Topic 1 - Tectonics
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Intra-plate earthquakes
Can occur anywhere
The cause is not fully understood but is thought to be:
Tectonic stresses causing ancient fault lines to reactivate
The plates are moving over a spherical surface and this causes zones of weakness
Hotspot volcanoes
These occur over stationary magma plumes (columns of rising magma) in the asthenosphere
The tectonic plate moves over the plume leading to the formation of a chain of volcanic islands (Hawaii)
The oldest island is the one furthest away from the plume
Plate boundary types
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
Main layers of Earth
The crust
The mantle
The core
Crust Characteristics
There are two types of crust:
Continental - a thicker (45-50km), less dense layer (mostly granite)
Oceanic - a thinner (6-10km), denser layer (mostly basalt)
The crust consists of seven major and several minor tectonic plates
Mantel Characteristics
The mantle is between the crust and core and is the widest layer
The upper mantle has two layers:
The rigid layer above the asthenosphere, which together with the crust, makes up the lithosphere
The asthenosphere is a semi-molten, plastic type layer, which moves under high pressure
The lower mantle is hotter and denser than the upper mantle
The intense pressure, at depth, keeps the lower mantle solid
Core Characteristics
The core is made up of two parts:
Inner Core - solid centre, mostly composed of iron
Outer core - semi-molten, mostly liquid iron and nickel
Convection Currents
The heat from radioactive decay in the core moves upwards into the mantle
It creates convection currents, which push up into the spreading mid-ocean ridges, forcing them further apart (ridge push)
Ridge Push
Magma rises as the plates move apart. The magma cools to form new plate material. As it cools It becomes denser and slides down away from the ridge. This causes other plates to move away from each other.
Slab Pull
The denser plate sinks back into the mantle under the influence of gravity. It pulls the rest of the plate along behind it.
Seafloor spreading
Palaeomagnetism provides evidence that the sea floor has gradually moved apart at a mid-ocean ridge
Lava cools and solidifies with the minerals lining up with the magnetic field
The direction of the minerals on either side is a mirror image
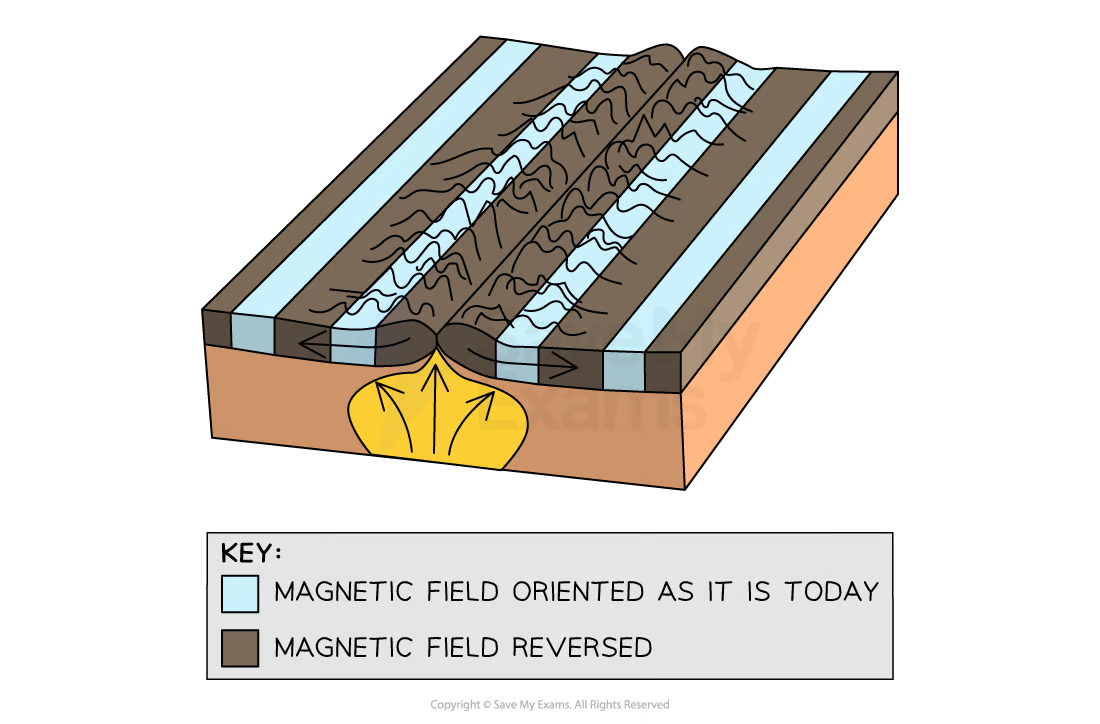
Subduction and slab pull
Convection currents in the mantle drag the overlying lithosphere towards each other
A subduction zone is formed when two plates meet
The heavier, denser plate subducts under the lighter, less dense plate
As oceanic crust cools, it becomes denser and thicker, and gravity forces the lithosphere down into the subduction zone
As it sinks, it drags or pulls the plate with it
This is known as slab pull
Convergent plate boundary (Oceanic/Continental)
The denser, heavier oceanic plate subducts under the lighter, less dense continental plate
This forms deep ocean trenches in the subduction zone
Found at convergent plate boundaries (Oceanic/Continental)
Volcanic eruptions, fold mountains, and earthquakes (at Benioff Zone)
Convergent plate boundary (Oceanic/Oceanic)
The heavier of the two oceanic plates subduct
Found at convergent plate boundary (Oceanic/Oceanic)
deep ocean trenches and island arcs
Island arc formation
A series of volcanic islands, formed in an arc shape, e.g. the Caribbean
Submarine volcanic eruptions, lead to crust building up and rising above sea level
Constructive/divergent plate boundary (Oceanic/Oceanic)
plates are moving apart, volcanic eruptions and earthquakes
Collision plate boundary (Continental/Continental)
Two plates of similar density move towards each other
As neither plate can sink into the denser rocks below, they are crushed, crumpled and forced upwards, usually folding in the process
Found at Collision plate boundary (Continental/Continental)
collision fold mountains, earthquakes
Transform/conservative plate boundary
Plates move slowly past each other, they become stuck and pressure builds, the plates eventually 'snap' past each other
These can be called ‘strike-slip’ faults as they strike/stick and then slip/release past each other
Magnitude/magma at divergent boundaries
Earthquakes tend to be mild and shallow
Eruptions tend to be small and effusive
The eruptions are usually of basalt lava:
Low gas content
Low viscosity
Higher temperature
Magnitude/magma at convergent boundaries
Friction and pressure build up in the Benioff zone (the area within the subduction zone where most friction and pressure build up occurs) causes strong earthquakes
Volcanic eruptions tend to be explosive as the magma is forcing its way to the surface
These eruptions are often rhyolite lava:
High gas content
High viscosity
Lower temperature
Magnitude at transform boundaries
Plates can stick causing a significant build up of pressure and powerful earthquakes
Characteristics of basalt magma
Black/dark grey
45-55% silica content
1000-1200°C
Low viscosity
Easy gas escape
Gentle eruption
Characteristics of andesite magma
medium/dark grey
55-65% silica content
800-1000°C
Medium viscosity
Medium gas escape
Medium eruption
Characteristics of rhyolite magma
Light colour
65-75% silica content
600-900°C
High viscosity
Difficult gas escape
Effusive eruption
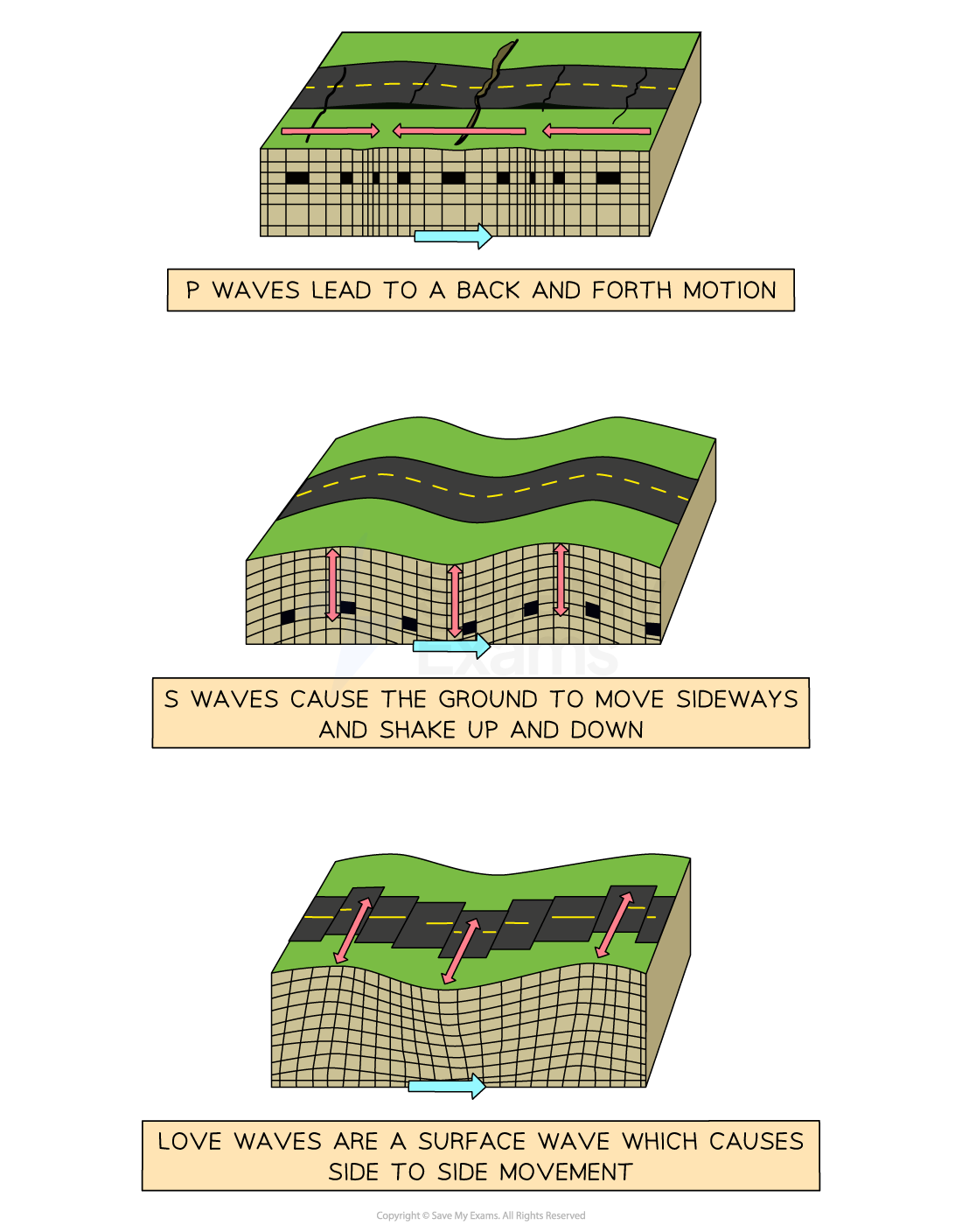
Primary (P) Wave Characteristics
Body wave
Fastest
Reach the surface first
Travel through liquids and solids
Cause backwards and forwards shaking
Least damaging
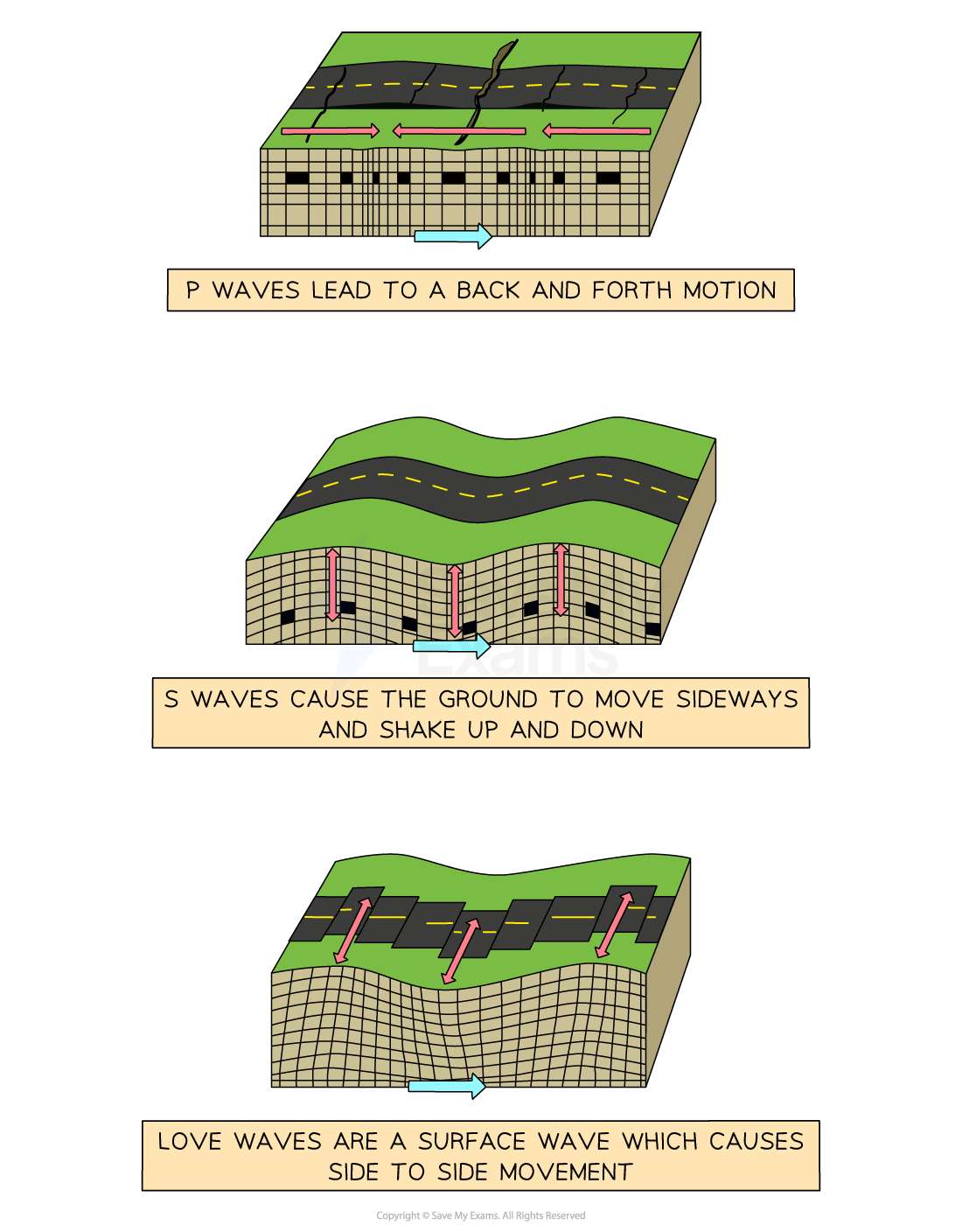
Secondary (S) wave characteristics
Body wave
Slower than P waves
Only travel through solids
Cause a sideways motion
More damaging
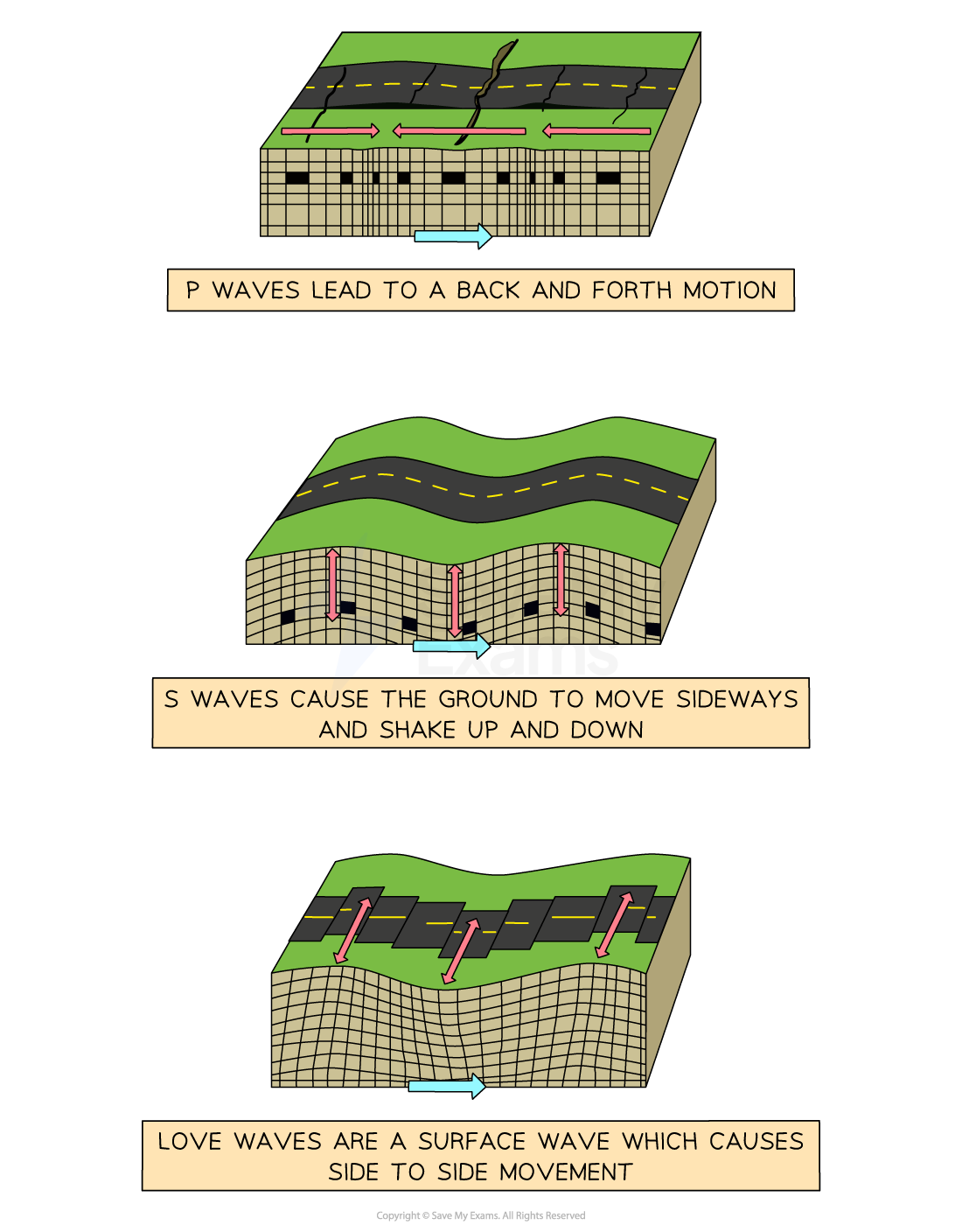
Love (L) wave characteristics
Surface wave
Slowest
Cause a side to side motion
Larger and energy is focussed on the surface
Most damaging
Primary hazards of earthquakes
Direct results of earthquakes
Ground shaking
Crustal Fracturing
Secondary hazards of earthquakes
Result of primary hazards
Landslides
Avalanches
Liquefaction
Flooding
Primary hazards of volcanic eruption
Direct result of eruption
Pyroclastic flow
Lave flow
Ash fall
Gas eruption
Secondary hazards of volcanic eruption
result of the primary hazards
Lahars
Jokulhlaups
Jokulhlaups
Floods caused by sudden release of water and rock when glacial ice is melted in an eruption
Causes of Tsunamis
As the sea bed jolts from an earthquake, water is displaced and forced upwards to create a wave
As it approaches land wave length becomes compressed and waves get taller
As it reaches shore a vacuum is created and pulls back water, leaving the sea bed exposed
Can also be caused by landslides and volcanic eruption underwater
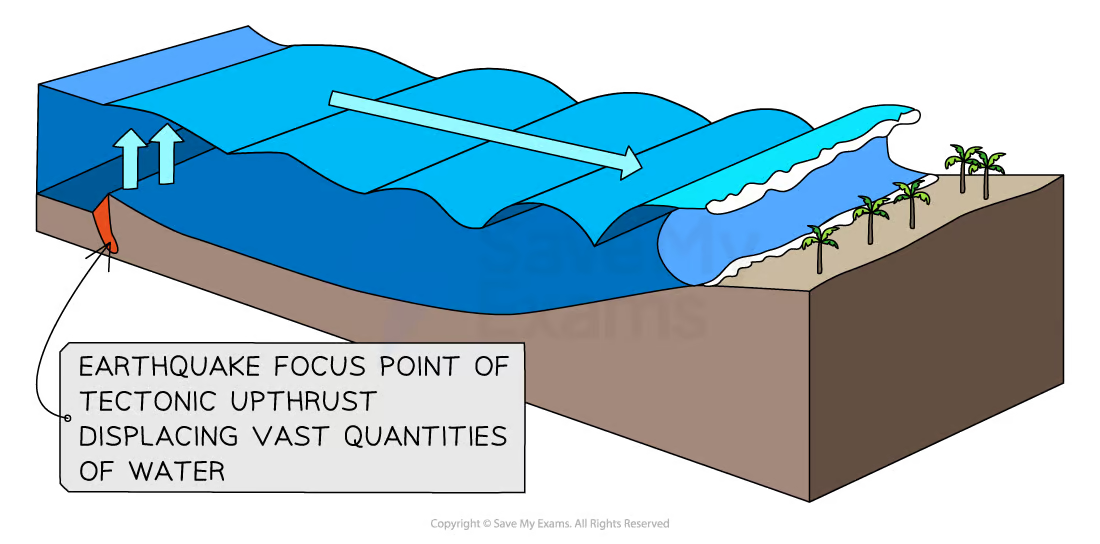
Natural hazard
An even with the potential to cause harm to the environment, people, or economy, caused by nature
Disaster
When a hazard causes actual harm to the environment, people, or economy
UN definition of a disaster
‘A serious disruption of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic or environmental losses and impacts, which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources’
Vulnerability
How susceptible an area/population is to damage from a hazard event
Factors affecting vulnerability
Level of development
Population density
Size of hazard
Preparation and planning
Hazard risk equation
Allows judgment to be made regarding resilience

Factors affecting resilience
Building construction
Population density
Level of urbanisation
Infrastructure
`Wealth
Healthcare system
Emergency services
Education
Level of corruption
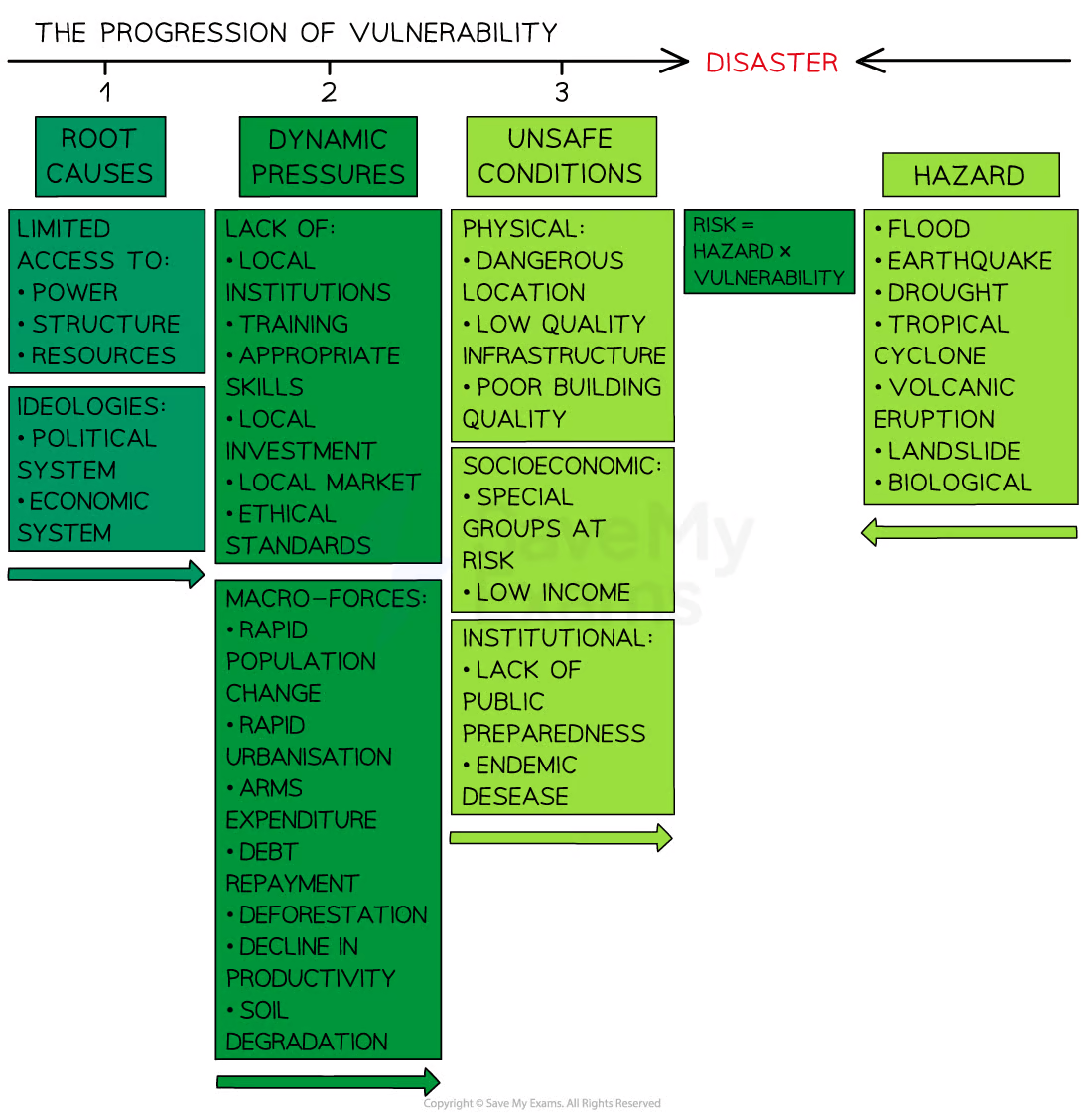
Pressure model
Demonstrates how there is a range of factors that increase vulnerability and why some areas lack resilience. Its made up of 3 sections:
Root causes
Dynamic pressures
Unsafe conditions
It is the combined with the hazard
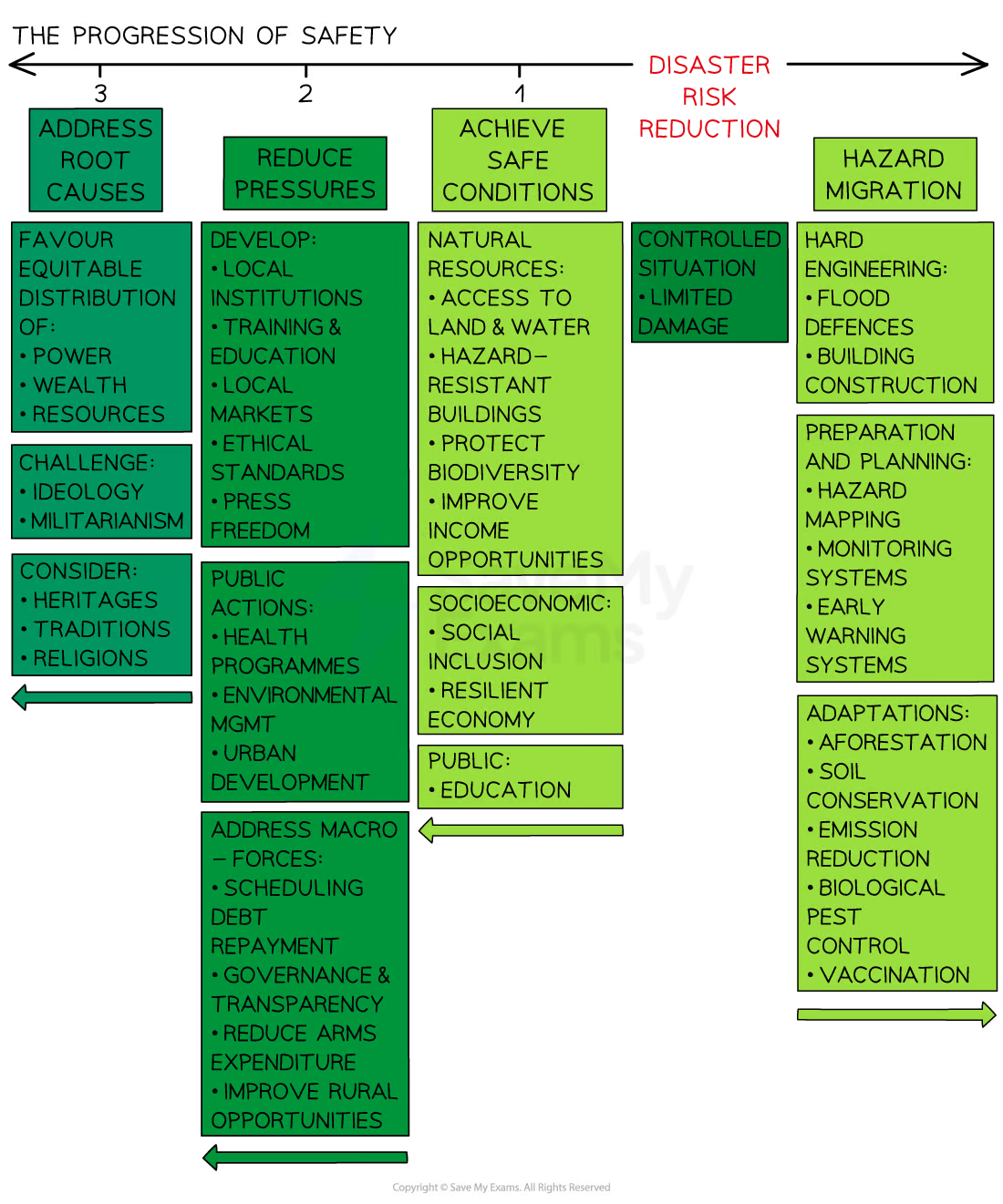
Release model
Demonstrates how vulnerability can be reduced and resilience increased by addressing 4 things:
Safety
Reducing the pressures
Addressing root causes
Hazard mitigation
Moment Magnitude Scales (MMS)
Measured with seismographs
Measures energy released from the focus
Goes from 1 (Nothing felt) to 10
Logarithmic scales (Factor 10)
Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale (MMIS)
Measures impact on people and environment
Goes from I to XII
Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI)
Measures size of eruption based on observations and measurements, including height of material ejected, volume of material, and eruption duration
Logarithmic scale (0-8)
Hazard profiles
Used to compare tectonic events, usually. include the same factors
Magnitude
Speed of onset
Areal extent (Area affected)
Duration
Frequency
Spatial predictability (Is the a pattern to where)
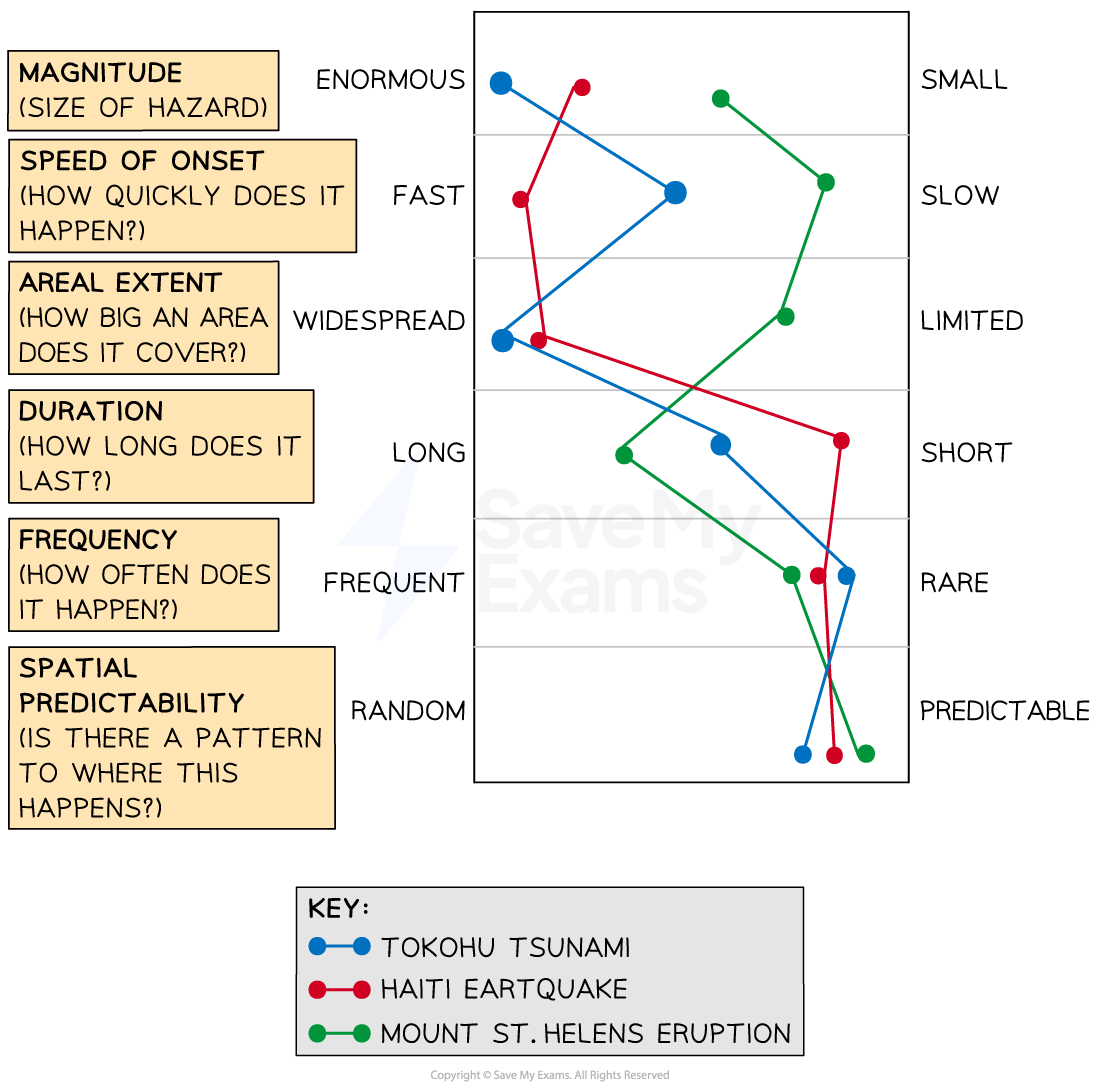
Advantages of hazard profiles
Can compare multiple hazards
Can help plan for future events
Disadvantages of hazard profiles
Doesn’t account for all factors
Focuses on physical not human
Multi-hazard events are hard to represent
Subjective
Reasons for an increase in global disasters
Population increases (more people to be affected)
Increased monitoring and reporting
Global warming
Where are some multi-hazard zones?
Phillipines (earthquakes, typhoons, tsunamis, volcanoes, landslides)
Hazard prediction
Knowing when (temporal scale) and where (spatial scale) a hazard will occur, earthquakes cannot be predicted
Hazard forecasting
Gives a percentage chance of a hazard occurring over a set period
Earthquakes and prediction/forecasting
Cannot be predicted, just known on plate boundaries
Can be forecast by studying seismic gap theory, radon emissions, and animal behaviour
Seismic gap theory
Highlights areas most at risk of an earthquake due to time since the last one and historical frequency
Volcanoes and prediction/forecasting
Warning signs beforehand (magma rising, surface level changes, increased gas emission, increased seismic activity)
Changes monitored with GPS, tilt meters, satellites, seismometer and gas detectors
Tsunamis and prediction//forecasting
Can’t predict earthquake induced
Ocean monitoring tech can be used post earthquake
Hazard Management Cycle
Shows how the events of one hazard inform planning and prep for the next one
Stages of hazard management cycle
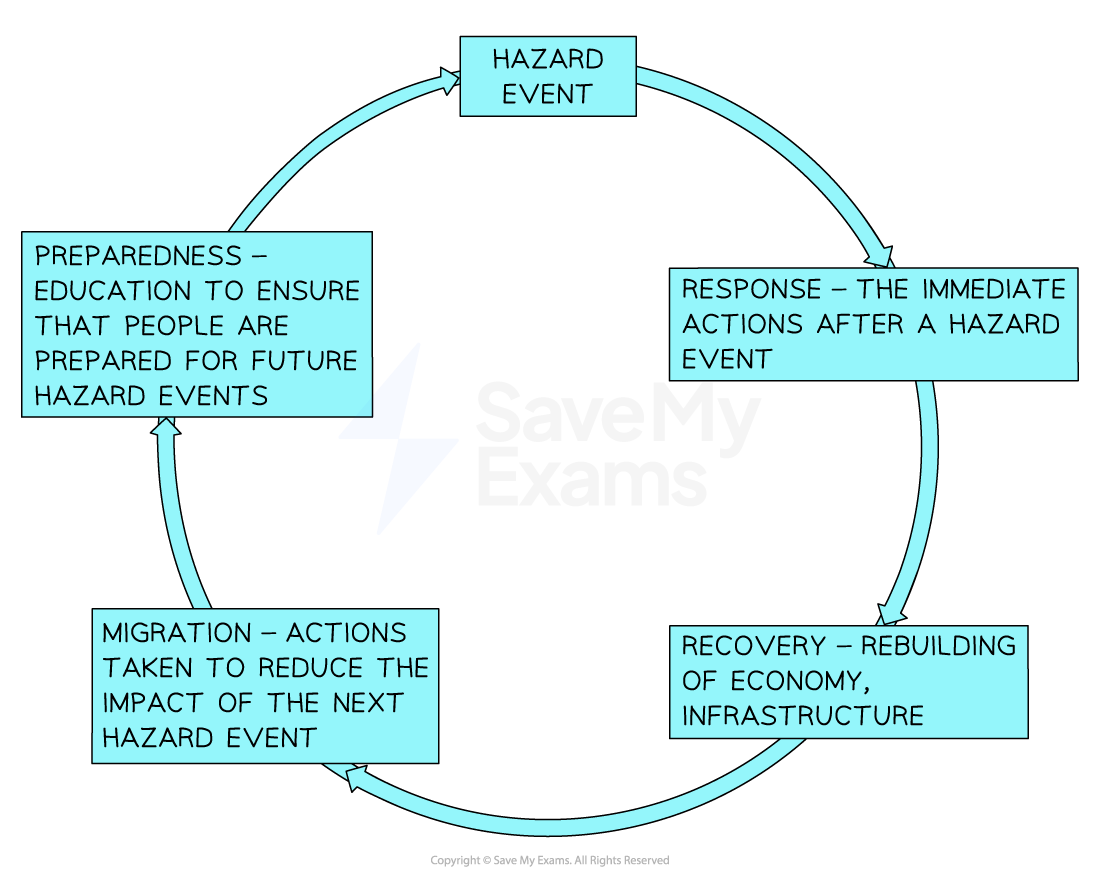
Advantages of hazard management cycle
Can be used by organisations and individuals
Allows for preparation and response to hazardous events
Identifies potential hazards
Reduces risk/saves lives
Improves level of preparation
Disadvantages of hazard management cycle
Might not be possible for smaller/poorer communities to implement
Some hazard are less predictable, management can happen for every eventuality
Community may oppose aspects implemented
Park’s model
Shows the impact of a hazard event on peoples quality of life over time
shows where different management strategies are implemented before, during, and after the event
Varies for each event depending on levels of prep and planning, development, and aid (national and international)
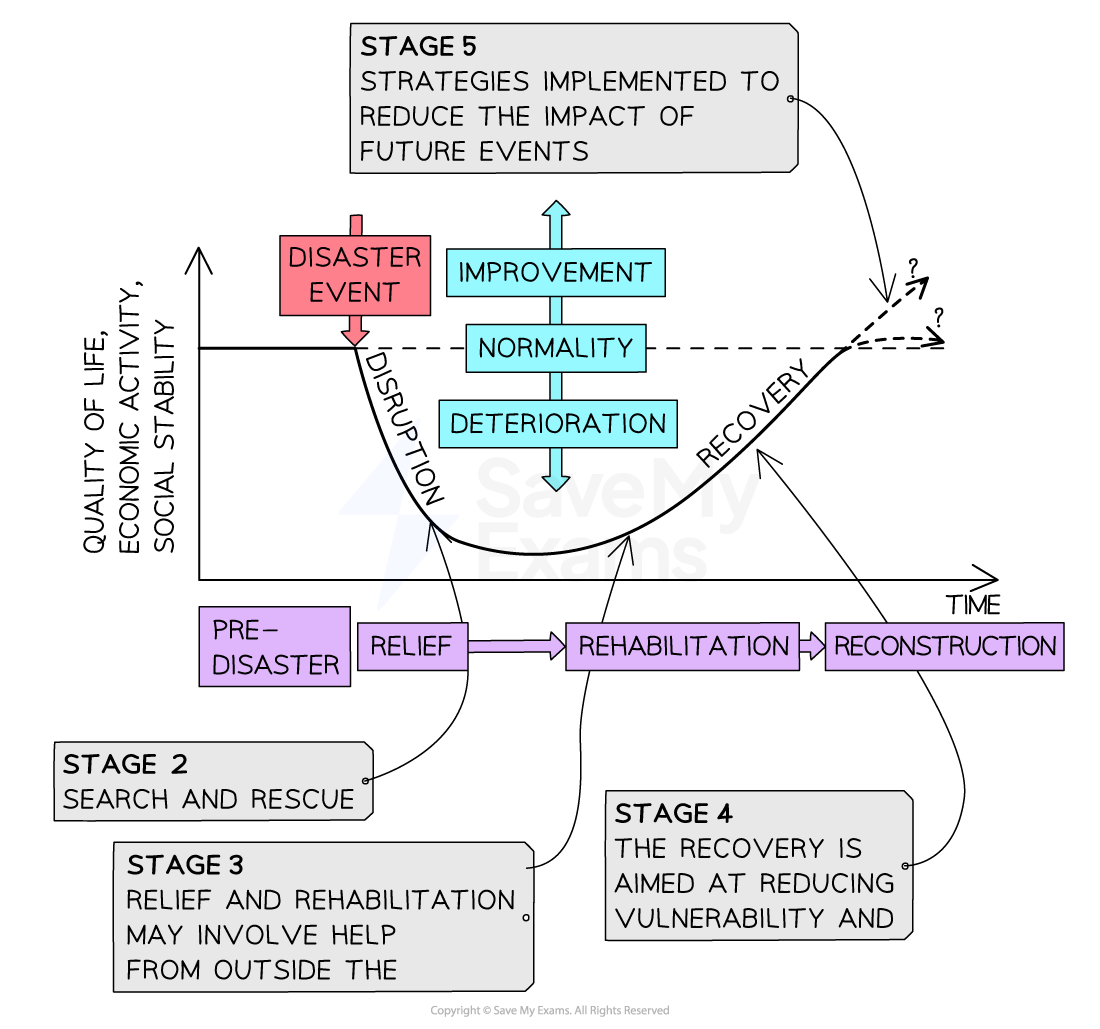
Advantages of Park’s model
Applicable to range of hazards
Can be used for risk assessment and preparation framework
Level of economic activity and social stability take into account
Useful to analyse response
Disadvantages of Park’s model
Only shows single event
Quantitative data not shown (Eg. death count)
Preventative measures not shown
Resources required may not be an option to implement for smaller/poorer communities
3 aspects of disaster modification
Event
Vulnerability (increasing resilience)
Loss
Modification of event (earthquakes)
Happens prior to event, challenging as prediction isn’t possible but can build resistant buildings
Modification of event (volcanoes)
Draining crater lakes to reduce lahars
Barrier and channel construction to divert lava flow
Hazard risk mapping and land use zoning to prevent development of high risk areas
Modification of event (tsunamis)
Land use zoning
Building offshore barriers/sea walls
Replanting mangroves
Modification of vulnerability (increasing resistance)
Happens before event occurs
Land use zoning - ensuring that people are not living in high-risk areas
Hazard resistant buildings
Improved services and infrastructure
Hazard risk mapping to identify areas at highest risk
Planning of evacuation routes
Education of the population to ensure that they know the actions to take when a hazard event occurs - earthquake drills
Improved storage of food, water and medical supplies so
Monitoring and warning systems to allow people time to evacuate
Modification of loss
Happens after event occurs
Evacuation
Search and rescue teams
Emergency aid
Short-term aid - shelter, reconnecting of water and electricity supplies
Development aid - long-term aid to help with reconstruction and recovery
Insurance
Local communities - supporting each other, providing shelter and helping with the search and rescue effort