Y4 Unit 2a - Reproduction in humans
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
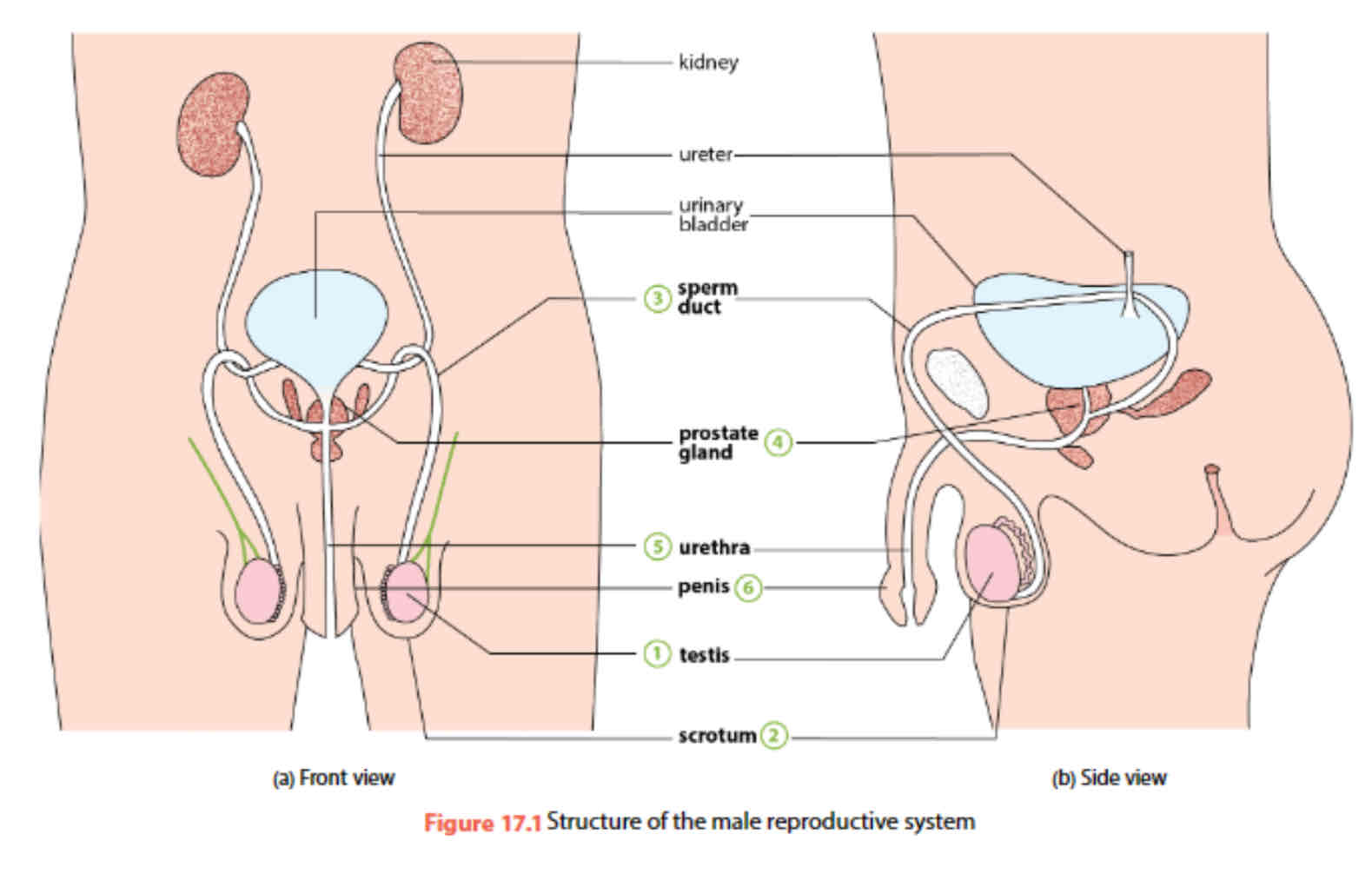
Parts of the male reproductive system
testis, scrotum, sperm duct, prostate gland, urethra, penis
Main function of male reproductive system
Produce store transport sperm and protective, nutritious fluid (semen)
Discharge sperm within female reproductive tract
Produce, secrete male sex hormones
Testis (p. Testes)
produces sperm and testosterone (male sex hormone) → develop and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics
Male gonads located outside abdominal cavity in scrotum
Outside the main body, so sperm-forming cells 2ºC cooler than body temperature, allowing them to function normally
scrotum
loose pouch like sac of skin that hangs behind penis
Has special muscles in wall of scrotum allowing contraction and relaxation, move testicles closer to body (warmth) or further (cool temperature)
sperm duct
(Vas deferens)
deliver sperm —> urethra during ejaculation
Ejaculation: caused by contraction of muscles along sperm ducts release 5ml of semen
Only 5% semen consists sperm
Prostate gland
prostate gland is at the base of the urinary bladder, in front of rectum
Secretes fluid that nourishes sperm and provides protection from natural acidity of vagina
Semen
has nutrients and enzymes to nourish sperm and stimulate them to actively swim
Urethra
tube passes from bladder → centre of penis → outside of body
direct connection of male reproductive and urinary system
Penis
Erectile tissue that can fill with blood, causes erection
Deliver sperms to vagina
Head covered by foreskin (that can be removed via circumcision)
Sections of the sperm and physical characteristic
Head, middle piece, tail (flagellum); streamlined shape
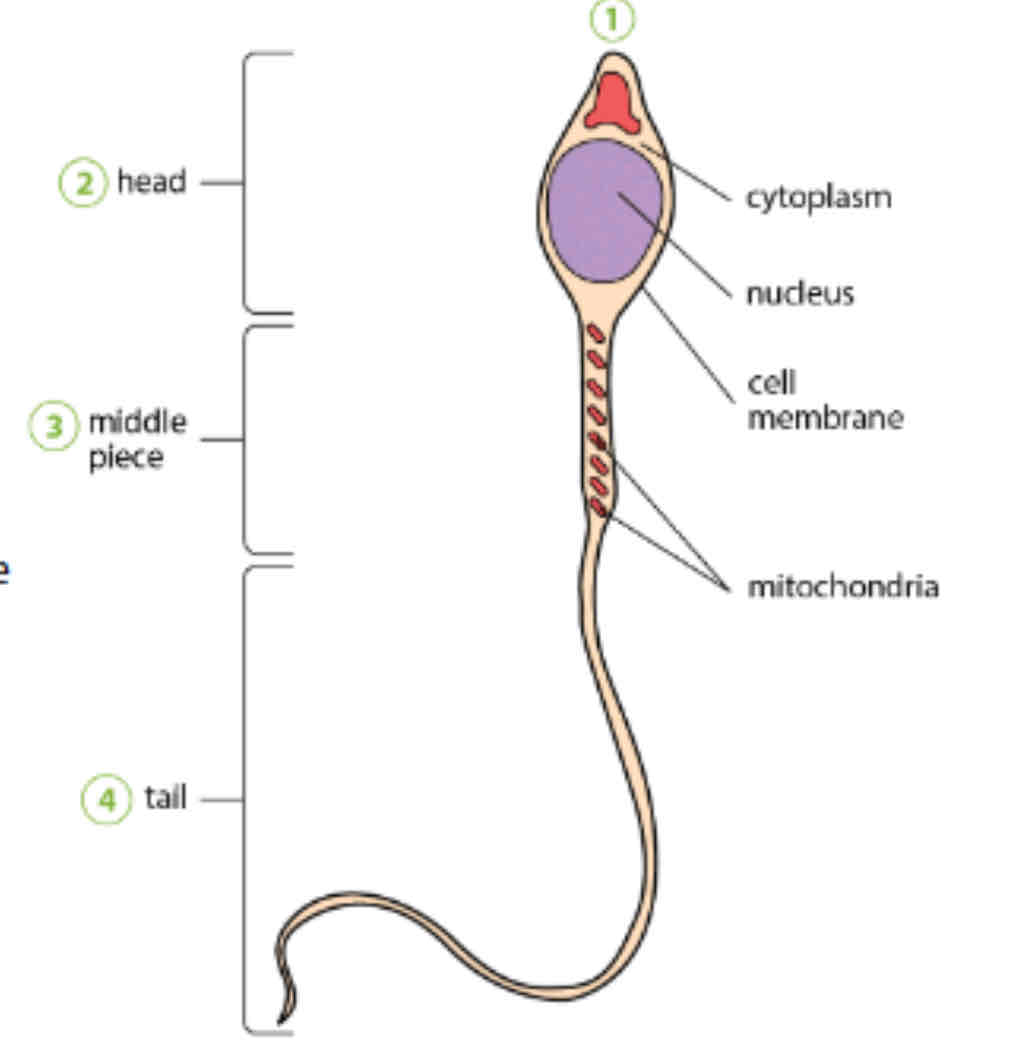
Head
2.5 micrometer
✅large nucleus with small amount of cytoplasm + haploid set chromosomes
Middle piece
Has many mitochondria → provide energy for sperm to swim
Tail (flagellum)
Beating movement enables swimming, letting sperm become motile
Sperm
Male gamete, many produced after maturity
60 micrometer
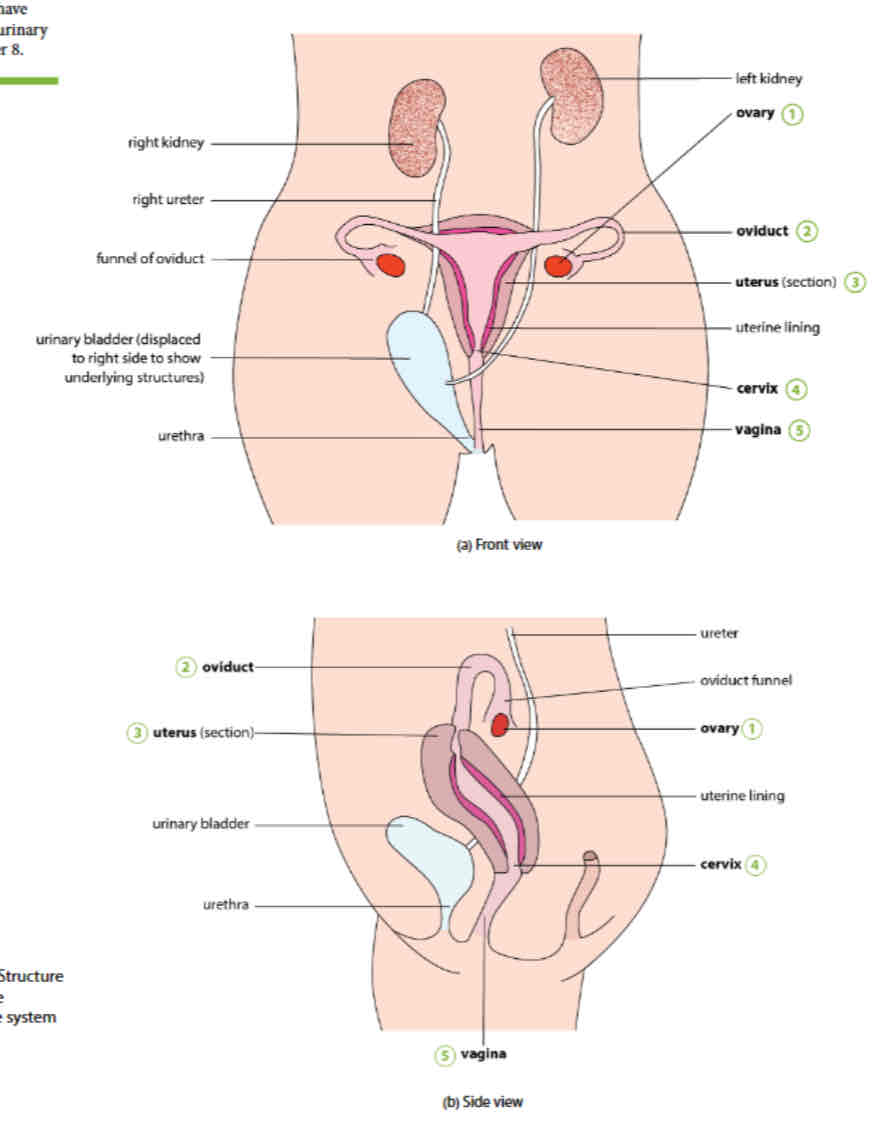
Parts of female reproductive system
Ovary, oviduct, uterus, cervix, vagina
Main function of female reproductive system
Produce ova/egg cells (singular ovum) for reproduction
Transport ova to site of fertilisation (oviduct/fallopian tube)
Provide safe and favourable environment for fetal development in uterus
Product female sex hormone that maintain reproductive cycle
Ovary
site of gamete production
Follicles have: 1 developing egg cells (ovum) surrounded by cells to nourish, protect it
Produce oestrogen and progesterone (by corpus luteum)
Born with 1 - 2 million follicles with immature eggs, only several hundred mature ova will be released
1 cycle = 1 follicle = 1 egg released
Purpose of female hormone production
Development and maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics in females
Oviduct/fallopian tube
where matured egg is released by ruptured follicle and fertilised
Narrow muscular tube (ovary to uterus)
Has funnel like opening lying close to ovary
Make easier for egg to enter oviduct
Inner surface lined with cilia
Cilia sweeps egg towards uterus
Uterus
where fetus will develop
Has thick elastic muscular wall (smooth tissue muscle)
Contracts
Lined with endometrium wall where embryo will implant and grow
Cervix
narrow ring of muscle at bottom of uterus
Opens up into vagina, allows flow of menstrual blood out and direct sperm to uterus
Vagina
Lead from cervix to outside, where semen deposited, just behind opening of urethra
Ovum (general)
Female gamete
fixed number at birth
70 000 potential egg cells about 500 ever become mature within 2 ovaries
1 mature egg released every month from time of physical maturity until 45 -55 years old
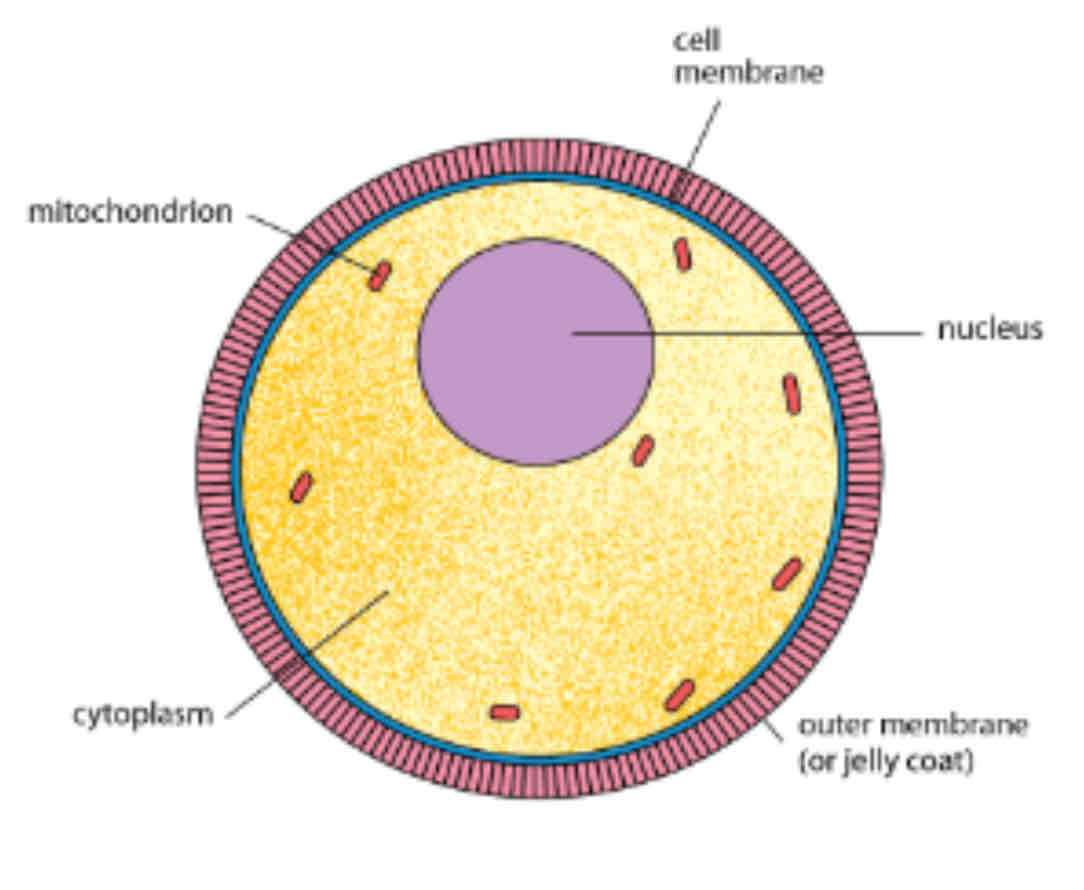
Ovum (cellular)
spherical, 120 - 150 micrometer
Has abundant cytoplasm that may contain small amount of yolk
Surrounded by cell membrane → surrounded by outer membrane (jelly coat)
Jelly coat changes during fertilisation, prevent more sperms from entering
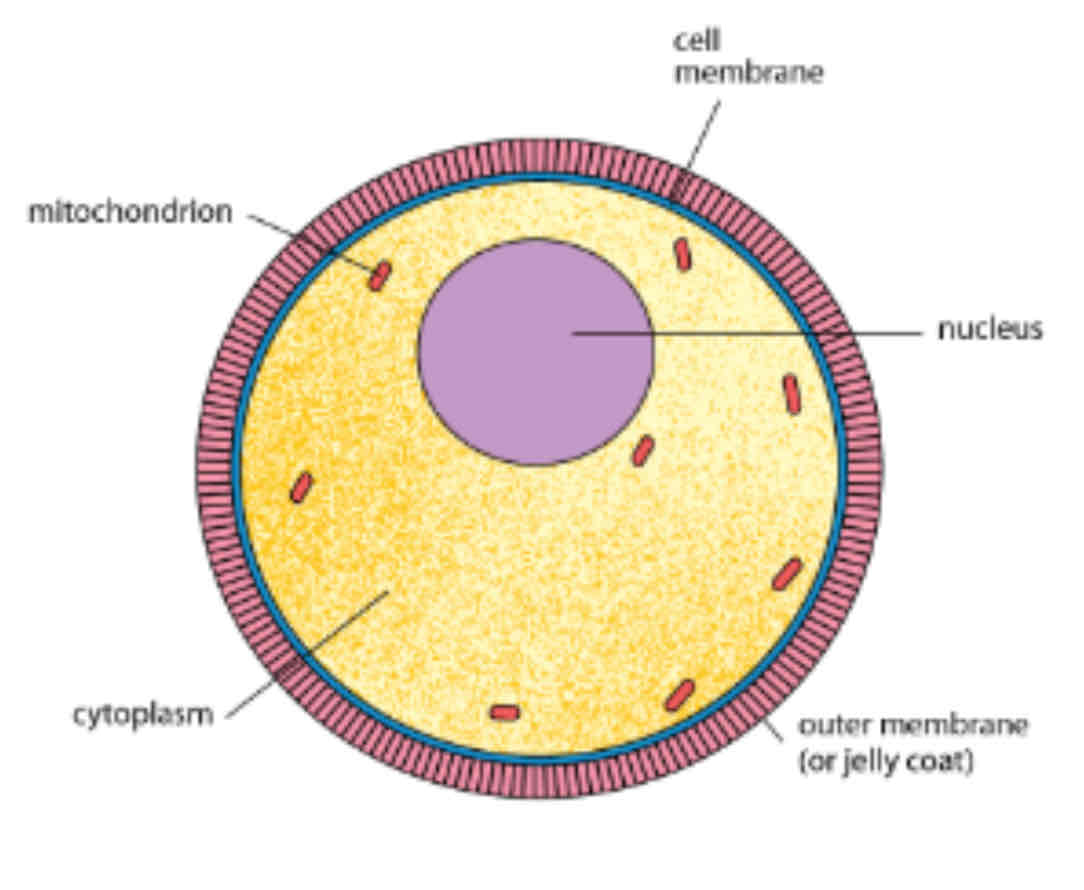
Differences between male female gamete
Male gamete
has head middle piece tail
Nucleus has either X or Y chromosome
60 micrometer long, diameter 2.5 micrometer for head
Has tail to enable swimming
Large number released per ejaculation
Female gamete
spherical in shape
1 X chromosome
Diameter 120 - 150 micrometer
Passive movement of egg along oviduct as movement of cilia and peristalsis of oviduct wall takes place
One egg released per month