Week 11(L20-21): Transmembrane proteins, Golgi, COP, endocytosis, autophagy, cytoskeleton
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:51 PM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
How are transmembrane proteins integrated into a membrane?
single-pass transmembrane
* TMD gets stuck in translocon
* TMD released into ER membrane
* TMD gets stuck in translocon
* TMD released into ER membrane
2
New cards
What are the 2 options for a protein targeted to the ER lumen after fully synthesized and folded?
1. retained in ER lumen
2. transported ER→golgi complex for further modification + delivered to distal parts of biosynthetic pathway
3
New cards
The Golgi complex receives transport vesicles at the __ and sends them off from the ____
CGN
TGN
TGN
4
New cards
What is critical for cell function?
getting proteins to where they need to be
5
New cards
What does the **Golgi** **complex** do?
* receives proteins + lipids from ER
* sorts to other organelles, PM, or cell exterior
* sorts to other organelles, PM, or cell exterior
6
New cards
In what direction do materials move from ER→Golgi→other compartments?
proximal → distal
7
New cards
Describe the structure of Golgi complex
* smooth, flattened, disk-like cisterna
* diameter = 0.5-1 micron
*
* diameter = 0.5-1 micron
*
8
New cards
Golgi complex shows polarity
cis-medial-trans cisternae
9
New cards
Cisternae are …
biochemically unique; different cisternae contain different enzymes to modify proteins
10
New cards
The golgi complex membrane is supported by what?
protein skeleton - actin, spectrin
11
New cards
Scaffold linked to ________ that direct vesicle movement in/out of Golgi
motor proteins
12
New cards
What does the CGN act as?
sorting station
13
New cards
What does the CGN do?
sort whether protein continues to next Golgi station OR shipped back to ER
14
New cards
What does TGN do?
sorts proteins into different vesicles
15
New cards
Where do the vesicles go?
* other **PM**
* other **intracellular** destinations (lysosomes)
* other **intracellular** destinations (lysosomes)
16
New cards
Golgi is the ________ of the cell
processing plant
17
New cards
In addition to sorting, what else is the Golgi involved in?
* polysaccharide synthesis
* protein + lipid modification (glycosylation + proteolytic)
* protein + lipid modification (glycosylation + proteolytic)
18
New cards
proteins are modified ______ as traverse the Golgi
step-wise
19
New cards
Where are proteins fully processed?
at the TGN
20
New cards
Fully processed proteins are sorted to the _________, then sorted/delivered to final destinations
TGN
21
New cards
Mucin secretion is an example of what?
**constitutive** secretory pathway
22
New cards
Insulin and neurotransmitter release is an example of what?
**regulated** secretory pathway
23
New cards
What does the goblet cell in the GI tract produce?
protective mucus containing glycoprotein mucin
24
New cards
Describe **cystic** **fibrosis**
CFTR mutated and degraded in ER
* fails to reach surface/other sites
* fails to reach surface/other sites
25
New cards
In CF, what does an F508 mutation cause?
* deletion of 3 nucleotides
* loss of phenylalanine (F) at 508th position of protein
* loss of phenylalanine (F) at 508th position of protein
26
New cards
How is the transfer of vesicles ER→Golgi + b/t Golgi sub-compartments achieved?
coat proteins
27
New cards
Coat proteins have 2 functions:
1. form vesicle
2. select cargo for vesicle
28
New cards
What are **COPI** + **COPII**?
* **coat protein** **complexes**
* assemble on the cytosolic surface of donor compartment membranes where budding takes place
* assemble on the cytosolic surface of donor compartment membranes where budding takes place
29
New cards
What direction do COPI-coated vesicles move?
retrograde
30
New cards
What direction do COPII-coated vesicles move?
anterograde
31
New cards
What direction does retrograde run in?
distal-proximal
32
New cards
What direction does anterograde run in?
proximal→distal
33
New cards
Lysosomes are ______ organelles
digestive
34
New cards
What is the size of lysosomes?
25 nm → 1 μm
35
New cards
What is the internal pH of lysosomes?
4\.6
36
New cards
What do lysosomes contain?
hydrolytic enzymes - acid hydrolases
37
New cards
The lysosomal membrane is composed of what?
glycosylated proteins
38
New cards
What do glycosylated proteins act as?
protective lining next to acidic lumen
39
New cards
What directs vesicles to other parts of the cell in late biosynthetic secretory pathway?
* trans golgi → endosomes
* trans golgi → lysosomes
* PM → endosomes
* trans golgi → lysosomes
* PM → endosomes
40
New cards
What does a two-layered coat consist of?
* clathrin
* AP complex
* AP/clathrin-coated vesicles
* AP complex
* AP/clathrin-coated vesicles
41
New cards
What is clathrin?
* coat protein - OUTER layer
* vesicle formation + structure
* vesicle formation + structure
42
New cards
AP complex
* clathrin adaptor protein complex - INNER layer
* 3 diff AP complexes
* select cargo
* different complexes associated with different trafficking routes
* 3 diff AP complexes
* select cargo
* different complexes associated with different trafficking routes
43
New cards
AP/Clathrin coated vesicles move ______-
from TGN →other compartments
44
New cards
Autophagy
normal disassembly of unnecessary/dysfunctional cellular components -organelle turnover
45
New cards
What are the phases of autophagic pathway?
autophagasome formation → lysosome recruitment → autolysosome → digestion & release
46
New cards
Describe steps of autophagy
1. isolation membrane engulfs target organelles → forms autophagosome/autophagic vesicle
2. lysosome fuses w/ER-derived AV to form an autolysosome
3. autolysosome content enzymatically digested and released (EXOCYTOSIS)
47
New cards
What is the isolation membrane derived from?
ER
48
New cards
Degradation of internalized material
* recycling plasma membrane components (receptors/extracellular material)
* destroy pathogens - only in phagocytic cells
* destroy pathogens - only in phagocytic cells
49
New cards
Describe **phagocytosis**
* pathogen internalized by phagocytic cell
* pathogen degraded by lysosomes associated w/pathogen-containing vesicle
* hydrolytic enzymes degrade + kill pathogen
* debris released from cell
* pathogen degraded by lysosomes associated w/pathogen-containing vesicle
* hydrolytic enzymes degrade + kill pathogen
* debris released from cell
50
New cards
Describe the plant cell wall
rigid barrier composed of polysaccharides
51
New cards
Plant vacuoles take up ____% of the cell’s volume
90%
52
New cards
Vacuoles are _____-filled__ and ___-bound
fluid
membrane
membrane
53
New cards
Chloroplasts enable plant cells to do what?
harness sunlight energy to synthesize sugars
54
New cards
What do plasmodesmata connect?
neighbouring plant cells
55
New cards
What are vacuoles?
organelles contributing to structural rigidity of plants by maintaining turgor pressure against cell walls
56
New cards
Vacuoles are involved in what?
* cytoplasmic pH regulation
* cell turgor (rigidity) regulation
* toxic ion sequestration
* AA, sugar, CO2 storage in form of malate
* cell turgor (rigidity) regulation
* toxic ion sequestration
* AA, sugar, CO2 storage in form of malate
57
New cards
Tonoplast
* vacuolar membrane
* contains active transport systems
* allow ion + molecule transport
* contains active transport systems
* allow ion + molecule transport
58
New cards
What are the 3 functions of plant vacuoles?
1. intracellular digestion
2. mechanical support
3. storage
59
New cards
intracellular digestion
* similar to lysosomes
* pH = 5
* acid hydrolases
* pH = 5
* acid hydrolases
60
New cards
Vacuole mechanical support
* turgor pressure
* gives plant rigidity
* supports soft tissues
* stretches cell wall during growth
\
* gives plant rigidity
* supports soft tissues
* stretches cell wall during growth
\
61
New cards
Vacuole storage
* solutes
* macromolecules
* chemical storage → anthocyanin (pigment)
* macromolecules
* chemical storage → anthocyanin (pigment)
62
New cards
Cytoskeleton
* dynamic network of interconnected filaments and tubes
* extends through cytosol of eukaryotes
* extends through cytosol of eukaryotes
63
New cards
What are the functions of the cytoskeleton?
* structural support
* spatial organization
* intracellular transport
* contractility
* motility
* spatial organization
* intracellular transport
* contractility
* motility
64
New cards
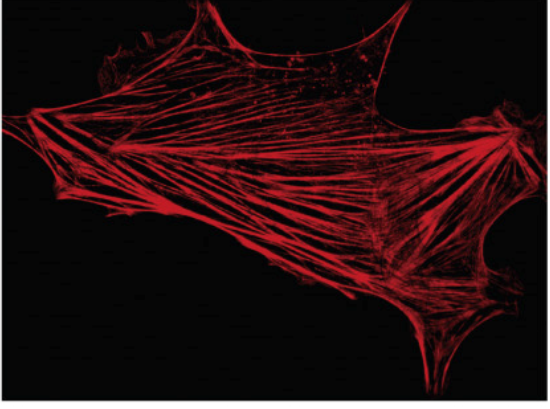
Microfilaments
subunit = actin
structure = 7-9 nm
structure = 7-9 nm
65
New cards
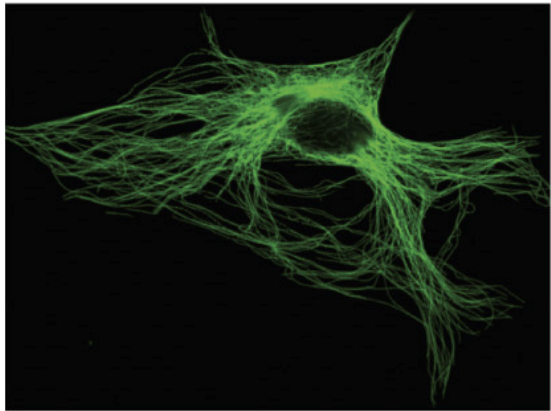
Microtubules
subunit = alpha beta-Tubulin dimer
structure = 25 nm
structure = 25 nm
66
New cards
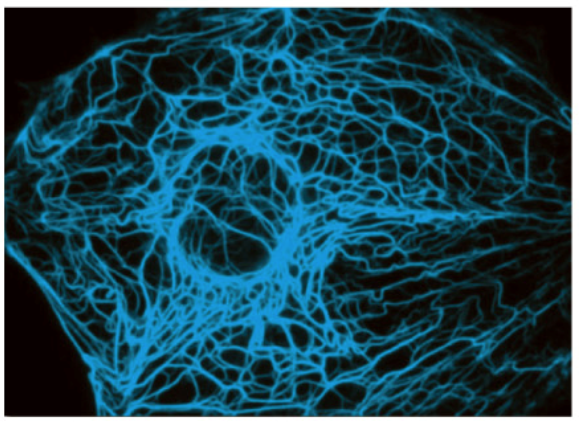
intermediate filaments
subunit = various
structure = 10 nm
structure = 10 nm