AP Biology Unit 1 Review
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
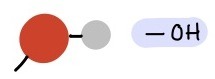
Hydroxyl Group
(-OH), Polar/hydrophilic
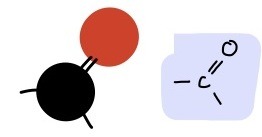
Carbonyl Group
(>C=O), polar/hydrophilic
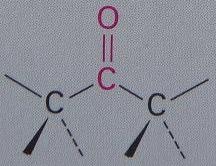
Ketone
Carbonyl group is w/in a carbon skeleton (Ex: Acetone)
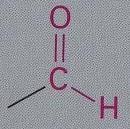
Aldehyde
Carbonyl group is at the end of a carbon skeleton (Ex: Propanal)
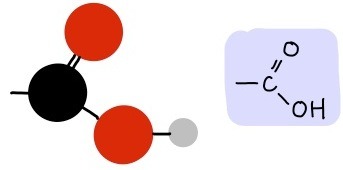
Carboxyl Group
(-COOH), polar/hydrophilic, an acid (releases H+ in ionized form)
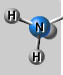
Amino group
(-NH2), polar/hydrophilic, a base (absorbs H+ in ionized form)
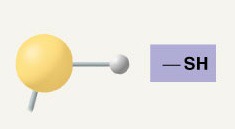
Sulfhydryl Group
(-SH), polar/hydrophilic, In disulfide bridges (protein folding)
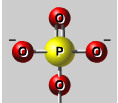
Phosphate Group
(-OPO3^2-), Strong - charge (polar)/hydrophilic
Methyl Group
(-CH3), nonpolar/hydrophobic
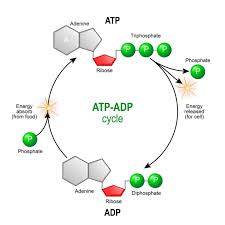
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
triple phosphate groups bonded w/ adenosine
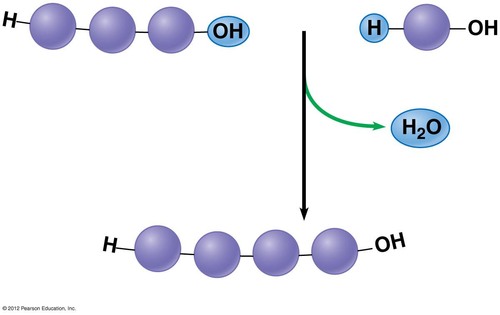
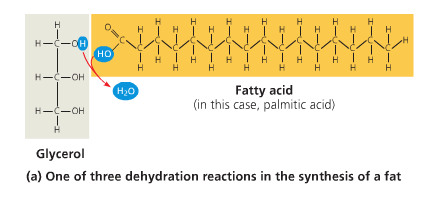
Dehydration Reaction
chem reaction in which 2 molecules become covalently bonded w/ the removal of a water molecule (from H or OH on either monomer)
Ends of poly/monomers must have an -H or -OH (hydroxyl group)
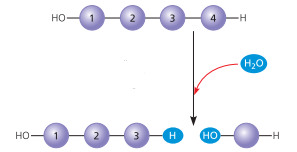
Hydrolysis
chem reaction in which 2 molecules are separated w/ the addition of a water molecule.
organic compound
Compounds that contain carbon
hydrocarbon
An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen, nonpolar/hydrophobic
Types of macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Types of Monomers
Monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides
Elements of Lipids
CH (very little O)
(P in phospholipids)
Elements of Carbs
CHO
Elements of Proteins
CHON
Elements of Nucleic Acids
CHONP
Ratio of CHO in monosaccharides
some multiple of CH2O
A sugar has
a carbonyl group (>C=O) (ketone or aldehyde) and multiple hydroxyl groups (-OH)
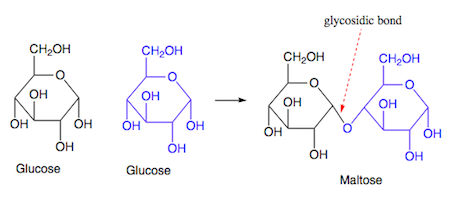
glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
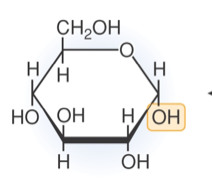
Which is a monosaccharide?
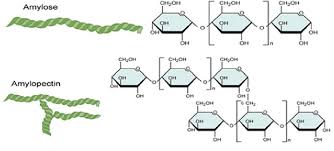
Starch
storage polysaccharide in the form of glucose monosaccharides in plants.
spiraling, can be unbranched (amylose) or somewhat branched (amylopectin)
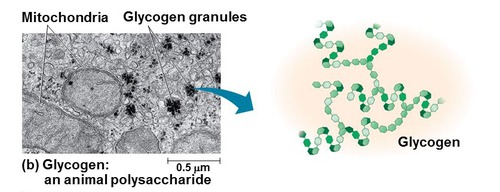
Glycogen
SHORT TERM storage polysaccharide in the form of glucose monosaccharides in animals (found in liver or muscles)
spiraling, extensively branched
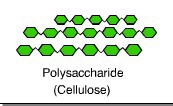
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide in the form of glucose monosaccharides that makes up the cell wall in plant cells
Straight chains held together by hydrogen bonds
Chitin
structural polysaccharide in the form of glucose monosaccharides that makes up the exoskeletons of arthropods and cells walls of fungi
Glucose monosaccharides have N containing-attachment, unlike Cellulose
Which macromolecule is not made of polymers?
Lipids
All lipids are
hydrophobic/nonpolar (mostly hydrocarbon regions)
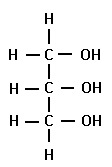
Glycerol
an alcohol composed of a three-C chain, each with a hydroxyl group (-OH)
serve as the backbone for a triglyceride.
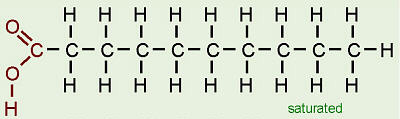
fatty acid
A long carbon skeleton (16-18 C's) w/ a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a hydrocarbon (makes it an acid)
Fat (triglyceride)
3 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol with an ester linkage. Long term energy storage in animals
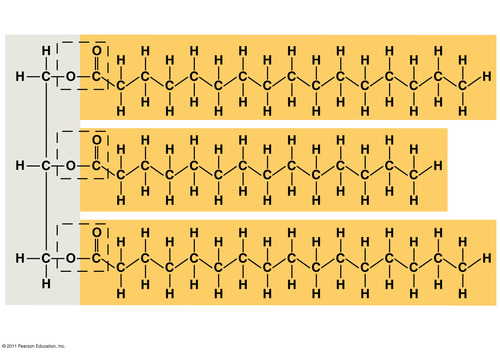
Ester linkage
a covalent bond between a hydroxyl group (glycerol) and a carboxyl group (fatty acid) created with a dehydration reaction
Saturated fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain has no double bonds between carbon atoms (max # of H's)
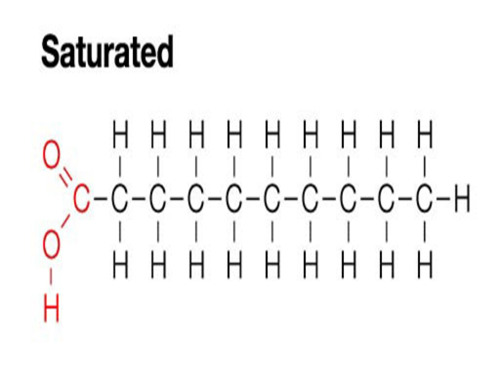
Sat fats are
solid at room temperature - hydrocarbon chains (tails) lack double bonds, making them flexible enough to pack together
Unsaturated Fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain has double bonds between carbon atoms (missing H's)
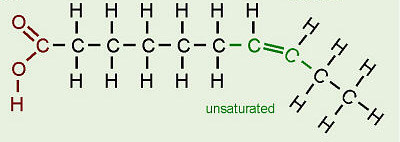
Trans fats
unsaturated fats that are artificially altered to be more saturated (H's added, allowing them to solidify). Unhealthy
Unsat fatty acids are
liquid at room temperature (emergent property) - hydrocarbon chains (tails) have double bonds, preventing them from packing together/creating space
Phospholipid
2 fatty acids and a phosphate group (-OPO3^2-) attached to a glycerol. amphipathic (part hydrophobic/philic)
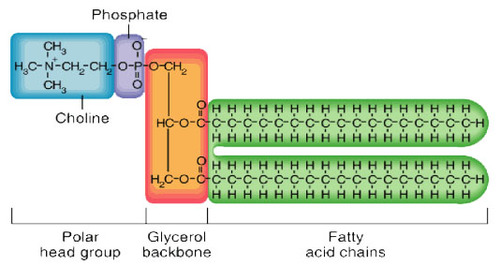
Phospholipid tails
hydrophobic/nonpolar
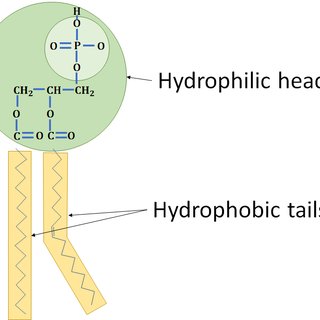
Phospholipid heads
hydrophilic/polar (- charge from phosphate group)
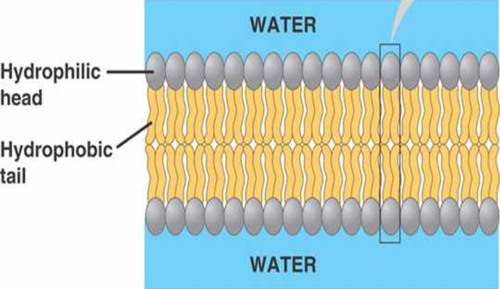
When phospholipids are added to water
they self-assemble into a bilayer, a double-layered structure, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior and the hydrophilic heads towards the exterior (ex: cell membranes)
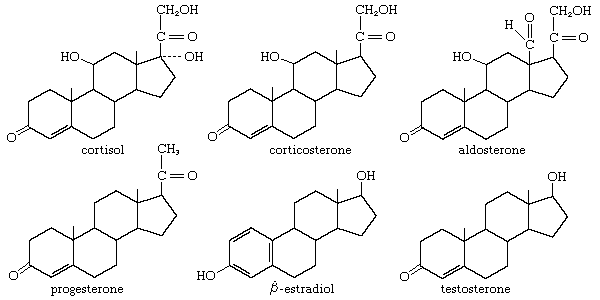
steroid
A type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings with various functional groups attached.
How many amino acids are there?
20 different amino acids
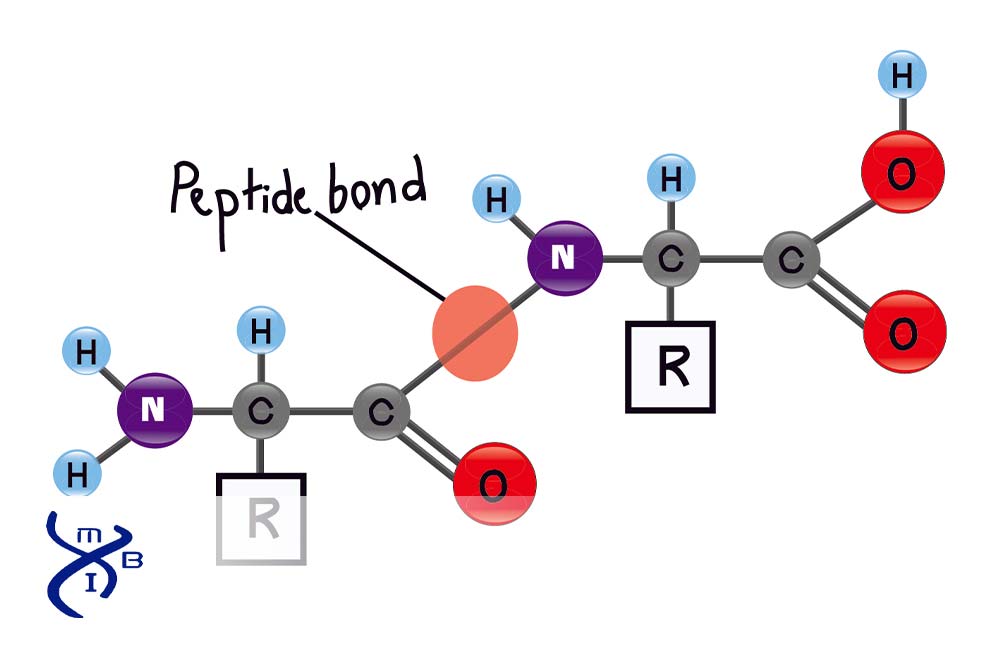
peptide bond
covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid and the amino group (-NH2) of another with a dehydration reaction
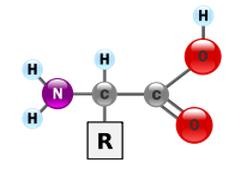
identify the amino acid
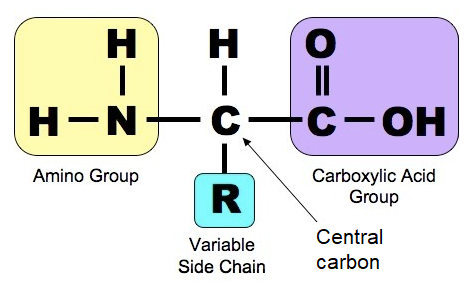
Parts of an amino acid
Central Carbon, Amino group, carboxyl group, Hydrogen, R group
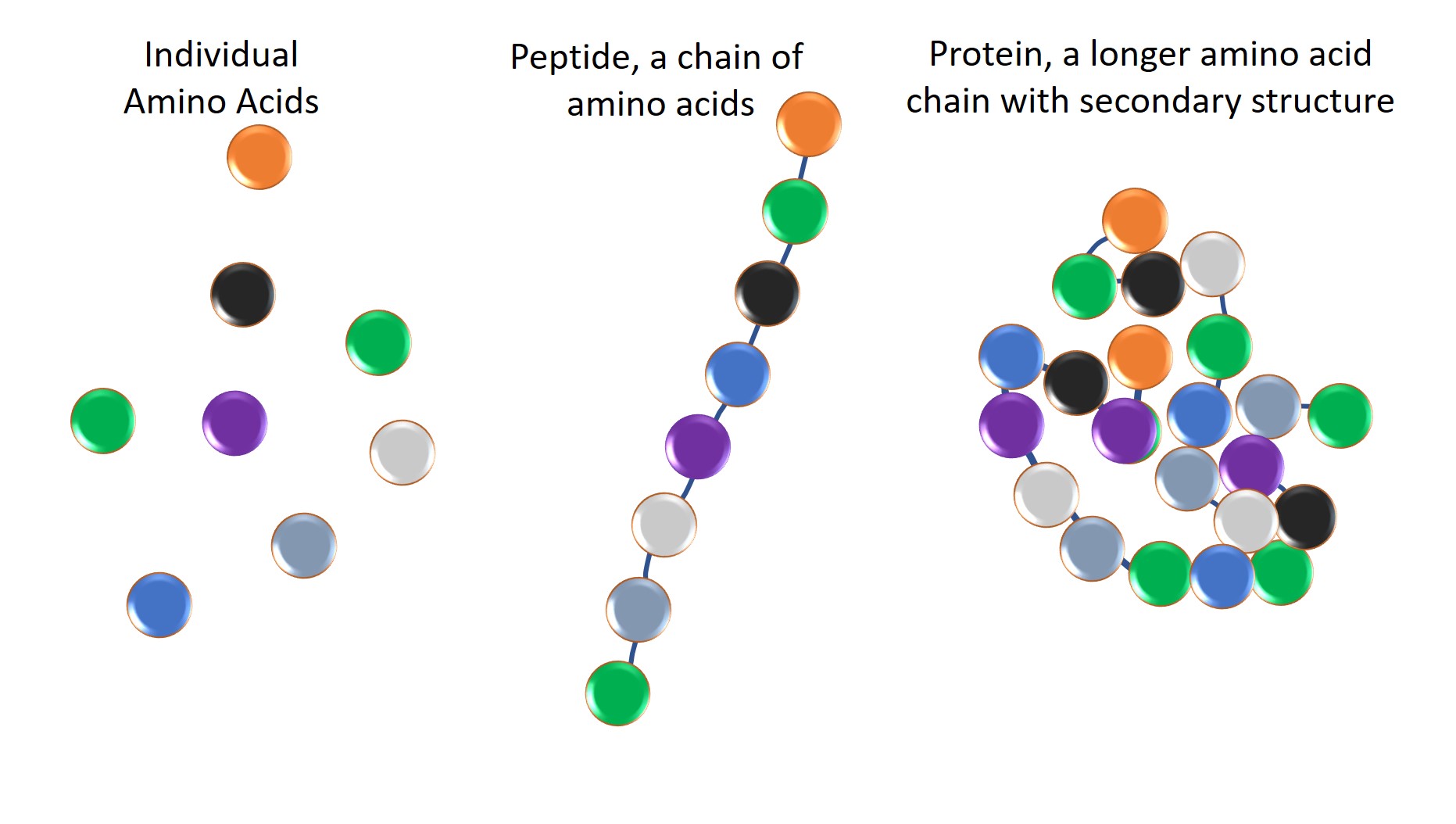
protein vs polypeptide
A protein is one or more polypeptides that has been folded into a fixed structure. A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids
R group/side chain
part of amino acid extending from the backbone that determines the molecule's physical and chemical properties
can be nonpolar/hydrophobic, polar/hydrophilic, or electrically charged/hydrophilic (acid= - / basic= +)
What is the shape of a protein determined by?
the sequence of amino acids determined by DNA
How many levels of protein structure are there?
4; primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary (2+ polypeptides)
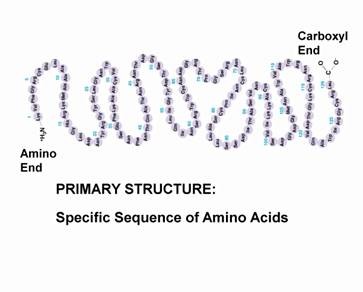
primary structure
linear chain of amino acids determined by DNA that ends with an amino group or a carboxyl group
dictates secondary and tertiary structure due to backbone and r groups interacting between the amino acids
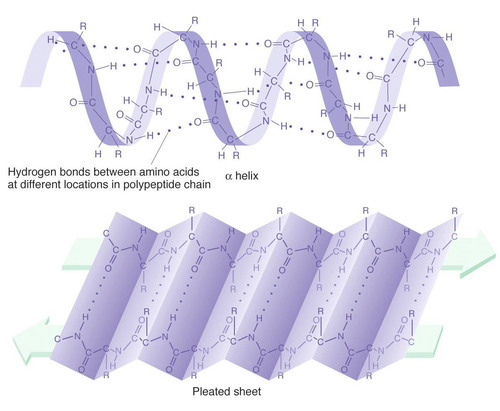
Secondary structure
regions stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone (NOT R groups)
the coils (alpha helixes) and folds (beta pleated sheets) of a protein
Tertiary structure
3D, overall unique shape of a polypeptide, stabilized by interactions between R groups
Largely determined by the hydrogen bonds betw. polar r groups and ionic bonds betw. +/- r groups
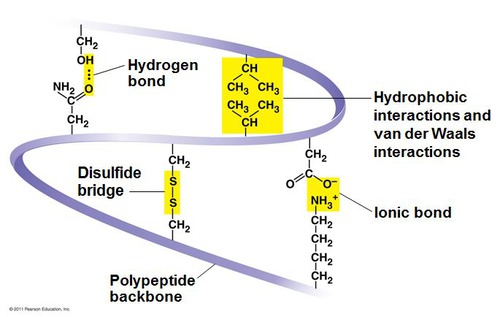
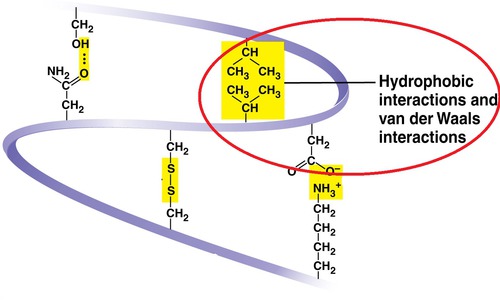
hydrophobic interactions
tertiary structure - when hydrophobic/nonpolar side chains end up in clusters on the inside of the protein (out of contact with water), held together by van der Waal interactions
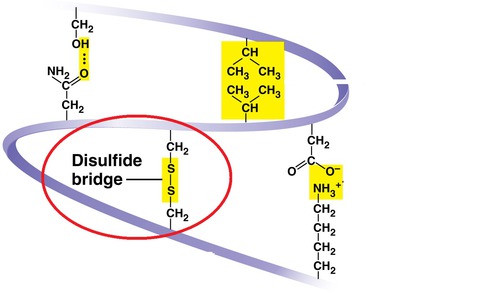
disulfide bridges
tertiary structure- A strong (and ONLY) covalent bond formed when the sulfur of one cysteine monomer's sulfhydryl (-SH) r group bonds to the sulfur of another cysteine monomer's sulfhydryl (-SH) r group
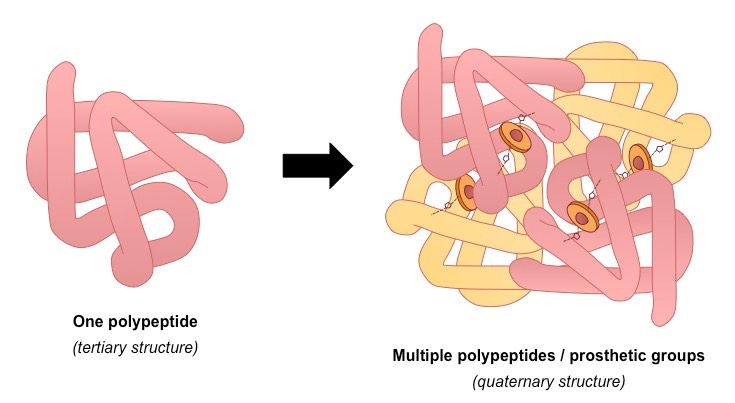
Quaternary structure
association of two or more polypeptide subunits aggregated into one functional macromolecule (some proteins only)
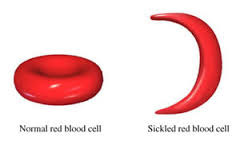
Mutations in primary structure (Sickle Cell Disease example)
Mutation causes glutamic acid (normal hydrophilic r group) to be replaced by valine (hydrophobic r group) in the hemoglobin protein --> abnormal fiber-shaped cells clump together --> reduced ability to carry oxygen
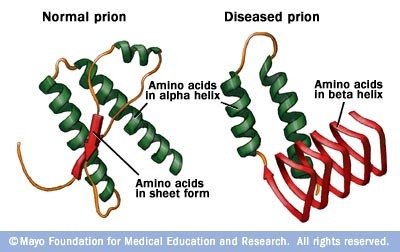
Misfolding proteins
Causes malfunctional/nonfunctional proteins
-Diseases: Alzheimer's, mad cow disease, Parkinson's, dementia
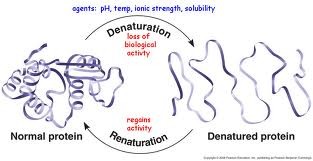
Denaturation
a process in which a protein unravels/loses its native conformation (back to primary structure), thereby becoming biologically inactive, due to unsuitable chemical/physical environments breaking the interactions and bonds within it
Ex:) pH levels, salt concentrations, temperature (fevers), aqueous -> nonpolar solvent (some proteins)
Nucleic Acid polymers
DNA and RNA
gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
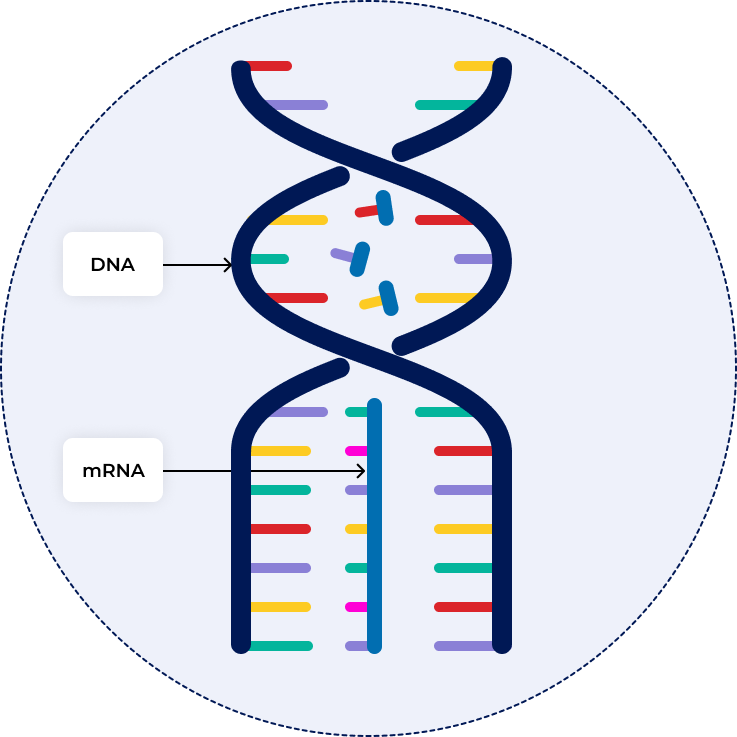
DNA vs RNA
DNA: deoxyribose sugar, thymine base, double strand
RNA: ribose sugar, uracil base, single strand
deoxyribose sugar vs ribose sugar
deoxyribose lacks an O atom on the 2nd C of the ring
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
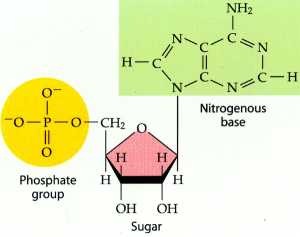
nucleotide parts
phosphate group, nitrogenous base, and pentose sugar (base + sugar = nucleoside)
N base = basic bc N usually takes up H+'s
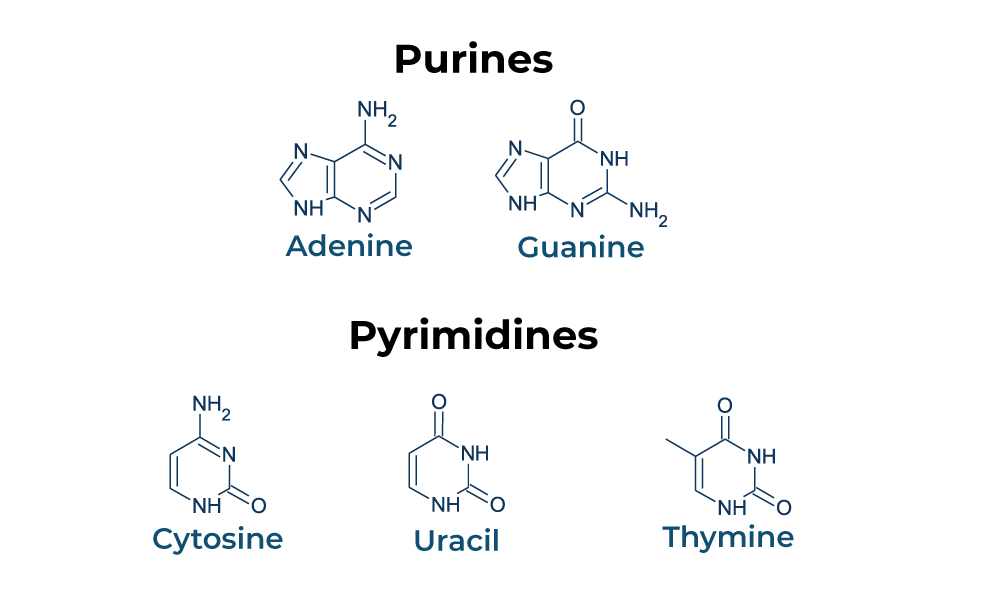
pyrimidines
Cytosine (C) - DNA + RNA
Thymine (T) - DNA
Uracil (U) - RNA
has one 6-memebered C and N ring, differing in functional groups
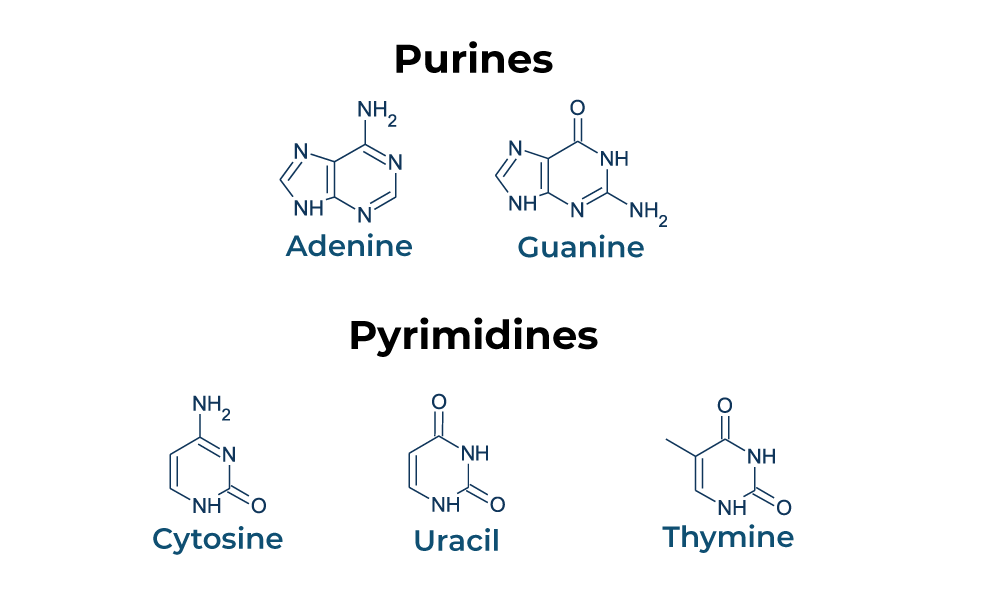
Purines
Adenine (A), Guanine (G) - DNA + RNA
has a 6-membered ring fused to a 5-membered ring, differing in functional groups
phosphodiester linkage
covalent bonds from a dehydration reaction that join adjacent nucleotides between the -OH group of the 3' carbon of one nucleotide and the phosphate on the 5' carbon of the next (creates sugar-phosphate backbone (excludes base))
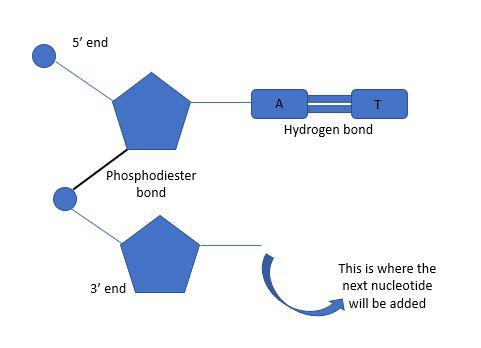
What direction do the polynucleotide backbones of DNA strands go in?
antiparallel/opposite of each other (5' to 3' and 3' to 5')
5’ Carbon end
phosphate group
3’ Carbon end
hydroxyl group
structure of a DNA double helix
antiparallel sugar-phosphate backbones on the outside, and bases paired on inside, held by hydrogen bonds
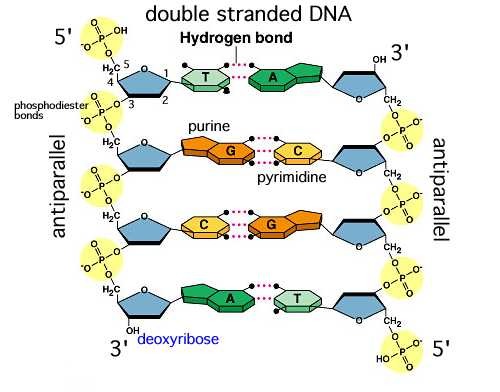
Base pairings (DNA)
A-T
G-C
Base pairings (RNA)
A-U
G-C
Sections of DNA (% example)
a percentage of one base is going to match its complementary base (Ex: 17% T, 17% A, 33% G, 33% C)
Comparing DNA and/or protein sequences can be used to find
closely related species
Genomics
study and comparison of genomes within a single species or among different species
proteomics
the study and comparison of all the proteins that result from an organism's genome
emergent property
a characteristic of a system that does not appear in any of the system's component parts
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
the total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus.
atomic mass
The average mass of all the isotopes of an element
isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
radioactive isotope
An isotope whose nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy (unstable)
potential energy
stored energy (capacity to cause change) that results from the position or shape of an object
stability of electrons
most stability: closest shell to nucleus/low energy (lost energy = heat)
least stability: farthest shell from nucleus/high energy
valence electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell (valence shell) of an atom; these are the electrons involved in forming bonds/determine chemical behavior
full valence shell = unreactive
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
types of covalent bonds
single, double, triple pairs
an atom's valence (bonding capacity) is determined by the number of electrons needed to fill the valence shell
electronegativity
a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons
nonpolar covalent bond
a bond in a molecule with a neutral charge (e- are equally shared/equal electronegativity). hydrophobic
polar
a molecule with positive and negative charges (e- are unequally shared/one atom is more electronegative). hydrophilic
ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge after gaining/losing electrons
cation
A positively charged ion
anion
A negatively charged ion
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
**electron transfer does NOT create the bond; it allows a bond to form bc it results in 2 ions of opposite charges
ionic compounds (salts)
compounds composed of cations and anions, connected by ionic bonds
hydrogen bonds
when an H atom that is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (creating + charge in the H) attracts another atom (- charge) nearby