Chapter 6 - Selecting Employees Who Fit
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Personnel Selection
This process through which organizations make decisions about who will or will not be allowed to join the organization
Selection begins with the candidates identified through recruitment.
It attempts to reduce their number to the individuals best qualified to perform available jobsIt ends with the selected individuals placed in jobs with the organization
Steps in the Selection Process
Screening Applications and Resumes
Testing and Reviewing Work Samples
Interviewing candidates
Checking References and Background
Making a Selection
Aligning Talent and HR Strategy
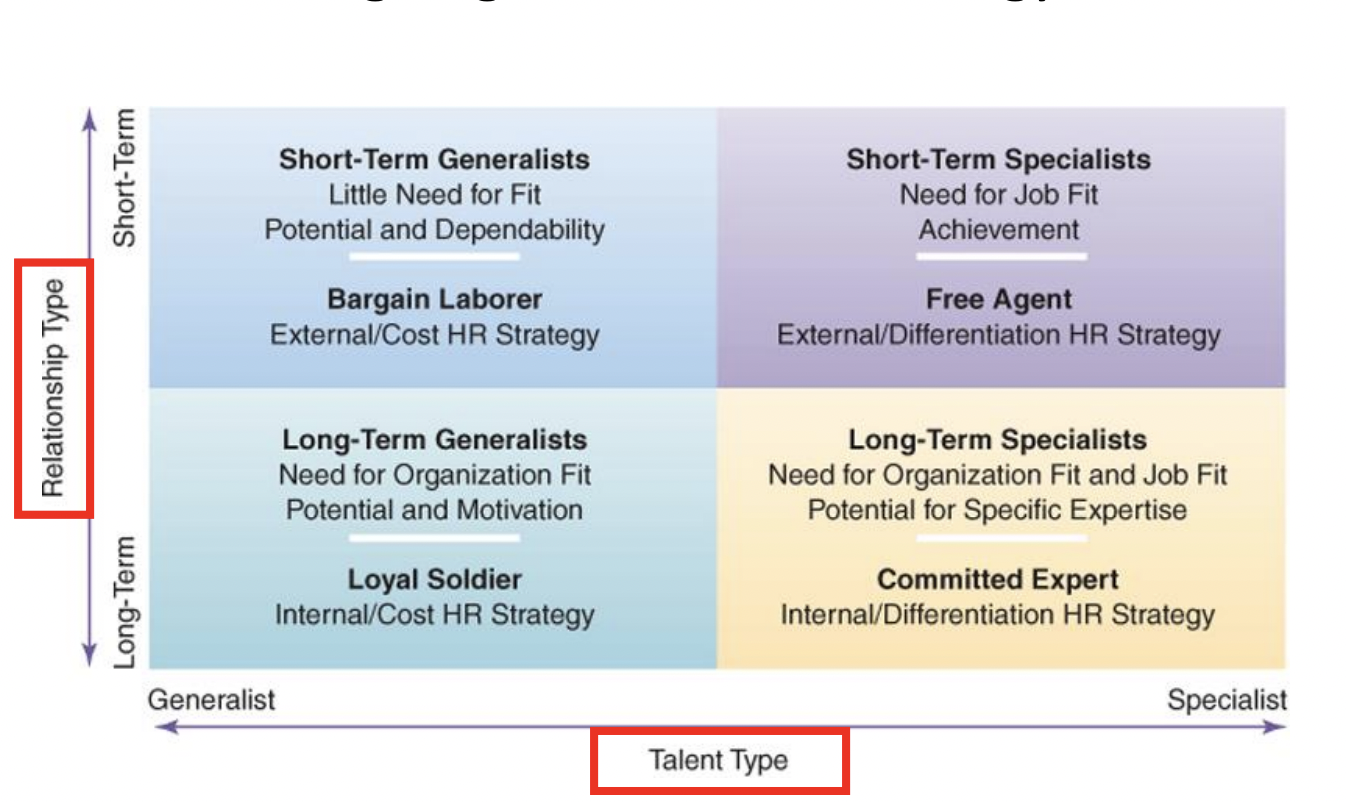
Short-Term Generalists
Provide a variety of different inputs but do not have areas of special skill or ability
This is most often associated with the Bargain Laborer HR Strategy
Most positions are filled by hiring people away from other organizations
The objective is to identify and hire employees to produce low-cost goods and services
To selection people who can perform simple tasks that require little specialized skill
Benefits of Short-term Generalist Strategy
People without specialized skills do not generally demand high compensation, which keeps payroll costs as low as possible
Because Short Term Generalist lack Specific expertise, they are also usually more willing to work in routine jobs and do whatever they are asked
The number of fixed employees working for the organization can be flexed up or down as demand for goods and services increases or decreases.
Work Procedures are simple, and employees who demand higher wages are simply replaced by new workers
Long-Term Generalists
Individuals who have developed skills and knowledge concerning how things are done in a specific organization
Long-term generalists are beneficial for organizations using the Loyal Soldier HR strategy
HR strategy is focused on keeping employees once they are hired
Benefits of Long-Term Generalist Strategy
Lack of specific expertise allows firms to reduce payroll costs
Employees have developed skills and abilities that are only valuable to the specific organizations, which reduces the likelihood that they will move to another employer
Reduction in the recruitment, selection, and training expenses
Because they stay long, they tend to develop relationships and form a strong sense of commitment to the organization
Long-Term Specialist
These are people who have an expertise in a particular area, such as pharmaceutical sales representative and research scientists
The use of long-term specialists fits the committed Expert Hr strategy
Selection is to identify people who can assist the company in innovating and produce superior goods and services over time
People are hired who can develop specialized skills over time and create a resource of talent
Benefits of long-term specialists
it enables organizations to create and keep a unique resource of talent that other organizations do not have
Employees are given the time and assets to develop the skills they need to be the best at what they do and add value back to the organization
Short-term Specialists
Are employees who provide specific inputs for relatively short-periods of time
Associated with the Free Agent HR strategy
Staffing is aimed at hiring people who have already developed skills that they can bring to the organization to produce innovative goods and top-quality service
Benefits of Short-term specialists
Employees provide services for relatively short periods
Allows the organization to quickly acquire needed expertise, without waiting for hire to acquire the skills
The organization pays premium dollars for this knowledge and skills but makes no long-term commitments and both parties can end the employment relationship at any time
Making Strategic Selection Decision
Focus is on two factors
Job-Based Fit
Seeks to match an individual’s abilities and interests with the demands of.a specific jobs
Organization-based fit
Is concerned with how well the individual’s characteristics match the broader culture, values, and norms of the firm.
Criteria for Measuring the Effectiveness of Selection Tools and Methods
Reliability
Validity
Utility
Legality/Fairness
Acceptability
Reliability
The extent to which a measurement is free from random error
a reliable measurement generates consistent results
Organizations use statistical tests to compare results over time
correlation coefficients
A higher correlation coefficient signifies a greater degree of reliability
Validity
The extent to which the performance on a measure (such as a test score) is related to what the measure is designed to assess (such as job performance)
Three ways of measuring validity
Criterion-related
Content
Construct
Consistency between a high score on a test and a high level of a construct as well as between mastery of this construct and successful performance of the job
Criterion - Related
A measure of validity based on showing a substantial correlation between test scores and job performance scores
Two kinds of research are possible for arriving at criterion-related validity
Predictive Validation
Concurrent Validation
Predictive Validation
Research that uses the test scores of all applicants and looks for a relationship between the scores and future performance of the applicants who were hired
Concurrent Validation
Research that consist of administering a test to people who currently hold a job, and then comparing their scores to existing measures of job performance
Content Validity
Consistency between the test items or problems and the kinds of situations or problems that occur on the job
Utility
Selection methods should cost significantly less than the benefits of hiring new employees
Legality
All selection methods must conform to existing laws and legal precedents
Acceptability
How does the applicant view the selection process and consequently the organization
Three most common Selection methods
Gathering
Application forms and resumes, biographical data, and reference checking
Testing
Interviewing
Application Forms
Used to make initial cuts among applicants
Applications are often used to verify resumes and set specific on employment history
Approx. 1/3 of applications have some form of misrepresentation
A low cost way to gather basic data from many applicants
Resume
Most valid when the content of the resume is evaluated in terms of the elements of a job description
Technology helps manage resumes
Letters of Reference
Issues?
Applicant selects referents → positive bias?
Too Vague?
“List strengths and Weaknesses”
Fear of Lawsuit?
Giving References on Former Employees
Risk: May be held liable for defamation, invasion of privacy, or retaliation for statements made about former employees.
Risk of Negligent Hiring
It occurs when an organization hires someone who harms another person and the organization could reasonably have determined that the employee was unfit
Four testing (Aptitude vs Achievement)
Cognitive ability
Physical Ability
Performance tests and work samples
Personality and Integrity
Aptitude test
Asses how well a person can learn or acquire skills and abilities
Achievement tests
Measures a person’s existing knowledge and skills
Cognitive Ability Testing
Ability to Learn, Problem-solving, Language Skills, Math skills, General Knowledge
Personality Testing
Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism
Situational Judgment Test
Ask the job applicant what they would do or should do in a hypothetical situation
Physical Ability Testing
Asses muscular strength, cardiovascular endurance, and coordination
Integrity Testing
Asses the likelihood that applicants will be dishonest or engage in illegal activity
Work sample Testing
Measures of actual or simulated on-the-job performance
What can it measure?
Most job-related KSAOs
Assessment Center
High validity - expensive to develop
Low EEO problems
Guidelines for use
Assess cost-to-benefit value of test
Often use after less expensive screening
Not useful if Provide lots of training in job
Interview
Most Commonly used selection tool, but can have low reliability and validity
Structure vs unstructured
Behavioral or situational
Panel or series
Advantages and Disadvantages of Interviewing
Advantages
Can provide evidence of communication and interpersonal skills
Most valid when they focus on job knowledge and skills
Disadvantages
Can be unreliable
Low of validity
Costly
Subjective / Biased
Types of Interviews
Structured Interviews
Unstructured Interviews
Structured Interviews
Uses a list of predetermined questions
all applicants are asked the same set of questions
Situational Interview
The interviewer asks questions about what the applicant would do in a hypothetical situation
Behavioral (Description) Interview
The Interviewer asks the candidate to describe how he or she handled a type of situation in the past
Unstructured Interviews
Open-ended questions are used such as “Tell me about yourself”
this allows the interviewer to probe and pose different sets of questions to different applicants
How to interview Effectively
Be prepared
Assign responsibilities
Put the applicant at ease
Ask about past behaviors
Figure out what your employees do, and ask questions that look for similar behaviors
At the end of the interview, make sure the candidate knows what to expect next
Background Checks
Prospective employers want them, but former employers are hesitant to give
Defamation suits are filed when poor references aren’t based on documented evidence
Predictor Weighting
Combines. a set of selection scores into an overall score in which some measures count more than others
Minimum Cutoff Approach
The applicant’s strength in one area to compensate for weakness in another area
Multiple-Hurdle Model
Applicants must meet the minimum requirements of one selection metho before they can proceed to the next
Banding Approach
Uses Statistical analysis to identify scores that may not be meaningfully different
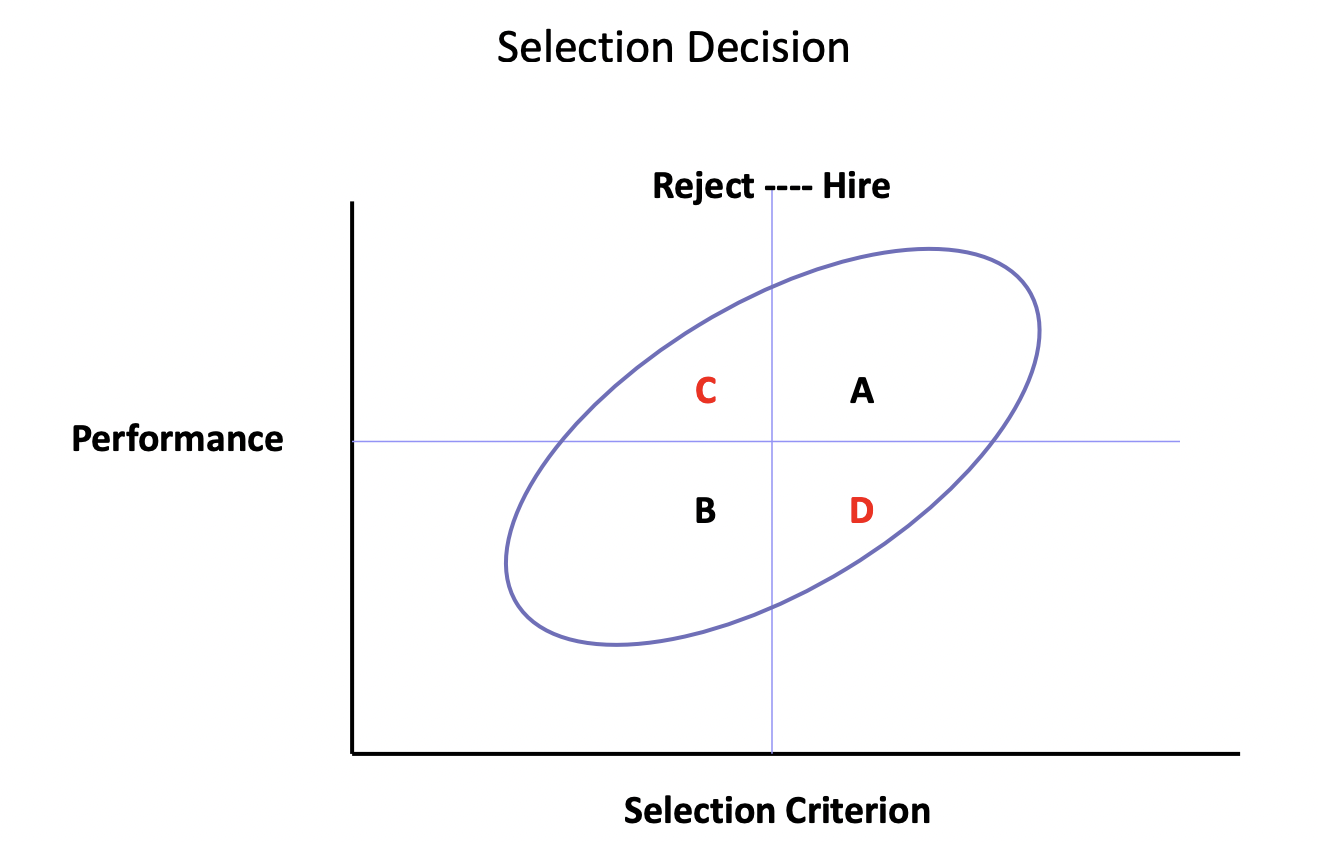
Selection Decision Model
Communicating the Decision
When a candidate has been selected, the organization should communicate the offer to the candidate
Job responsibilities
Work Schedule
Rate of Pay
Starting Date
Other relevant details