Urinalysis and Body Fluids | Quizlet
1/492
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
493 Terms
1. Why is the first-voided morning urine
specimen the most desirable specimen for
routine urinalysis?
A. Most dilute specimen of the day and
therefore any chemical compounds
present will not exceed the detectability
limits of the reagent strips
B. Least likely to be contaminated with
microorganisms because the bladder is
a sterile environment
C. Most likely to contain protein because
the patient has been in the orthostatic
position during the night
D. Most concentrated specimen of the
day and therefore it is more likely that
abnormalities will be detected
D. The first-voided morning urine specimen is
the most desirable for chemical and microscopic
analysis because it is the most concentrated specimen
of the day. Protein and nitrite testing is better
performed on a concentrated specimen, as are
the specific gravity determination and the examination
of urinary sediment. However, because of
the lack of food and fluid intake during the night,
glucose metabolism may be better assessed on
the basis of a postprandial specimen.
2. The physical characteristic of color
is assessed when a routine urinalysis
is performed. What substance is
normally found in urine that is principally
responsible for its yellow coloration?
A. Bilirubin
B. Melanin
C. Carotene
D. Urochrome
D. Urochrome, a yellow-brown pigment derived
from urobilin, is principally responsible for the
yellow coloration of normal urine. Urochrome is
excreted at a constant rate, showing no diurnal
variation. Therefore, the color of normal urine,
which may range from straw to deep amber, is
dependent on the concentrating ability of the kidney
and the volume of urine excreted
3. In certain malignant disorders, what
substance is found in the urine that turns
the urine dark brown or black on exposure
of the urine to air?
A. Urobilinogen
B. Indican
C. Melanin
D. Porphyrin
C. Melanin, a substance derived from tyrosine,
is responsible for the pigmentation of the eyes,
skin, and hair.
4. What is the expected pH range of a freshly
voided urine specimen?
A. 3.5-8.0
B. 3.5-9.0
C. 4.0-8.5
D. 4.5-8.0
D. pH is a representative symbol for the hydrogen
ion concentration. The kidney plays an
important role in the maintenance of the acidbase
balance of body fluids by either excreting
or retaining hydrogen ions. A normally functioning
kidney will excrete urine with a pH between
4.5 and 8.0, depending on the overall acid-base
needs of the body
5. Urine specimens should be analyzed as
soon as possible after collection. If urine
specimens are allowed to stand at room
temperature for an excessive amount of
time, the urine pH will become alkaline
because of bacterial decomposition of
A. Protein
B. Urea
C. Creatinine
D. Ketones
B. At room temperature, the amount of bacteria
present in a urine sample will increase. The bacteria
are capable of metabolizing the urinary urea
to ammonia. The ammonia formed through this
process will cause an alkalinization of the urine
6. Which term is defined as a urine volume
in excess of 2000 mL excreted over a
24-hour period?
A. Anuria
B. Oliguria
C. Polyuria
D. Hypersthenuria
C. On the average, a normal adult excretes
1200-1500 mL of urine daily. "Polyuria" is a
term used to describe the excretion of a urine
volume in excess of 2000 mL/day
7. The reagent test strips used for the
detection of protein in urine are most
reactive to
A. Albumin
B. Hemoglobin
C. Alpha-globulins
D. Beta-globulins
A. In healthy individuals the amount of protein
excreted in the urine should not exceed 150
mg/24 hr. When
8. A urine specimen that exhibits yellow
foam on being shaken should be suspected
of having an increased concentration of
A. Protein
B. Hemoglobin
C. Bilirubin
D. Nitrite
C. Normal urine does not foam on being shaken.
However, urine containing bilirubin will exhibit
yellow foaming when the specimen is shaken
9. How should controls be run to ensure the
precision and accuracy of the reagent test
strips used for the chemical analysis of
urine?
A. Positive controls should be run on a
daily basis and negative controls when
opening a new bottle of test strips.
B. Positive and negative controls should
be run when the test strips' expiration
date is passed.
C. Positive and negative controls should
be run on a daily basis.
D. Positive controls should be run on a
daily basis and negative controls on a
weekly basis.
C. For quality control of reagent test strips, it is
recommended that both positive and negative
controls be used daily. It is necessary that any
deterioration of the strips
10. The colorimetric reagent strip test for
protein is able to detect as little as 5-20 nig
of protein per deciliter. What may cause a
false-positive urine protein reading?
A. Uric acid concentration is greater than
0.5 g/day.
B. Vitamin C concentration is greater
than 0.5 g/day.
C. Glucose concentration is greater than
130mg/day.
D. pH is greater than 8.0
D. The principle of the reagent strip method for
the detection of protein in urine is based on a
color change in an indicator system, such as
tetrabromophenol blue, that is buffered to pH 3.
11. "Isosthenuria" is a term applied to a series
of urine specimens from the same patient
that exhibit a
A. Specific gravity of exactly 1.000
B. Specific gravity less than 1.007
C. Specific gravity greater than 1.020
D. Fixed specific gravity of approximately
1.010
D. "Isosthenuria" is a term applied to a series of
urine specimens that exhibit a fixed specific gravity
of approximately 1.010
12. A urine specimen is tested by a reagent
strip test and the sulfosalicylic acid test to
determine whether protein is present. The
former yields a negative protein, whereas
the latter results in a reading of 2+
protein. Which of the following statements
best explains this difference?
A. The urine contained an excessive
amount of amorphous urates or
phosphates that caused the turbidity
seen with the sulfosalicylic acid test.
B. The urine pH was greater than 8,
exceeding the buffering capacity
of the reagent strip, thus causing
a false-negative reaction.
C. A protein other than albumin must be
present in the urine.
D. The reading time of the reagent strip
test was exceeded (the reading being
taken at 2 minutes), causing a falsenegative
reaction to be detected
C. When globulin, mucoprotein, or Bence Jones
protein is present in a urine specimen, the reagent
strip test may give a negative result because the
strip is more sensitive to the presence of albumin
than to the presence of other proteins in urine
13. Which of the following is the major
organic substance found in urine?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Glucose
D. Urea
D. Although sodium is the major inorganic molecule
found in urine, urea is the major organic
molecule excreted. Urea is a waste product of
protein/amino acid metabolism.
14. Each of the following is included in the
quality assurance program for a urinalysis
laboratory. Which one represents a
preanalytical component of testing?
A. Setting collection guidelines for
24-hour urines
B. Setting a maintenance schedule for
microscopes
C. Reporting units to be used for crystals
D. Requiring acceptable results for
control specimens before any patient
results are reported out
A. Preanalytical components of laboratory testing
include all variables that can affect the
integrity or acceptability of the patient specimen
prior to analysis, such as correct collection technique.
15. The presence of ketone bodies in urine
specimens may be detected by use of a
reagent strip impregnated with sodium
nitroprusside. This strip test is sensitive
to the presence of
A. Acetoacetic acid and betahydroxybutyric
acid
B. Acetoacetic acid and acetone
C. Diacetic acid and beta-hydroxybutyric
acid
D. Beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone
B. Under normal metabolic conditions, the
body metabolizes fat to carbon dioxide and
water. With
16. A routine urinalysis is performed on a
young child suffering from diarrhea. The
reagent test strip is negative for glucose
but positive for ketones. These results may
be explained by which of the following
statements?
A. The child has Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
B. The child is suffering from lactic
acidosis, and the lactic acid has falsely
reacted with the impregnated reagent
area for ketones.
C. The child is suffering from increased
catabolism of fat because of decreased
intestinal absorption.
D. The reagent area for ketones was read
after the maximum reading time
allowed.
C. Although a positive result on a urine test for
ketones is most commonly associated with
increased urinary glucose levels, as in diabetes
mellitus, other conditions may cause the urine
ketone test to show positive results
17. The principle of the colorimetric reagent
strip test for hemoglobin is based on the
peroxidase activity of hemoglobin in
catalyzing the oxidation of a dye with
peroxide to form a colored compound.
This method may yield false-positive
results for the presence of hemoglobin
when the urine specimen contains
A. Ascorbic acid
B. Tetracycline
C. Myoglobin
D. Nitrite
C. The colorimetric reagent strip test for the
detection of hemoglobin in urine utilizes a
buffered test zone impregnated with a dye and
organic peroxide.
18. A reagent test strip impregnated with
a diazonium salt such as diazotized
2,4-dichloroaniline may be used to
determine which analyte?
A. Glucose
B. Ketone
C. Hemoglobin
D. Bilirubin
D. Bilirubin is a compound that is formed as a
result of hemoglobin breakdown. The majority
of bilirubin in the blood is bound to albumin and
is known as unconjugated bilirubin
19. Which of the following will contribute to a
specimen's specific gravity if it is present
in a person's urine?
A. 50-100 RBC/hpf
B. 85 mg/dL glucose
C. 3+ amorphous phosphates
D. Moderate bacteria
B. Only dissolved solutes affect specific gravity
(e.g., glucose). Cells, mucus, crystals, or any
other formed elements will have no effect, regardless
of concentration.
20. With infections of the urinary system,
white blood cells are frequently seen in
the urine sediment. What type of white
blood cell is seen the most frequently in
urine sediment?
A. Eosinophil
B. Lymphocyte
C. Monocyte
D. Neutrophil
D. The majority of renal and urinary tract diseases
are characterized by an increased number
of neutrophilic leukocytes in the urine
21. A random urine is collected from a patient
and the results obtained are as follows:
urine albumin =16 mg/dL and urine
creatinine = 140 mg/dL. These findings
are consistent with
A. Microalbuminuria
B. Macroalbuminuria
C. Nephrotic syndrome
D. Obstructive jaundice
A. The ratio of urine albumin to creatinine in a
random specimen is commonly used to evaluate
microalbuminuria, especially in patients with diabetes
mellitus. This
22. To detect more easily the presence of casts
in urine sediments, which microscopic
method can be used?
A. Fluorescent microscopy
B. Phase-contrast microscopy
C. Polarized microscopy
D. Brightfield microscopy
B. To better diagnose renal and urinary tract
diseases, it is necessary to examine urinary sediment
carefully by the most appropriate microscopic
method available
23. Which substance found in urinary
sediment is more easily distinguished
by use of polarized microscopy?
A. Lipids
B. Casts
C. Red blood cells
D. Ketone bodies
A. Fatty materials in urinary sediment may be
identified by means of staining techniques using
Sudan III and oil red O or by means of polarized
microscopy. Polarized
24. "Glitter cell" is a term used to describe
a specific type of
A. Ketone body
B. Oval fat body
C. Fatty droplet
D. Neutrophil
D. When neutrophils are exposed to hypotonic
urine, their physical appearance becomes altered.
Under hypotonic conditions, the neutrophils
tend to swell and the cytoplasmic granules contained
within the cells exhibit Brownian movement.
25. The final phase of degeneration that
granular casts undergo is represented
by which of the following casts?
A. Fine
B. Coarse
C. Cellular
D. Waxy
D. Waxy casts represent the final phase of granular
cast degeneration. As the fine granules of
the granular casts lyse, highly refractive, smooth,
blunt-ended waxy casts are formed.
26. A 40-year-old female patient with a history
of kidney infection is seen by her physician
because she has felt lethargic for a few
weeks. She has decreased frequency of
urination and a bloated feeling. Physical
examination shows periorbital swelling
and general edema, including a swollen
abdomen. Significant urinalysis results
show the following: color = yellow;
appearance = cloudy/frothy; specific
gravity = 1.022;pH = 7.0; protein =
4+; 0-3 WBC/hpf; 0-1 RBC/hpf; 0-2
renal epithelial cells/hpf; 10-20 hyaline
casts/lpf; 0-1 granular casts/lpf; 0-1 fatty
casts/lpf; occasional oval fat bodies. Her
serum chemistries show significantly
decreased albumin, increased urea
nitrogen, and increased creatinine. These
findings suggest which condition?
A. Multiple myeloma
B. Glomerulonephritis
C. Nephrotic syndrome
D. Chronic renal failure
C. Nephrotic syndrome is suggested by the
increased urine protein (with serum albumin significantly
decreased), the hyaline and fatty casts,
and the presence of oval fat bodies
27. A 47-year-old female patient with
controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus
complains of urinary frequency and
burning. She provides a first-morning,
clean-catch specimen. Results show
color = yellow; appearance = cloudy;
pH = 6.5; a representative microscopic
high-power field is shown in Color
Plate 46B. Which of the following is true
for this patient?
A. The number of bacteria seen would
result in a positive nitrite.
B. The major formed elements are white
blood cells and yeast.
C. The type and number of epithelial
cells suggest incorrect sample
collection.
D. The red blood cells would be sufficient
to give a positive blood result on the
reagent strip.
B. There are minimal bacteria present in Color
Plate 46B. Both budding yeast and white blood
cells predominate this microscopic field

28. Alkaptonuria, a rare hereditary disease, is
characterized by the urinary excretion of
A. Alkaptone
B. Phenylalanine
C. 5-Hydroxyindole acetic acid
D. Homogentisic acid
D. Alkaptonuria is a rare hereditary disease that
is characterized by excessive urinary excretion
of homogentisic acid. T
29. A 22-year-old female clinical laboratory
student performs a urinalysis on her own
urine as part of a lab class. Significant
results include: color = yellow;
appearance = cloudy; pH = 7.5;
nitrite = positive; leukocyte
esterase - 2+; 25^0 WBC/hpf;
0-3 RBC/hpf; 2-5 squamous epithelial
cells/hpf; moderate bacteria. All other
chemistries and microscopic results
were normal. These findings suggest
A. Glomerulonephritis
B. Upper urinary tract infection
C. Lower urinary tract infection
D. Nephrolithiasis
C. This student has a lower urinary tract infection
(UTI), also known as cystitis.
30. Metastatic carcinoid tumors arising from
the enterochromaffin cells of the gastrointestinal
tract are characterized by
increased excretion of urinary
A. Serotonin
B. 5-Hydroxytryptophan
C. Homogentisic acid
D. 5-Hydroxyindole acetic acid
D. The intestinal enterochromaffin cells, sometimes
called the argentaffin cells, produce a substance
known as serotonin from the amino acid
tryptophan.
31. Some clinical conditions are characterized
by unique urinalysis result patterns.
Which of the following shows such a
relationship?
A. Nephrotic syndrome: positive protein
on reagent strip, negative protein with
sulfosalicylic acid
B. Intensive dieting: increased ketones,
negative glucose
C. Multiple myeloma: positive protein
by both reagent strip and sulfosalicylic
acid
D. Cystitis: positive nitrite and protein
B. Because of increased lipid metabolism in
long-term, intensive dieting, ketone body formation
will increase
32. Nitrite in a urine specimen suggests the
presence of
A. White blood cells
B. Red blood cells
C. Bacteria
D. Yeasts
C. Bacteria of the Enterobacter, Citrobacter,
Escherichia, Proteus, Klebsiella, and Pseudomonas
species produce enzymes that catalyze
the reduction of nitrate, a substance normally
found in urine, to nitrite.
33. If a fasting plasma glucose level of 100
mg/dL is obtained on an individual, what
is the expected fasting cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) glucose level in mg/dL?
A. 25
B. 50
C. 65
D. 100
C. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless
liquid that may be described as a modified
ultrafiltrate of blood. Both active transport and
passive diffusion are involved in the passage of
glucose from the blood into the CSF
34. A 35-year-old man has just experienced
severe crush injuries sustained in a car
accident. He has a broken pelvis and right
femur and has numerous abrasions and
contusions. A random urinalysis specimen
shows a brown color and clear appearance.
pH is 6.0, protein is 1 + , and blood is 3+.
There is, however, only 0-1 RBC/hpf,
along with 0-3 WBC/hpf. Casts found
include hyaline (0-2/lpf) and granular
(0-1/Ipf). Other urine results are normal.
Which of the following is true about this
patient?
A. The positive blood result is from a
hemolytic anemia.
B. The bilirubin result should have also
been positive for this patient.
C. Rhabdomyolysis may be a cause for
the discrepant chemical/microscopic
blood findings.
D. The bone crushing led to the increased
protein result.
C. In addition to hemoglobin, the muscle protein
myoglobin can cause a positive blood result
in chemical reagent strip testing
35. A 67-year-old male has routine testing
done and shows an estimated glomerular
filtration rate (eGFR) of 42 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Which of the following is true for this
patient?
A. This test requires a 24-hour urine
collection.
B. The patient does not have chronic
kidney damage, based on these results.
C. Similar results would be obtained
using the Cockgroft-Gault formula.
D. The patient is in Stage 3 chronic
kidney damage.
D. The eGFR calculation is based on the "modification
of diet and renal disease" formula recommended
by the American Kidney Foundation
36. Which is true about the formed element
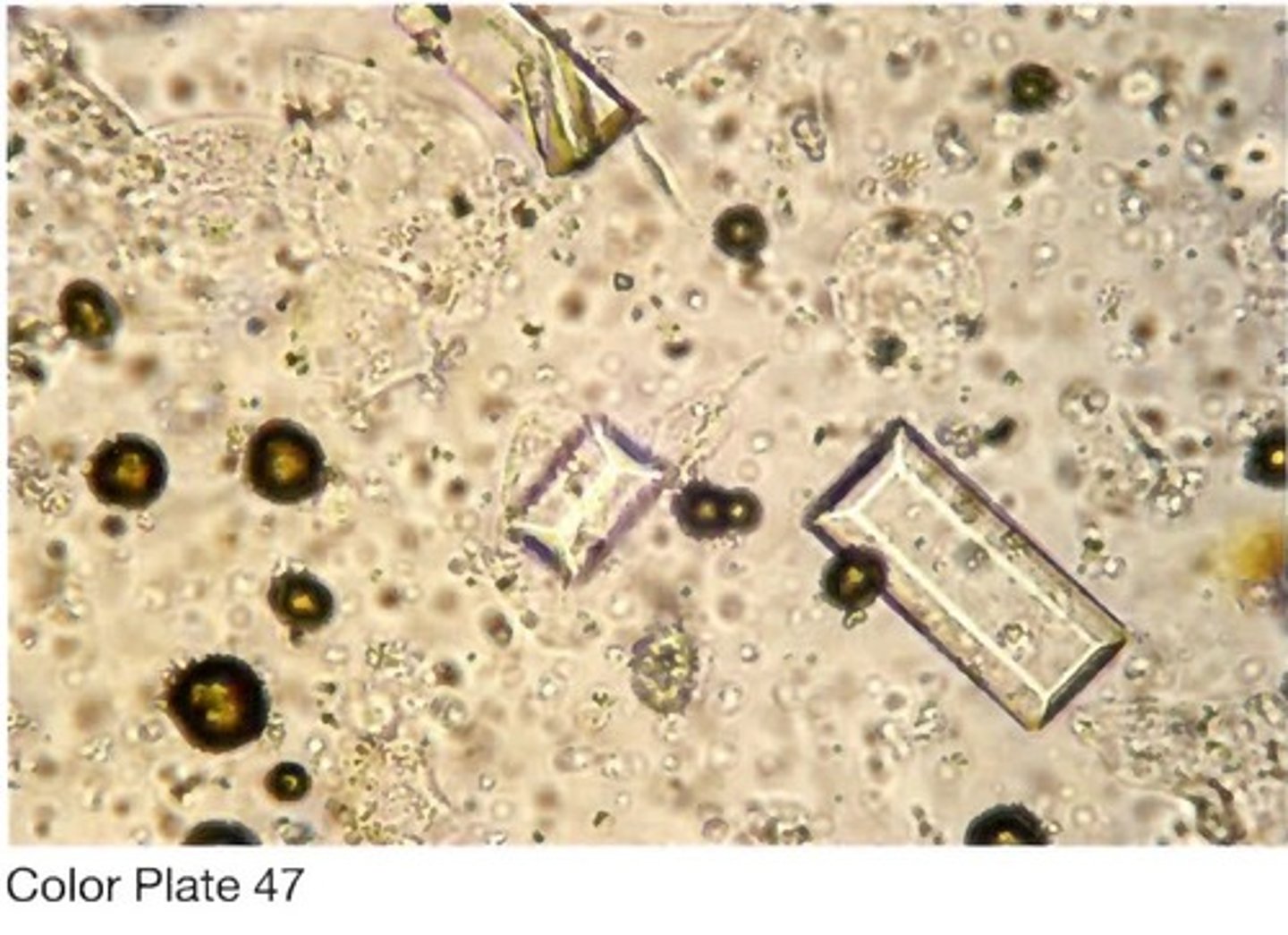
shown in Color Plate 47 •?
A. May be found in normal alkaline urine
B. Associated with renal pathology
C. Characteristic of glomerulonephritis
D. Associated with lung pathology
A. Normal alkaline (or neutral) urine may contain
triple phosphate crystals, as seen in Color
Plate 47 •. These crystals can be identified by the
characteristic "coffin lid" appearance

37. The major formed element in the highpower
field shown in Color Plate 48 •
is most likely a
A. Granular cast
B. Hyaline cast
C. Waxy cast
D. Fiber artifact
D. Refer to Color Plate 48 •. The fringed appearance
at the one end of the major formed element
strongly suggests that this is a fiber artifact, most
likely placed in the sample at the time of collection.

38. Which of the following is true about the
final concentrating of urine in the kidney?
A. The distal convoluted tubule, through
active transport, reabsorbs water.
B. Water is reabsorbed under the direct
influence of angiotensin II.
C. Vasopressin controls the collecting
duct reabsorption of water.
D. Water reabsorption is influenced by
urine filtrate levels of potassium
C. The distal convoluted tubule and collecting
duct provide water reabsorption through the
action of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin).
39. If a urine specimen is left standing at room
temperature for several hours, which of
the following changes may occur?
A. Multiplication of bacteria
B. An increase in the glucose concentration
C. Production of an acid urine
D. Deterioration of any albumin present
A. Only freshly voided urine specimens should
be used for urinalysis testing. If the specimen cannot
be examined within 1 hour after collection, it
should be refrigerated to help preserve the
integrity of the specimen
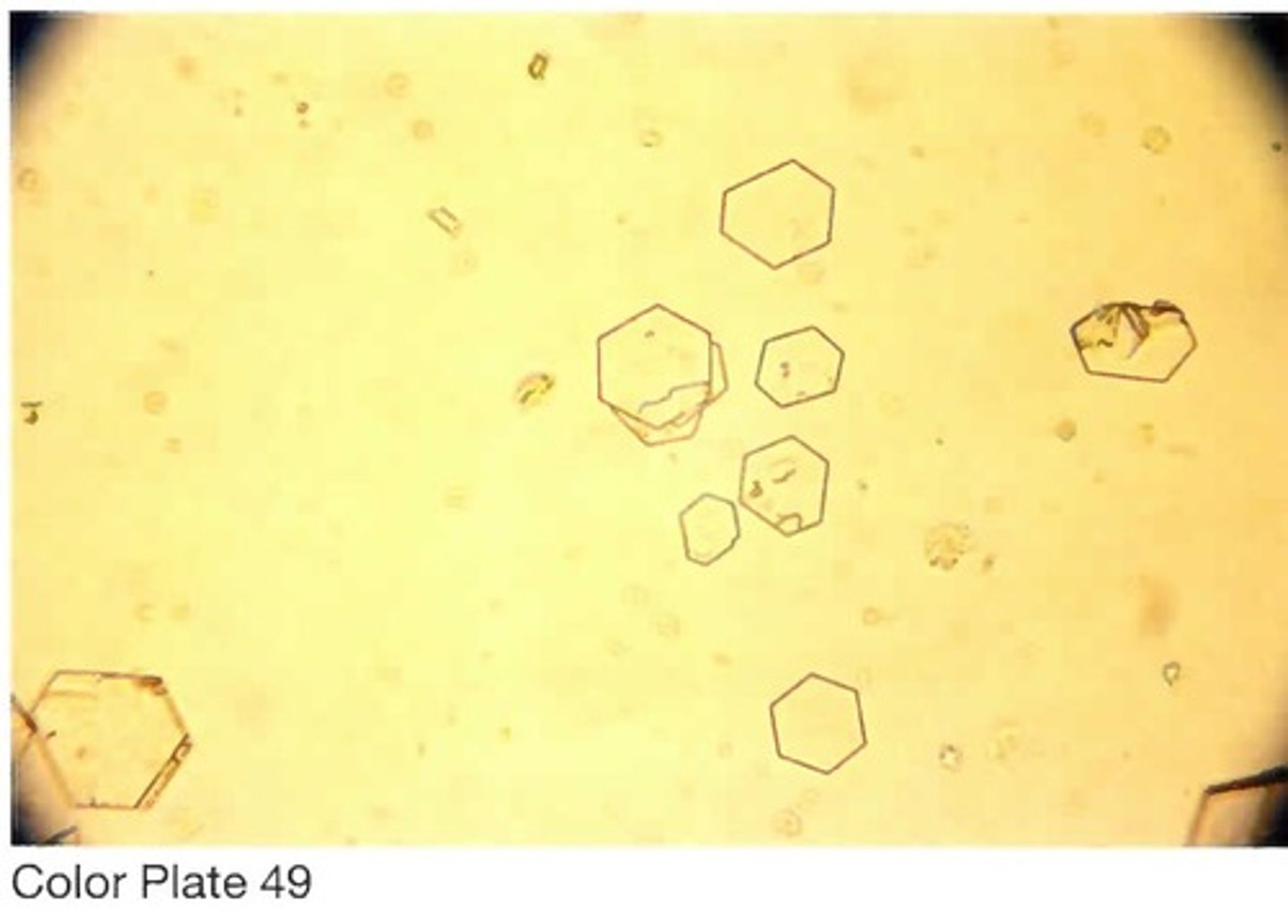
40. The formed element shown in Color
Plate 49B would usually be found in the
patient's urine along with which soluble
biochemicals?
A. Phenylalanine and tyrosine
B. Ornithine and arginine
C. Isoleucine and leucine
D. Acetoacetic acid and (3-hydroxybutyric
acid
B. The presence of cystine crystals in a patient
sample is always a cause for immediate notification
of the physician.

41. A 13-year-old ice skater is having her
routine physical before the school year.
Her first morning urinalysis results
include color = straw; appearance =
hazy; pH = 6.0; protein = trace; a
representative microscopic high-power
field is shown in Color Plate 50B. All
other chemical results were normal. The
major formed elements are and
suggest .
A. Hyaline casts and waxy casts;
nephrotic syndrome
B. Mucus and fibers; no pathology
C. Granular casts and red blood cells;
glomerulonephritis
D. Hyaline casts and mucus; normal
sediment
D. The major formed elements in Color Plate
50B are hyaline casts and mucus fibers, which
are normal in the numbers shown in this field
42. Phenylketonuria may be characterized
by which of the following statements?
A. It may cause brain damage if
untreated.
B. It is caused by the absence of the
enzyme, phenylalanine oxidase.
C. Phenylpyruvic acid excess appears
in the blood.
D. Excess tyrosine accumulates in the
blood.
A. Phenylketonuria is inherited as an autosomal
recessive trait that manifests itself in the homozygous
form.
43. What condition is suggested by the
number of the formed element that
predominates in the high-power field
of Color Plate 5 !•?
A. Glomerulonephritis
B. Improperly collected specimen
C. Pyelonephritis
D. Normal sample
D. Color Plate 51B demonstrates sperm and calcium
oxalate crystals. Both formed elements are
found in correctly collected normal urines from
either gender.

44. Xanthochromia of cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) samples may be due to increased
levels of which of the following?
A. Chloride
B. Protein
C. Glucose
D. Magnesium
B. A variety of substances in CSF specimens
have been associated with a xanthochromic
appearance. Among those substances are oxyhemoglobin,
carotenoids, bilirubin, and protein
45. Which of the following will be characterized
by an increased number of the urinary
component seen in Color Plate 52M?
A. Acute glomerulonephritis
B. Biliary tract obstruction
C. Contamination from vaginal discharge
D. Nephrotic syndrome
A. Refer to Color Plate 52B. Erythrocytes or
red blood cells (RBCs) occur in small numbers
(0-2/hpf) in a normal urine. Using brightfield
microscopy, unstained RBCs appear as colorless
discs with an average size of 7 jam in diameter

46. To determine amniotic fluid contamination
with maternal urine, which of the
following measurements could be used?
A. Creatinine concentration
B. Delta absorbance at 410 nm
C. Albumin/globulin ratio
D. Lactate dehydrogenase
A. Because there may be technical problems
associated with amniocentesis, contamination
with maternal urine should be considered in
evaluating specimens submitted for amniotic
fluid analysis.
47. With the development of fetal lung
maturity, which of the following phospholipid
concentrations in amniotic fluid
significantly and consistently increases?
A. Sphingomyelin
B. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
C. Phosphatidyl inositol
D. Phosphatidyl choline
D. The alveolar concentrations of the various
phospholipids (surfactants) change during fetal
lung development, and because these changes
are reflected directly in the amniotic fluid, a
number of investigations have shown that
analysis of the fluid can provide good predictive
information for the development of respiratory
distress syndrome in the newborn
48. A patient has been diagnosed with an
upper gastrointestinal bleed. Which of the
following would be characteristic for this
condition?
A. Brown stool with streaks of bright red
B. Stool with lack of brown color
("clay-colored")
C. Stool with a much darker brown/black
color
D. Yellow stool with increased mucus
C. The hemoglobin released from red blood
cells in an upper gastrointestinal bleed will have
time to become denatured and oxidized as it
travels the entire intestinal tract
49. A pleural effusion is found to have 3000
white blood cells per microliter and 5 g/dL
total protein. From this it can be determined
that the patient's effusion is
A. A transudate
B. An exudate
C. Noninflammatory
D. Hemorrhagic
B. Effusions can be transudates or exudates, and
the distinguishing characteristics are cell number
and total protein.
50. Patients with diabetes insipidus tend to
produce urine in volume with
specific gravity.
A. Increased; decreased
B. Increased; increased
C. Decreased; decreased
D. Decreased; increased
A. Diabetes insipidus is caused by a deficiency
in antidiuretic hormone. Such deficiencies will
result in the kidney's inability to reabsorb water
at the distal and collecting tubules. This affects
only water reabsorption and not the
51. The estimation of hyaluronic acid
concentration by measurement of
viscosity is useful in evaluating which
type of fluid?
A. Spinal
B. Peritoneal
C. Pleural
D. Synovial
D. Synovial fluid is a form of plasma ultrafiltrate
with added hyaluronic acid. Decreased viscosity
and poor mucin clot formation are indications of
the decreased hyaluronate concentration of synovial
fluid
52. Which of the following is characteristic of
an exudate effusion?
A. Leukocyte count >1000/uL
B. Clear appearance
C. Protein concentration <3.0 g/dL
D. Absence of fibrinogen
A. Effusions result from an imbalance of the
flow of body fluids. Effusions are classified as
exudates or transudates on the basis of certain
characteristics.
53. Which of the following systems utilizes
polyelectrolytes to determine the specific
gravity of urine?
A. Refractometer
B. Osmometer
C. TS meter
D. Reagent strip
D. A clinically useful test for assessing the concentrating
and diluting ability of the kidneys is
the determination of urine specific gravity. The
specific gravity is a measure of the proportion of
dissolved solids in a given volume of solvent
54. Which methods may be used to quantify
protein in both cerebrospinal fluid and
urine specimens?
A. Trichloroacetic acid and bromcresol
green
B. Ponceau S and Coomassie brilliant
blue
C. Bromcresol green and Coomassie
brilliant blue
D. Coomassie brilliant blue and
trichloroacetic acid
D. Trichloroacetic acid is a turbidimetric method
used to quantify small amounts of protein, less
than 100 mg/dL, in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and
urine specimens.
55. Which of the following characteristics is
true of the primary urinary components
shown in Color Plate 53B?
A. Consist of uromodulin protein
B. Presence always indicates a disease
process
C. Can be observed with polarized
microscopy
D. Appear yellowish in brightfield
microscopy
A. As seen in Color Plate 53B, hyaline casts are
the most commonly observed cast, and they consist
completely of uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall)
protein.
56. A characteristic of substances normally
found dissolved in the urine is that they
are all
A. Water soluble
B. Inorganic
C. Organic
D. Waste products
A. To be found in urine, a solute must be water
soluble. Solutes can be inorganic (e.g., sodium)
or organic (e.g., urea).
57. Which of the following statements applies
to the proper collection and handling of
CSF?
A. The second tube collected should be
used for chemistry analyses.
B. The third tube collected should be
used for bacteriologic studies.
C. CSF collected in the evening should
be refrigerated and assays performed
only by day-shift personnel.
D. With low-volume specimens, a culture
is performed first, before cell counts
are done.
D. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) must be collected
in sterile tubes. The first tube is generally used for
chemistry and serology studies, the second tube is
employed for bacteriologic examination, and the
third tube is used for cell counts. Tubes used for
chemistry and bacteriologic studies should be
centrifuged before use
58. Which of the following characteristics is
true for the urinary components shown in
Color Plate 54B?
A. Never should appear in a freshly
collected sample
B. Can also resemble cysteine crystals
C. Appear insoluble in alkaline urine
D. Presence indicates an inborn error of
metabolism
B. Uric acid crystals, as seen in Color Plate 54B,
are commonly encountered in normal acidic urine
but may be observed in neutral urine and rarely in
an alkaline urine, because uric acid is soluble at
alkaline pH.

59. A patient sends the following question to
an online consumer health Web site: "I am
a 22-year-old female who experienced
increasing headaches, thirst, and decreasing
energy. I was studying in the library
when I felt lightheaded and passed out.
I was taken to a hospital emergency
department and they told me that my
serum Acetest® was 40 mg/dL and urine
glucose was 500 mg/dL. What does this
mean?" How would you reply?
A. Your lab results pattern suggests
diabetes mellitus.
B. You probably have been crash dieting
recently.
C. The two results do not fit any disease
pattern.
D. The tests need to be repeated because
they could not possibly occur together
A. A positive urine glucose plus a positive
serum ketone strongly suggest uncontrolled diabetes
mellitus.
60. Which urinalysis reagent strip test will
never be reported out as "negative"?
A. Protein
B. Urobilinogen
C. Bilirubin
D. Nitrite
B. The sensitivity of a method is the lowest
concentration of the analyte that will result in a
detectable reaction signal.
61. The following urinalysis results were
obtained on a 40-year-old white male
whose skin appeared yellowish during the
clinical examination. Color and clarity—
dark brown, clear; protein—negative;
glucose—negative; blood—negative;
ketones—negative; bilirubin— moderate;
urobilinogen—0.2 mg/dL. These results
are clinically significant in which of the
following conditions?
A. Bile duct obstruction
B. Cirrhosis
C. Hepatitis
D. Hemolytic anemia
A. In the hepatic phase of bilirubin metabolism,
bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid to
form water-soluble conjugated bilirubin. The
conjugated bilirubin passes into the bile duct and
on to the intestinal tract.
62. Compared to the fecal occult blood test,
which of the following is a disadvantage
of performing a DNA-based test to detect
colon cancer?
A. The DNA test is more invasive.
B. The DNA test is less sensitive.
C. The DNA test is more expensive.
D. Additional diet restrictions are needed
for the DNA test
C. DNA-based tests for detecting mutations
within colon cells are generally more expensive
than the fecal occult blood (FOB) methods using
the pseudoperoxidase property of hemoglobin
63. Which of the following may be associated
with morphologic examination of
spermatozoa?
A. Evaluation should include assessment
of 1000 spermatozoa.
B. A small number of sperm should have
normal morphologic characteristics.
C. Papanicolaou stain may be used.
D. Presence of red or white cells and
epithelial cells need not be noted
C. The morphologic characteristics of spermatozoa
are best evaluated by means of smears
stained with Papanicolaou stain. Other stains
used include Kemechtrot, Giemsa, basic fuchsin,
crystal violet, and hematoxylin
64. Which condition is characterized by
increased levels of immunoglobulins in
the cerebrospinal fluid, originating from
within the central nervous system and not
from the general blood circulation?
A. Gout
B. Erythroblastosis fetalis
C. Multiple myeloma
D. Multiple sclerosis
D. Immunoglobulins (IgGs) are normally present
at less than 1 mg/dL in the CSF. Increased
CSF IgG can result from increased CSF production
(e.g., multiple sclerosis) or from increased
transport from the blood plasma (compromised
blood-brain barrier).
65. Which of the following statements
pertains to screening methods used to
determine pregnancy?
A. Immunoassays will use reagent
anti-hCG to react with patient hCG.
B. A random urine specimen is the
preferred specimen for pregnancy
screening tests.
C. Internal controls provided within the
kit will assess if the patient's specimen
was collected correctly.
D. External quality control is not needed
with these methods
A. Many simplified yet immunologically sophisticated
methods exist currently for determining
pregnancy. All are based on the reaction between
patient human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and
anti-hCG.
66. The following urinalysis biochemical
results were obtained from a 4-month-old
infant who experienced vomiting and
diarrhea after milk ingestion and failed to
gain weight: pH—6; protein—negative;
glucose—negative; ketone—negative;
bilirubin—negative; Clinitest®—2+.
These results are clinically significant in
which of the following disorders?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Ketosis
C. Starvation
D. Galactosemia
D. Galactosemia, an inborn error of metabolism,
is characterized by the inability to metabolize
galactose, a monosaccharide that is contained in
milk as a constituent of the disaccharide lactose
67. Which of the following is a true statement?
A. Renal tubular cells originate from the
renal pelvis.
B. Red blood cells in acid urine (pH 4.5)
will usually be crenated because of the
acidity.
C. Bacteria introduced into a urine
specimen at the time of the collection
will have no immediate effect on the
level of nitrite in the specimen.
D. Pilocarpine iontophoresis is the
method of choice for the collection of
pericardial fluid.
C. Renal tubular cells originate from the renal
medulla or cortex. Red blood cell crenation is a
phenomenon reflecting increased solute concentration
(hyperosmolality) and is not caused by
urine pH.
1. Which statement regarding renal function is true?
A. Glomeruli are far more permeable to H2O and
salt than other capillaries
B. The collecting tubule reabsorbs sodium and
secretes potassium in response to antidiuretic
hormone (ADH)
C. The collecting tubule is permeable to H2O only
in the presence of aldosterone
D. The thick ascending limb is highly permeable to
H2O and urea
A. Glomeruli are far more permeable to H2O and
salt than other capillaries
2. Which statement regarding normal salt and H2O
handling by the nephron is correct?
A. The ascending limb of the tubule is highly
permeable to salt but not H2O
B. The stimulus for ADH release is low arterial
pressure in the afferent arteriole
C. The descending limb of the tubule is impermeable
to urea but highly permeable to salt
D. Renin is released in response to high plasma
osmolality
A. The ascending limb of the tubule is highly
permeable to salt but not H2O
3. Which statement concerning renal tubular
function is true?
A. In salt deprivation, the kidneys will conserve
sodium at the expense of potassium
B. Potassium is not excreted when serum
concentration is below 3.5 mmol/L
C. No substance can be excreted into urine at a rate
that exceeds the glomerular filtration rate
D. When tubular function is lost, the specific
gravity of urine will be below 1.005
A. In salt deprivation, the kidneys will conserve
sodium at the expense of potassium
4. Which of the following is inappropriate when
collecting urine for routine bacteriologic culture?
A. The container must be sterile
B. The midstream void technique must be used
C. The collected sample must be plated within
2 hours unless refrigerated
D. The sample may be held at 2°C-8°C for up
to 48 hours prior to plating
D. The sample may be held at 2°C-8°C for up
to 48 hours prior to plating
5. Which statement about sample collection for
routine urinalysis is true?
A. Preservative tablets should be used for collecting
random urine specimens
B. Containers may be washed and reused if rinsed
in deionized H2O
C. Samples may be stored at room temperature for
up to 2 hours
D. First morning voided samples are not acceptable
when renal disease is suspected
C. Samples may be stored at room temperature for
up to 2 hours
6. Which urine color is correlated correctly with the
pigment-producing substance?
A. Smoky red urine with homogentisic acid
B. Dark amber urine with myoglobin
C. Deep yellow urine and yellow foam with
bilirubin
D. Red-brown urine with biliverdin
C. Deep yellow urine and yellow foam with
bilirubin
7. Which of the following substances will cause urine
to produce red fluorescence when examined with
an ultraviolet lamp (360 nm)?
A. Myoglobin
B. Porphobilinogen (PBG)
C. Urobilin
D. Coproporphyrin
D. Coproporphyrin
8. Which of the following conditions is associated
with normal urine color but produces red
fluorescence when urine is examined with an
ultraviolet (Wood's) lamp?
A. Acute intermittent porphyria
B. Lead poisoning
C. Erythropoietic porphyria
D. Porphyria cutanea tarda
B. Lead poisoning
9. Which statement regarding porphyria is accurate?
A. Porphyria is exclusively inherited
B. All types cause an increase in urinary porphyrins
C. All types are associated with anemia
D. Serum, urine, and fecal tests may be needed for
diagnosis
D. Serum, urine, and fecal tests may be needed for
diagnosis
10. Which is the most common form of porphyria?
A. Erythropoietic porphyria
B. Acute intermittent porphyria
C. Variegate porphyria
D. Porphyria cutanea tarda
Body fluids/Apply knowledge
D. Porphyria cutanea tarda
Body fluids/Apply knowledge
11. Which of the following methods is the least
sensitive and specific for measuring PBG in urine?
A. Watson-Schwartz test
B. LC-MS
C. Ion exchange chromatography-Ehrlich's reaction
D. Isotope dilution-MS
A. Watson-Schwartz test
12. A brown or black pigment in urine can be
caused by:
A. Gantrisin (Pyridium)
B. Phenolsulfonphthalein
C. Rifampin
D. Melanin
D. Melanin
13. Urine that is dark red or port wine in color may be
caused by:
A. Lead poisoning
B. Porphyria cutanea tarda
C. Alkaptonuria
D. Hemolytic anemia
B. Porphyria cutanea tarda
14. Which of the following tests is affected least by
standing or improperly stored urine?
A. Glucose
B. Protein
C. pH
D. Bilirubin
Body fluids/Apply
B. Protein
15. Which type of urine sample is needed for a
D-xylose absorption test on an adult patient?
A. 24-hour urine sample collected with 20 mL
of 6 N HCl
B. 2-hour timed postprandial urine preserved with
boric acid
C. 5-hour timed urine kept under refrigeration
D. Random urine preserved with formalin
C. 5-hour timed urine kept under refrigeration
16. Which of the following is inappropriate
when collecting a 24-hour urine sample for
catecholamines?
A. Urine in the bladder is voided and discarded at
the start of the test
B. At 24 hours, any urine in the bladder is voided
and added to the collection
C. All urine should be collected in a single container
that is kept refrigerated
D. Ten mL of 1N sodium hydroxide should be
added to the container before collection
D. Ten mL of 1N sodium hydroxide should be
added to the container before collection
17. Urine production of less than 400 mL/day is:
A. Consistent with normal renal function and
H2O balance
B. Termed isosthenuria
C. Defined as oliguria
D. Associated with diabetes mellitus
Body fluids/Correlate clinical and laboratory
C. Defined as oliguria
18. Which of the following contributes to SG, but
not to osmolality?
A. Protein
B. Salt
C. Urea
D. Glucose
A. Protein
19. Urine with an SG consistently between 1.002
and 1.003 indicates:
A. Acute glomerulonephritis
B. Renal tubular failure
C. Diabetes insipidus
D. Addison's disease
C. Diabetes insipidus
20. In which of the following conditions is the urine
SG likely to be below 1.025?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Drug overdose
C. Chronic renal failure
D. Prerenal failure
C. Chronic renal failure
21. Which statement regarding methods for
measuring SG is true?
A. To correct a urinometer, subtract 0.001 per each
3°C below 15.5°C
B. Colorimetric SG tests are falsely elevated when a
large quantity of glucose is present
C. Colorimetric SG readings are falsely elevated
when pH is alkaline
D. Refractometry should be performed before the
urine is centrifuged
A. To correct a urinometer, subtract 0.001 per each
3°C below 15.5°C
22. What is the principle of the colorimetric reagent
strip determination of SG in urine?
A. Ionic strength alters the pKa of a polyelectrolyte
B. Sodium and other cations are chelated by a
ligand that changes color
C. Anions displace a pH indicator from a mordant,
making it water soluble
D. Ionized solutes catalyze oxidation of an azo dye
A. Ionic strength alters the pKa of a polyelectrolyte
23. Which statement regarding urine pH is true?
A. High-protein diets promote an alkaline urine pH
B. pH tends to decrease as urine is stored
C. Contamination should be suspected if urine pH
is less than 4.5
D. Bacteriuria is most often associated with a low
urine pH
C. Contamination should be suspected if urine pH
is less than 4.5
24. In renal tubular acidosis, the pH of urine is:
A. Consistently acid
B. Consistently alkaline
C. Neutral
D. Variable, depending upon diet
B. Consistently alkaline
25. The normal daily urine output for an adult is
approximately:
A. 0.2-0.5 L
B. 0.6-1.6 L
C. 2.7-3.0 L
D. 3.2-3.5 L
Body fluids/Apply
B. 0.6-1.6 L
26. The SG of the filtrate in Bowman's space is
approximately:
A. 1.000-1.002
B. 1.004-1.006
C. 1.008-1.010
D. 1.012-1.014
Body fluids/Apply knowledge
C. 1.008-1.010
27. A patient with partially compensated respiratory
alkalosis would have a urine pH of:
A. 4.5-5.5
B. 5.5-6.5
C. 6.5-7.5
D. 7.5-8.5
D. 7.5-8.5
28. Which of the following is most likely to cause a
false-positive dry reagent strip test for urinary
protein?
A. Urine of high SG
B. Highly buffered alkaline urine
C. Bence-Jones protein
D. Salicylates
B. Highly buffered alkaline urine
29. When testing for urinary protein with
sulfosalicylic acid (SSA), which condition
may produce a false-positive result?
A. Highly buffered alkaline urine
B. The presence of x-ray contrast media
C. Increased urinary SG
D. The presence of red blood cells (RBCs)
Body fluids/Apply knowledge to identify sources
B. The presence of x-ray contrast media
30. A discrepancy between the urine SG determined
by measuring refractive index and urine osmolality
would be most likely to occur:
A. After catheterization of the urinary tract
B. In diabetes mellitus
C. After an intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
D. In uremia
C. After an intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
31. Which of the following is likely to result in a
false-negative dry reagent strip test for
proteinuria?
A. Penicillin
B. Aspirin
C. Amorphous phosphates
D. Bence-Jones protein
D. Bence-Jones protein
32. Daily loss of protein in urine normally does not
exceed:
A. 30 mg
B. 50 mg
C. 100 mg
D. 150 mg
D. 150 mg
33. Which of the following is least likely to cause a
false-positive result with turbidimetric protein
tests?
A. Tolbutamide
B. X-ray contrast media
C. Penicillin or sulfa antibiotics
D. Ascorbic acid
Body fluids/Apply knowledge
D. Ascorbic acid