technology and outsourcing exist to improve all three
Key considerations
Cost
Speed (delivery time)
Availability of shipping modes
Type of material shipped
Flexibility
Environmental impact
Common shipping modes:
Truck
Rail
Air
Water
Time-cost trade off
Faster shipping -> higher cost
Slower shipping -> lower cost
Choice depends on:
Business strategy (low cost vs. responsive)
Urgency of the shipment
Managerial insight
When urgency is low, firms compare:
Shipping cost savings vs. additional inventory holding cost
Incremental holding cost equation
(H * d)/ 365
H = annual holding (earning) cost of the item
d= difference in delivery time(days)
Decision rule -
Choose slower shipping if
Shipping cost savings> incremental holding cost
Choose faster shipping otherwise
Creative an effective supply chain
Foundations of an effective supply chain - begins with strategic sourcing
Focuses on:
Reducing waste and non-value added activities
Lowering costs and risks
Improving supplier performance
Key enablers for creating an effective supply chain
trust
Effective communication
Fast information flow
Supply chain visibility
Event management capability
Performance metrics
SCOR framework
A standard model for designing and managing supply chains.
Parts of framework:
Plan
Source
Make
Deliver
Return
Managing returns (reverse logistics)
managing the flow of returned products
Elements of return management:
Gatekeeping - screen returns to prevent incorrect acceptance
Avoidance - reduce the number of returns
Closed loop supply chain
firm manages both forward and reverse logistics
Key challenges in creating effective supply chains
Organizational integration barriers
Gaining top management support
Managing trade offs (cost, speed, flexibility, service)
Resource constraints for small businesses
Variability and uncertainty in demand and supply
Meeting required response times.