Lecture 3b - Design Methods + Prototyping
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Describe → Interactive System Development Process
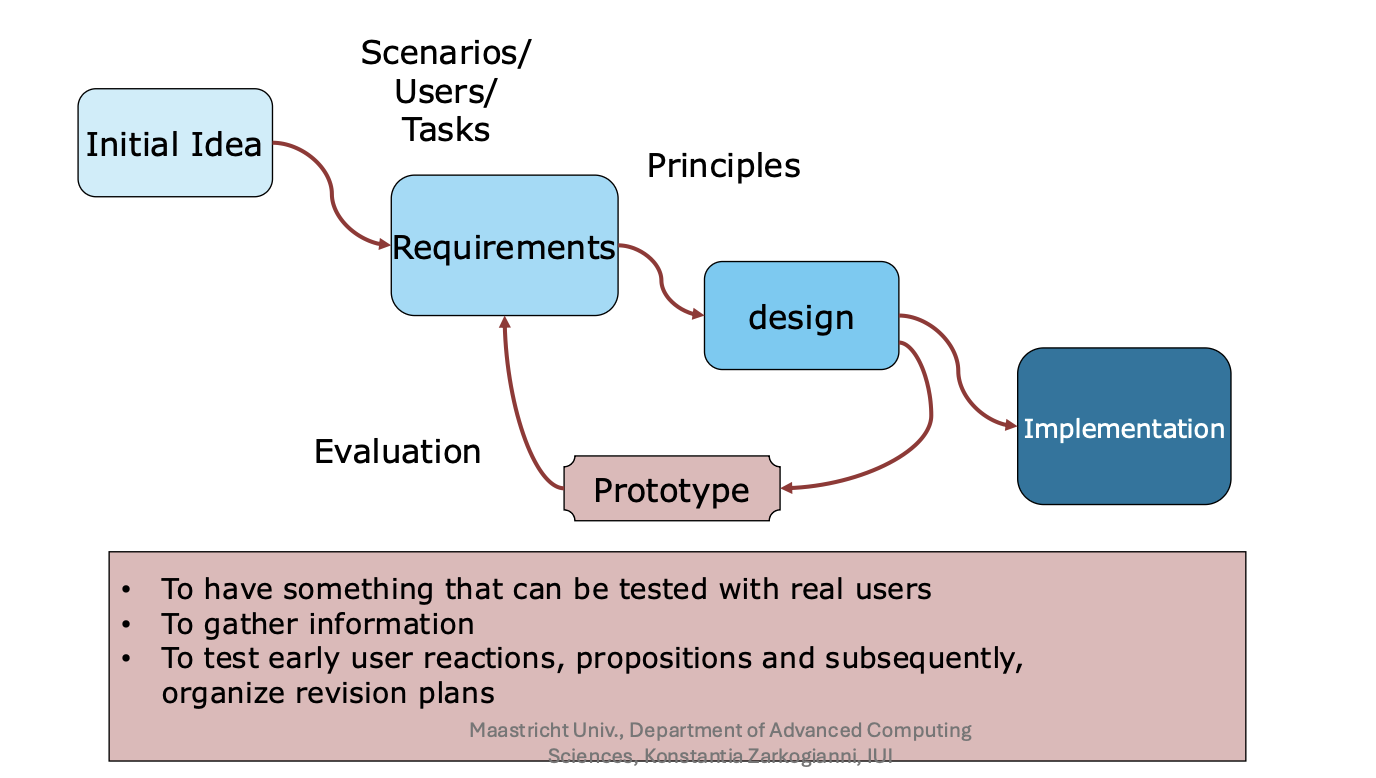
What is the Interactive System Development Process?
• problem solving procedure, driven by user requirements and intended use of product + defined by the application area, materials, cost, technical feasibility studies
• about technical steps + creativity + decision-making on trade-offs + compromising
• representation of how concrete + precise system will be built + what alternatives will be followed + at what sequence
What is a Human Centric Design?
User responses can be registered and analyzed through
• Co-creation activities + System simulation
• Usability analysis activities on advanced prototypes
• Such procedures must be repetitive + should allow for gradual improvement of system features
Prototyping
gathering info
we need them to test user reactions, propositions, and then organise revision plans
good basis for testing, if seen as intermediary products, aim is to have something be test by users
prototyping can be embedded in a system’s development lifecycle or can be performed independently as an alternative
Cost of prototyping
Cheaper than not doing it, usability work (including prototyping) should amount to 5-10% of budget
testing early + iterating often makes the product cheaper, prototyping is a cheap way to test a product early in its lifecycle
Horizontal Prototyping
✔ Shows the entire interface (broad but shallow)
❌ Limited real functionality
✔ Helps visualize the full system + shows top-level functionality
Vertical Prototyping
✔ Focuses on a small part but in-depth
✔ Helps test real user tasks
❌ Users can’t navigate freely + limited # of functionalities
What is fidelity in prototyping?
Fidelity = How realistic a prototype is, judged by how it appears to the person viewing it
High Fidelity – Looks like the final product, uses similar media
Low Fidelity – Basic sketches or paper models, proof of concept, low-cost; produces prototype early during requirements specification phase
High fidelity prototyping: WOz
User thinks they are interacting with a device, but a human is responding to output rather than the system; often done early in design to understand users’ expectations
Low fidelity prototyping methods
Storyboards – Step-by-step sketches of user interaction
Sketching – Simple drawings of the interface
Videos – Animated/narrated walkthroughs
Index Cards – Each card represents a screen in the system (used slightly later in design process when content + functionalities have been defined)
Why is prototyping important?
Saves money – Fixing mistakes early is cheaper
Tests usability – Helps create a better user experience
Guides development – Ensures final product meets needs
Encourages iteration – Continuous improvements make it better