Unit 6 - Cities and Urban Land-Use Patterns and Processes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Site factors
Include climate, availability of water, soil quality.
Situation factors
The connections between one site and another.
Urban sprawl
Unrestricted growth in urban area of housing, commercial development, and roads over large areas of land.
Suburbanization
Movement of upper & middle class people from urban areas to surrounding city outskirts.
Boomburbs
Rapidly growing suburban cities that represent a new metropolitan form.
Exurbs
Prosperous residential districts beyond the suburbs.
Edge cities
Economic center on the fringe of a city with an extensive amount of office and retail space.
World City (Global city)
A city with influence within its region as well as all around the world.
Primate city
Lead city in a country in terms of size and influence, where all resources are centered in one place.
Rank size rule
Statistical relationship between largest city and next largest city based on population.
Gravity model
Predicts the degree of interaction (ESPn) and probability of mobility between two places.
Christaller's central place theory
Explains the distribution of goods and services across a region.
Threshold
Size of population necessary for services to exist and be profitable.
Range
Distance people will travel for services or goods.
Megacities
Cities with 10+ million residents.
Sprawling urban areas
Urban areas with 20+ million residents.
Locational advantages
Important factors for the earliest cities included productive agricultural land and defensible sites.
Economic development
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Government policies
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Population growth
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Migration
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Communication
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Transportation
One of the factors that can drive urbanization and suburbanization.
Interactions between edge cities and cities
Reflect in the availability of goods and services, and whether they are high/low range & threshold.
Closer to CBD
means higher land cost
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
looks at relationship between socio-economic status of household and distance from CBD
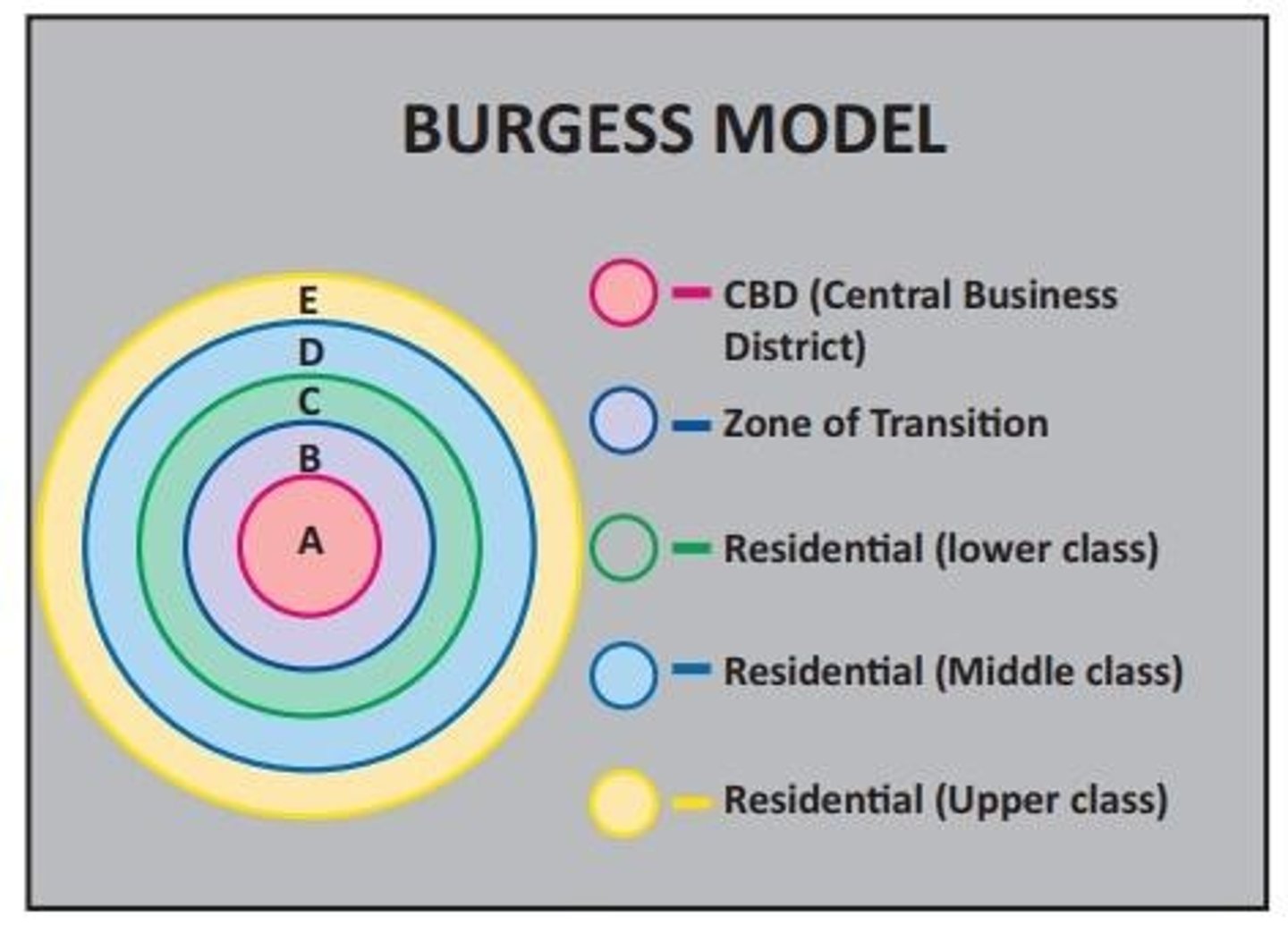
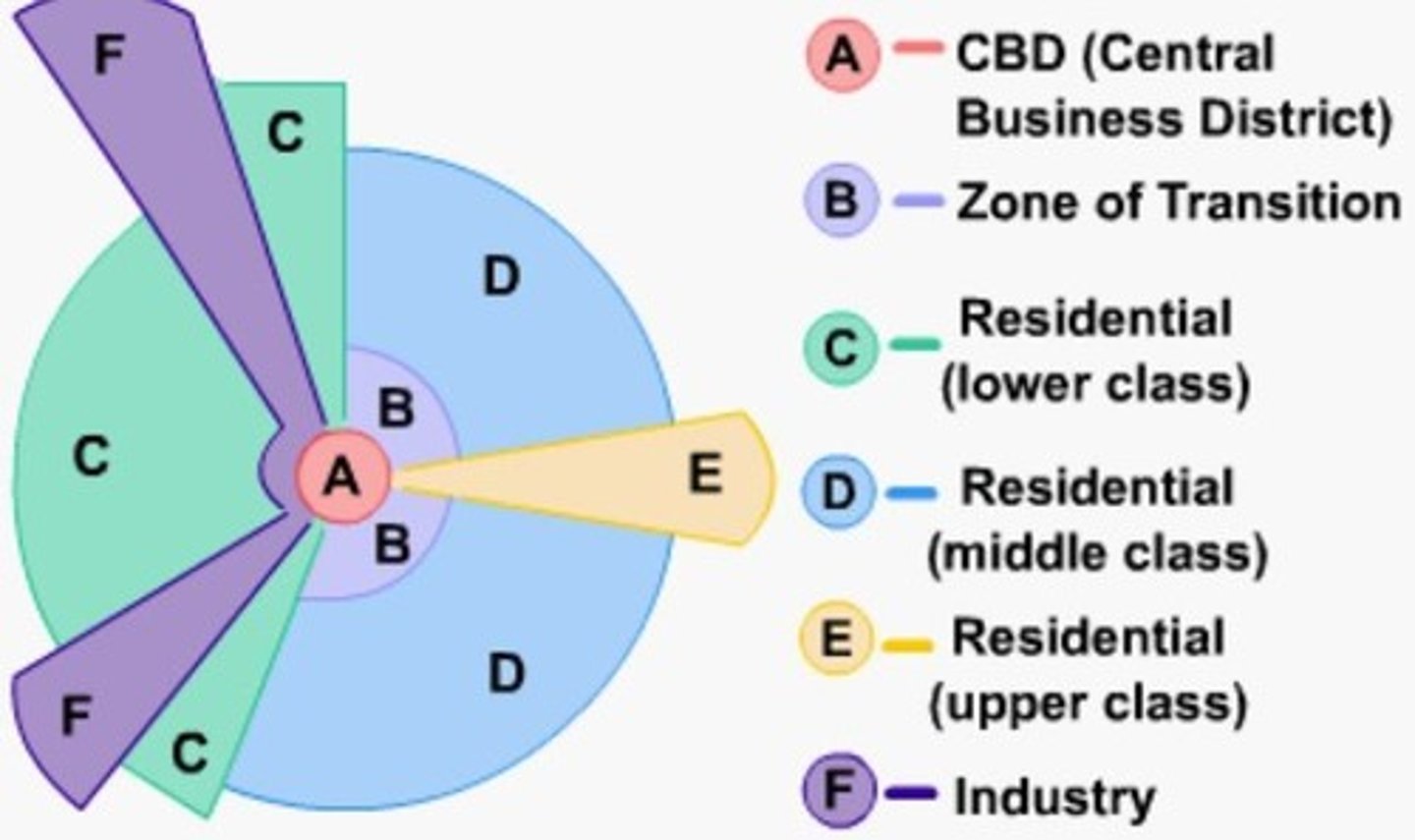
Hoyt sector model
claims cities develop in wedge sectors instead of rings
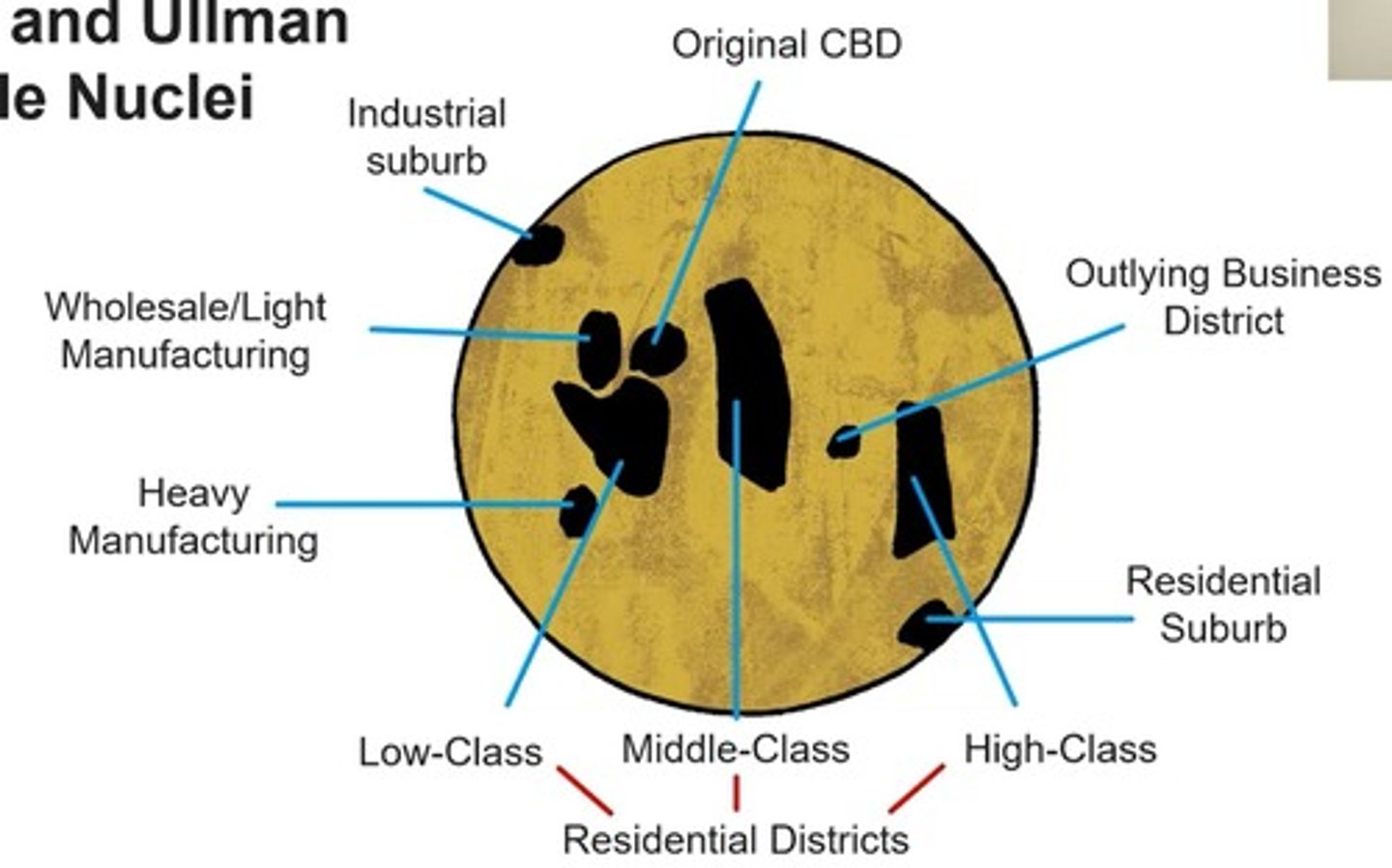
Harris and Ullman multiple nuclei model
there are multiple CBDs in a city
Galactic city model (aka Peripheral model)
shows services along intersections of main transportation routes coming from CBD
Multiple nuclei model applicability
tends to be most applicable to newer faster growing cities
Density and Land Use
Look for patterns regarding high, medium, and low density of cities as you get closer and farther from CBD
Infrastructure
the basic structures and facilities needed for the operation of a society
Examples of infrastructure
Roads, Public transportation, Educational systems, Electric grids, Hospital, Sewage systems
Urban Sustainability Solutions
Greenbelt, Smart growth policies, New urbanism
Pros of urban design initiatives
Ease of accessibility to services and jobs, Increase sense in community, Less travel time, Decrease energy use, Increase real estate value, Preserving conservation of parks, Curbing urban sprawl
Cons of urban design initiatives
High housing costs, Decreased diversity, Strain on infrastructure, Placelessness
Quantitative data
data that can be counted, measured and expressed with numbers
Examples of quantitative data
survey data, census
Qualitative data
data that is descriptive and conceptual
Census tract
the area unit that best approximates a city neighborhood in size in the U.S. and Canada
Blockbusting
one ethnic group is convinced to sell their houses at a low price once they hear another ethnic group is moving into the neighborhood
Redlining
banks refusing loans to certain groups to purchase homes in certain areas
White flight
movement of white residents out of city in response to black residents moving in
Gentrification
the rebuilding of lower income neighborhoods into middle & upper middle class neighborhoods
Pros of gentrification
Property value increase, Investment opportunities, Architectural enhancement
Cons of gentrification
Tenants cannot afford new higher rents, Displacement of groups of people
Squatter settlements
a residential area that has developed without legal claims to the land
Causes of squatter settlements
rapid urbanization, demand for affordable housing, failure to enforce land use policies
Locations of squatter settlements
Edges of cities, Vacant and undesirable land
Negative effects of squatter settlements
Increased crime rates, Pollution, Soil erosion from homemade houses
Challenges to urban sustainability
Suburban sprawl, Traffic, Sanitation, Climate change, Pollution, ecological footprint, Energy use
Responses to urban sustainability challenges
Regional planning efforts, Farmland protection policies, Urban growth boundaries
Brownfields
a site that has been abandoned and has some level of environmental contamination