Biopsych - Unit 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Neurons
100 Billion
Cells that communicate
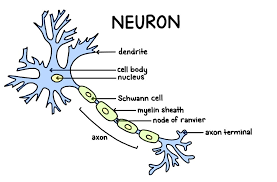
Structure of Neuros
Neurogenisis
growth of neuron
Glial Cells
support friends
provide nutrients, clean waste
compromise mylein
Dendrites
Receive info, input to soma
Soma
Cell Body
Keeps cell alive
Axon
tunnel highway
Myelin Sheath
Fatty layer / protection
Terminal
End of Neuron, releases neurotransmitters
Synpase
Junction to other neuron
Tiny gap
Receptors
On end of dendrites, next neuron
Neural Transmission
electrochemical communication within/between neurons
Resting potential
normal difference in electrical charge
Action Potential
electrical signal pulse, sent through neuron
Refractory/Recovery Period
work to restore
All or None Principle
stimulus has to reach a certain threshold in order for it to fire
Axon Collateral
action potential impacts all branches equally
Saltatory Conduction
“to leap” - action potential jumps from node to node of myelinated axon
Neurotransmitters
Chemical Messengers, can excite or inhibit
ACH - Acetylcholine
Muscle Contraction : stimulate muscle to contract
Memory + Learning : Plays crucial role in memory + learning (Alzheimers")
Automatic Nervous System : Regulates rest and digest functions
DOPAMINE (DA)
Reward + Motivation: reward system
Movement Control: regulates voluntary movement (Parkinson’s Disease)
Mood + Emotion: emotional response, low = depression + anhedonia
NOREPINEPHRINE (NE)
Fight or Flight : sympathetic nervous system (prepare body)
Attention & Arousal : focus & vigilance
Mood Regulation : Imbalances (depression + anxiety disorders)
SEROTONIN (5 - HT)
Mood Regulation:
Sleep + Wakefulness : regulates sleep cycle
Appetite + Digestion : Controls gastrointestinal
GABA
Inhibition of neuronal activity : preventing overstimulation & calm
Anxiety Regulations : anxiety reducers, 🔽 anxiety disorders, insomnia, seizures
Muscle Relaxation : Control muscles, 🔽 muscle spasm or tremors
Hind Brain
lowest set of structures (reptilian brain)
coordinates messages coming in & out of spinal cord, controls basic function of life
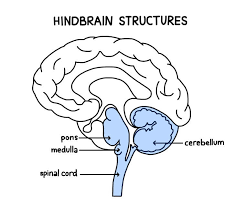
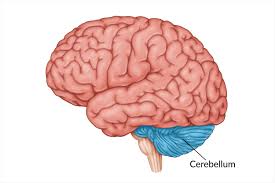
Cerebellum (sarah balance)
nonverbal learning, coordinates voluntary movements
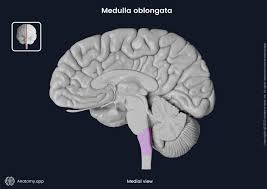
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing ; part of brain stem
Pons
regulates sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder, SOME senses, part of brain stem
MidBrain
“bird” or “amphibian” brain
sensory processing (vision and hearing)
Motor control and reflexes
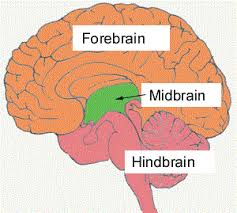
ForeBrain
highest level of brain
critical for complex cognitive, emotional, sensory, & motor functions
Cerebral Cortext
outermost layer
Subcortical Structures
inner structures
Gyri
folds
Sulci
grooves/gaps
Frontal Lobe
personality/decision making/impulse control
Parietal Lobe
helps process sensory info
Occipital Lobe
Vision/Visual data
Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing - through ears
memory
Basal Ganglia
intentional movements, rewards
Limbic System
emotion, learning, and memory
Thalamus
sensory gateway, directing signals, traffic control
HYPOthalamus
regulates body function, (fight or flight)
Amygdala
Emotions
emotions
esp. anger + stress
Hippocampus
Memory
Central Nervous System
brain, brainstem, spine
Peripheral
everything else
Automatic
involuntary & automatic commands (breathing, heart beat)
Somatic
voluntary commands (Info in+out of CNS)
Sympathetic
Fight or flight, heightening, action, arousel
Parasympathetic
Calms you down, normal, resting
Two Hemispheres
cerebral cortex, left + right
Corpus Callosum
Middle, bridge connecting halves, communicates
Left hemishpere
VERBAL PROCESSING : language, speech, reading, writing (CONTROLS RIGHT SIDE OF BODY
Right Hemisphere
NONVERBAL PROCESSING : spatial, musical, and visual (CONTROLS LEFT SIDE OF BODY)