MAB 3.1 Unit 3 Genetic Engineering Test 2023
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Gene Cloning
Creating a copy of an organism or molecule from another entity
Restriction Enzymes
DNA-cutting enzymes that cleave phosphodiester bonds in DNA strands
Plasmid DNA
Circular, self-replicating DNA found in bacteria, used to carry and clone other DNA fragments
Recombinant DNA Technology
Technology that allows for the cutting and joining of DNA fragments, and insertion into a plasmid
Bacteriophage vectors
clone DNA fragments up to 15 kb; infect the bacterial species
Restriction Site
Specific sequence of bases in DNA recognized and cut by restriction enzymes
Palindrome
Sequence that reads the same forward and backward on opposite strands of DNA
Sticky Ends
Overhanging single-stranded ends of DNA fragments created by certain restriction enzymes
Blunt Ends
Double-stranded ends of DNA fragments created by certain restriction enzymes
Recombinant DNA
DNA formed by joining together DNA fragments from different sources
Transformation
Process of inserting foreign DNA into bacterial cells
Antibiotic Selection
Process of selecting transformed bacteria by growing them on plates with different antibiotics
Blue-White Selection
used to distinguish cells containing recombinant vs non-recombinant plasmids, utilizes lacz gene, and XGAL in agar
Dna Libraries
Collections of cloned DNA fragments from a particular organism stored i
Genomic DNA Libraries
Libraries containing fragments of an organism's entire genome
cDNA Libraries
Libraries containing complementary DNA synthesized from mRNA
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences in a short period of time
Taq DNA Polymerase
DNA polymerase isolated from Thermus aquaticus, used in PCR due to its heat stability
Cloning PCR Products
Rapid and effective method of cloning DNA fragments amplified by PCR
PCR primers
Primers are created to match the beginning and end sequence of certain sections
These are short DNA sections that set the boundaries for what will be copied
DNA probes are
short, single-stranded segments of DNA used in DNA hybridization experiments.- complementary to sequence of interest
multiple cloning site (MCS)
site that can be recognized by multiple restriction enzymes
cloning vector
DNA molecules that can carry foreign DNA into a host cell and replicate there.
gel electrophoresis process
enzymes are used to chop DNA from sample into fragments, fragments are then placed into wells; electrical current is run through the gel and fragments are attracted depending on charge; smallest/lightest/most charged move far, thus creating banding pattern used to identify and compare
DNA ligase
enzyme that chemically links DNA fragments together
bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)
A large plasmid that acts as a bacterial chromosome and can carry inserts of 100,000 to 300,000 base pairs., cannot properly fold eukaryotic proteins
reverse transcriptase
An enzyme encoded by certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis.. Used for cDNA libraries,
insulin
first protein made through recombinant DNA technology
Hybridization
binding of complementary DNA strands through hydrogen bonding. Used in library screening, DNA probes, Southern blotting, PCR
Linker sequences
synthetic DNA element in a cloning vector with unique restriction sites used for insertion of foreign DNA
Luciferase
Enzyme used in bioluminescence
Chemiluminescence
the emission of light from a chemical reaction
ethinium bromide
dye that binds to DNA in agarose gel, and fluoresces under UV light
CRISPR/Cas9
a unique technology that researchers to edit parts of the genome by removing, adding or altering sections of the DNA sequence, naturally occurring in bacteria
Southern Blot
A DNA sample is electrophoresed on a gel and then transferred to a filter. The filter is then exposed to a labeled DNA probe that recognizes and anneals to its complementary strand. The resulting ds labeled piece of DNA is visualized when the filter is exposed to film.
Northern Blot
Similar technique [to Southern], except that Northern blotting involves radioactive DNA probe binding to sample RNA .
Western blot
Similar technique (to Southern ) except it involves antibodies binding to proteins
prodigiosin
The red pigment produced by S. marcescens.
dideoxynucleotide
type of nucleotide used during DNA sequencing to terminate synthesis
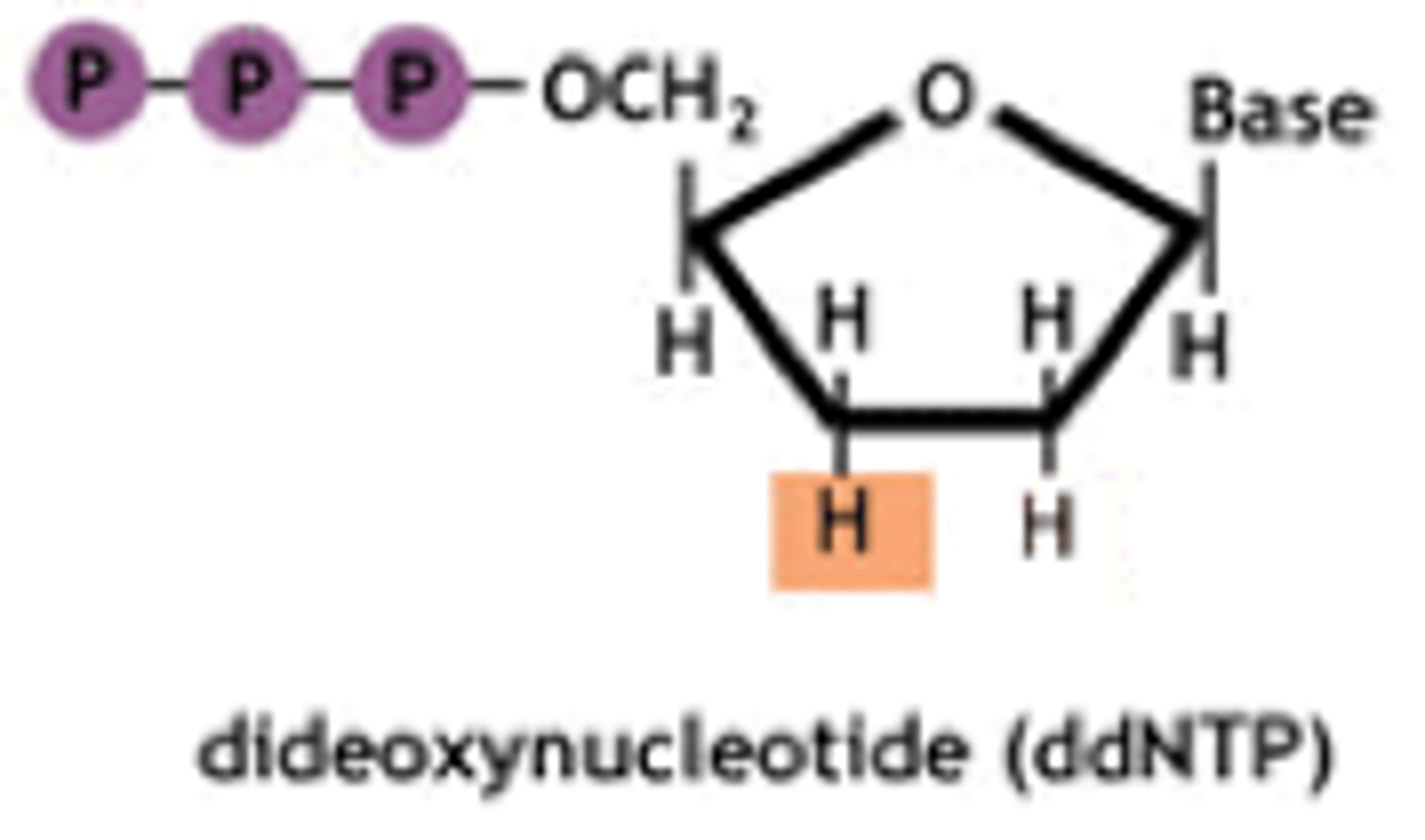
Sanger sequencing method
There are 4 test tubes each one containing ddNTP (only one), dNTP (all 4), DNA Polymerase, Primer, ssDNA template, . Synthesis occurs until a ddNTP is incorporated. You use gel electrophoresis to see the fragements. Read the gel bottom to top for the sequence.. Also known as chain termination sequencing, used in Human Genome project
FISH
Technique used to identify the location of a gene directly in a chromosome
RNAi (RNA interference)
inhibition of gene expression by RNA molecules, naturally occurring in bacteria
RT-PCR
A technique in which RNA is first converted to cDNA by the use of the enzyme reverse transcriptase, then the cDNA is amplified by the polymerase chain reaction.
DNA microarray
A microarray of immobilized single-stranded DNA fragments of known nucleotide sequence that is used especially in the identification and sequencing of DNA samples and in the analysis of gene expression (as in a cell or tissue).
SOLiD Sequencing (NextGen)
sequencing technique uses short fragments of DNA (oligonucleotides) attached to beads
3rd generation sequencing
uses nanotechnology to cleave and sequence single nucleotides at a time
tryp operon
repressible operon; activated when tryptophan is absent, inactivated when tryptophan is present.