Psych Unit 1 Part 1 & 2
1/90
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Psychology
The study of behavior and mental processes of humans and other animals
Behaviorist Perspective / Learning perspective
Observable and measurable behavior should only be studied ; Learned and observable behaviors
Psychodynamic Perspective
Unconscious forces and early childhood experiences affect our behavior and mental processes
Biological Perspective
Examine how biological and physiological processes impact behavior and mental process
Evolutionary Perspective
Natural selection ; The study of how behavioirs and mental processes present in the species today exist because of natural selection
Humanistic Perspective
Drive of personal growth and self-actualization impact behavior and mental process; how you see yourself
Cognitive Perspective
Interpretation of situations and mental process impact behavioral and mental processes ; Thinking, perceiving, learning, communication, solving problems
Social-Cultural Perspective
How behavior and thinking vary according across situations and cultures
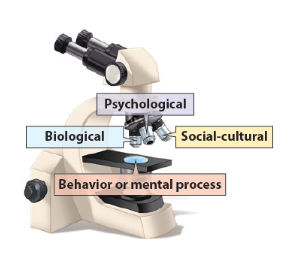
Biopsychosocial Approach
Understanding behavior and mental processes from three key viewpoints

Biopsychosocial Perspective
Biological - Genes and Nutrition
Psychological - Emotions and Behaviors
Social - Stress, Trauma, and Environment
Positive Psychology
The scientific study of human flourishing ; studying people who don’t have depression, etc. to help everyone
Developmental Psychology
(Field of Psychology) The study of how our behaviors and mental processes changes as we age ; Childhood → Adolescent → Lifespan
Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Nature
-Behaviors and Mental processes are in born or innate
-Biological
-Genetics Influence
Nature vs. Nurture Debate
Nurture
-Behaviors and Mental process are result of the environment or experiences
-Learned behaviors
-Observed behaviors
Personality Psychology
(Field of Psychology) The enduring distinctive, and unique characters/traits of an individual
Industrial Organizational Psychology (I/O) Psychology
(Field of Psychology) The study of the relationship between people and our work environments. ; How well people work in school or at work or smth
Counseling Psychology
Help people to cope with adjustments and crises
Challenges related to work, school, family, and relationships
Therapy and counseling
ur classic therapist
Clinical Psychologist
Assess, Diagnose, and treat mental, emotional, emotional, and behavioral disorders
Administer and interpret psychological test
Therapy and counseling
May conduct research
More medical
Psychiatry
Medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of deleterious (causing harm or damage) mental conditions. Related to: Mood, behavior, cognition, perception, and emotion. (like schizophrenia????)
Educational Psychology
the study of how humans learn and retain knowledge, primarily in educational settings like classrooms
Mean
Mathematical average of a set of numbers. ; Add the scores and divide by the number (N) of scores.
Median
Middle score in a distribution. ; Arrange scored from highest to lowest with half of the data above and half below this number.
Mode
Most frequently occurring data point in a distribution
Range
Difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. ; Subtract the lowest from the highest
Experimental Research
Only method used to determine cause and effect
Independent Variable (IV)
“If” factor ; factor being manipulated/changed
Dependent Variable (DV)
“Then” factor ; Outcome measured ; the factor changing BECAUSE of the Independent variable
Confounding variables
Variables controlled so do not influence the study ; control group ; the normal one
Descriptive statistics
Data used to measure and describe a population or data set
Used measures of central tendency (mean, median and mode)
Use measures of variation (range and standard deviation)
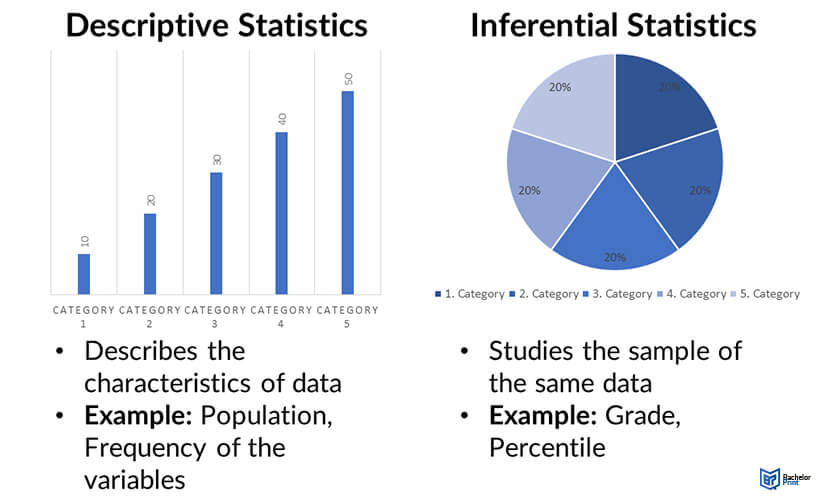
Inferential statistics
examine relationships between variables in sample
Data that allow us to infer/predict trends based on data taken from a sample of a population
Population
the entire group to be studied
Random Sample
everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected
Representative Sample
sub groups in the population are represented proportionally ; EX: Surveys that select individuals from every age, race, and socio-economic group
Convenience Sample
Selection of participants that is not random or systematic rather what is easiest available
Cannot be used to generalized results
Could results from Sampling Bias
EX: asking acquaintances, and surveying people in a mall, on the street, and in other crowded locations.
what does the experimental group receive/do not receive?
the IV (independent variable)
What does the Control group receive/do not receive?
Does NOT receive IV ; comparison group ; normal group
Random Assignment
Assigning subjects randomly to experimental and control groups
Reduces third variable problem
Skewed distribution
few high incomes (outliers) make the mean deceptively high
Standard Deviation
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Meaning of the Mean
Shows whether scores are parked together (similar) or dispersed (varied).
Low standard deviation indicated that the data points tend to be close to the mean of the data set.
How far off something is
lower the number the more similar
higher the number the more different
Statistical Significance
Statistical statement of how likely it is that a result occurred by chance
Typically reported as a ‘p’ value. A ‘p’ value of .05 or less means that it is 95% likely the results did not occur by chance
The claim that a set of observed data are not the result of chance but can instead be attributed to a specific cause
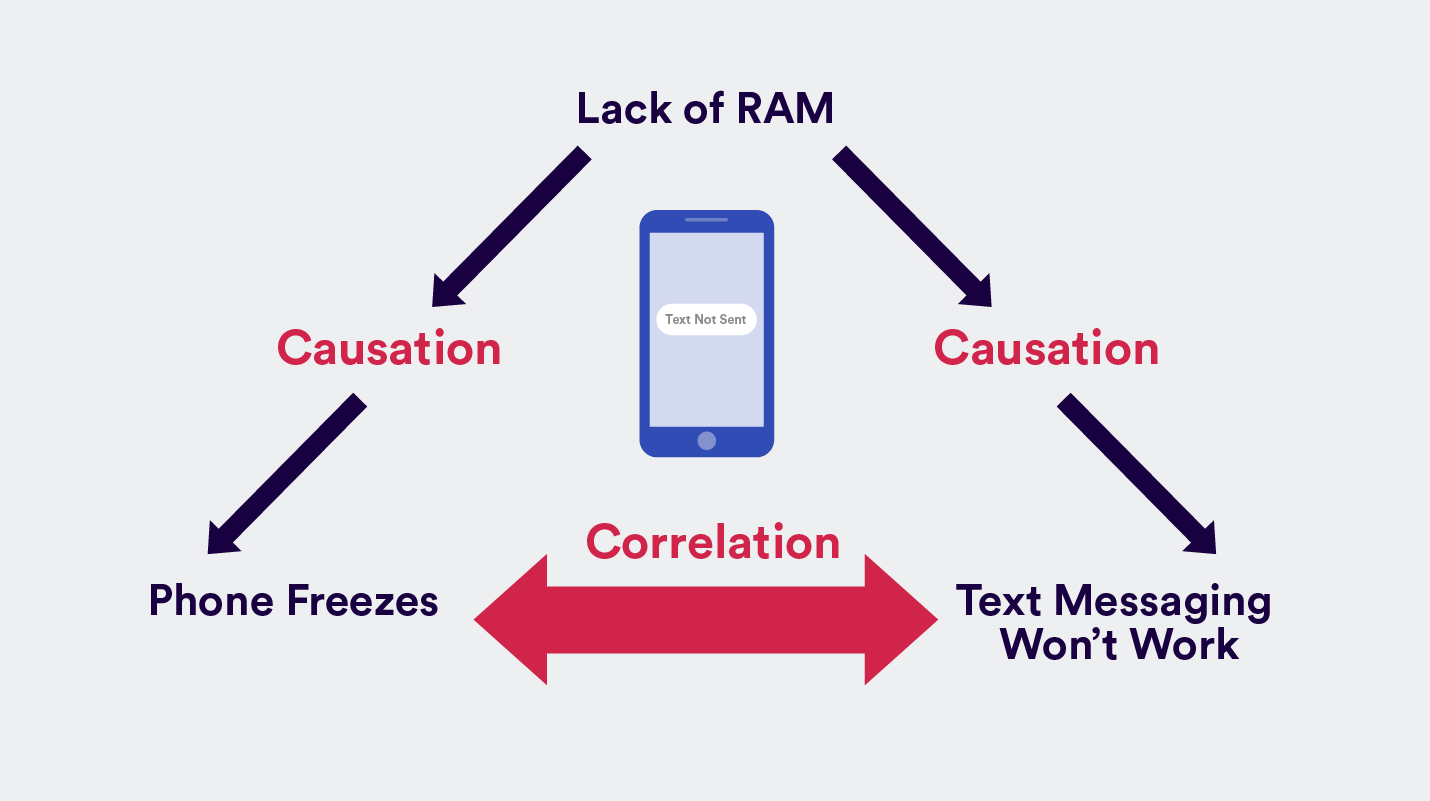
Third Variable Problem
confounding variable affects both variables but they are not related
Placebo Effect
Wen subjects react because of expectations alone not the treatment
Placebo
fake treatment given to subject in control group ; EX: fake pill
Self-report Bias
A possible methodology problem if research relies on participants descriptions of thoughts, feelings, or behaviors rather than direct observation and measurements
ex: practically a guess of “uuhhh 9 ig??”
Social Desirability Bias
Tendency for participants to attempt to present themselves in a favorable manner
EX: to appease someone based on their preferences
Single-Blind Study
Participants do not know which group they are assigned in
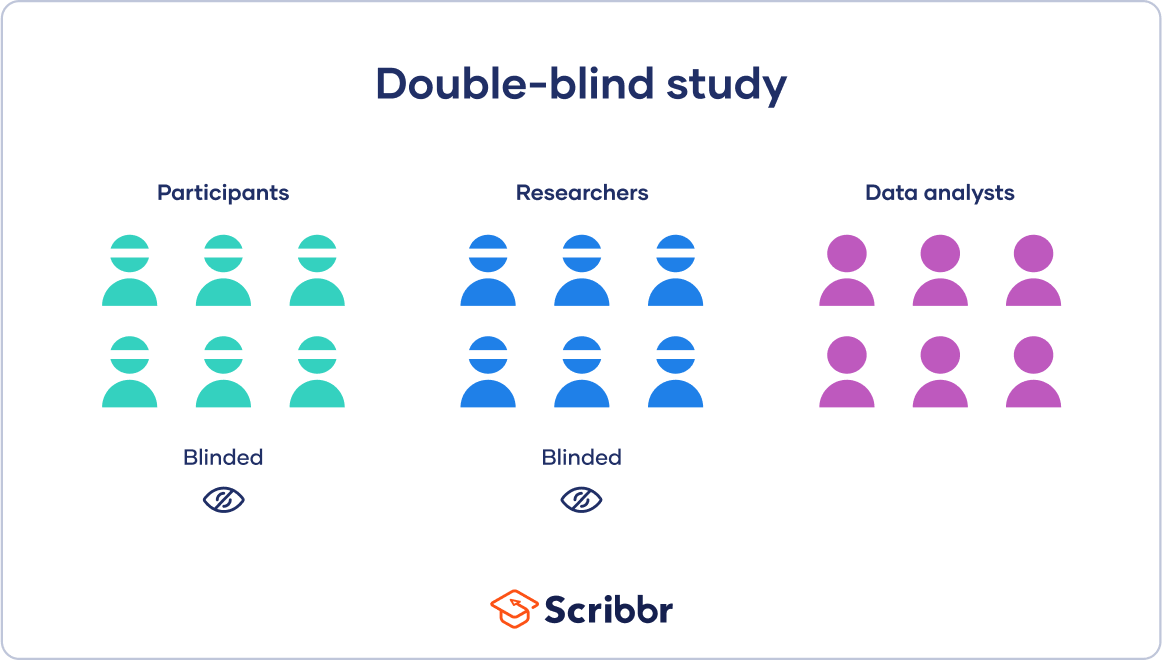
Double-Blind study
Both participants and experiments do not know which group subjects are assigned
Experimenter Bias
Experimenters to believe, certify, and publish data that agree with their expectations for the outcome of an experiment, and to disbelieve, discard, or downgrade the corresponding weightings for data.
simplified ex: having a big ass ego / being delusional
Experimental Method
the systematic procedures and steps followed in a research study to conduct experiments, gather data, and analyze results
Hypothesis
Predictions about behavior that can be tested
The best possible explanation for what you have observed, must be a testable hypothesis
Theory
Rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking
An explanation using an intergrades set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
Hindsight Bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that we would have foreseen it.
EX: “I knew that would happen.”
practically lying atp bruh to look cool or wtv
Overconfidence
The tendency to think we know more than we do
having a ego bru
False Consensus Effect
The tendency to assure one’s once opinions, briefs, attributes, or behaviors are more widely shared than is actually the case.
practically overexaggrations
Falsifiable
The logical possibility that a hypothesis or theory can be shown false by an observation or an experiment
Qualitative Research
Research methods that provides descriptive data
the quality of something
Quantitative Research
Research methods measuring variables using a numerical system
How much of something or the amount
Case study
In depth study of a person or small group
PRO: unique cases, a lot of information gathered
CON: inability to generalize to large population; observer bias
Survey
Method collecting self-reported attitudes, opinions, behaviors - best use with likert-scale
PRO: cheap, quick, and large number of people
CON: inaccuracy of self-reports; biased wording of questions
“trust me bro”
Psychological tests
Procedures designed assess specific traits, intellect, behaviors
PRO: reliable information that can predict behavior
CON: difficult to create; question bias
Naturalistic Observation
Subjects in their own environment with no interaction from researcher
PRO: spontaneous behavior
CON: observer bias; no control or repeats
Lab Obervation
Subjects observed in setting where researchers have some control
PRO: use of specialized equipment
CON: subjects know they are being watched; observer bias

Meta-Analysis
Synthesizing the results of multiple studies of a similar research question or topic
Method allows for compint a combined size effect across of all of the studies
Effect size - how meaningful the relationship between variables or the difference between groups; practical significance of research finding
Benefit allows small studies to be combined into one larger study
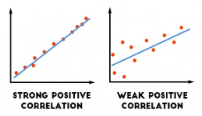
Positive correlation
two sets of data (variables) tend to rise or fall together
direct relationship
.01 → +1.0
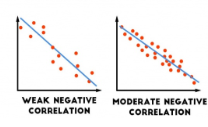
Negative Correlation
One set of data (variable) rises while the other falls.
Indirect relationship
-.01 → -1.0
No correlation
Scatter plot
uses dots to represent values for two different numeric variables
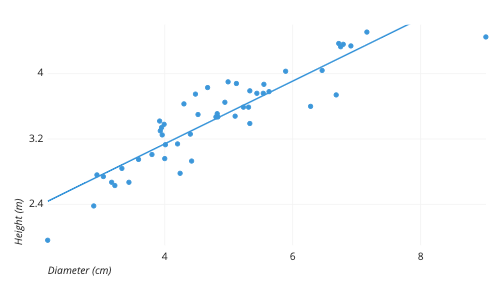
Correlational research
A measure of the extent which two factors vary together and how well each factor predicts change in the other
finding out the correlation coefficient
Correlation Coefficient
0 = no relationship
-1 or +1 perfect
Negative correlation - indirect relationship
Positive correlation - direct relationship
Peer review
Research proposal, results, articles, journals,
having other people look over your stuff
Normal curve
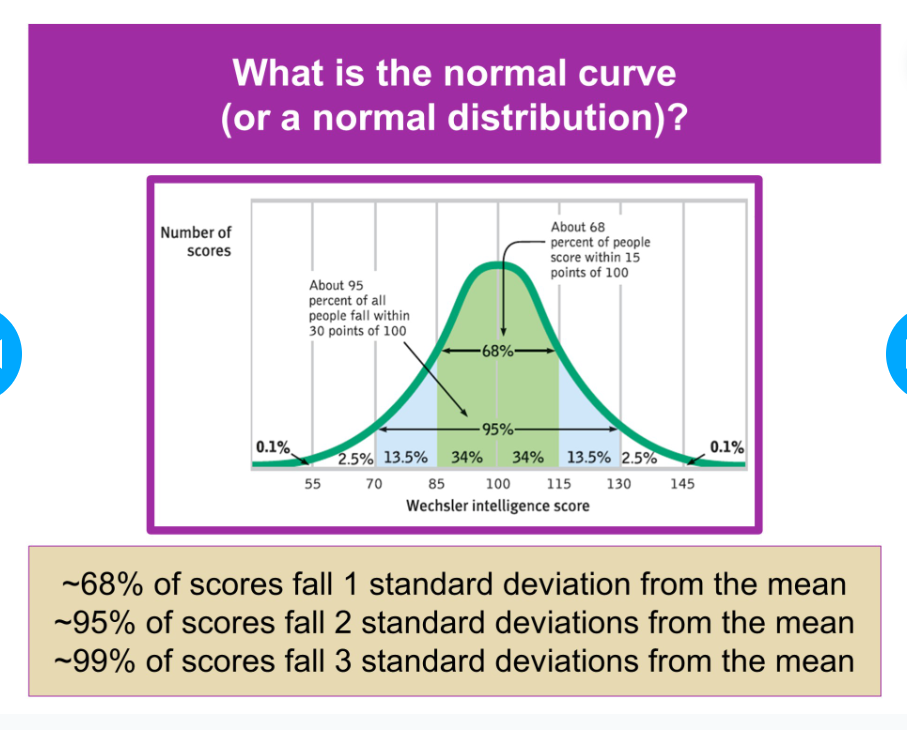
Central Tendency
Mean, Median, Mode, (maybe Range)
Likert-scale
a rating scale used to measure survey participants' opinions, attitudes, motivations, and more
Regression toward the mean
the tendency of results that are extreme by chance on first measurement—i.e. extremely higher or lower than average—to move closer to the average when measured a second time.
Directionality Problem
A situation where it is known that two variables are related but it is not known which is the cause and which is the effect
Illusory Correlations
Perceiving a relationship where non exists
Or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
basically what you think a superstition is
APA Ethical Guidelines
Informed Consent given by someone 18 or older
Informed Assent given by a minor
Confidentiality ; Anonymity
Deception only acceptable when benefits outweighs the risk and subject must be debriefed at the end.
Debriefing about the purpose of study and finding
Confederates - research actors
Replication
Reproducing a study to see if you get the same results
APA with animals
Treat animals humanely
Minimize the animals pain and discomfort
Must serve clear scientific purpose
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
Establishes ethical guidelines for human and animal research
Sampling bias
occurs when some members of a population are systematically more likely to be selected in a sample than others
somewhat like a preference
Effect size
How meaningful the relationship between variables or the difference between groups; practical significance of research findings
Causation vs. Relationship
Operational Definition
A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study, so study can be replicated
Generalizability
the measure of how useful the results of a study are for a larger group of people or situations
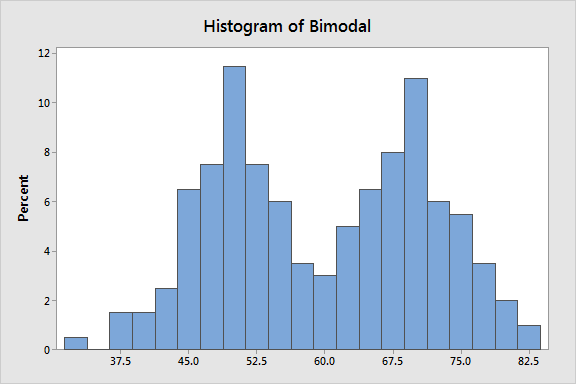
Histogram
a chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable's values as a series of bars ; another type of graph
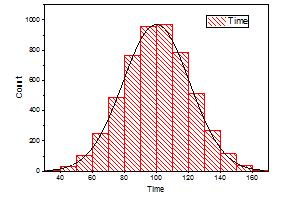
Bimodal Distribution
A type of distribution characterized by two distinct peaks.
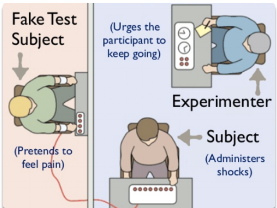
Milgram’s Study
The set-up and outcome caused the APA to revise their guidelines
He proves that humans would harm another person at the directive of an authority fire
Reliability
The consistency of the dinging or results of a psychology research study
Validity
Assumes that the test in question measures precisely what it aims to measure, meaning the data collected is accurate and represents some truth compared to others outside of the study
Simple: the quantity or quality of something being true