Proteins
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
Protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
How many different amino acids are there?
20
structure of amino acids
central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, R group
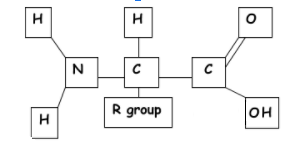
Monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
What type of reaction links amino acids together
Dehydration synthesis/condensation reaction
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
Polypeptide
A chain of greater then 50 amino acids
How many levels of protein structure are there?
four
primary protein structure
sequence of amino acids
Secondary protein structure
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
quaternary structure
Results from two or more polypeptide subunits connected to each other
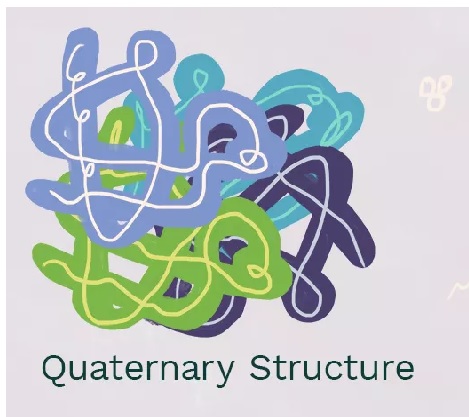
denauration
when proteins break apart or don't maintain their shape
Functions of proteins
Control rate of chemical reactions, fight disease, movement, cell signaling, structure, transport
Enzymes
A protein that changes the rate of a chemical reaction
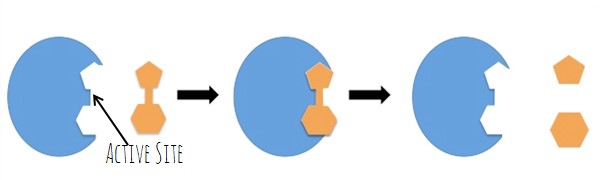
substrates
the reactants of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
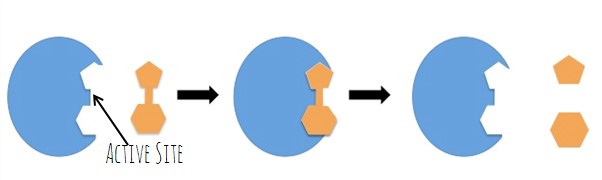
Active site of an enzyme
the region of an enzyme that attaches to a substrate
Elements that make up proteins
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
building blocks of proteins
amino acids