Gr.9 Geography Unit 2 - Landform Regions Test Review
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What three distinct landforms are Canada made of?
Highlands, lowlands, shield
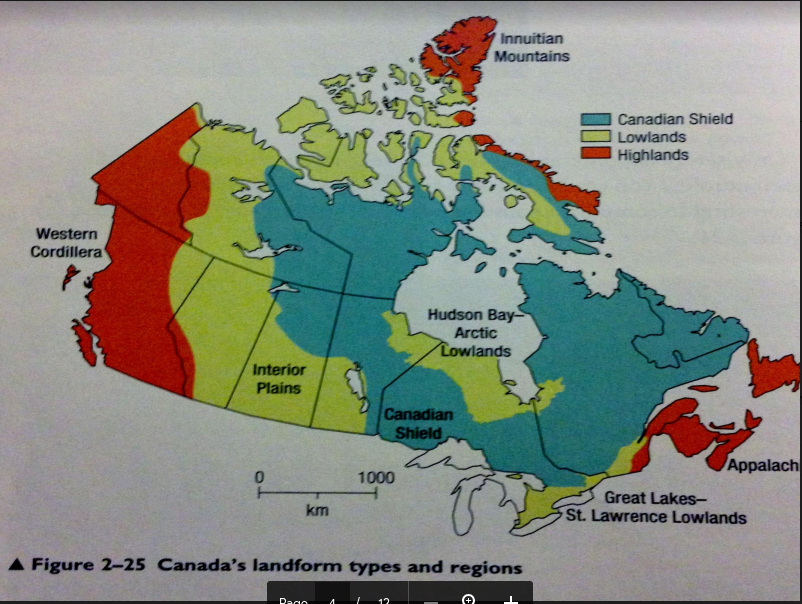
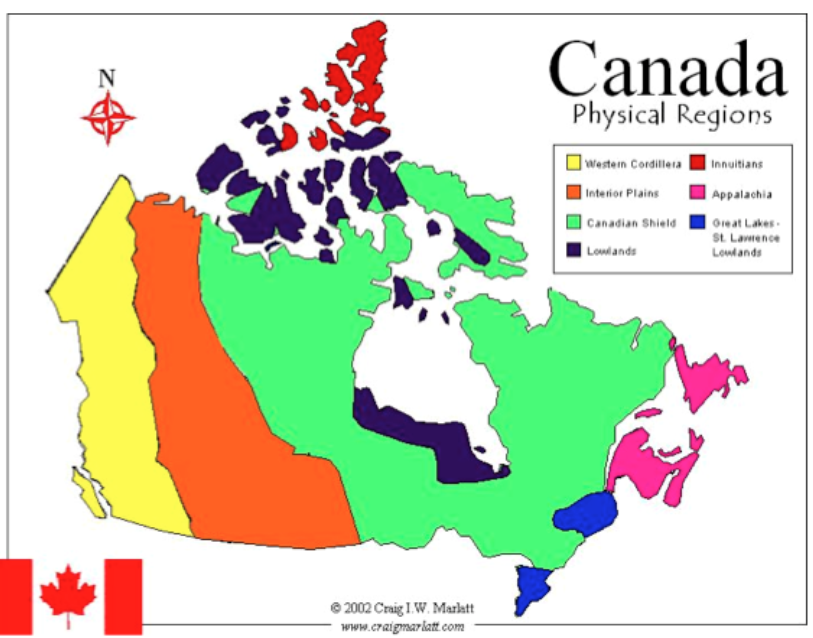
Name the seven landform regions of Canada
Western Cordillera
Appalachian mountains
Great Lakes/St. Lawrence
Canadian Shield
Interior Plains
Innuitian mountains
Hudson Bay and Arctic Lowlands
what is a landform is and how were they formed
A feature on Earth's surface that is part of the terrain.
Formed through forces such as weathering, erosion, and faults.
Theory of Continental Drift?
A theory created by Alfred Wegener stating all of Earth’s land was once a supercontinent called Pangaea which broke apart over time.
What was wrong the the Theory of Continental Drift?
There was no evidence proving how the broken pieces moved.
Theory of Plate Tectonics?
Theory that Earth's lithosphere consists of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving because of convection currents.
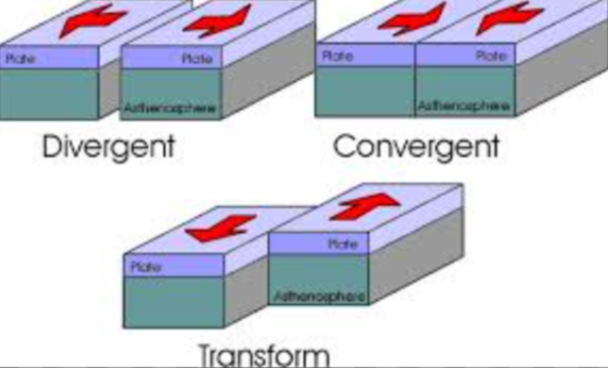
Three types of plate boundaries?
Convergent- Two plates pushing against each other
Divergent- Two plates pushing away from each other
Transform- Two plates moving in opposite directions.
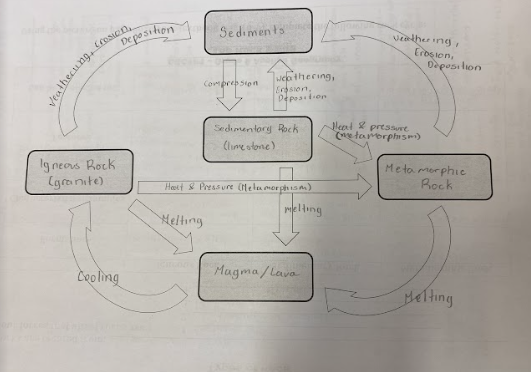
Name and describe the three types of rocks
Sedimentary formed by the accumulation of sediments under pressure
Metamorphic caused by changes in rocks due to high heat and pressure
Igneous, formed by the cooling of molten rock
2 kinds of igneous rock?
Intrusive: magma cools below the surface
Extrusive: magma cools near the surface
What is a volcano?
Openings where lava can erupt onto the Earth's surface.
What is mechanical weathering?
Physical processes affecting rock, such as changes in temperature, wind, rain or waves.
What is chemical weathering?
When a rock is dissolved as a result of chemical reactions
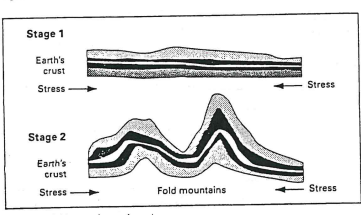
What is folding?
Over a long period of time rock layers slowly bend and break
(Anticlines bed upward & Synclines bend downwards)
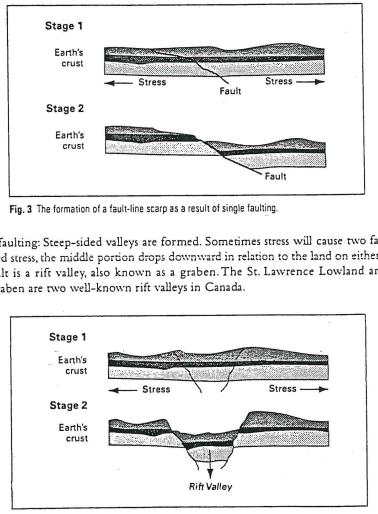
What is faulting?
Fractures in bedrock, produced in the Earth's crust by stress that convection currents create in the mantle.
Name each era
Precambrian (earliest life) (4600 million - 570 million years ago)
Paleozoic (ancient life) (570 million - 245 million years ago)
Mesozoic (middle life) (245 million - 66 million years ago)
Cenozoic (current life) (66 million years ago - current day)
Major Events of the Precambrian Era
Geological events:
Precambrian shields such as Canadian Shield have been formed
Biological events:
First multi-celled and single-celled organisms
Major Events of the Paleozoic Era
Geological events:
Large parts of North America covered by shallow seas
Appalachians formed
Biological events:
Age of amphibians and fish
First fish
Large swamps-coal formed vegetation
First plaints and animals on land
Major Events of the Mesozoic Era
Geological events:
Formation of rocky mountains began
Innuitian Mountains formed
Shallow seas at the interior of North America at various times
Biological events:
Age of reptiles (e.g dinosaurs)
First flowering plants
First birds and mammals
Major Events of the Cenozoic Era
Geological events:
Ice sheets cover much of North America
Continents take on current shape
Rocky mountains formations completed
Biological events:
Human beings develop
Age of mammals
Modern forms of life evolve
How old is Earth estimated to be?
4,600, 000, 000 years (4.6 billion)
What is a glacier?
A body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. Forms when accumulated snow doesn’t melt after winter’s end
2 Kinds of glacier?
Continental: forms in a central location with ice moving outward in all directions under it’’s own weight
Alpine: form in high mountains and travel through valleys and moves down them
What is a landform region?
An area on the Earth’s surface with a unique set of features
What natural processes are responsible for variations of landforms?
folding, faulting, weathering, erosion, glaciation
Canadian Shield
Type of Landform: Shield
Physical characteristics: thousands of small lakes, thin layers of soil and rolling hills, made of metamorphic and igneous rock
Resources: various minerals
Human activity: mining, recreation, fishing, boating, hunting, cross-country skiing
Appalachians (mountains)
Type of Landform: Highlands
Physical characteristics: old mountains, long broad ridges, steep slopes, deep gorges and wide valleys
Resources: farmland, cotton, tobacco, fruit, minerals
Human activity: mining, forestry, agriculture, manufacturing, tourism
Great Lakes/St.Lawrence
Type of Landform: Lowlands
Physical characteristics: fairly flat, rich soils, lakes, freshwater reaches
Resources: drinking water, minerals
Human activity: Mining, construction, energy production, manufacturing and farming
Interior Plains
Type of Landform: Lowlands
Physical characteristics: fairly flat, low hills, contains all rock types
Resources: fossil fuels, forests, farmland, rich in grains
Human activity: agriculture and mining
Hudson Bay and Arctic Lowlands
Type of Landform: Lowlands
Physical characteristics: flat, low area, swampy forests and the Arctic Lowlands is a region of tundra
Resources: deposits of minerals, volcanic and sedimentary rocks
Human activity: fishing, hunting, mining, forestry and hydroelectric development
Western Cordillera
Type of Landform: Highlands
Physical characteristics: plateaus, valleys, plains, rugged mountains
Resources: forestry, agriculture, mining and fish
Human activity: forestry, agriculture, mining and fisheries
Innuitian Mountains
Type of Landform: Highlands
Physical characteristics: young mountains, snowy, icy, contains all rock types but mostly sedimentary
Resources: minerals
Human activity: fishing, mining, fur trading, hunting, whaling, tourism