FPC2: Soft Tissue Tumors (Quiz 2)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Soft tissue
____ ___ tumors are derived from mesenchymal tissues, majority of these benign tumor types are reactive (due to low-grade chronic irritation) and some are neoplastic
Soft tissue
____ ____ pathology categories are the follow:
fibrous, adipose, vascular, lymphatic, neural, muscle and uncertain origin
Fibrous connective, hyperkeratosis
Fibromas are soft tissue tumors that's histopathology can be described as a nodular mass of ____ _____ tissue covered by stratified squamous epithelium, surface may exhibit _____ from secondary trauma
Any, mimic
For the treatment of fibromas, surgical excision is suggested and its important to submit ___ tissue removed for histopathologic examination, malignancies can ___ benign entities
Epulis fissuratum
Reactive hyperplasia due to an ill-fitting denture or alveolar resorption, clinically is often found in the vestibules with redundant folds, often rubbery, may be ulcerated with an overgrowth of tissue around the border of a denture. Its treated with excision (with histopathologic examination of the tissue) and/or a remake or reline the denture
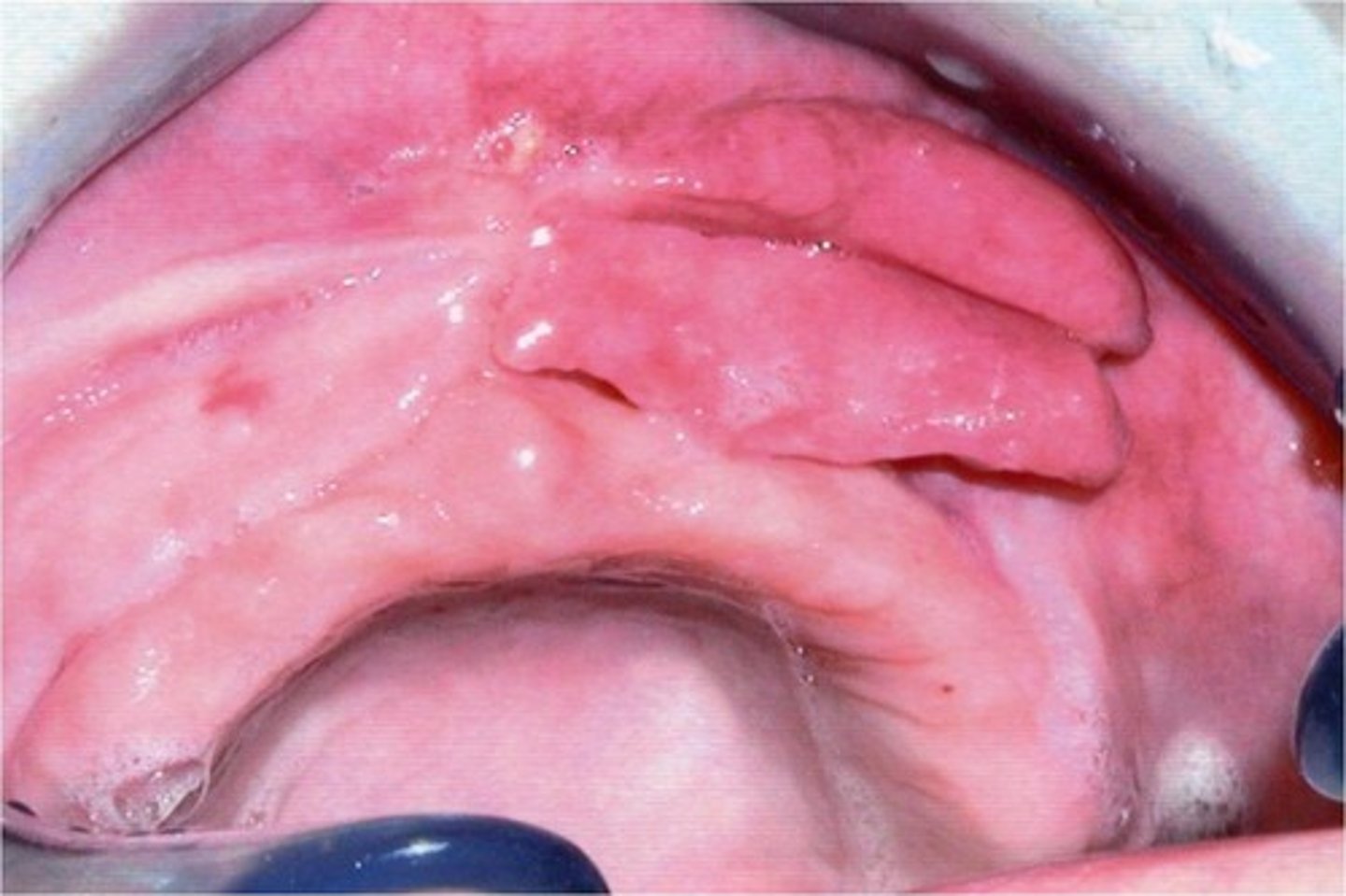
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
_____ ____ ____ is reactive tissue growth related to an-ill fitting denture, poor denture hygiene and 24-hour denture wearing and may also be seen in patients who are mouth breathers.
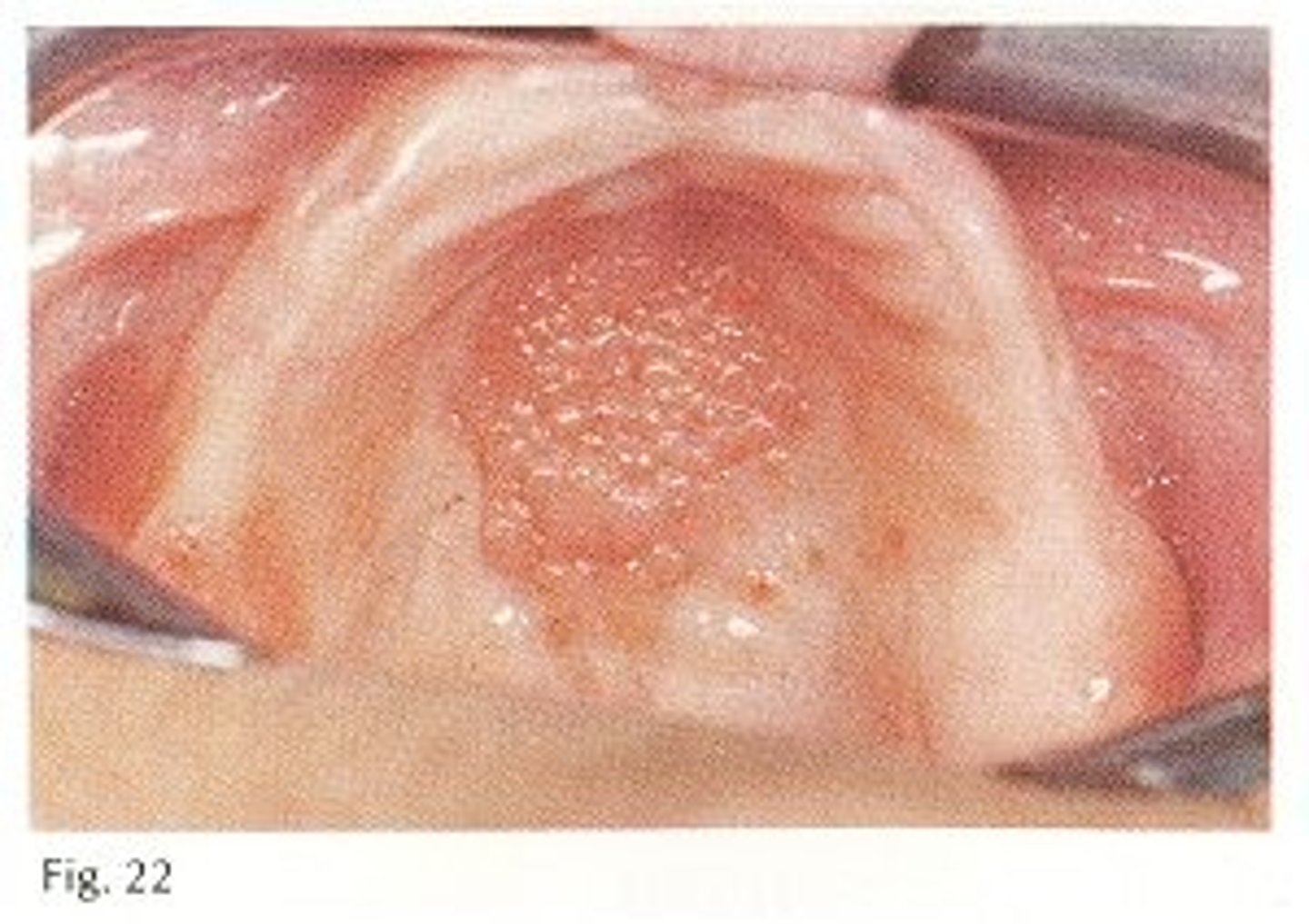
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
____ ___ ____ has clinical features such as it usually occurring on the hard palate beneath a denture base, usually asymptomatic, mucosa is erythematous and has a pebbly or papillary surface. Its treated by proper denture hygiene and removal of dentures at night, fabrication of new dentures, excise excessive tissue in necessary and antifungal therapy
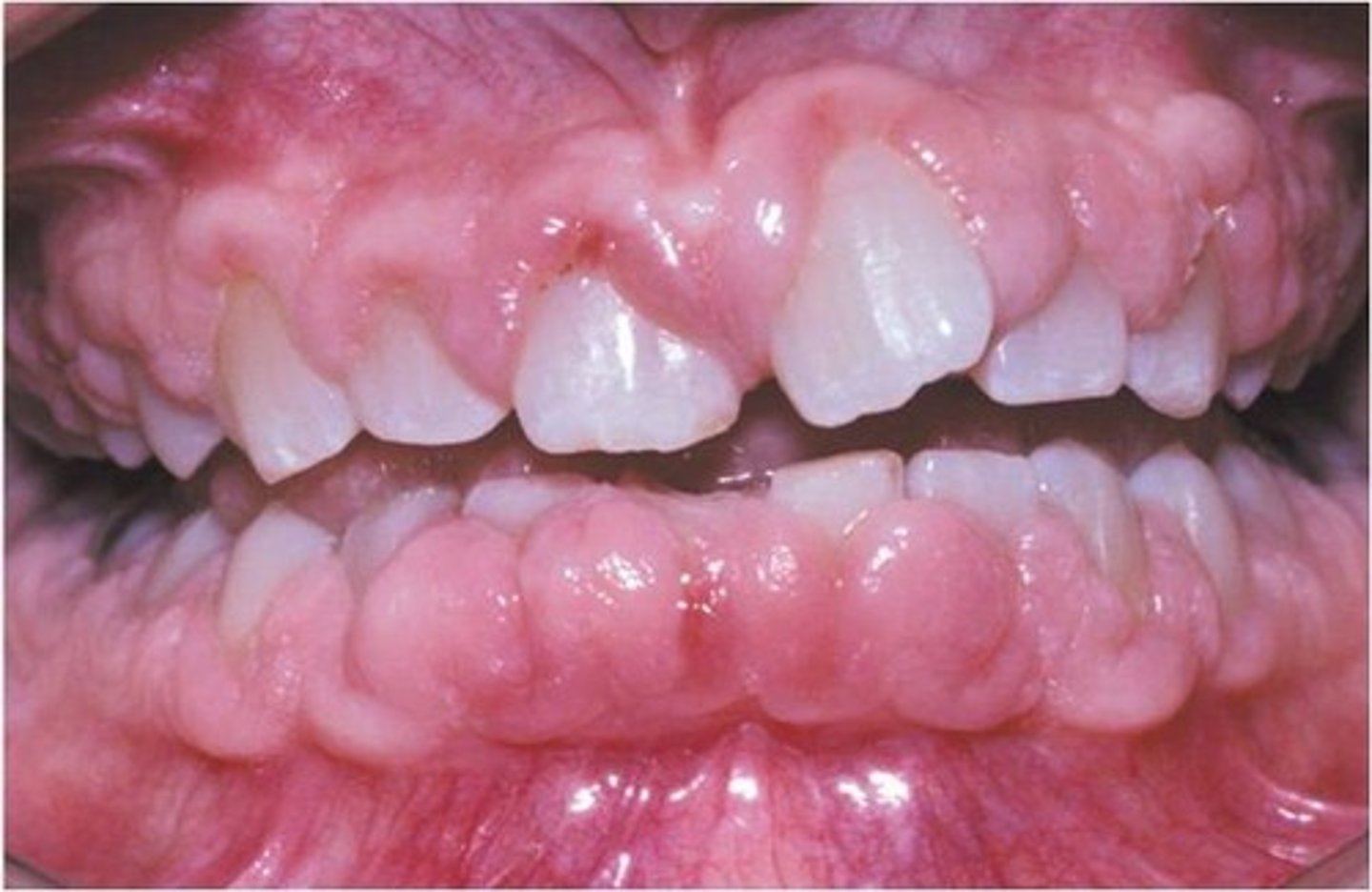
Gingival hyperplasia
*____ _____ begins in the interdental papillae, gingiva may cover the crowns and can be firm. It may be hereditary (not as common) and may be medication related (dilantin, cyclosporine, nifedipine COMMON BOARDS). Its treated by the discontinuation of the offending medication, improved oral hygiene (poor hygiene increases symptoms) with frequent recall visits, gingivectomy; recurrence is common
yes
are ALL 4 P's active lesions?
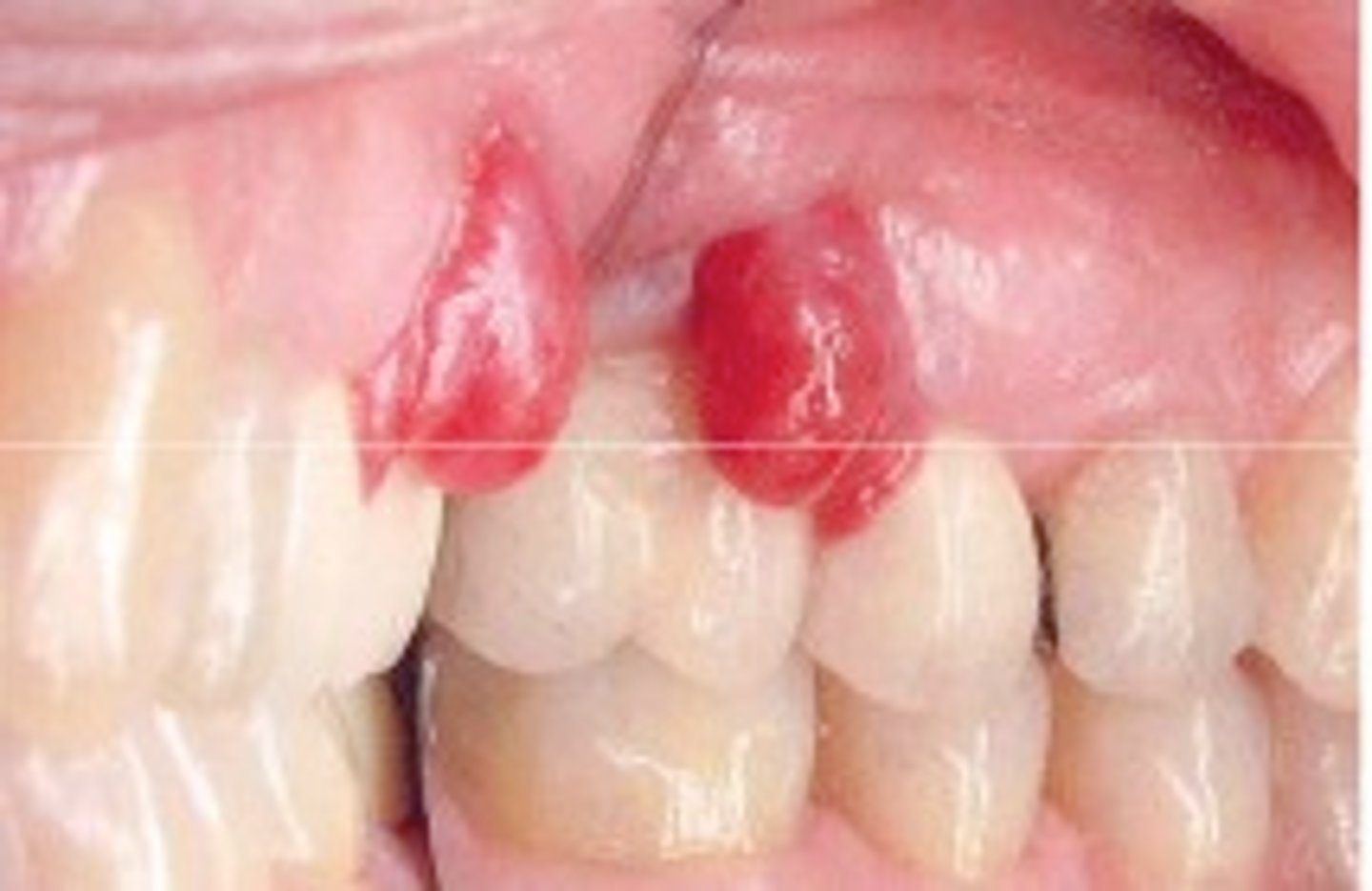
Pyogenic (AKA lobular capillary hemangioma)
____ _____ granuloma is VERY common and its cause is local irritation or trauma. Its 75% on the gingiva, sometimes called the "pregnancy tumor"., its smooth or lobulated vascular mass typically pink-red-purple and usually ulcerated
-KNOW THIS TERM
anywhere
where in the oral cavity can Pyogenic granulomas occur?
Pyogenic
_____ granulomas histopathology consists of ulcerated stratified squamous epithelium, vascularized fibrous connective tissue, mixed inflammatory infiltrate. It's treated with surgical excision with submission for histopathologic examination (excise to periosteum and scale adjacent teeth). In pregnant patients defer treatment until after delivery when possible (high recurrence rate) (KNOW THIS TERM)
Peripheral giant cell Granuloma
___ ____ ___ granuloma's are common and reactive lesions caused by local irritation or trauma. Its clinical features are that it occurs exclusively on the gingiva or edentulous alveolar ridge, a red or red-blue nodular mass (frequently ulcerated), "cupping" resorption of the underlying alveolar bone may be noted. Local surgical excision down to the underlying bone with submission of the substance for histopathologic examination, adjacent teeth should be carefully scaled
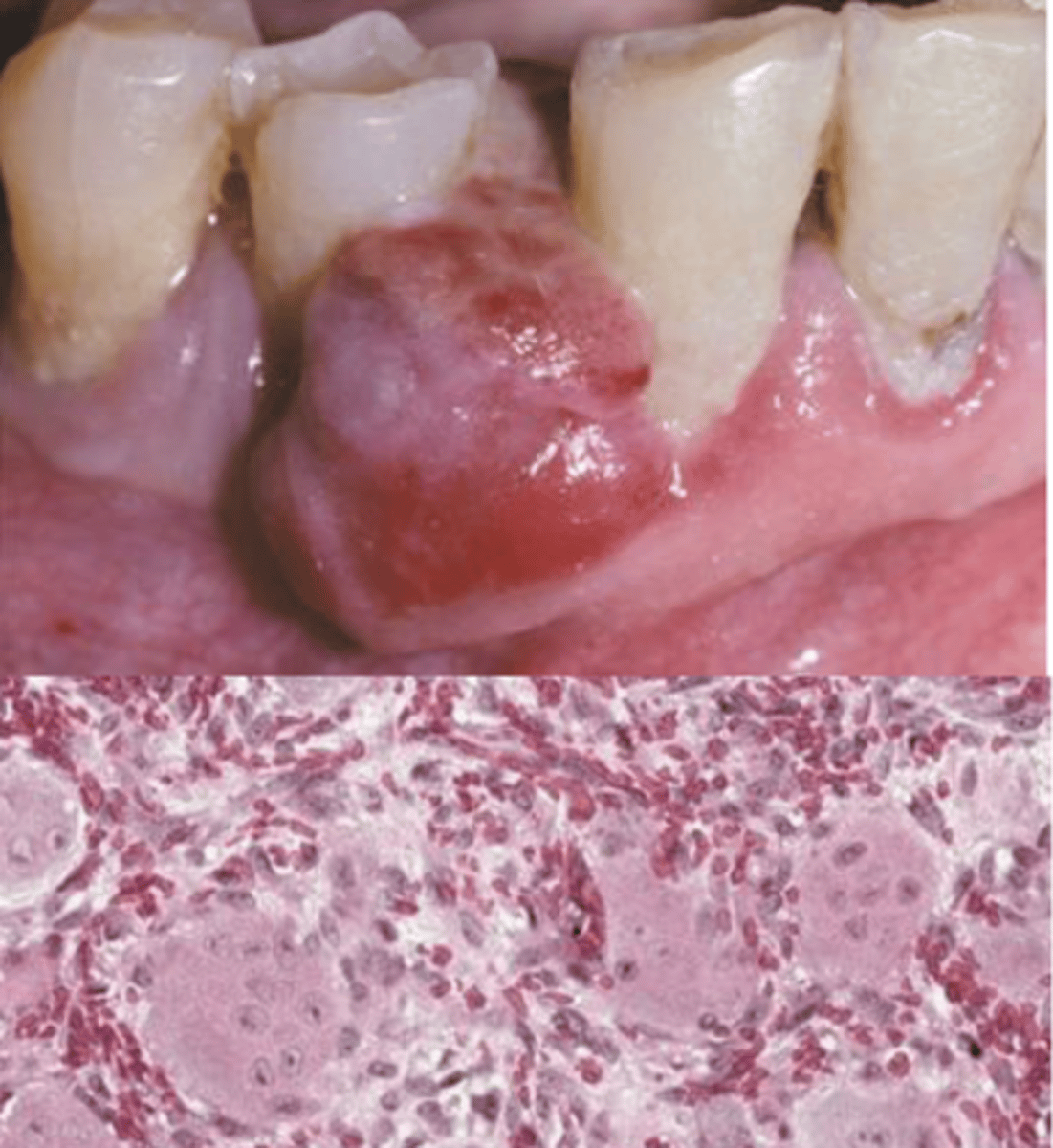
Peripheral ossifying
____ ___ fibromas are common reactive lesions caused by local irritation or trauma, it presents clinically exclusively on the gingiva as a nodular mass (frequently ulcerated), red to pink and seen most common in teens and young adults. Its treated by local surgical excision down to periosteum with submission of the specimen for histopathologic examination. Adjacent teeth should be thoroughly scaled
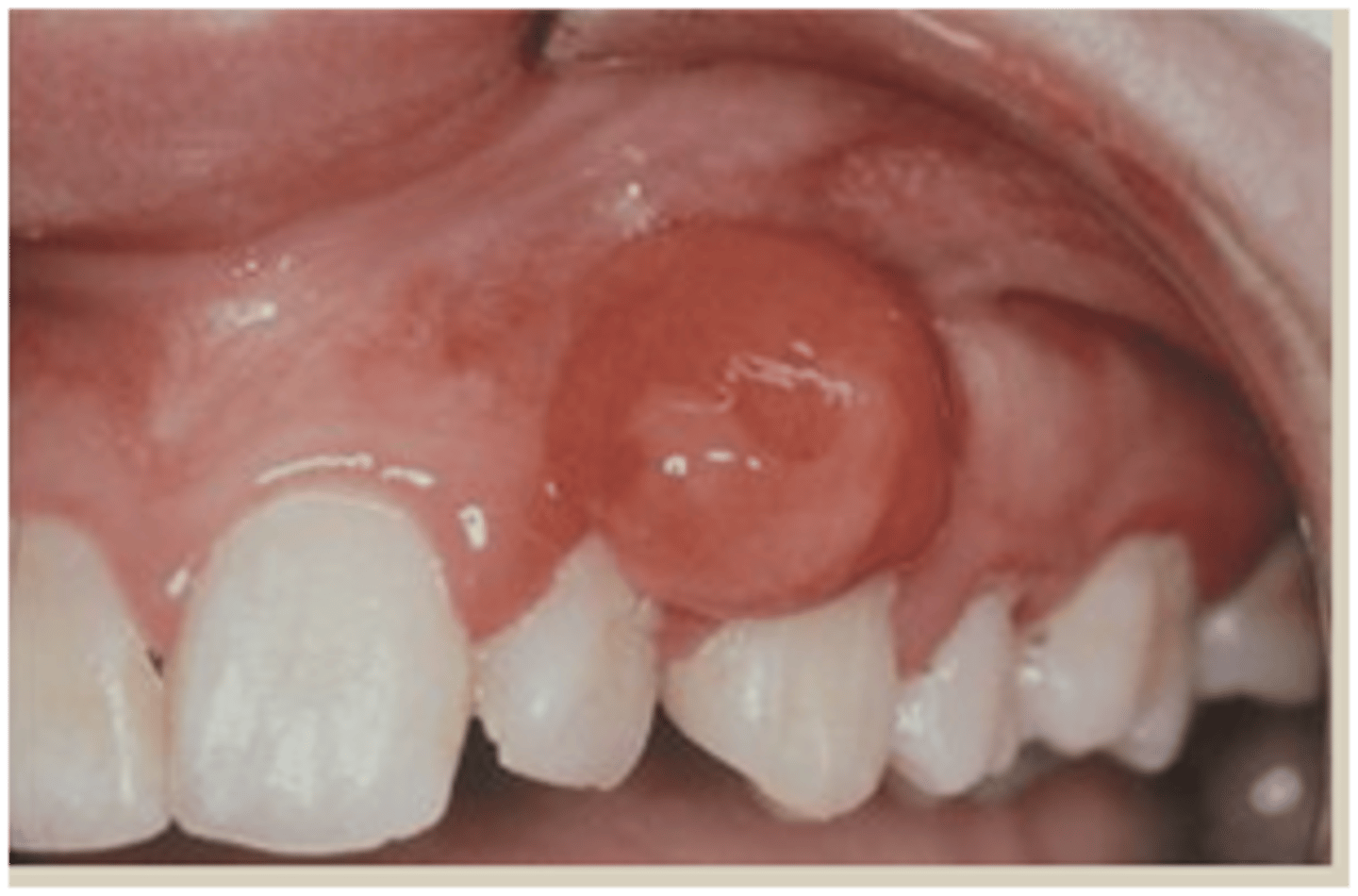
peripheral giant cell granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma
pyogenic granuloma and peripheral fibroma
**Which P's occur exclusively on the gingiva & which can occur anywhere in the oral cavity?
- KNOW THIS
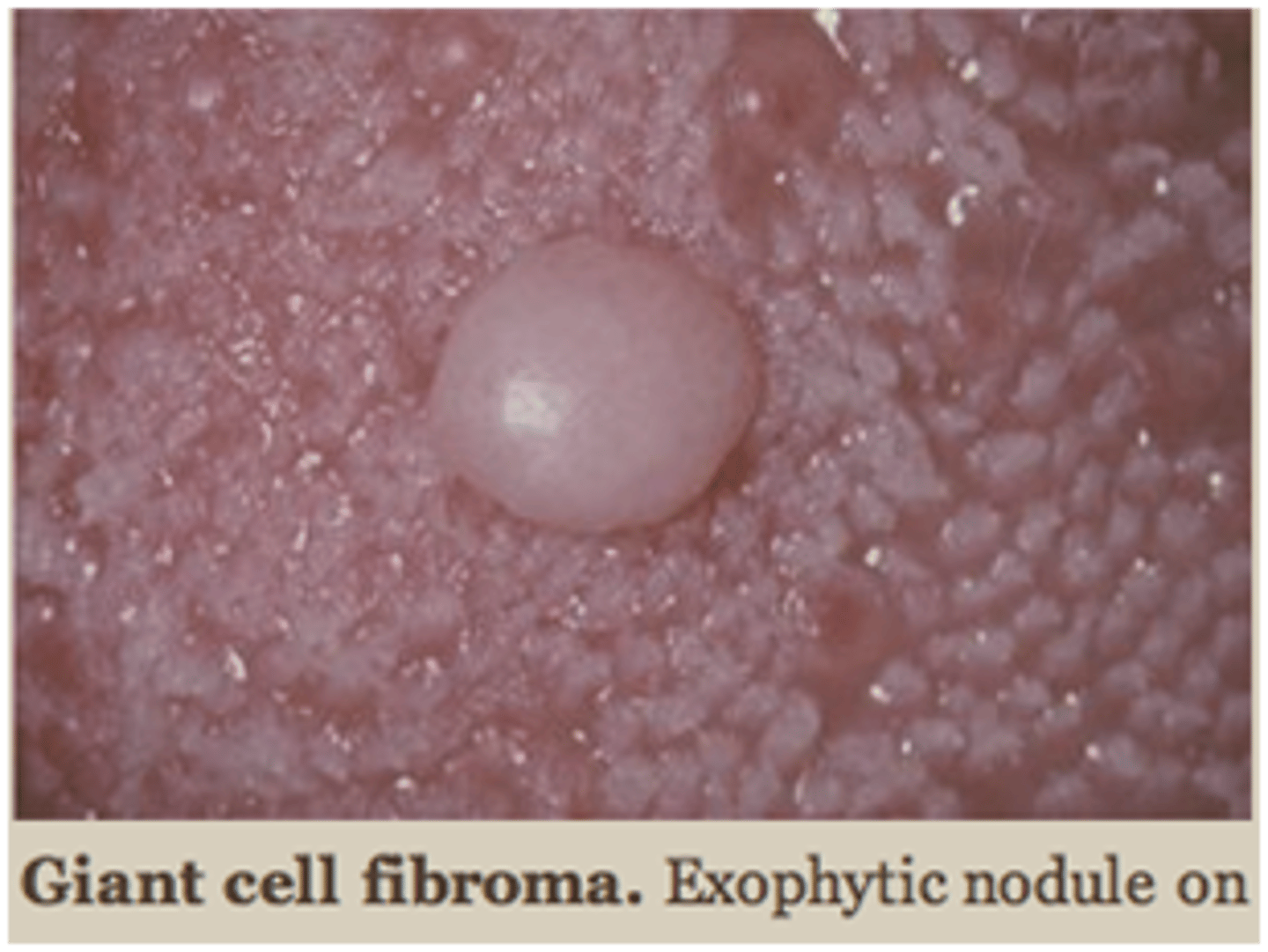
Giant cell fibroma
___ ___ fibroma are fibrous tumors that unlike traumatic fibroma, it does not appear to be associated with chronic irritation. It often presents clinically as asymptomatic, with a papillary surface, common in young patients, 50% of all cases occur on gingiva but tongue and palate are also common sites. Its treated with conservative surgical excision with submission of tissue for histopathologic examination and recurrence is rare
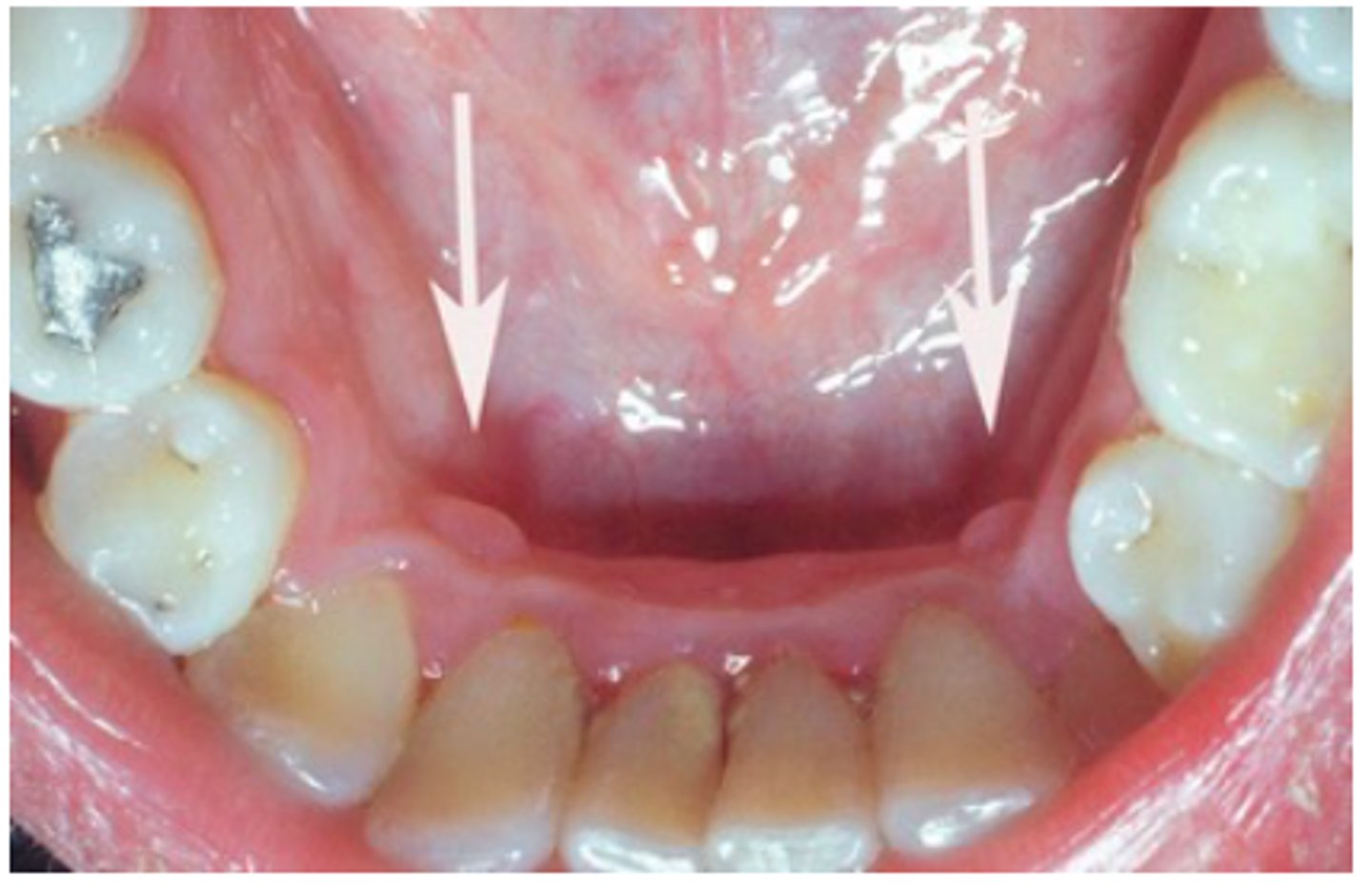
Retrocuspid papilla
Microscopically identical to giant cell fibroma this papillary-like growth is found in the mandibular gingiva lingual to canine and is frequently bilateral, 25-99% of children/YA, involutes with age and should be recognized clinically but does not need to be excised
- if bilateral= dont have to biopsy it
Granular cell tumor
____ ___ tumors are uncommon growths derived from schwann cells where the cytoplasm is granular because of lysosomes. Its most commonly found on the dorsal tongue, it's an asymptomatic sessile nodule that's pink to yellowish in color. It can be treated with conservative local excision with submission of tissue for histopathologic examination and recurrence is rare
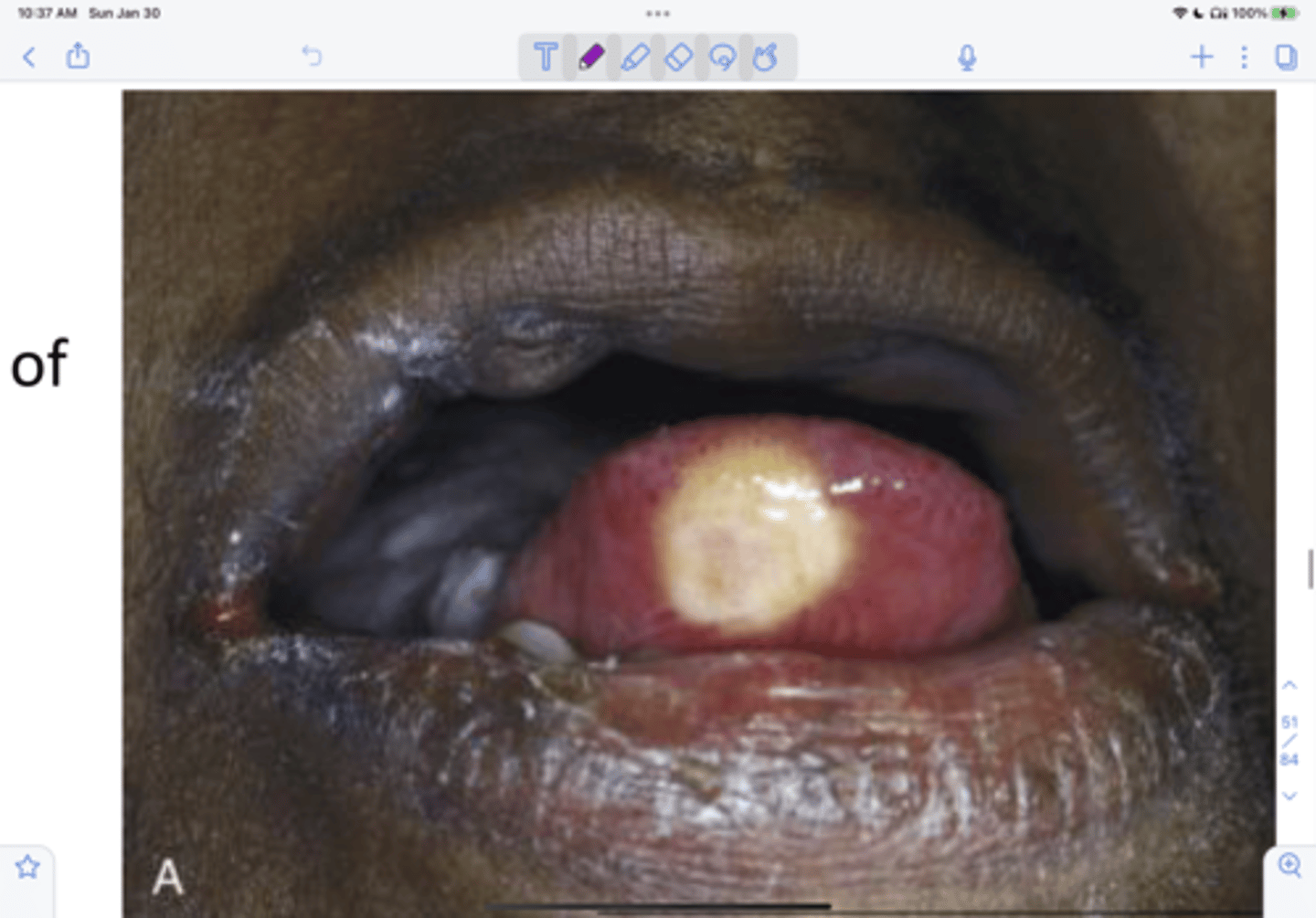
Congenital epulis (congenital granular cell lesion)
____ ___ is uncommon, occurs almost exclusively on the alveolar ridges of newborns, bears a microscopic resemblance to the granular cell tumor. It appears clinically pink-red, smooth-surfaced, polypoid mass on the alveolar ridge of a newborn, more common in maxilla and 90% occurs in female. It can be surgical excised with submission for histopathologic examination, no reports of recurrence, ever.
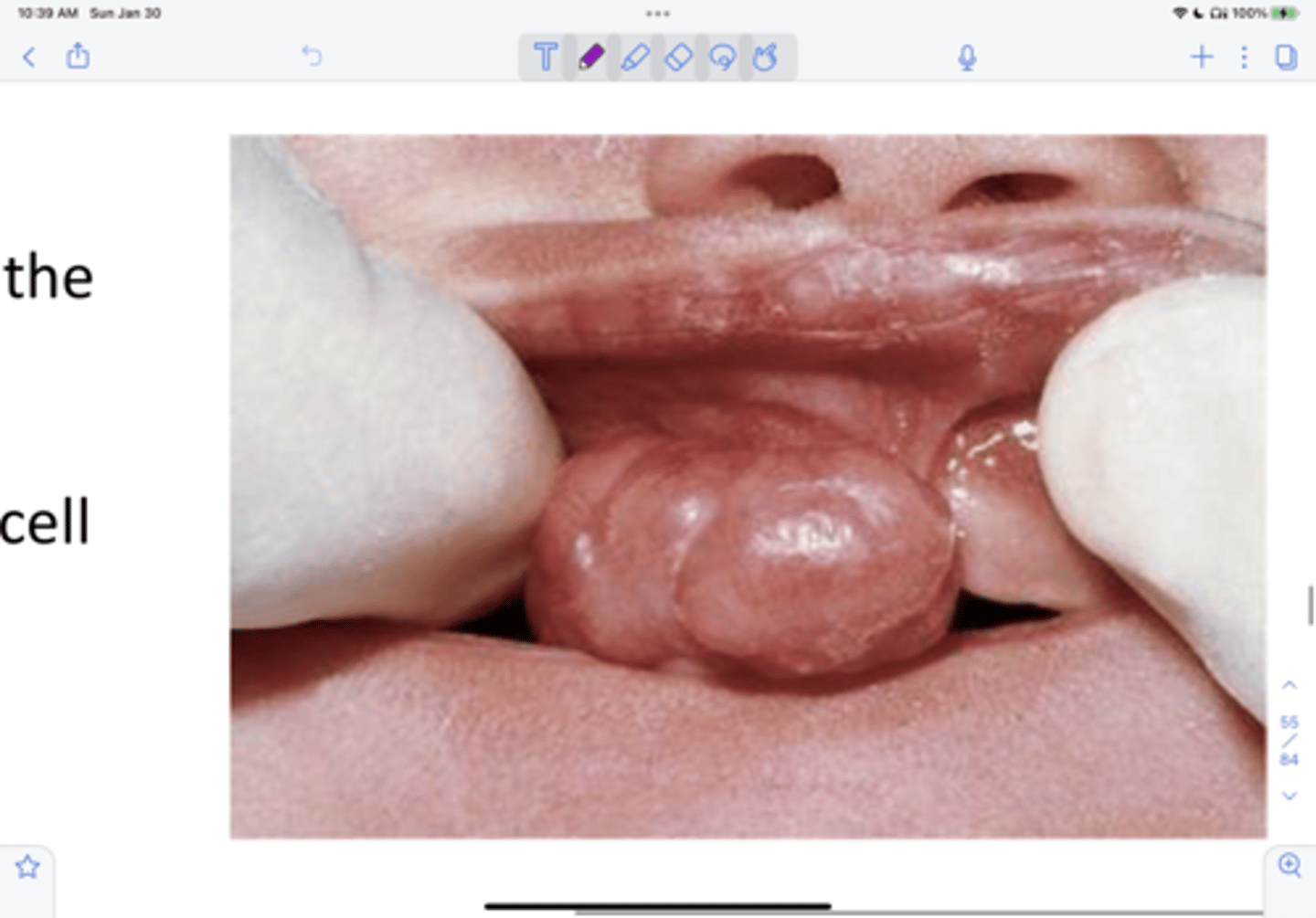
Lipoma
**A benign tumor of fat, 4% of mesenchymal tumors of the oral cavity, it has clinical features such as a soft, doughy, smooth-surfaced nodular, asymptomatic, pink to yellow in color. Its treated by conservative local excision with submission of tissue for histopathologic examination, recurrence in rare.
- KNOW THIS TERM
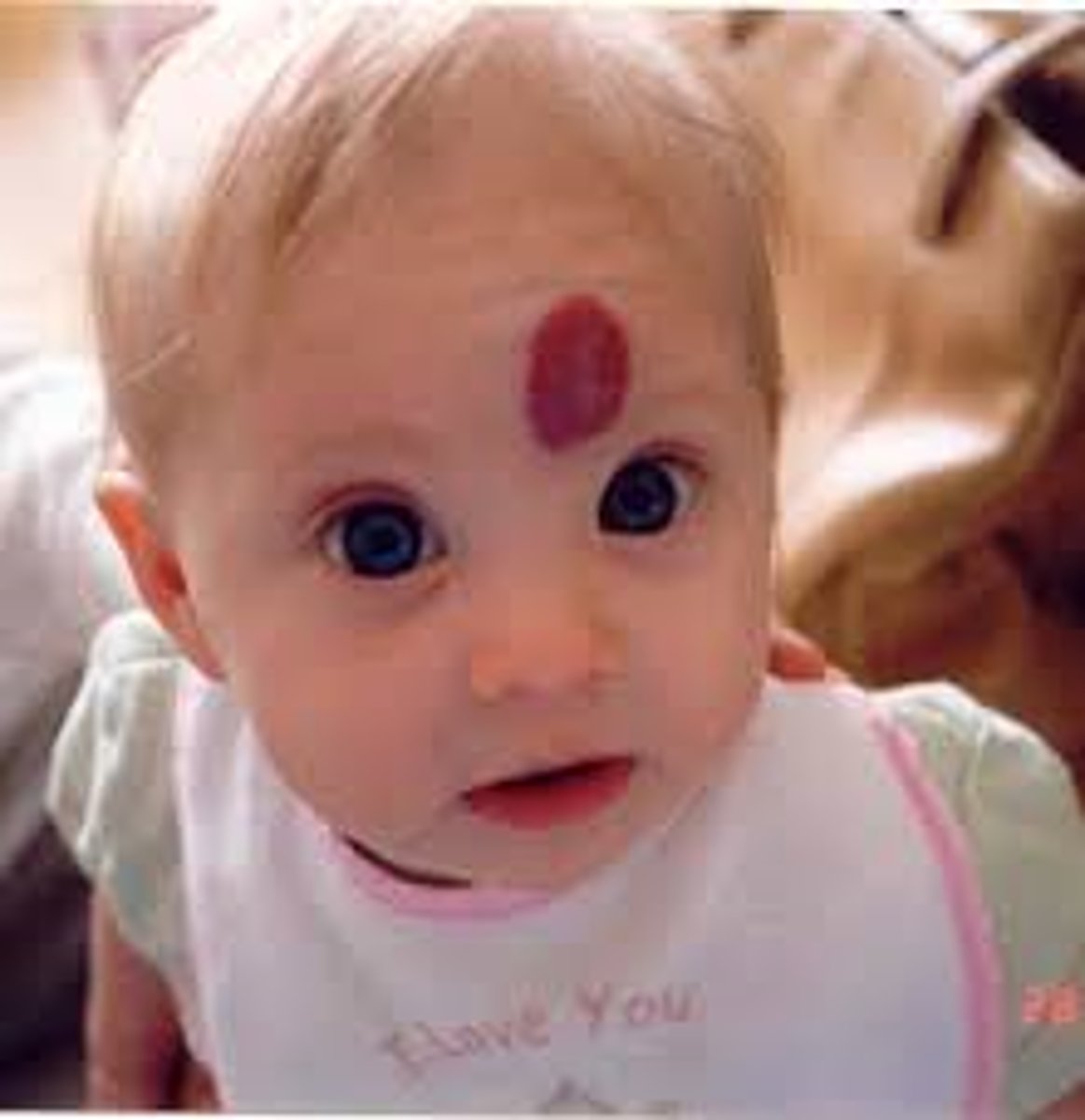
Hamangioma
________'s are congenital lesions that are the most common tumor of infancy, vascular proliferation, often red/blue, early rapid growth and followed by slow involution
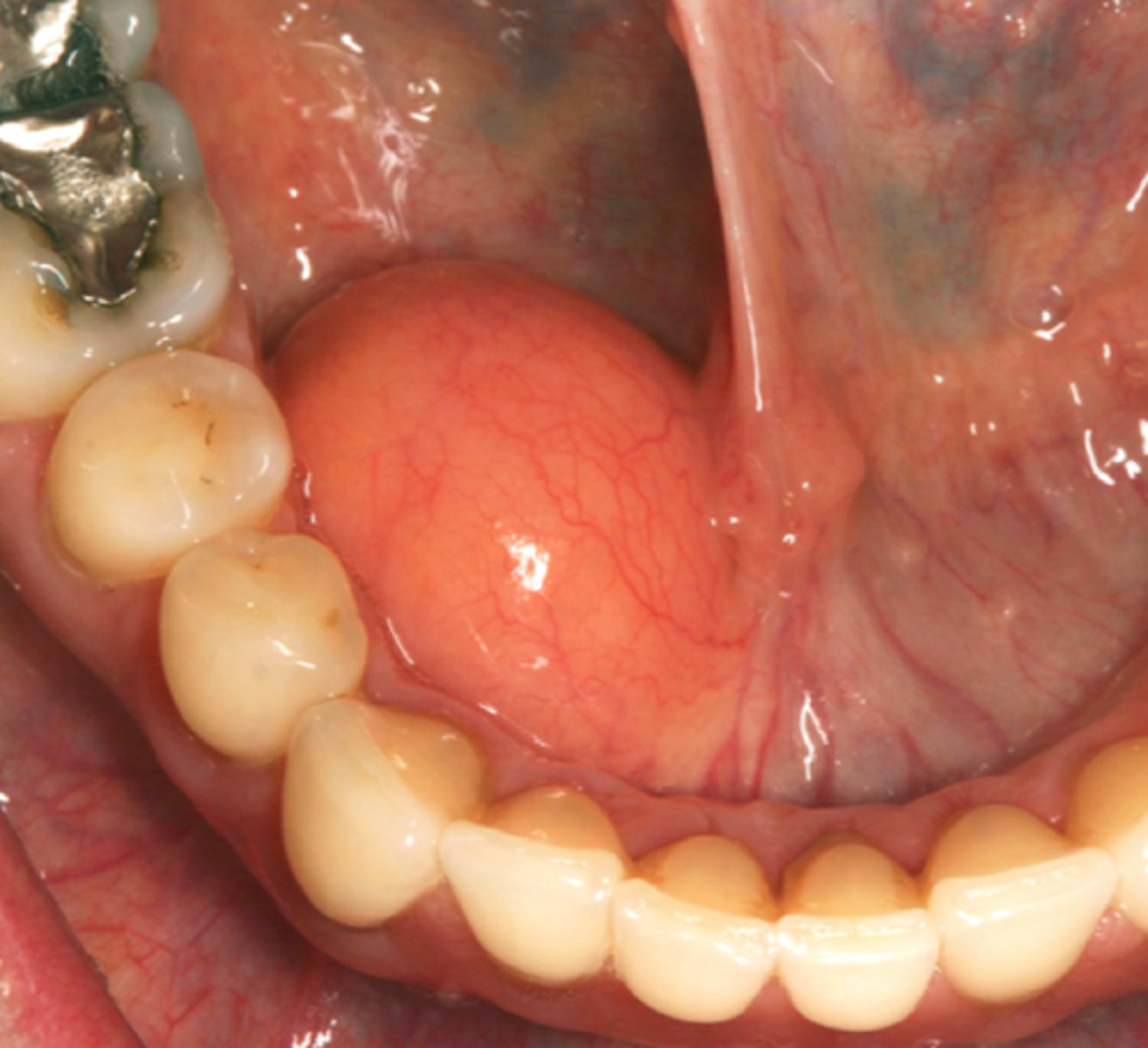
Vascular malformation
______ ______ has most common sites in the head and neck (lips, tongue, buccal mucosa or palate), deep red or blue compressible lesions, lesions can be in the soft tissue or central (intraosseous) in location. It can undergo spontaneous remission remission butt can be treated with surgery, embolization, sclerosing agents, cryotherapy and laser
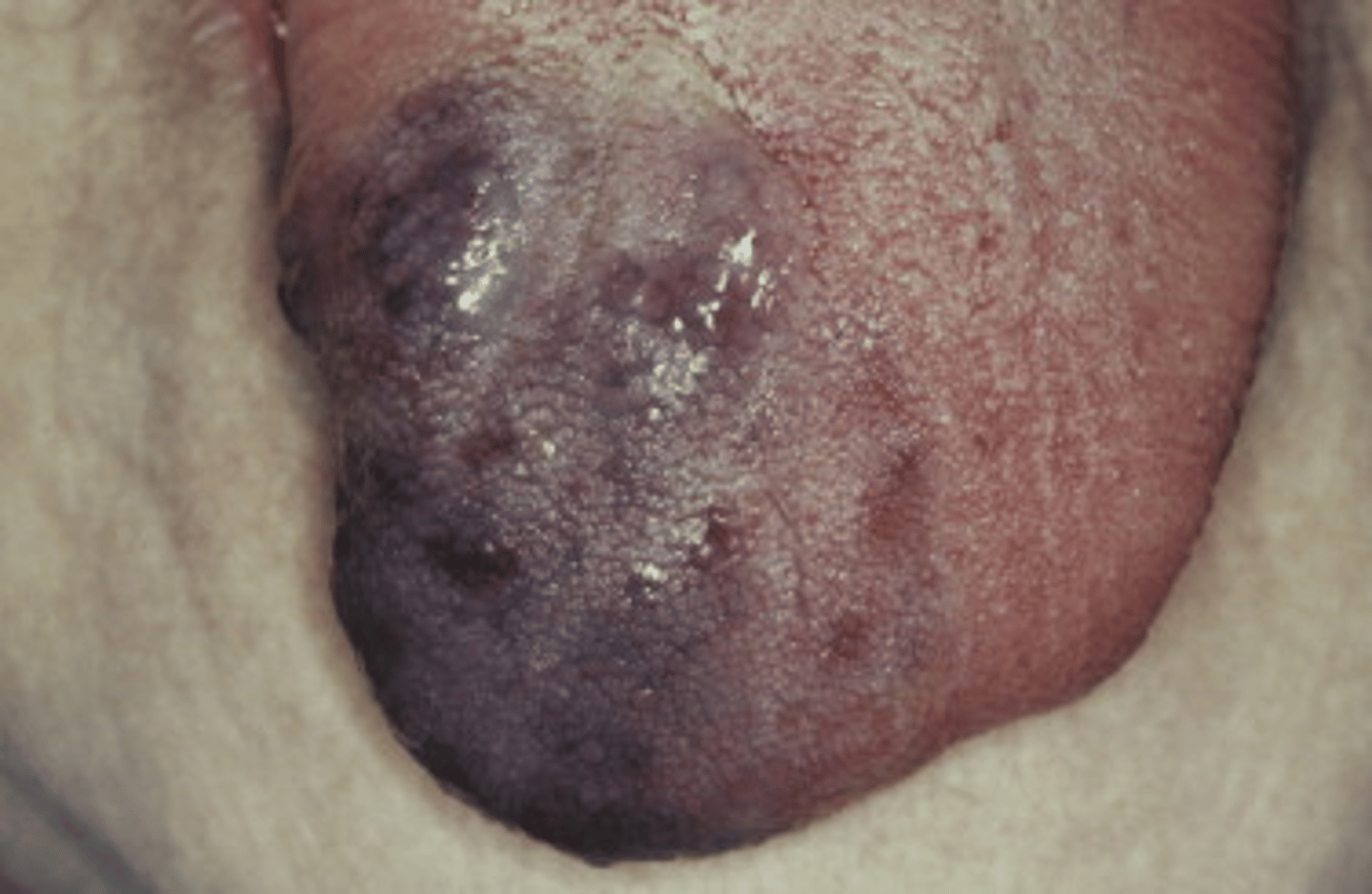
Lymphangioma
_____ is a benign, hamartomatous (non cancerous) tumorlike growths of lymphatic vessels and likely represent developmental anomalies that arise from sequestrations of lymphatic tissue that do not communicate normally with the rest of the lymphatic system
- looks like frog eggs
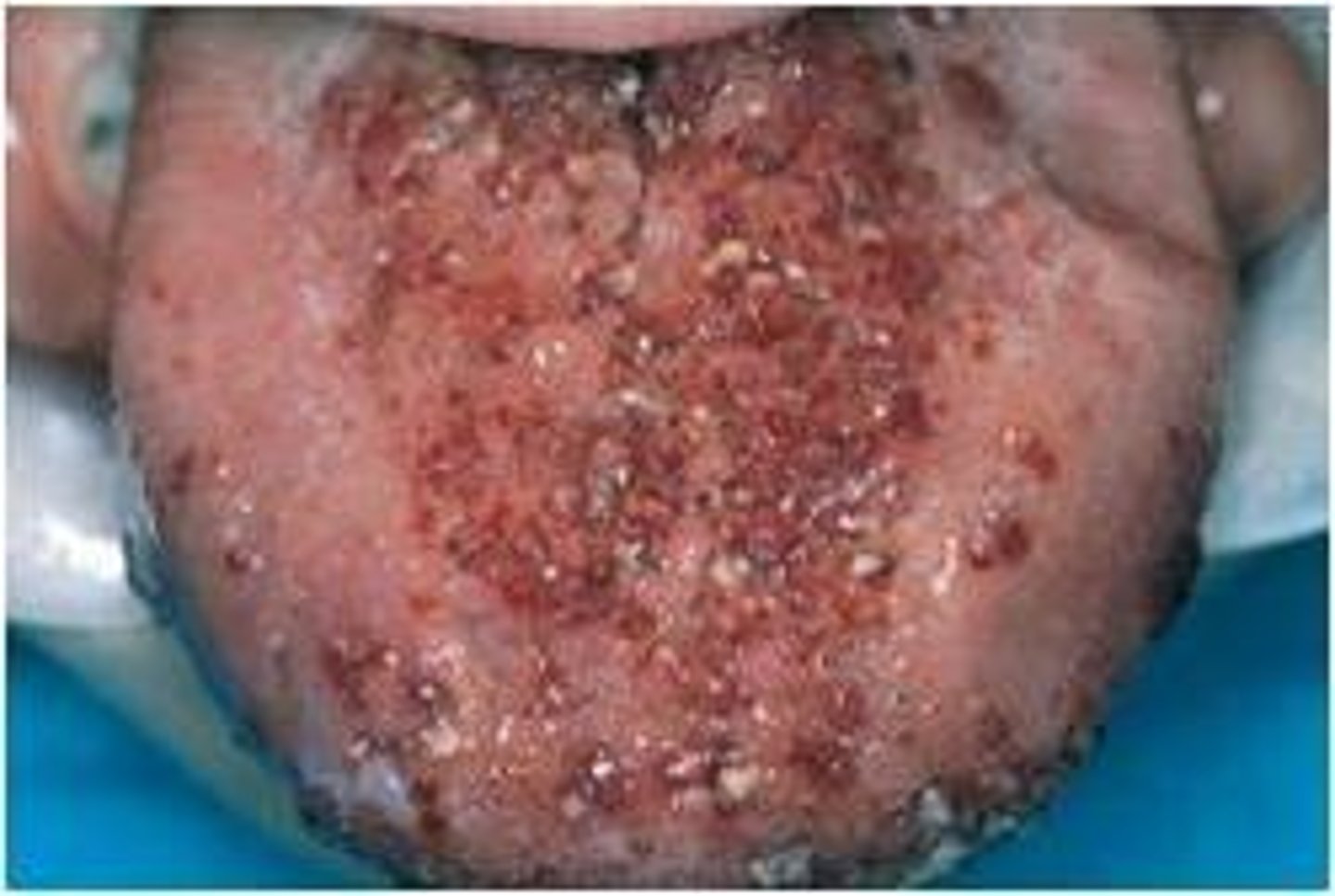
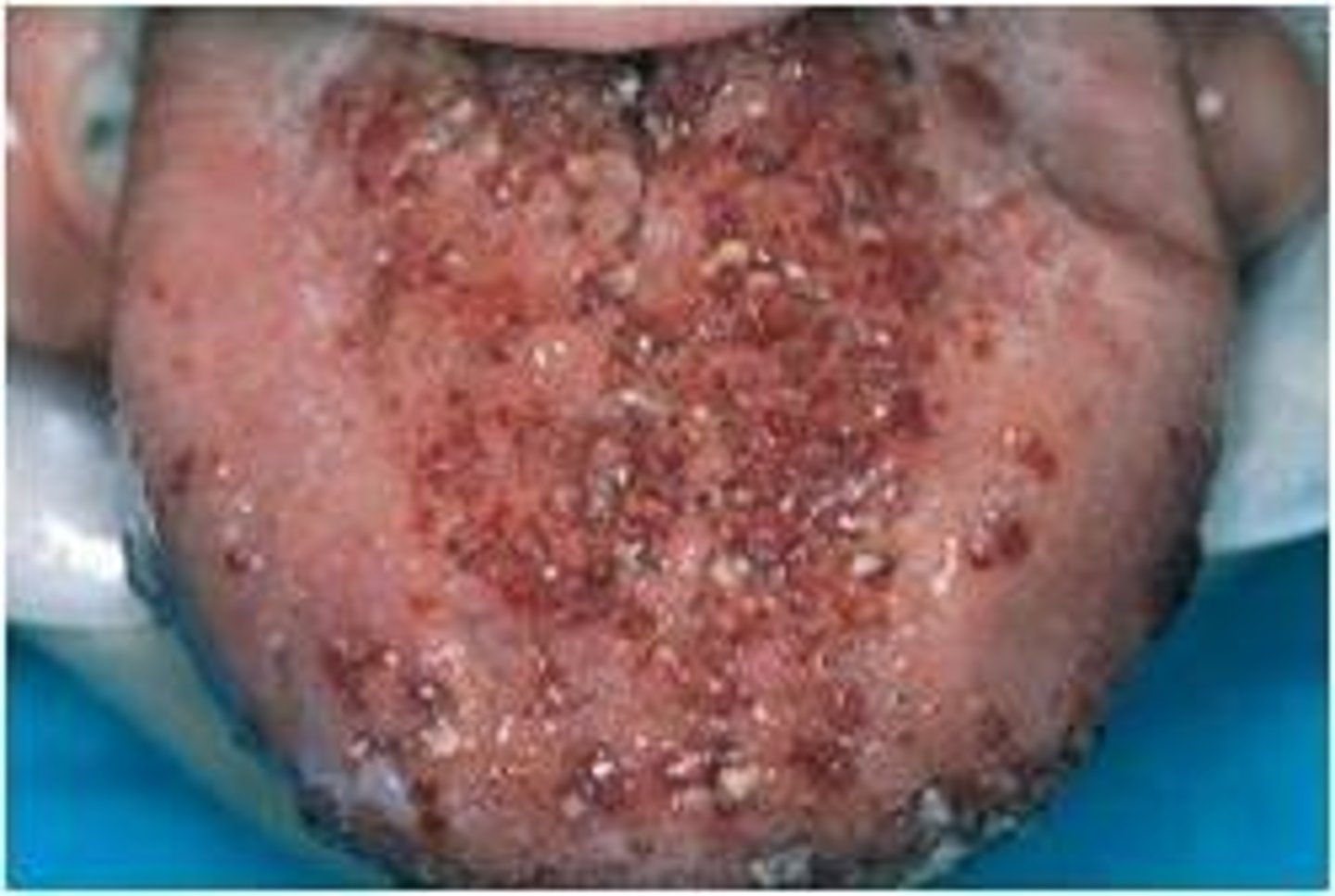
Lymphangioma
Clinical features of ______ is the predilection for the head and neck, oral lymphatic malformations are most frequent on the anterior two thirds of the tongue, where they often result in macroglossia and demonstrates a pebbly surface that resembles a cluster of translucent vesicles. Its treated with surgical excision, sclerotherapy, may recur
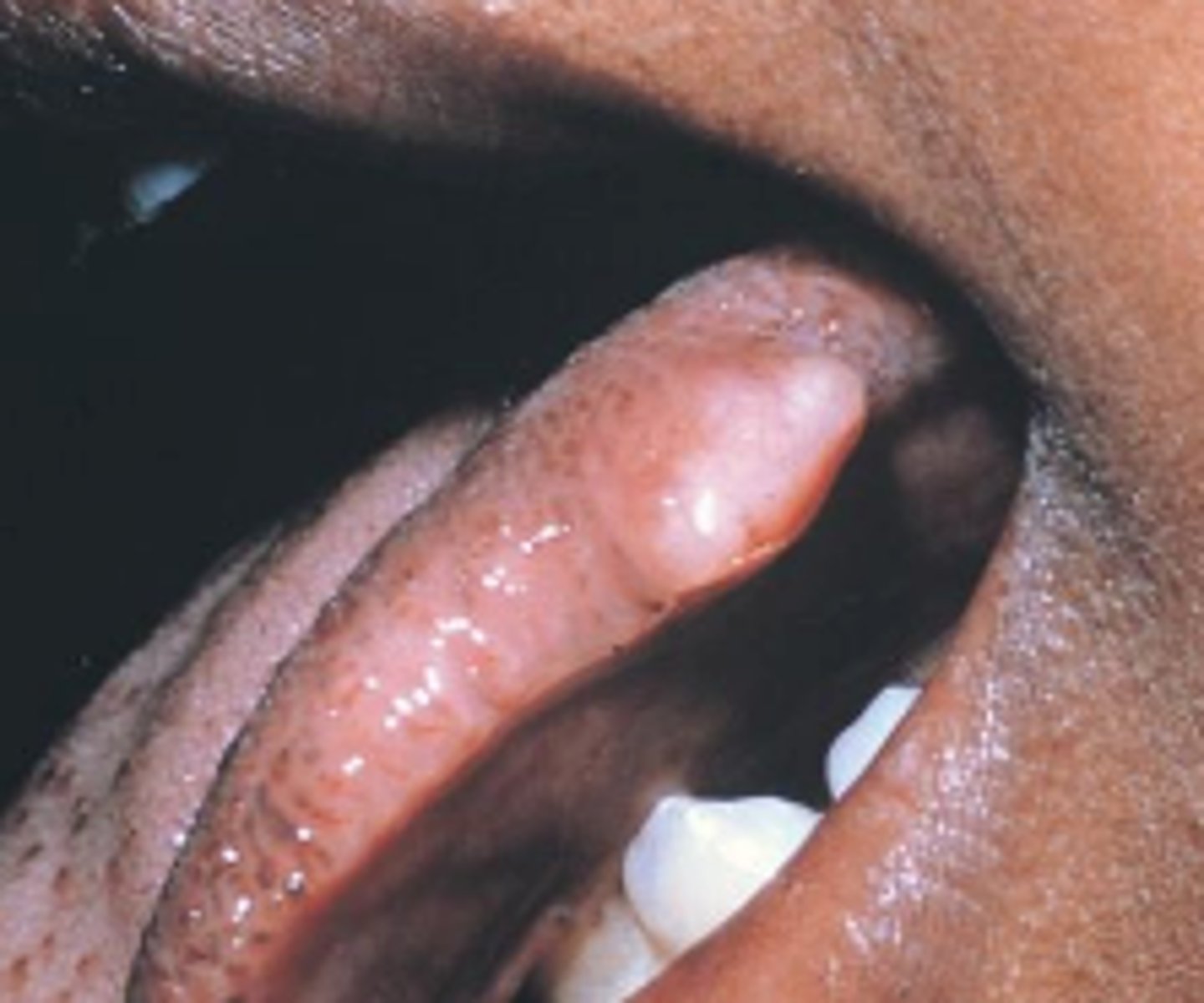
Neurofibroma
_____ is the most common peripheral nerve neoplasm, it can be a solitary tumor or be a component of neofibromatosis (don't worry about this).
Its slow-growing, soft, painless lesion that vary in size from small nodules to larger masses and can be in the soft tissue or central (in bone) and is treated by surgical excision.
-neoplasm= new or abnormal growth of tissue
-not very important
Schwannoma
______ is a benign neural neoplasm of Schwann cell origin and is uncommon. Its clinical features is slow-growing, encapsulated tumor that typically arises in association with a nerve trunk, its asymptomatic, the tongue is the most common location for oral schwannomas and can arise centrally.
Traumatic neuroma
____ ____ are the reactive proliferation of neural tissue after transection or other damage of a nerve bundle. Its clinical features are smooth surfaced, nonulcerated nodules, most common in the mental foramen area, tongue and lower lip, a history of trauma often can be elicited, may be intraosseous, about 1/3 are painful. Its treated with surgical excision
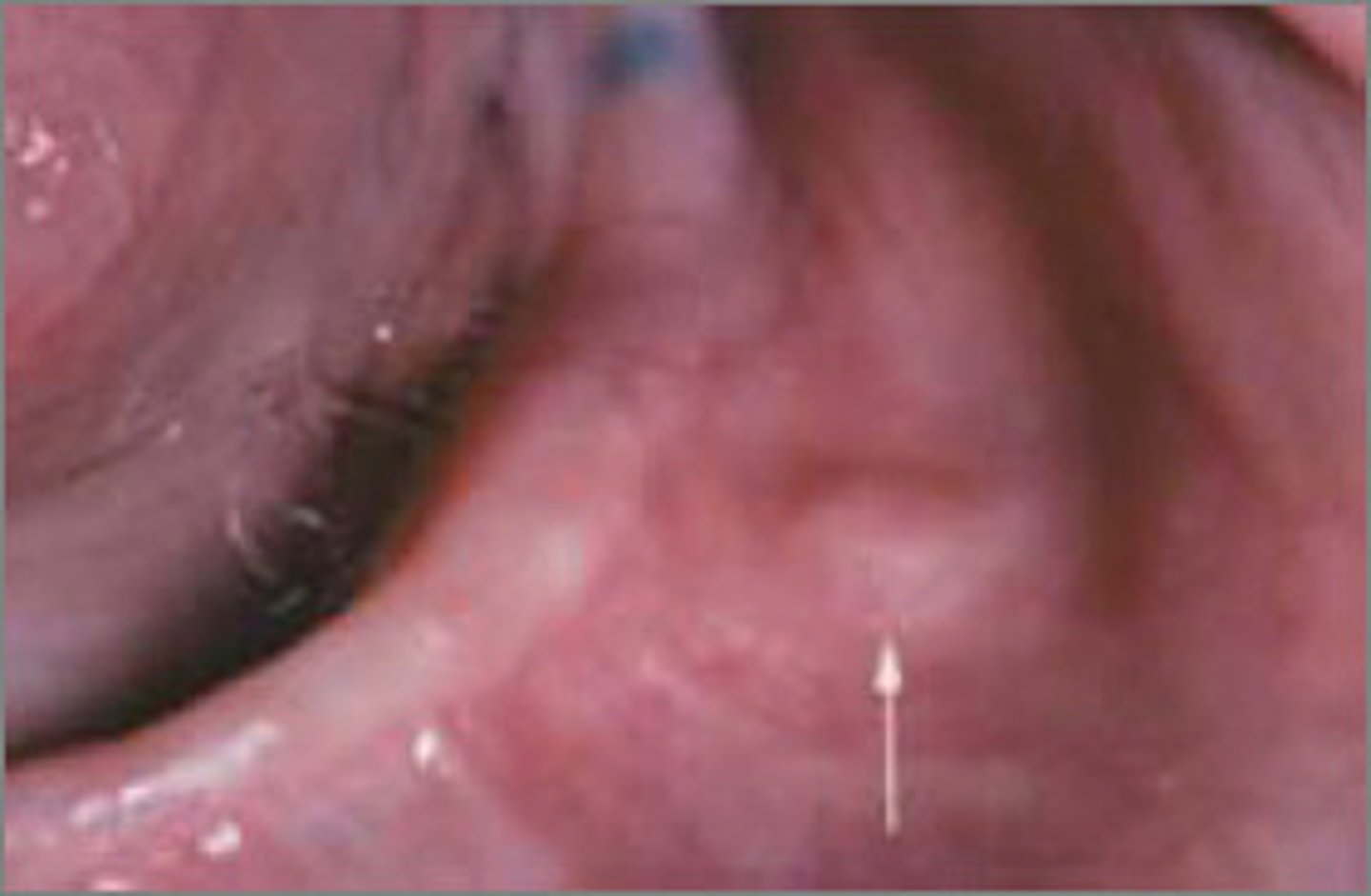
Mucosal neuroma
____ ____ are a benign neural lesion and is associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B), its soft painless papules or nodules located on the lips, anterior tongue, BM, gingiva and palate. Its treated by surgical excision, however, multiple lesions should be evaluated for MEN IIB
-not common
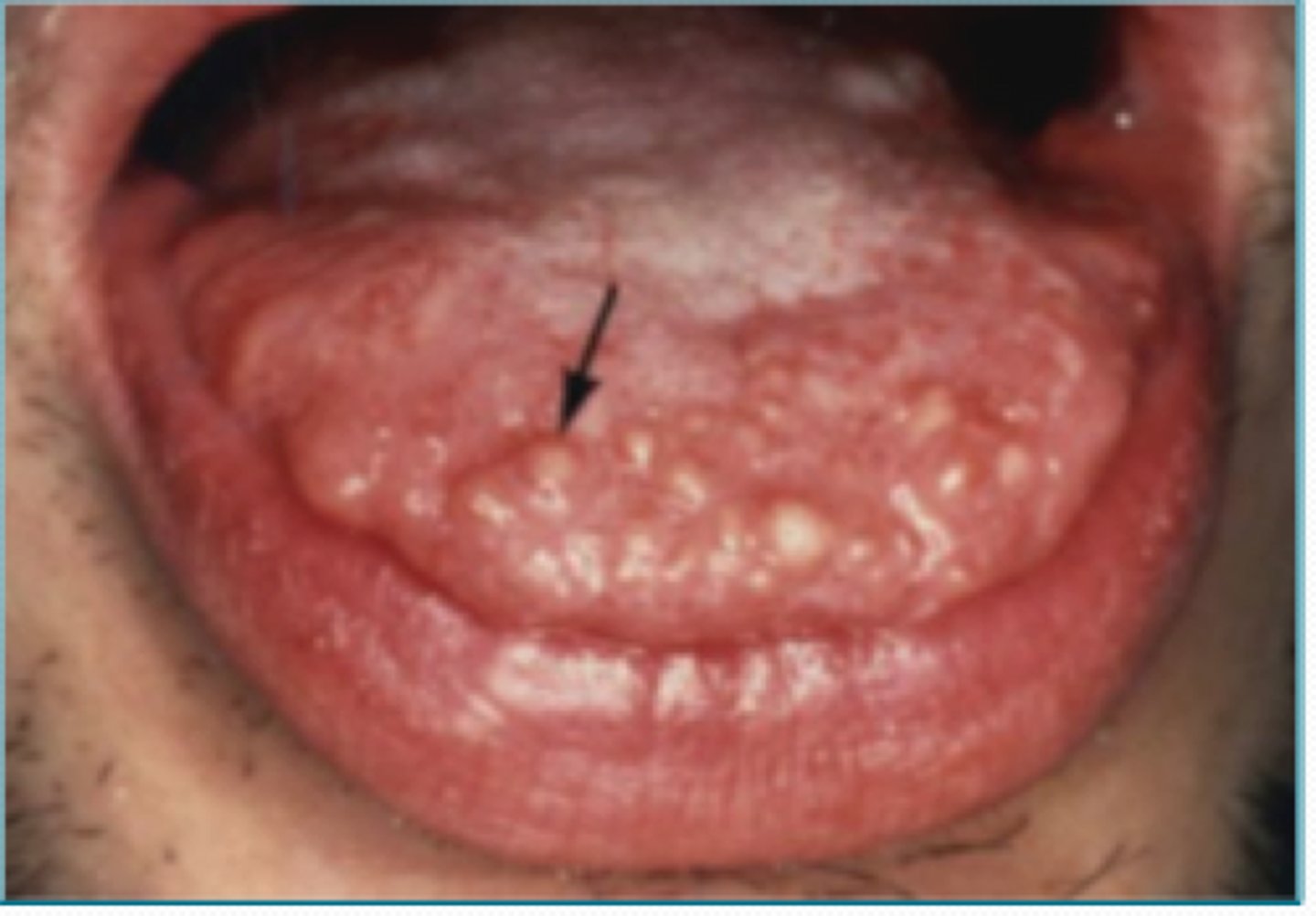
Giant cell granuloma, ossifying fibroma
Out of the 4 P's that commonly occur on gingiva, two of them exclusively occur on the gingiva which are the peripheral ____ ____ ____ and peripheral _____ ____
Pyogenic granuloma, peripheral fibroma
What two tumor types in the 4P's occur on the gingiva (oral cavity) but not exclusively?
None, all
what of the 4P's are considered neoplastic? Which are considered reactive?