Neurophysiology: Action Potentials
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3 Chapter 11.6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Action Potentials (APs)
do not die out over distance
only occur in the axon (graded, threshold required)
“nerve impulse”
all or none: stronger stimulus does not produce larger AP
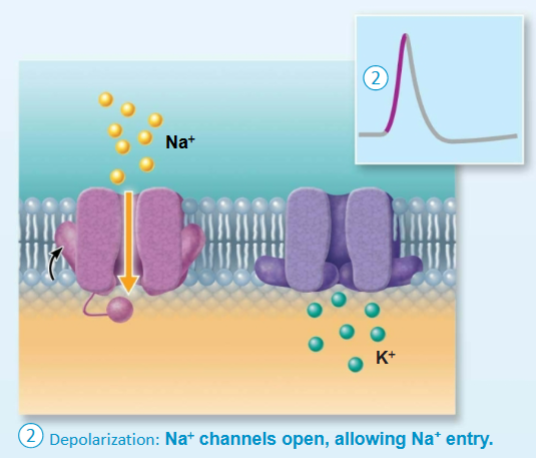
Depolarization of AP
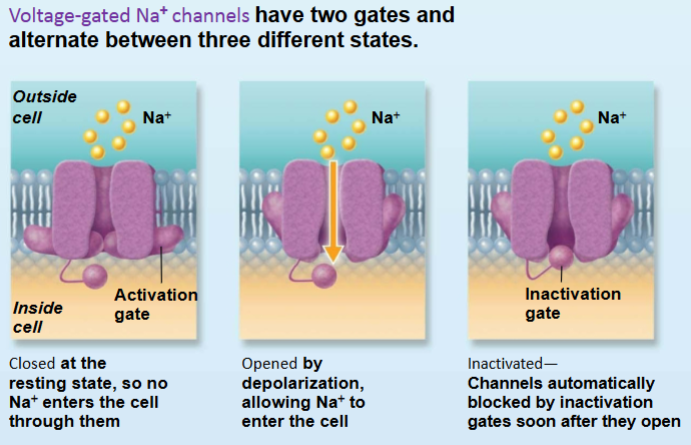
Voltage-gated Na+ channels
fast to open and to close
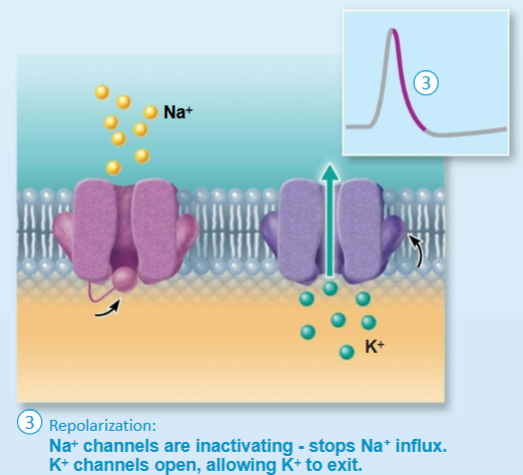
Repolarization of AP
Voltage-gated K+ Channels
slow to open and close
Hyperpolarization of AP
Slow closing K+ Gates

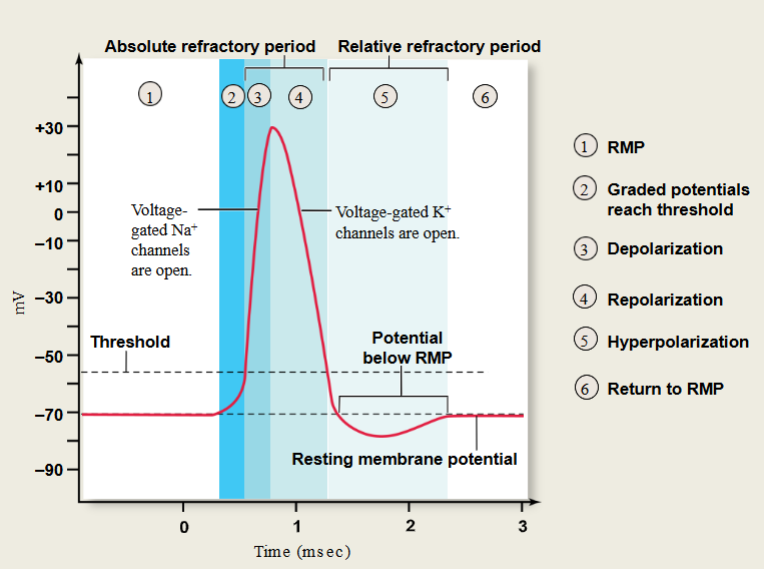
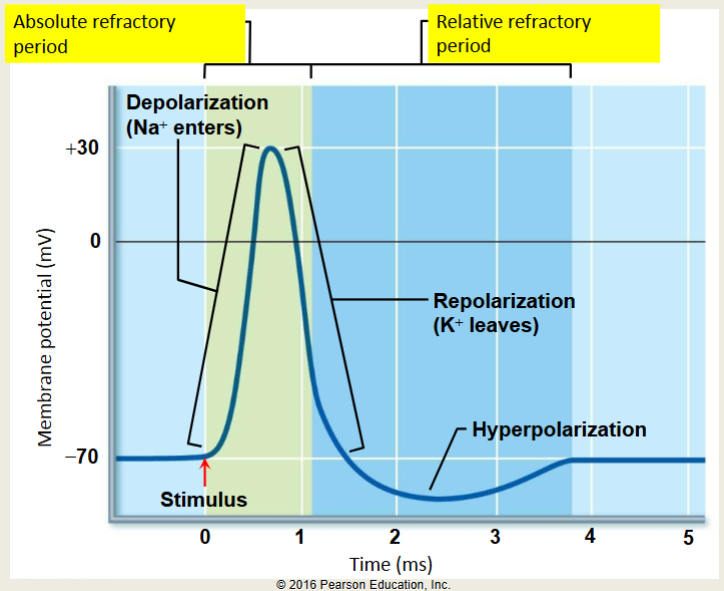
Action Potential graph
6 steps from RMP to return to RMP
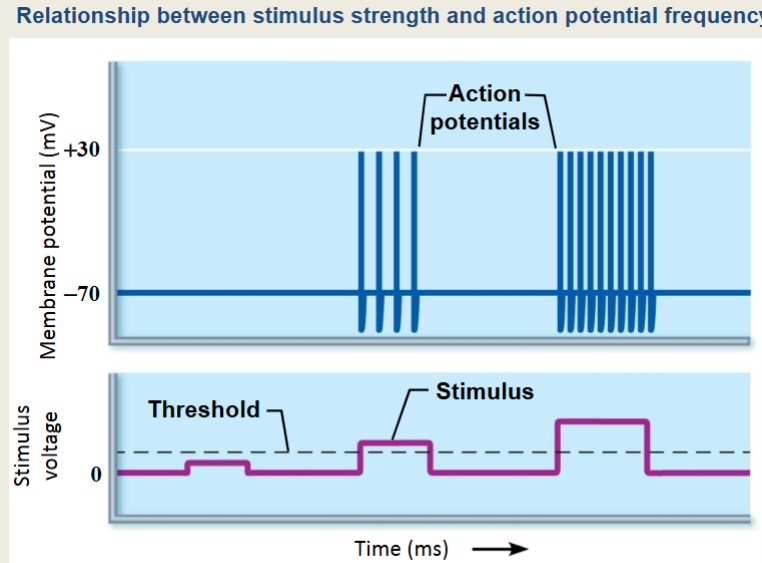
If all APs are the same, how does the integrator know that one stimulus is different from another?
Frequency!
stronger stimulus will produce MORE APs rather than larger ones
more NT = More APs
absolute refractory period
1-2 msec before another AP can be initiated
time to reset NA+ channel gates
keeps APs from overlapping
Relative Refractory Period
Stronger than normal stimulus required to reach threshold
K+ Channels still open
7 Characteristics of APs
APs are produced when a graded potential reaches threshold
all-or-none
Depolarization is a result of increased membrane permeability to NA+ and movement of NA+ into the cell. activation gates of the Voltage-gated Na+ channels open
Repolarization is a result of decreased membrane permeability to Na+ and increased membrane permeability to K+, which stops Na+ movement into the cell and increases K+ movement out of the cell. the inactivation gates of the v-g Na+ channels close, and the v-g K+ channels open.
During the absolute refractory period, no AP is produced by stimulus, no matter how strong. during the relative refractory period, a stronger-than-threshold stimulus can produce an AP
APs are propagated and, for a given axon/muscle fiber, the magnitude of the AP is constant
Stimulus strength determines the frequency of APs
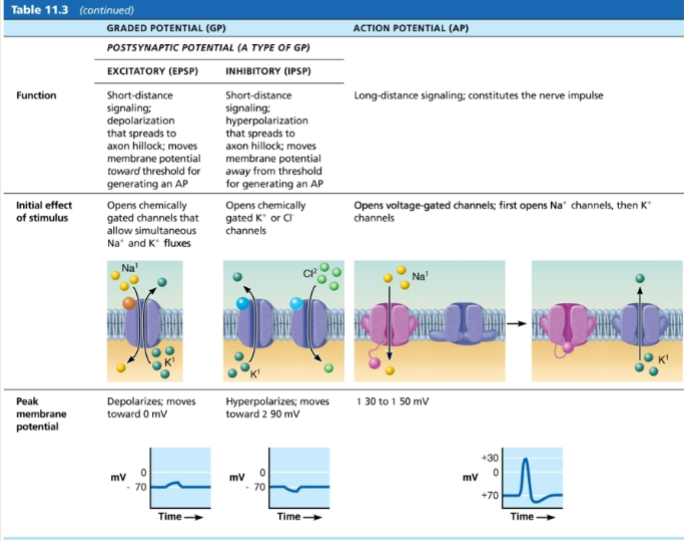
Graded potential vs Action Potential

GP and AP
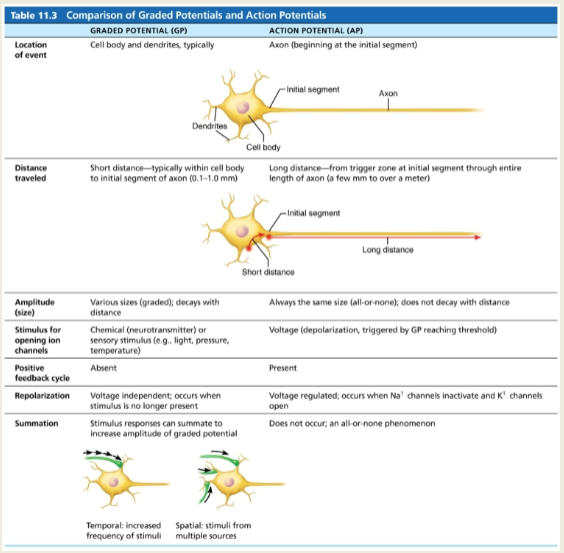
GP and AP cont.