Cell Structure and function homework
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Color is
Objects that are larger than the shortest wavelength of visible light
Nanometer nm is `
10^-19 m
Light microscopy can detect light
object that is less than 200nm but it will be blurry
Conventional light microscopy resolve
2 objects less than 200 nm apart
The greater the numerical aperture (n sin theta)
the better the resolution (resolve objects closer together)
Numerical aperture oil vs air
Oil is higher
Longer wavelength light from microscope light source
the worse the resolution (objects far apart to resolve)
Noise in a light image
random fluctuation in distribution of photos that pass through specimen
Not a good way to visualize living cell, but best for different feature distinguishing
Light microscopy of fixed and stained specimen
Dye hematoxylin has affinity for negatively charged macromolecules can reveal subcellular localization of
dna, rna, acidic proteins
In situ hybridization detects specific
RNA
In situ hybridization uses probes made out of
DNA
Fluorescence microscopy used to detect specific protein if
Protein fluorescent domain
antibody binds protein is attached to fluorophore
Fluorescent probes used in fluorescence microscopy
absorb light and then emit light at longer wavelength
Light absorbed by fluorophore, leading to later emission of light is
excitation light
Indirect immunocytochemistry, marker molecule leads to detection is attached to
secondary antibody that binds to primary antibody that binds a specific antigen
Confocal microscopy produced optical sections of specimen by
excluding out of focus light
Cause least amount of damage to specimen and allow deep imaging into sepectrum
infrared light in 2 photon applications
FRET absorbs what wavelength by one component and secon leads to emission of what wavelength
from shorter to longer
FRET signal
close together
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching detects
movement of tagged proteins or tagged molecules into bleached area
Method detect only targets close to surface of cover slip
TIRF
Switching fluorophores off and on can lead to pinpoint localization
Better than conventional or confocal fluorescence microscopy
Wavelength electron in electron microscope with 100,000 volts is 0.002 nm. So visible light with wavelength 400 nm has
200,000 fold longer wavelength than the wavelength of electrons
Which is better electron or light microscope
Electron because resolves objects closer together
Practical resolution of electron microscope for biological objects are 1 nm because
problems with specimen preparation
contrast with specimen
damage to specimen from high velocity electrons
practical resolution for electron microscopy is
200 times better than light microscopy with 200 nm wavelength
Beam electrons travels through specimen in
TEM transmission electron microscopy
Immunogold microscopy would be appropriate for
electron microscopy (gold particles)
3D images of specimen by
multiple TEM images taken at different angles then combined by image processing (em topography)
Taking images of identical molecules then combining them to product averaged image is
single particle reconstruction
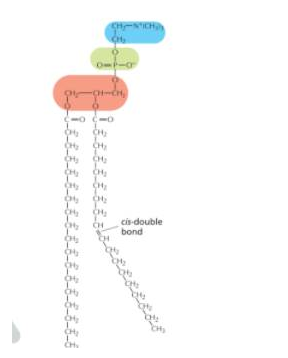
Phospholipid
Blue:polar end/ OH group/ WATER interacts with polar heads
Green: phosphate group/ WATER interacts with polar heads
Red: who knows
cis disulfite bonds: INCREASES FLUIDITY
How to know which is NOT phospholipid
The one without charge
Micelle

Least likely to move in lipid bilayer is
flipflop
Phospholipids synthesized on one leaflet of lipid bilayer, movement of one of these lipids to other leaflet
requires flippases or translocases (transport)
Lipid bilayer with greater distance/ longer membrane spanning proteins?
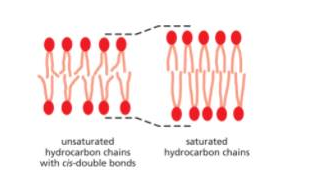
amphipathic lipid with SATURATED fatty acids. Saturated is straight, unsaturated is bend with cis bond
Greater fluidity in lipid bilayer
amphipathic lipid with UNSATURATED fatty acid tails (prevent tight packing)
Extracellular side has blue
Because GPI anchor is on top, extracellular on top
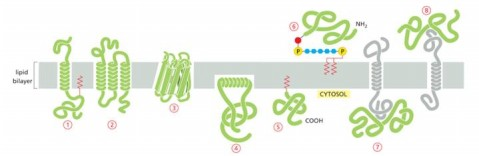
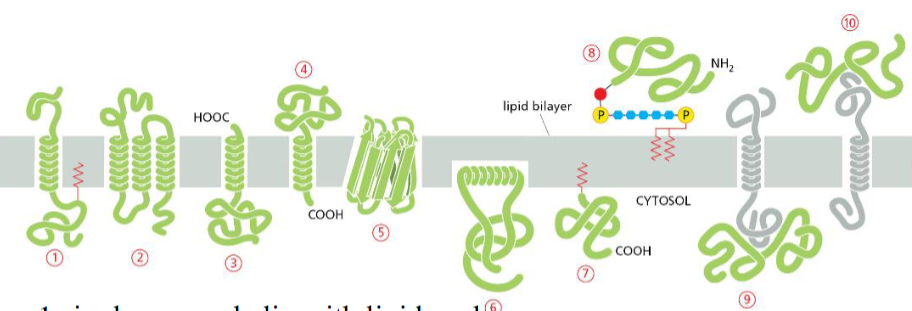

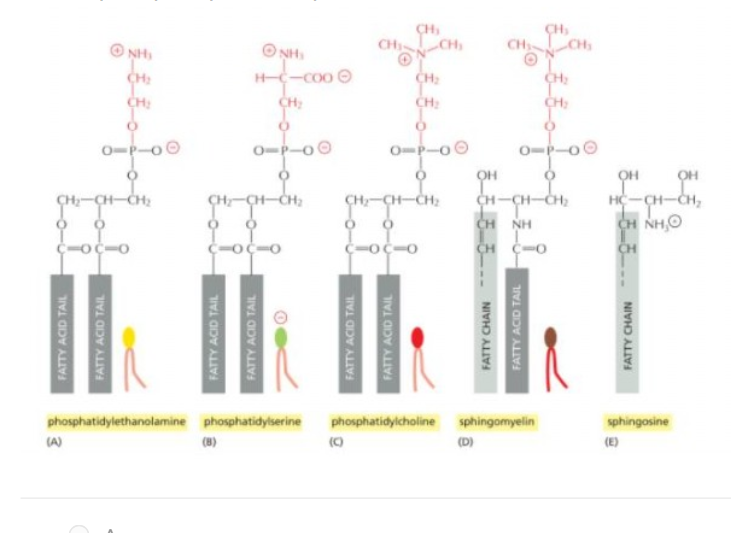
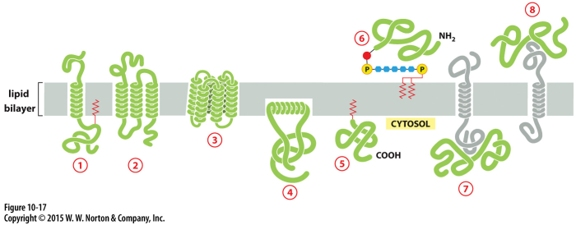
Protein that is integral membrane by means of lipid anchorage (no transmembrane) on cytosolic side
Number 5
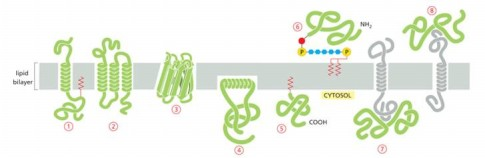
Peripheral membrane in cytosol
Number 7
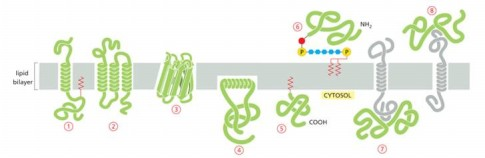
Protein anchored in membrane by a-helix interacts with only one membrane leaflet
Number 4
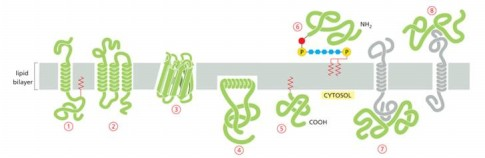
GPi anchored protein attached to
inside (lumen) of the ER on non-cytosolic side
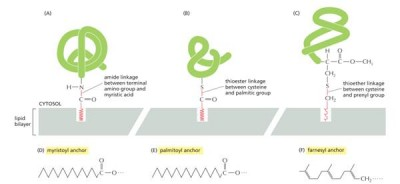
anchors are hydrophobic so they stick to membrane bilayer
GTPases of Rab protein can anchor in lipid bilayer because binding to GTP causes exposure of
hydrophobic peptide of lipid anchor domain of protein
Most common membrane spanning structure is
alpha helix. First is one membrane spanning, second is 7 membrane s[anning
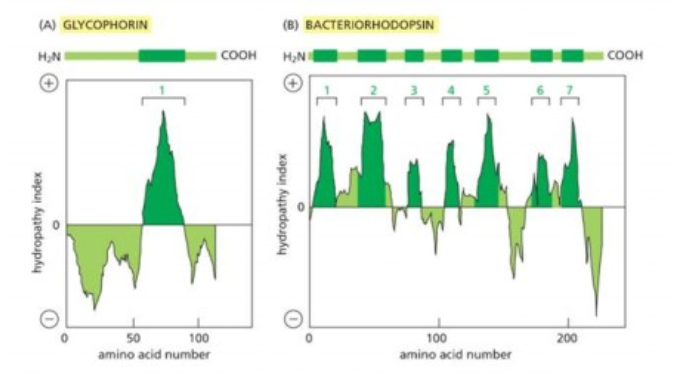
Which occurs first?
Insert hydrophobic helices
associate membrane spanning helices, displaces interactions
Insert hydrophobic helices
Amphipathic helices have hydrophobic side chains facing one side and semi-hydrophilic facing other.
The lipid portion is rich in hydrophobic side chains
Series of 10 amino acids to span membrane
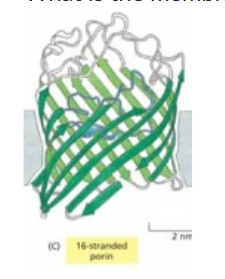
beta barrel
Proteins glycosylated in lumen of ER, if in plasma membrane then sugar faces
extracellular space
Disulfide bonds least likely to occur on surfaces of proteins
exposed to reducing environment of cytosol
Strongest detergent (polar end interacting strongly with water)
SDS
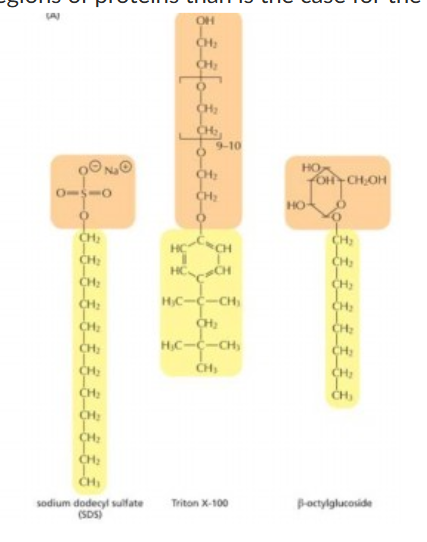
Detergents do
concentration increases linearly but then no longer rises once concentrations hit critical micelle concentration
1Hydrophobic portions of detergents interact with/ 2water react with
1hydrophobic amino acid side chains or lipids/ 2polar or charged groups
SDS is strong detergent because
interferes with protein secondary and non-covalent tertiary structure, denature proteins
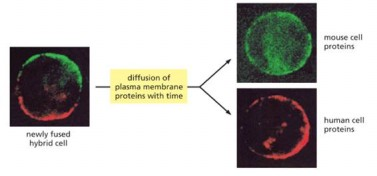
Experiment fused mouse cell with human cells show
proteins diffuse around leaflet of lipid bilayer
Access movement of membrane component into area of membrane bleaches with fluorescence of fluorescently tagged molecules is
FRAP= photobleaching
Which one restrict lateral diffusion of plasma membrane protein by cell to cell contact by cell surface proteins?
last one
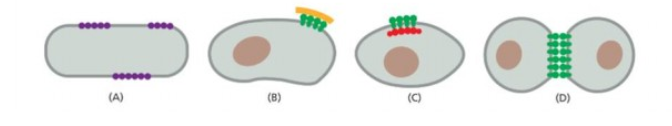
Which prevents protein diffusion around lipid bilayer by self association of particular protein into large aggregates
First one
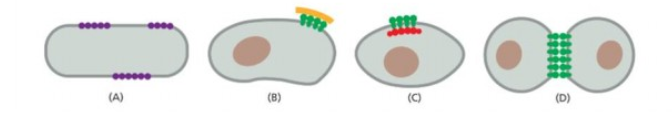
Which prevent lateral diffusion of transmembrane protein by anchorage to elements of cytokeleton
Third one
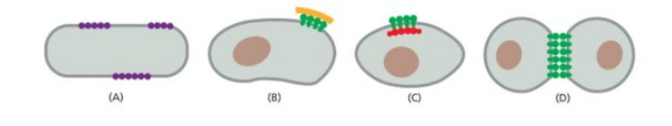
Membrane curvature caused by curved membrane surface
Third one
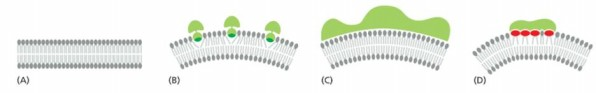
Microtubules have diameter 25 nm. Confocal microscopy, diameters appear to be 10x greater why?
best resolution with violet light is around 200 nm
If condenser lens move closer to specimen, what happens to theta and resolution
increases theta and improves resolution
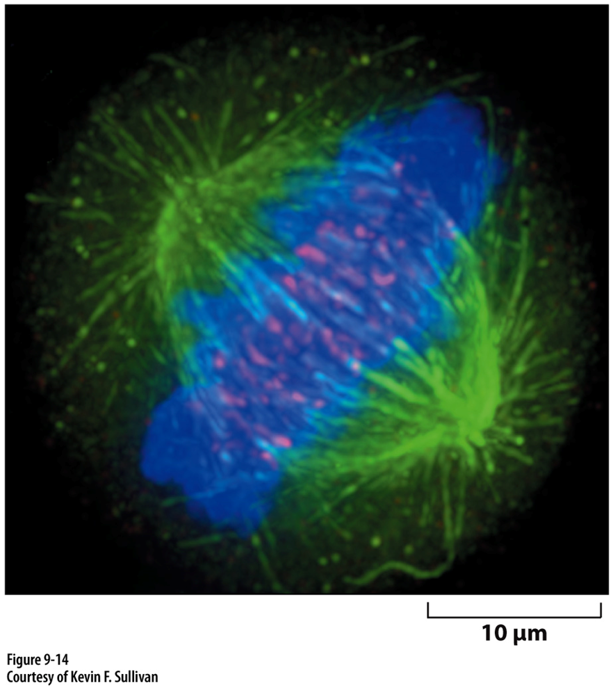
Combined fluorescence image of all that
Sequential collection of signa using 3 different excitation/emission filter sets then combining data into one image?
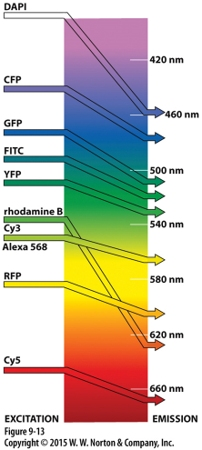
Good pair for fluorescence resonance energy transfer to assess interactions between 2 proteins?
CFP/GFP
Phase contrast imaging
looking at living cells without stan or fluorophore
TEM image/ forms image from electrons that
PASS THROUGH SPECIMEN
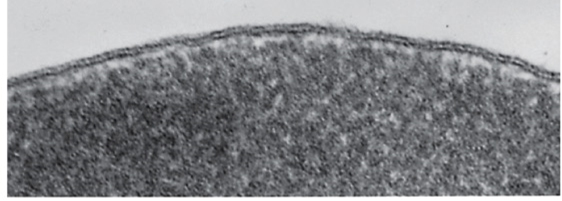
electron microscopy approach to generating 3d reconstruction
many TEM images of a single specimen that tilted between images.
2 different proteins using immunogold electron microscopy
2 different sized gold particles are used
Plasma membrane has low cholesterol content, so this membrane
is NOT lipid draft
Amphipathic lipid monolayer of intracellular lipid droplets is
derived from the cytosolic leaflet of the ER membrane
Which anchored by single amphipathic helix?
protein 4
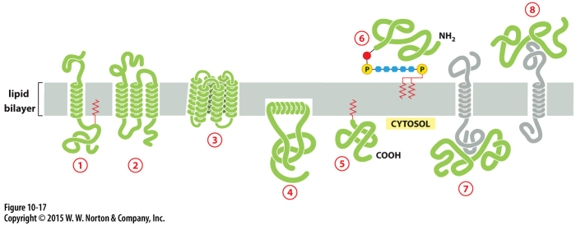
Glyco—-lol anchors insert into leaflet of membrane because
hydrophobic groups
Peripheral membrane protein covalently linked by disulfite bond to integral protein
in the extracellular space
Cytisolic, peripheral membrane protein?
protein 7
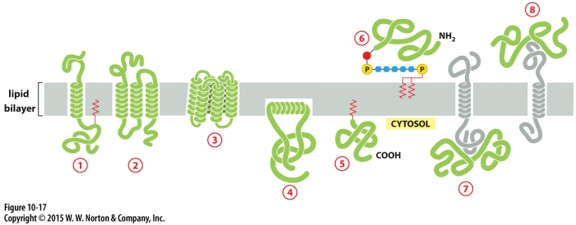
Which can be released into extracellular fluid by removing its anchor?
protein 6
NOT resolvable by conventional light microscopy?
ribosome
Detection of mRNA or base pairs by
in situ hybridization
Involve specimen staining before imagine?
bright field microscopy
Proteins in lipsosome
get their facing that way by random inforporation
Not required for Na=/k+ atphase moving Na+ out of liposome
extra liposomal na+
Ions
Extracellular: Na+, Ca2+
Cytosol: K+
pH higher in the
extracellular fluid in the cell
Cross a lipid bilayer
Easy: Non polar molecules like o2,co2
Hard: ions like H+,Na+,K+,
Limiting factor of simple diffusion of molecule across lipid bilayer is
ability to interact with hydrophobic interior of lipid bilayer
Hydrophobic group?
CH3
Carrier or transporter?
Left
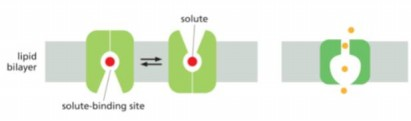
Direction of net movement of solutes shown is down concentration gradient, which way solutes move?
either in or out of the cell, depend on concentration gradient
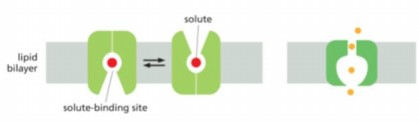
Kind if transporter/carrier- or channel mediated movement that goes in direction of concentration gradient from high to low
passive transport
Active transport channel is on thr
right
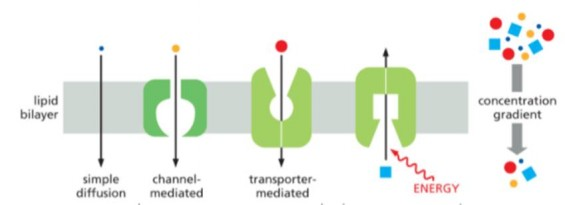
Simple diffusion
direct diffusion of molecule across lipid bilayer without involve membrane protein
Researcher does experiment involve rate of movement across lipid bilayer. Movement rate keeps going up as solute concentration increases and never saturated. This movement is
Simple diffusion or channel mediated transport
When protein couples ATP hydrolysis with pumping a solute across lipid bilayer to create chemical or electrochemical gradient for that solute, then solute back across lipid bilayer down gradient of another solute
secondary active transport
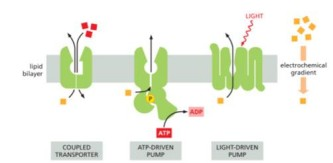
Common feature of
coupled to some potential energy source like atp
UNIPORTER SYMPORTER ANTIPORTER IN THAT ORDER
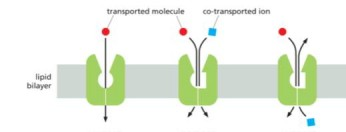
Sodium dependent glucose transporter is
symport
Na/K pump created gradient that drives glucose uptake by sodium dependent glucose is
secondary active transport
No need for active transport to create sodium gradient
small intestine after ingestion of foods or sodium beverages