AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.10: Aromatic Chemistry
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are aliphatic compounds? (1)
Compounds with carbon chains that do not contain benzene rings
What are aromatic compounds? (1)
Compounds that contain benzene rings
What was Kekule's proposed structure of benzene? (1)
- Proposed that benzene consisted of a six-carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds
- Cyclohexatriene
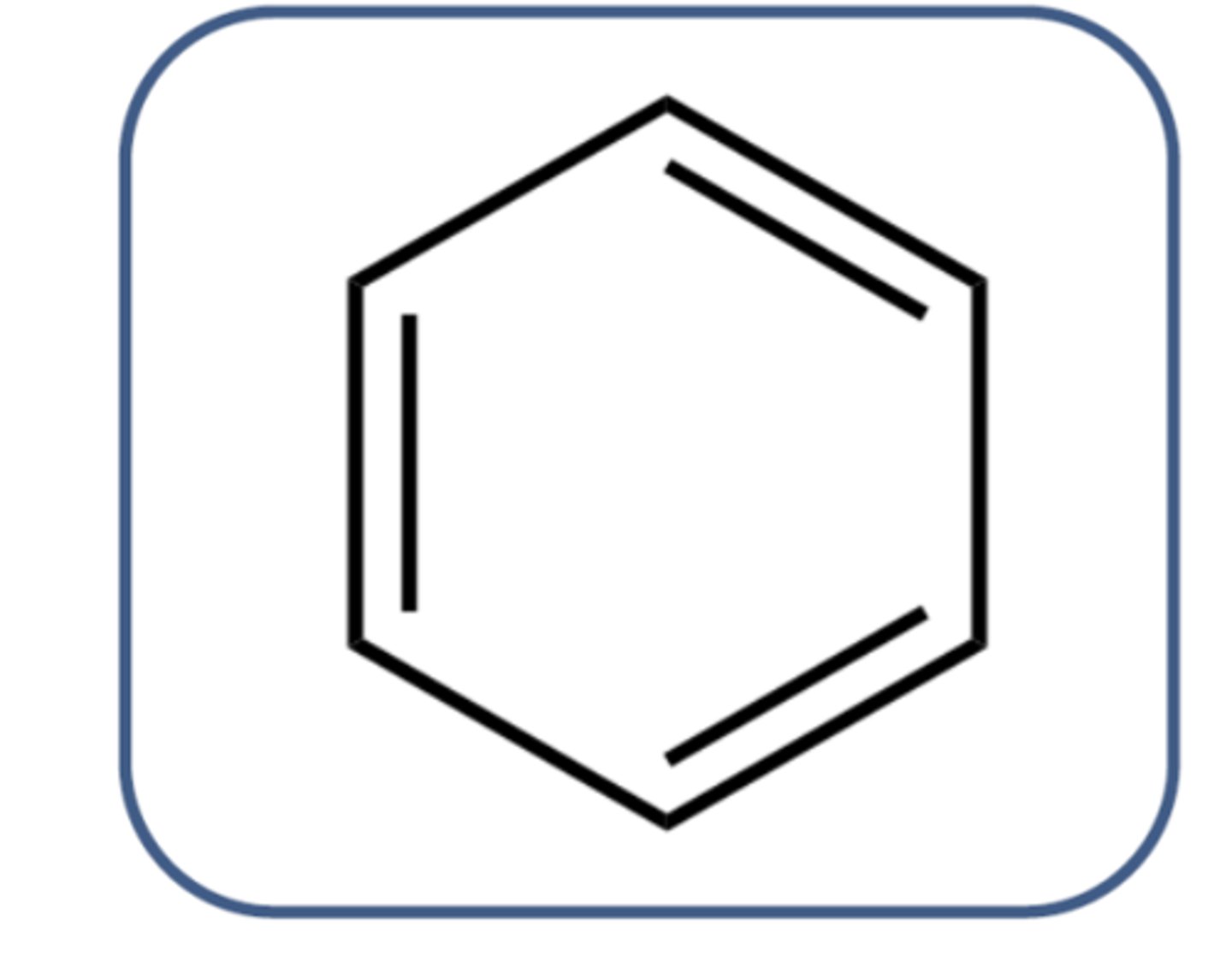
What were the problems with Kekule's structure? (2)
- Benzene does not colourise bromine water
- All the C-C bonds are the same length (an intermediate of the length of single and double bonds)
Why does benzene not decolourise bromine water? (1)
Because it does not undergo electrophilic addition reactions
What do electron density spectra reveal about benzene's carbon-carbon bonds? (1)
= Show that all the C-C bonds in benzene are the same length
- Indicating equivalence among the carbon atoms
Draw and describe the modern day structure of benzene (2)
Pi electrons in the middle are delocalised
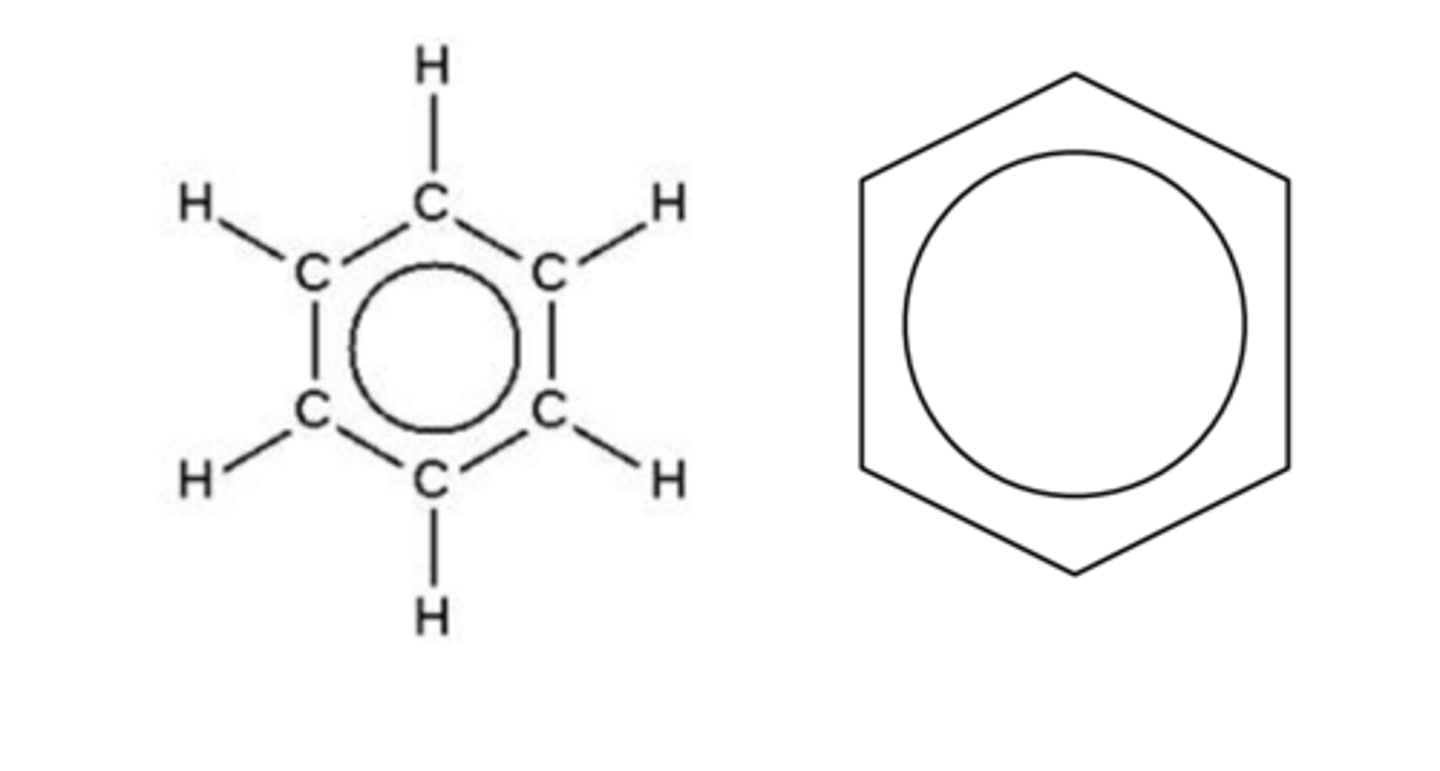
Describe the thermochemical evidence of the modern day structure of benzene (3)
1. The expected enthalpy of hydrogenation (of kekule's structure) is -360 kJ mol⁻¹.
2. The actual enthalpy change of hydrogenation for benzene is 152 kJ mol⁻¹ less exothermic than expected
3. With a value of -208 kJ mol⁻¹.
When do we use the naming root of 'benzene'? (4)
When the group attached to the benzene ring is:
1. An alkyl group (e.g., methyl, ethyl, propyl).
2. A halogen (e.g., bromo, chloro, fluoro).
3. A nitro group (NO₂).
4. A carboxylic acid (COOH).
When is the prefix name phenyl given? (1)
Any functional groups that do not lie in the benzene root rules
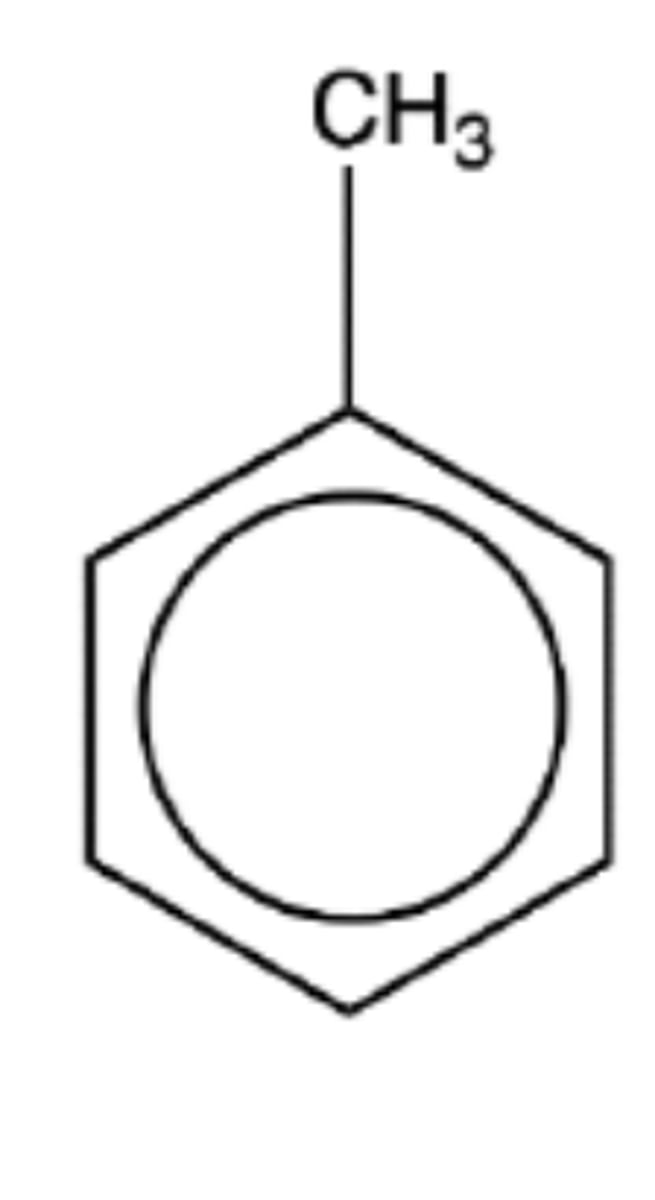
Draw the structure of methyl benzene (3)
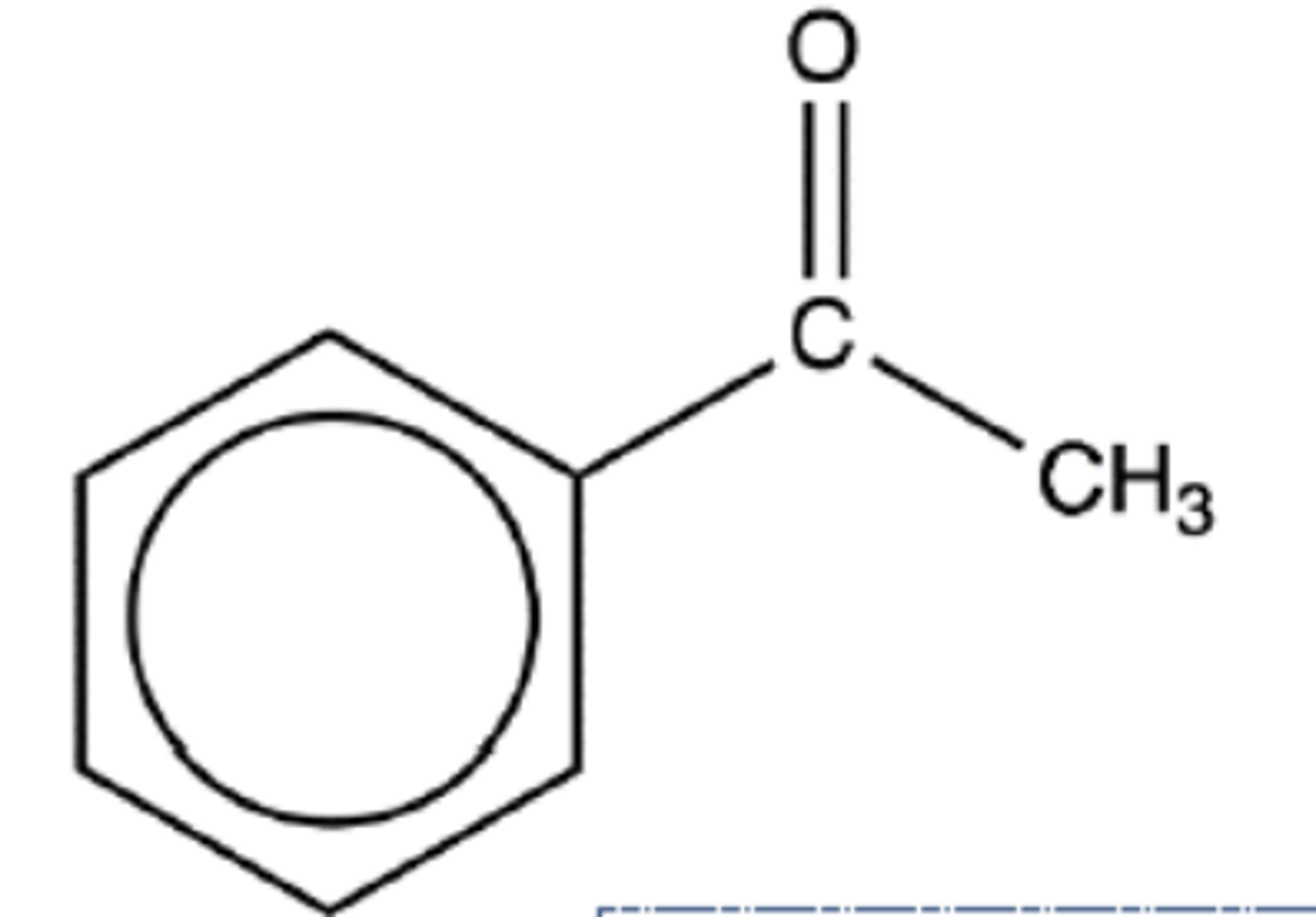
Draw the structure of phenylethanone (3)
What is the definition of an electrophile? (1)
An electrophile is an electron pair acceptor
Name two electrophiles involved in the electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene. (2)
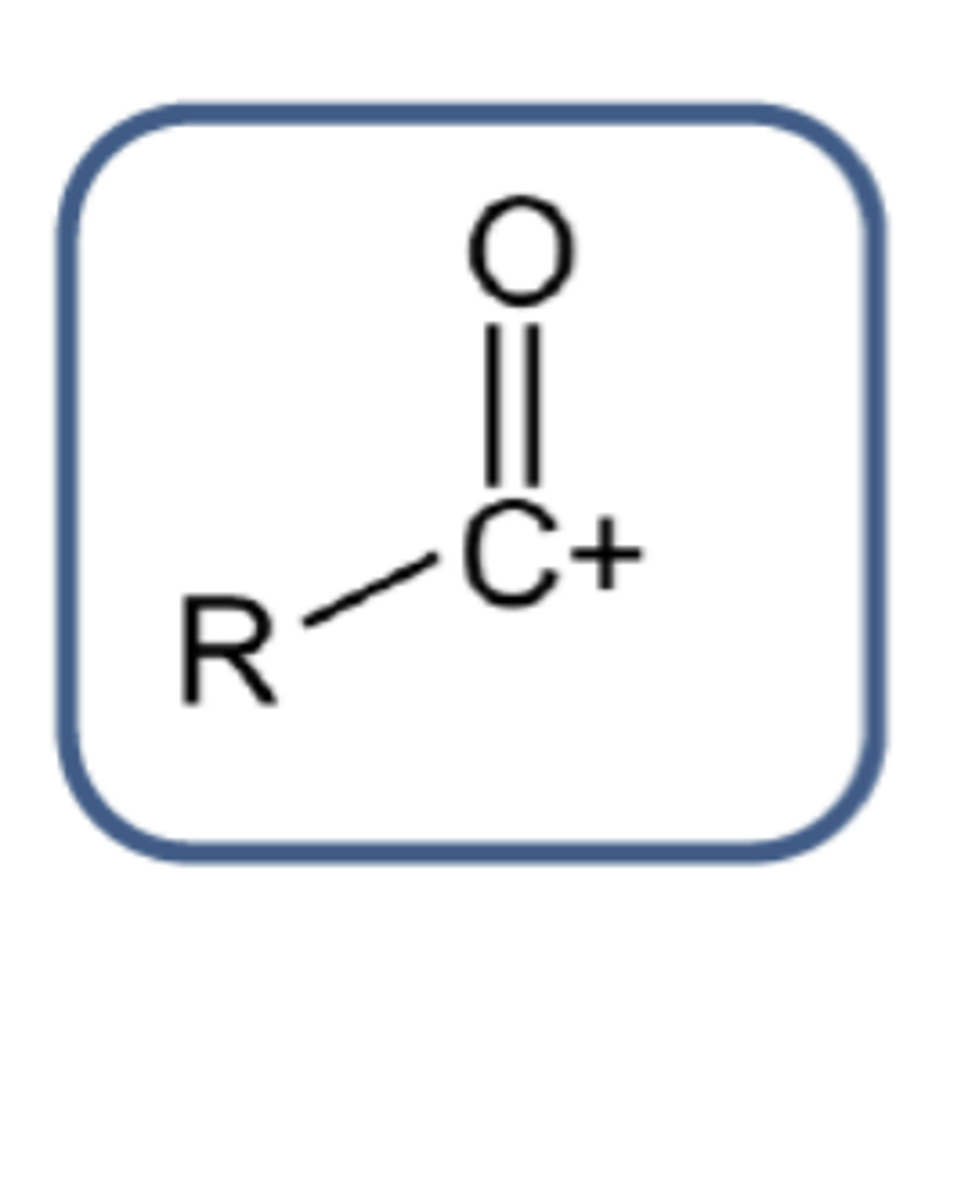
The nitronium ion (NO2⁺) and the acylium ion (RCO⁺)
What is the structure of the nitronium ion? (1)
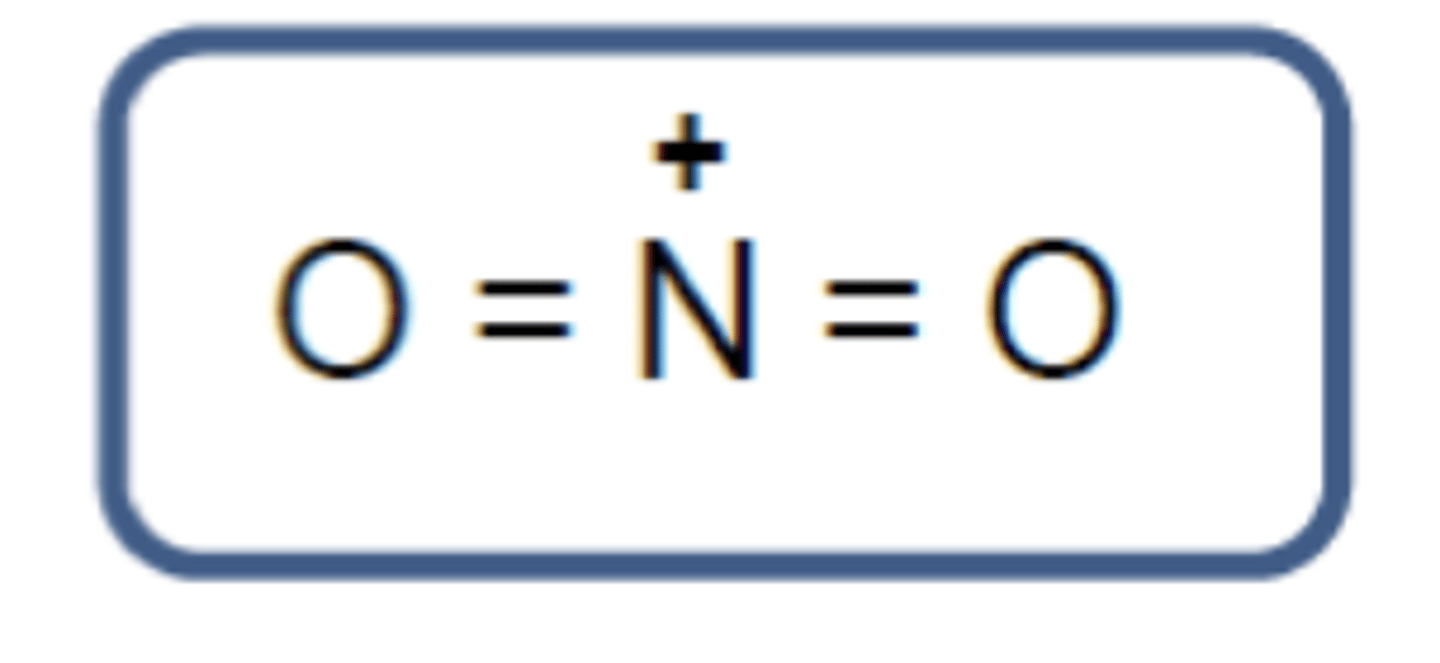
What is the general structure of the acylium ion? (1)
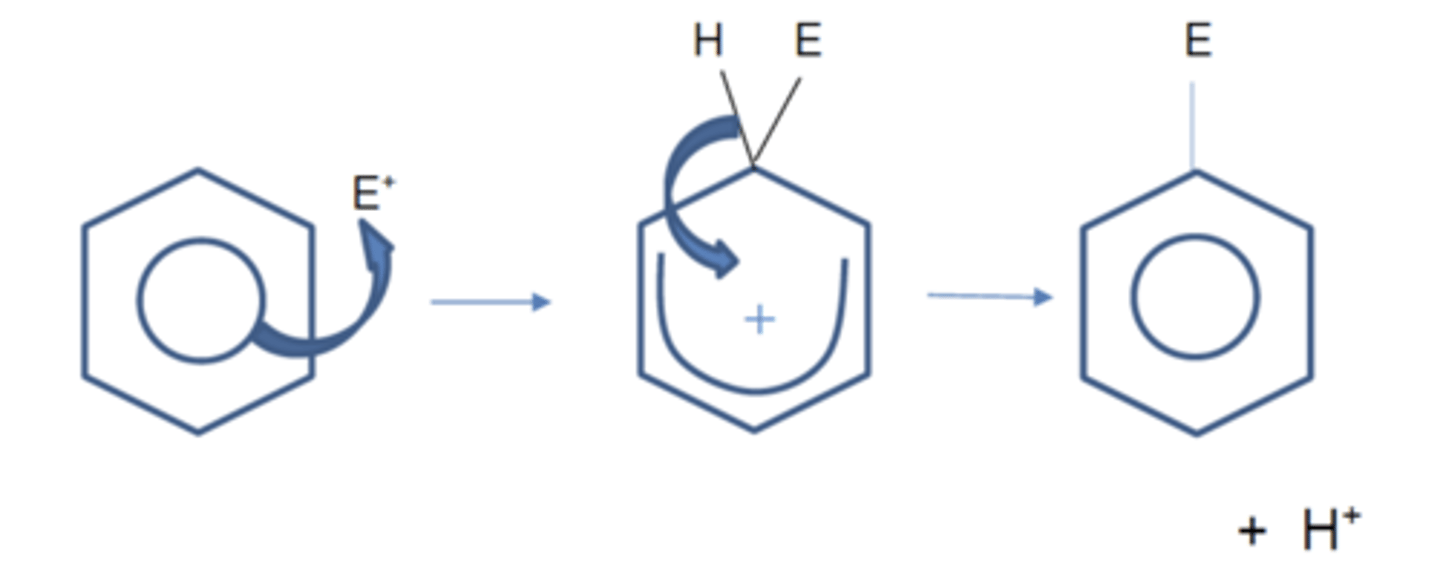
What are the three general steps for any reactions of benzenes? (3)
1. Generation of electrophile
2. Electrophilic substitution mechanism
3. Regeneration of catalyst - the H+ liberated from benzene reforms this
Draw the general electrophilic substitution mechanism in benzenes (3)
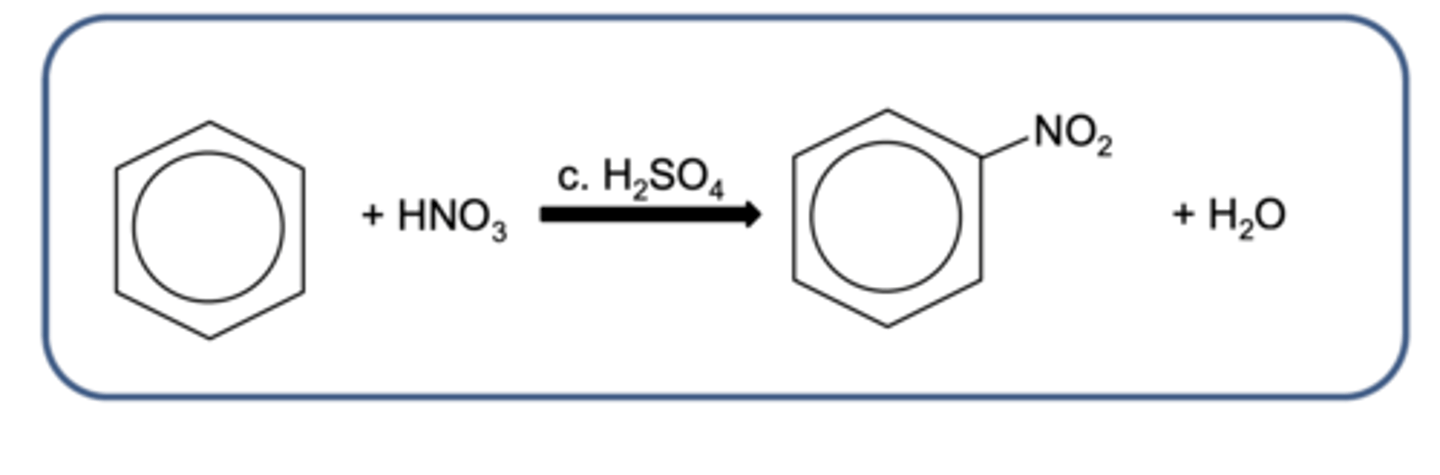
Draw the overall equation for the reaction of the nitration of benzene to form nitrobenzene (3)
What is the role of H₂SO₄ in the nitration of benzene? (2)
- H₂SO₄ acts as a catalyst by protonating HNO₃
- Forming the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺), the electrophile for the reaction.
Write the equation for the protonation of HNO₃ by H₂SO₄. (1)
H₂SO₄ + HNO₃ → HSO₄⁻ + H₂NO₃⁺
What happens to protonated nitric acid (H₂NO₃⁺) during the nitration of benzene? (1)
Protonated nitric acid (H₂NO₃⁺) breaks down to form the nitronium ion (NO₂⁺) and water (H₂O)
Write the single equation that represents the generation of the nitronium ion in the nitration of benzene. (1)
H₂SO₄ + HNO₃ → HSO₄⁻ + NO₂⁺ + H₂O
Write the equation for the breakdown of protonated nitric acid. (1)
H₂NO₃⁺ → NO₂⁺ + H₂O
Draw the electrophilic substitution mechanism for the nitration of benzene (3)
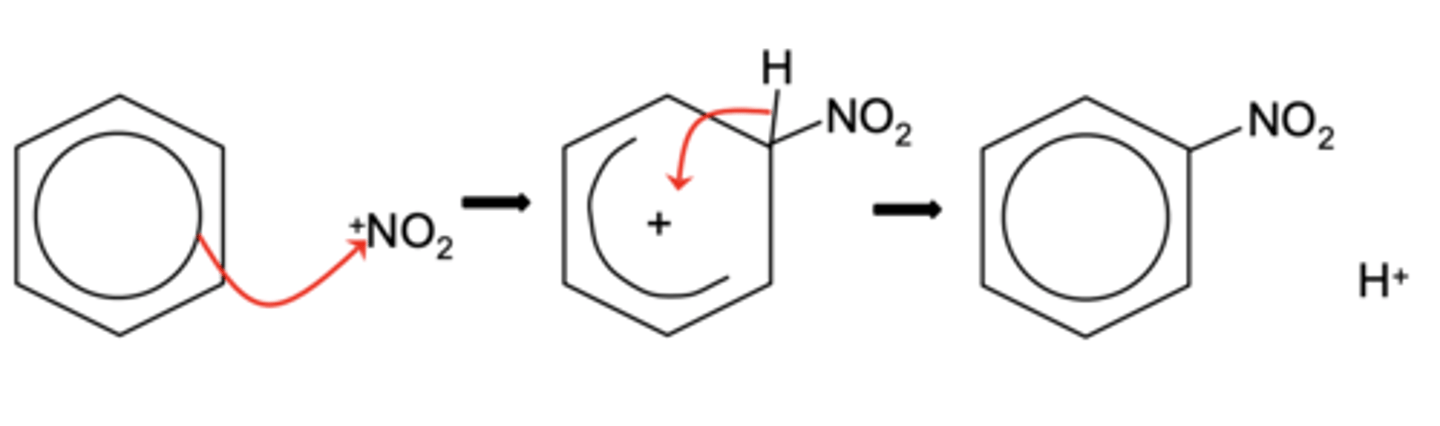
Write the equation for the regeneration of catalyst in the nitration of benzene (1)

What is nitrobenzene used for in synthetic chemistry? (1)
In the preparation of azo dye
How is the nitro group in nitrobenzene converted to an amine? (3)
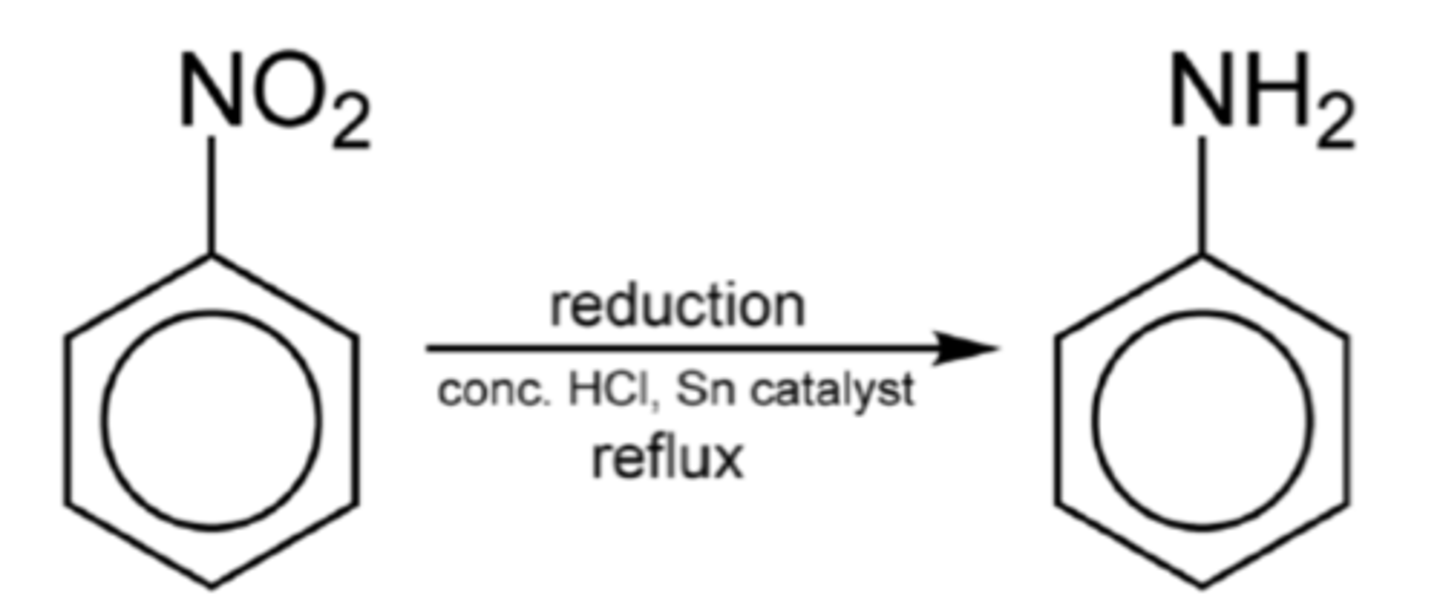
Write the balanced equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene to phenyl-amine. (1)
C₆H₅NO₂ + 6[H] → C₆H₅NH₂ + 2H₂O
What does TNT stand for in terms of its full name? (1)
TNT stands for Tri Nitro Toluene
What is the IUPAC name of TNT? (1)
2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene
What is toluene an alternative name for? (1)
Toluene is an alternative name for methylbenzene
What reagent and catalyst are used for the nitration of methylbenzene? (1)
The reagents are concentrated nitric acid and sulfuric acid
How many nitrations occur to form TNT? (1)
Three nitrations occur to form TNT
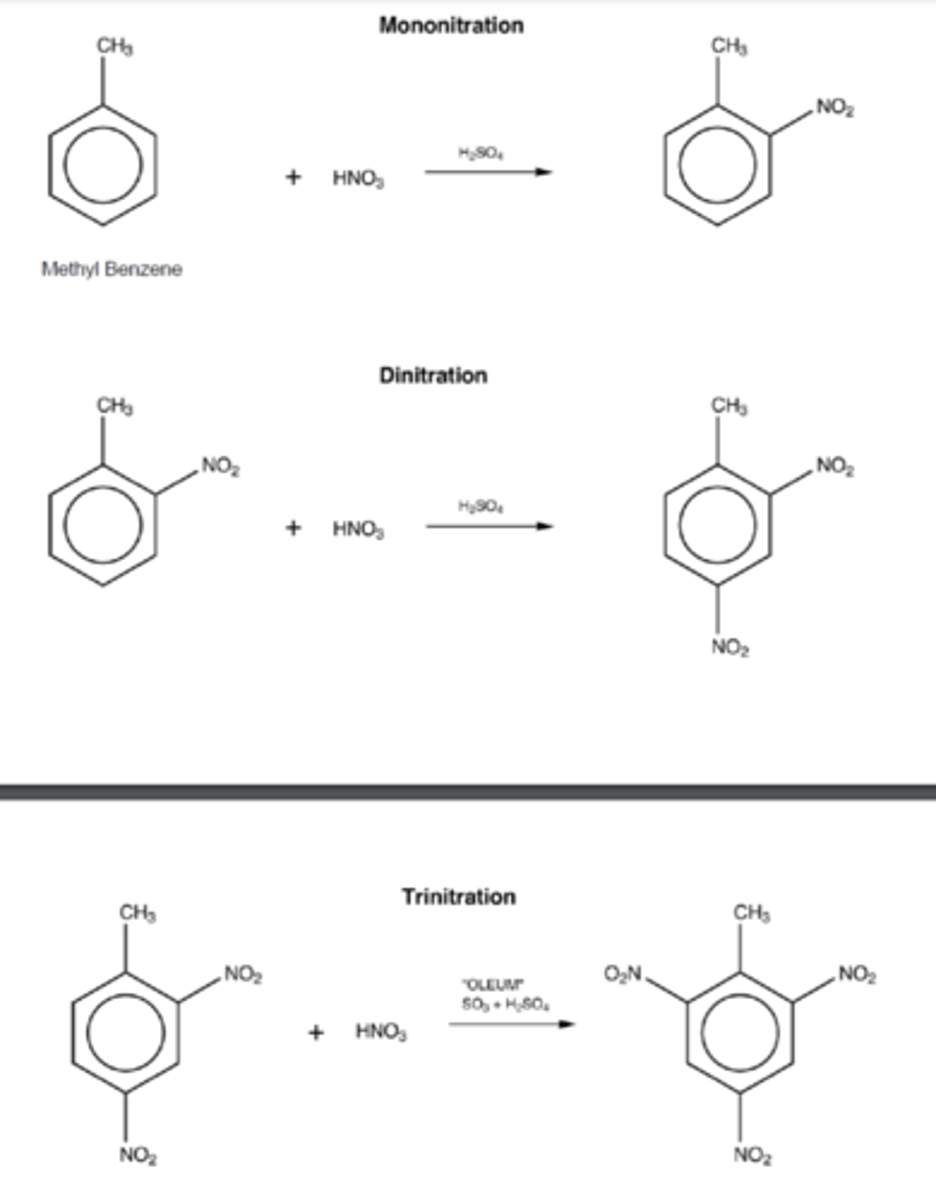
What is the intermediate product of dinitration of methylbenzene? (1)
The intermediate product is 2,4-dinitrotoluene
Why is methylbenzene more reactive than benzene? (3)
1. The methyl group pushes electrons towards the benzene ring (positive inductive effect)
2. There is a stronger attraction to the electrophile
3. Methylbenzene is a better nucleophile
Draw the overall equation for Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction of benzene (3)
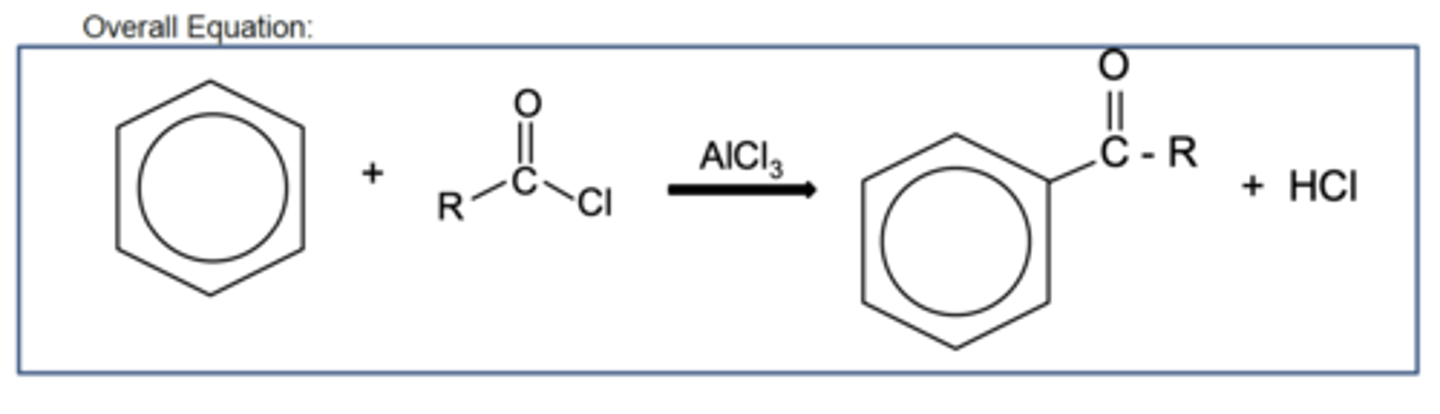
Draw the equation for the generation of the electrophile in Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction of benzene (3)
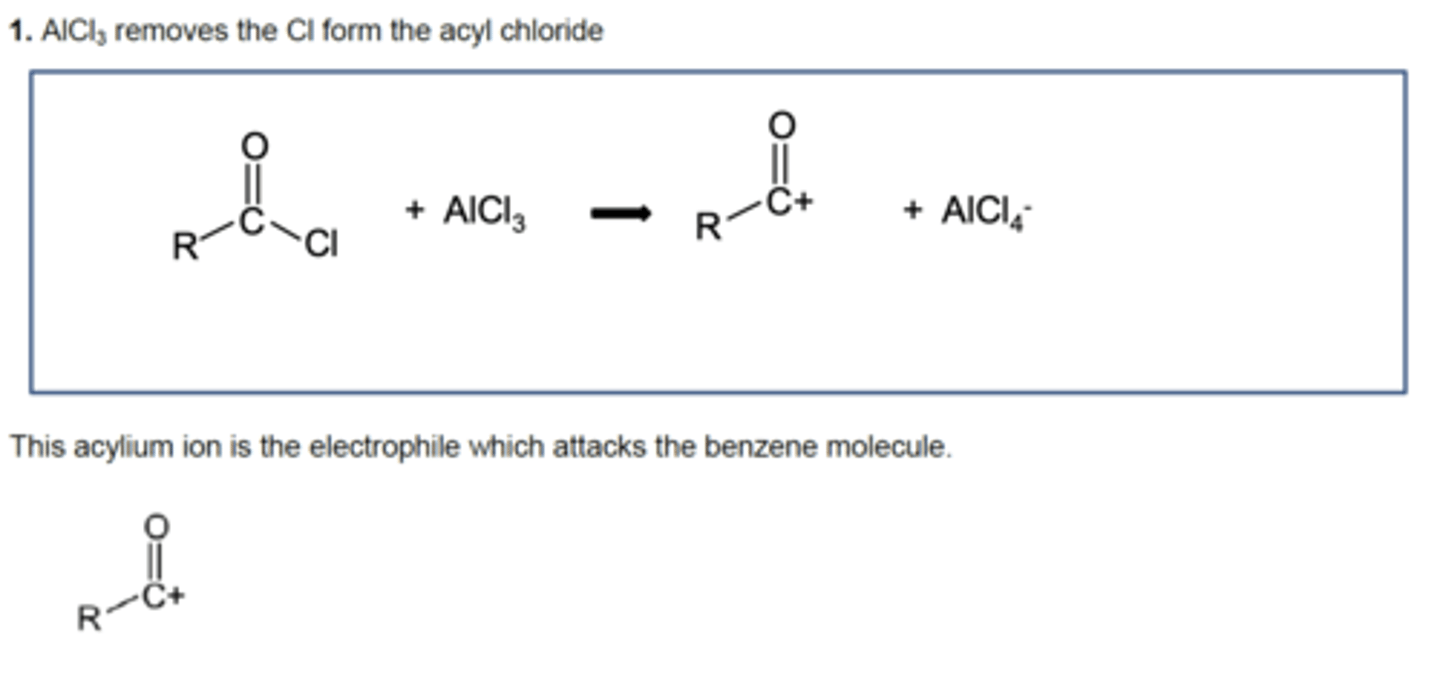
Draw the mechanism for the electrophilic substitution in the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction of benzene (3)
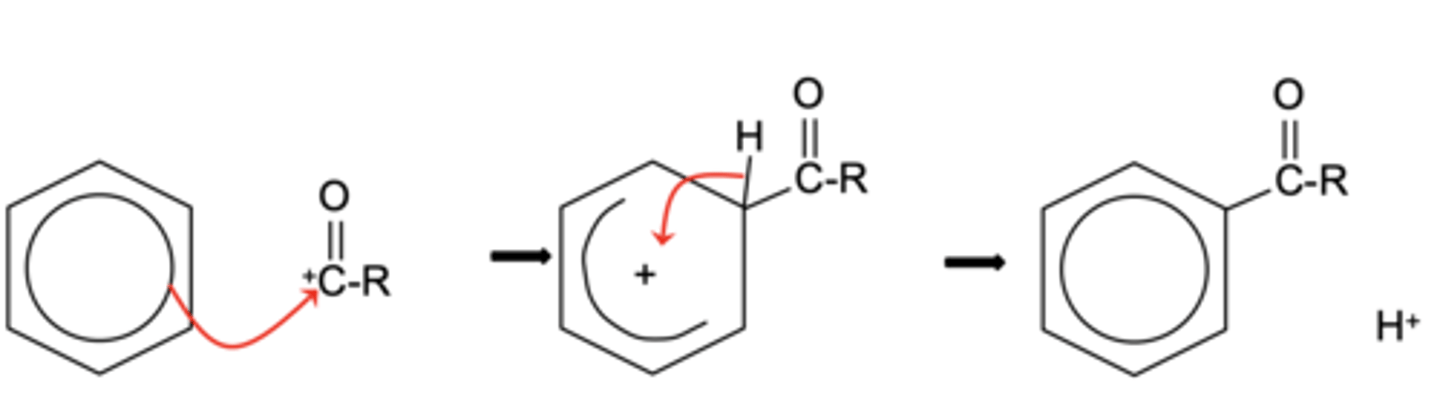
Write the equation for the regeneration of the catalyst in the Friedel-Crafts reaction. (1)
AlCl₄⁻ + H⁺ → AlCl₃ + HCl