Semester Final , Miller and Levine Biology
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
The steps to the scientific method

Hypothesis
a proposed scientific explanation for a set of observations in ways that support or reject it
Controlled experiment
an experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time
Theory
well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations that has been throughly tested
How do theories and hypothesis compare?
They're both an option and testable = http://ontrack-media.net/gateway/chemistry/g_sm0l4s5.html
Characteristics of living things
*living things grow and develop
*living things are based on a universal genetic code
*living things respond to the environment
*living things are made of cells
*living things reproduce
*living things maintain a stable internal environment
*living things obtain and use material and energy
*living things, as a group, evolve
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Why is carbon so special compared to other elements?
It is the primary atom for the molecular structure of life
What are the three statements that make up the cell theory
All living things are made up of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, new cells are produced from existing cells.
List three differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotes = nucleoid , Eukaryotes = nucleus
Prokaryotes = no organelles , Eukaryotes = organelles
Prokaryotes = circular DNA , Eukaryotes = Linear DNA
Robert Hooke
Discovered Cells
Principle of cell theory
fundamental concept of biology that states that all living things are composed of cells; that cells are the basic units of structure and function in living thingl and that new cells are produced from existing cells
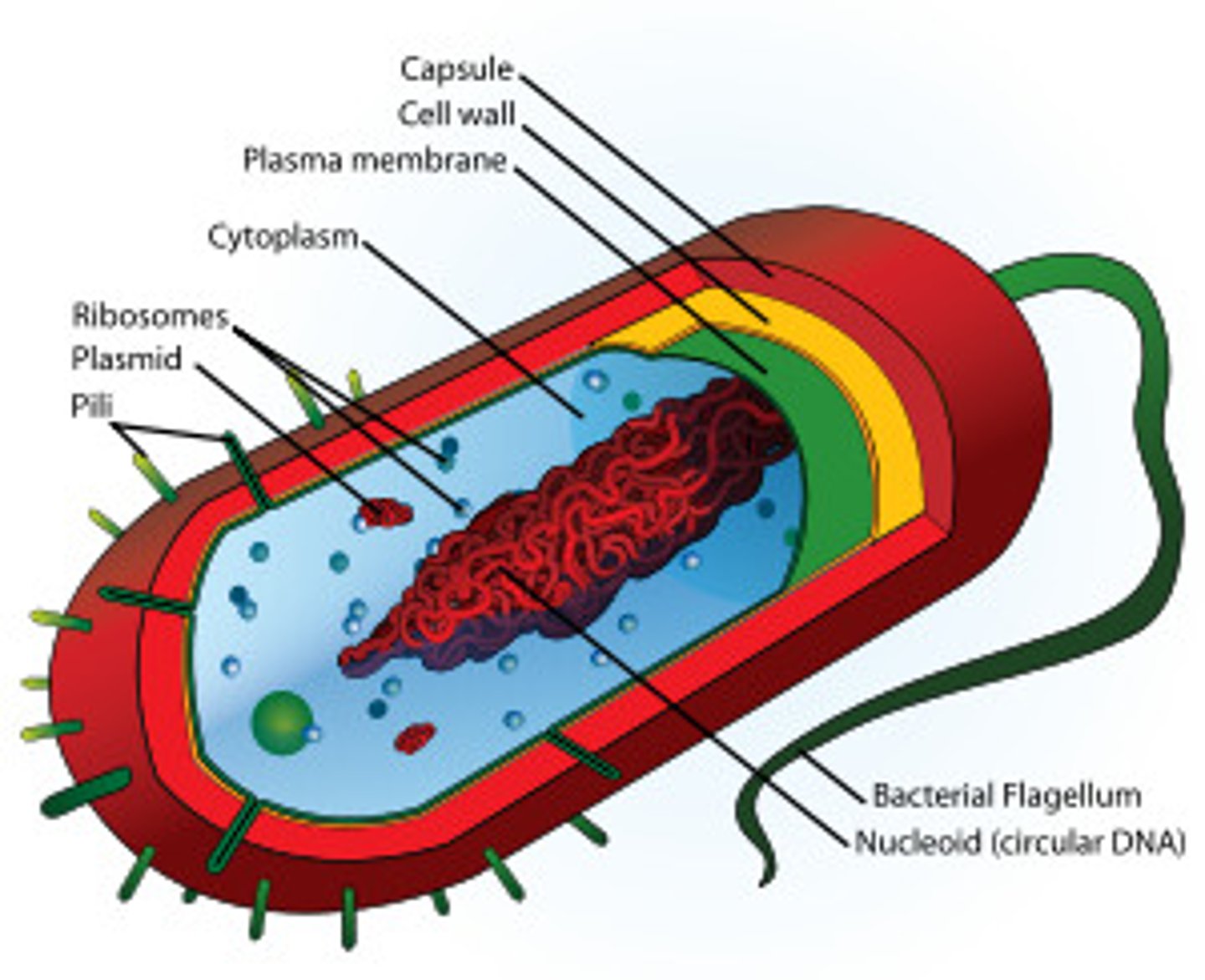
Prokaryotic cell
unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus
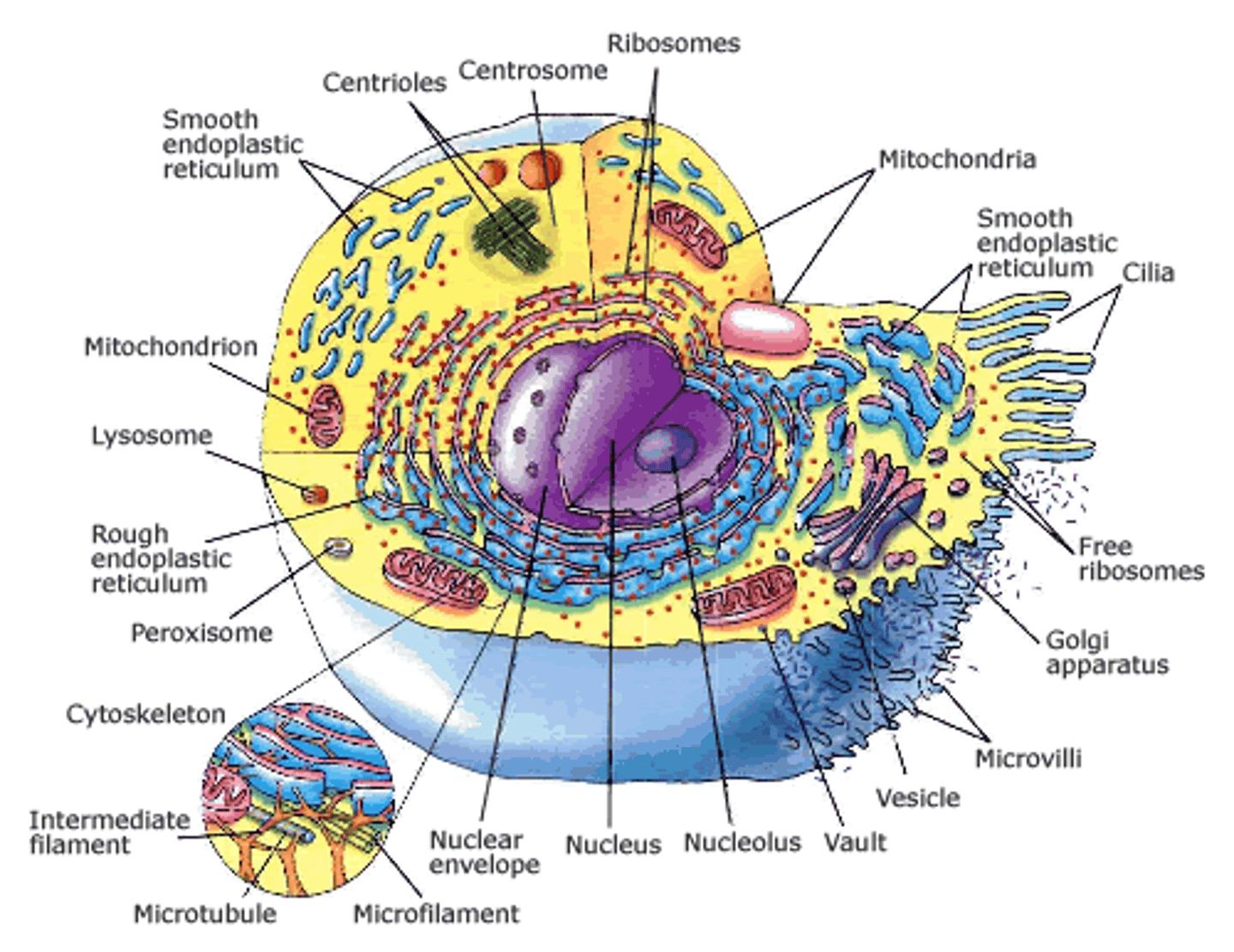
Eukaryotic cell
organism whose cells contain a nucleus
Example of an organism made of a prokaryotic cell
Bacteria
Function of the Nucleus
structure that contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA
Function of the Lysosome
cell organelle that breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell
Function of the ribosome
cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm in a cell
Function of the mitochondria
cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use
Function of the chloroplast
organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight and converts in into chemical energy
Function of the cell wall
strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane in some cells
Function of the cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Osmosis
diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Active transport
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration
Why is ATP useful to cells
Energy is usually liberated from the ATP molecule to do work in the cell
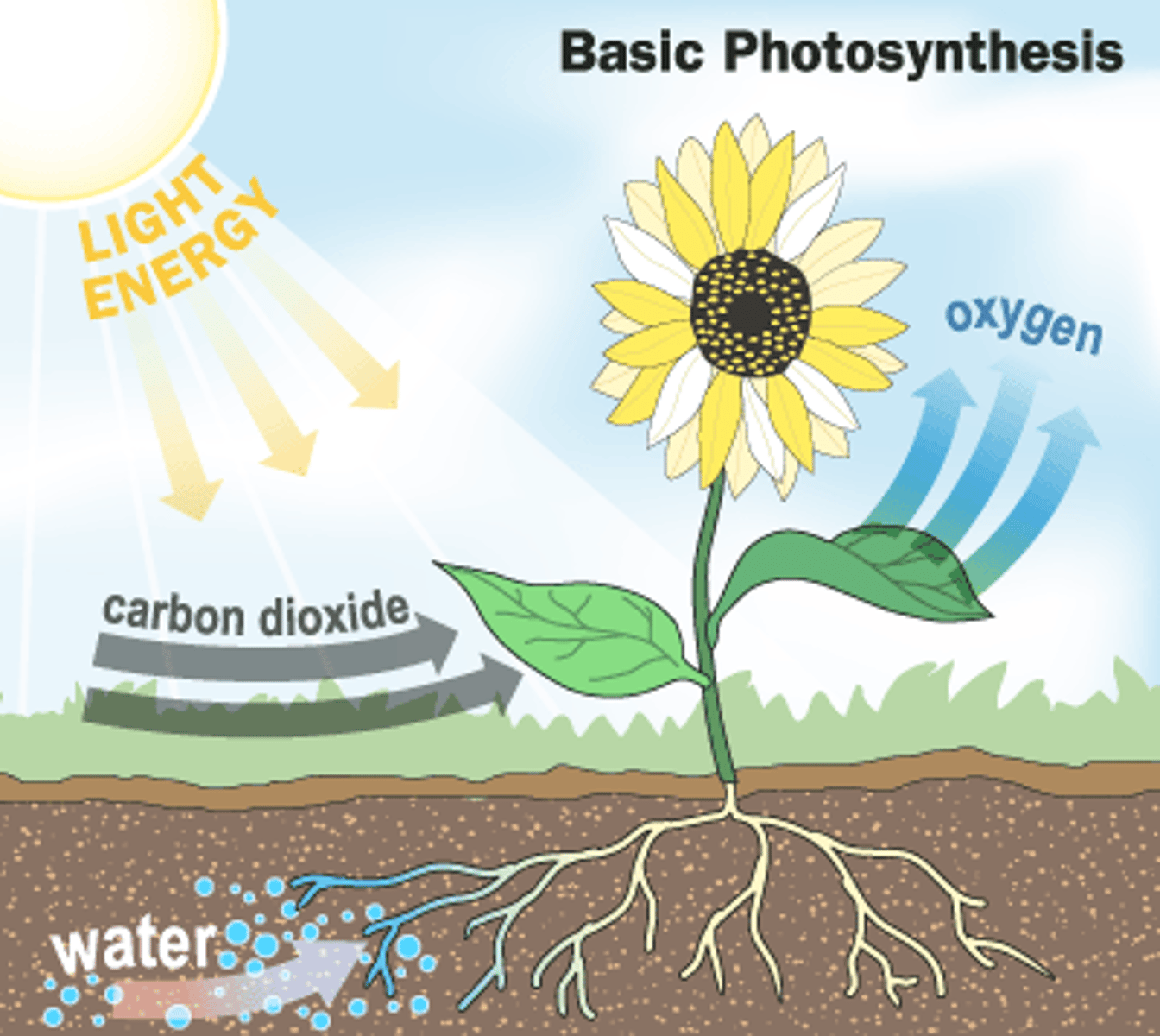
What happens during the process of photosynthesis
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, a green substance found in chloroplasts in some plant cells and algae. Absorbed light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide (from the air) and water (from the soil) into a sugar called glucose. Oxygen is released as a by-product.
Three parts of an ATP molecule
1. Adenine
2. Phosphate Groups
3. Ribose
When is energy released from ATP
When the terminal (third) phosphate is cut loose
Autotroph
organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds; also called a producer
Heterotroph
organism that obtains food by consuming other living things; also callled a consumer
Pigments
light absorbing molecules used by plants to gather the sun's energy
Granum
A stacked membranous structure within the chloroplasts of plants
Stroma
basically cytoplasm
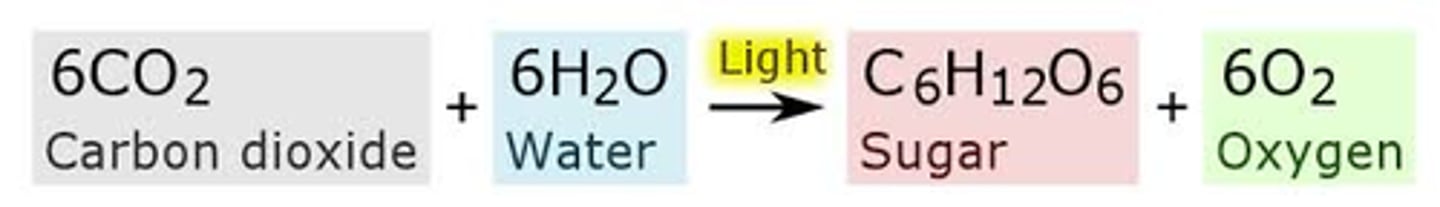
The chemical equation of photosynthesis
Where do light-dependent reactions take place
on the thylakoid membranes
What are the products of the light-independent reactions
NADPH and ATP
Calvin cycle
the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH used to build high-energy compounds
Where do organisms get energy
The sun
What is cellular respiration
enzymatic breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce cellular energy
How do organisms get the energy they need
Breaking down molecules
Correct sequence of the steps of cellular respiration
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport.
Chemical equation of cellular respiration
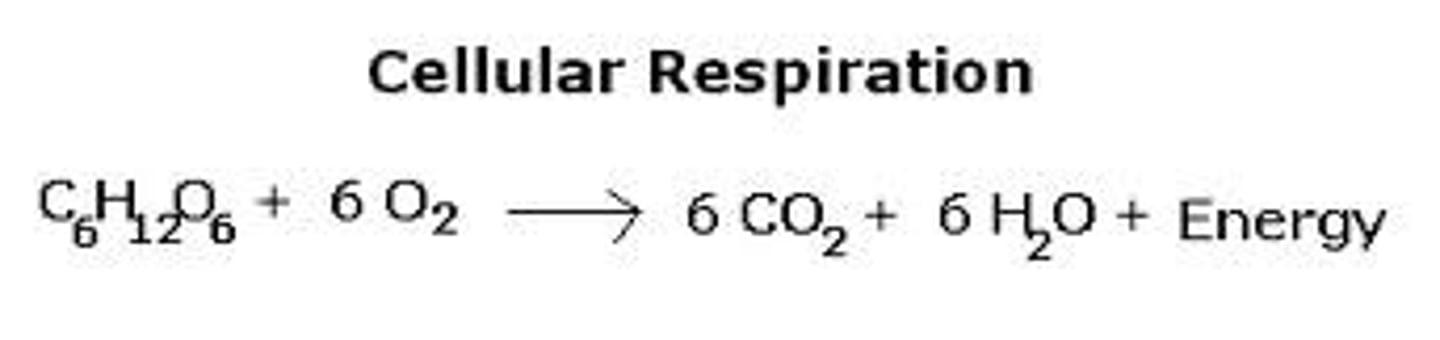
Reactants and products of the equation
ATP, Carbon dioxide, Water
Aerobic
process that requires oxygen
Anaerobic
process that does not require oxygen, such as glycolysis
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis opposite one another
the two equations are the opposite because the reactants of cellular respiration are the products of photosynthesis and vice versa
Where does glycolysis take place
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm
How many ATP are produced during glycolysis
Four total molecules of ATP are formed during glycolysis
Starting molecule for glycolysis?
glucose and 2 molecules of ATP
Starting molecule for krebs cycle
Pyruvic Acid
How many total ATP are produced during cellular respiration
36 ATP
Lactid Acid fermentation
process which produces lactic acid and NAD+ from pyruvic acid and NADH
Alcoholic fermentation
process which produces alcohol, CO₂, and NAD+ from pyruvic acid and NADH
what is the role of chromosomes in cell division
> They carry hereditary information in the genes from parents to off springs.
> They help cell grow, divide, maintain itself by directing synthesis of proteins.
> Control cell metabolism by directing the formating of necessary proteins.
> They undergo crossing over and mutations and thus contribute to the evolution.
> They guide cell differentiation during development.
> The sat chromosomes form nucleoli in daughter cells at nucleoli organization.
What are the main events of the cell cycle
1) Interphase (G1, S, and G2)
2) M phase( mitosis)
3) C phase (cytokinesis)
Interphase - G1, S, G2
-Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis.
-G1 phase is the time during which the cell makes more proteins so that it can grow to its proper size
-S phase, or synthesis phase, is the time during which the cell copies its DNA in preparation for mitosis
-the G2 phase is the time during which a cell replicates its organelles in preparation for mitosis
Mitosis - Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
-Mitosis- part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
-Prophase- first and longest phase of mitosis in which the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses and the chromosomes become visible
-Metaphase- phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
-Anaphase- phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
-Telophase- phase of mitosis in which the distinct individual chromosomes begin to spread out into a tangle of chromatin
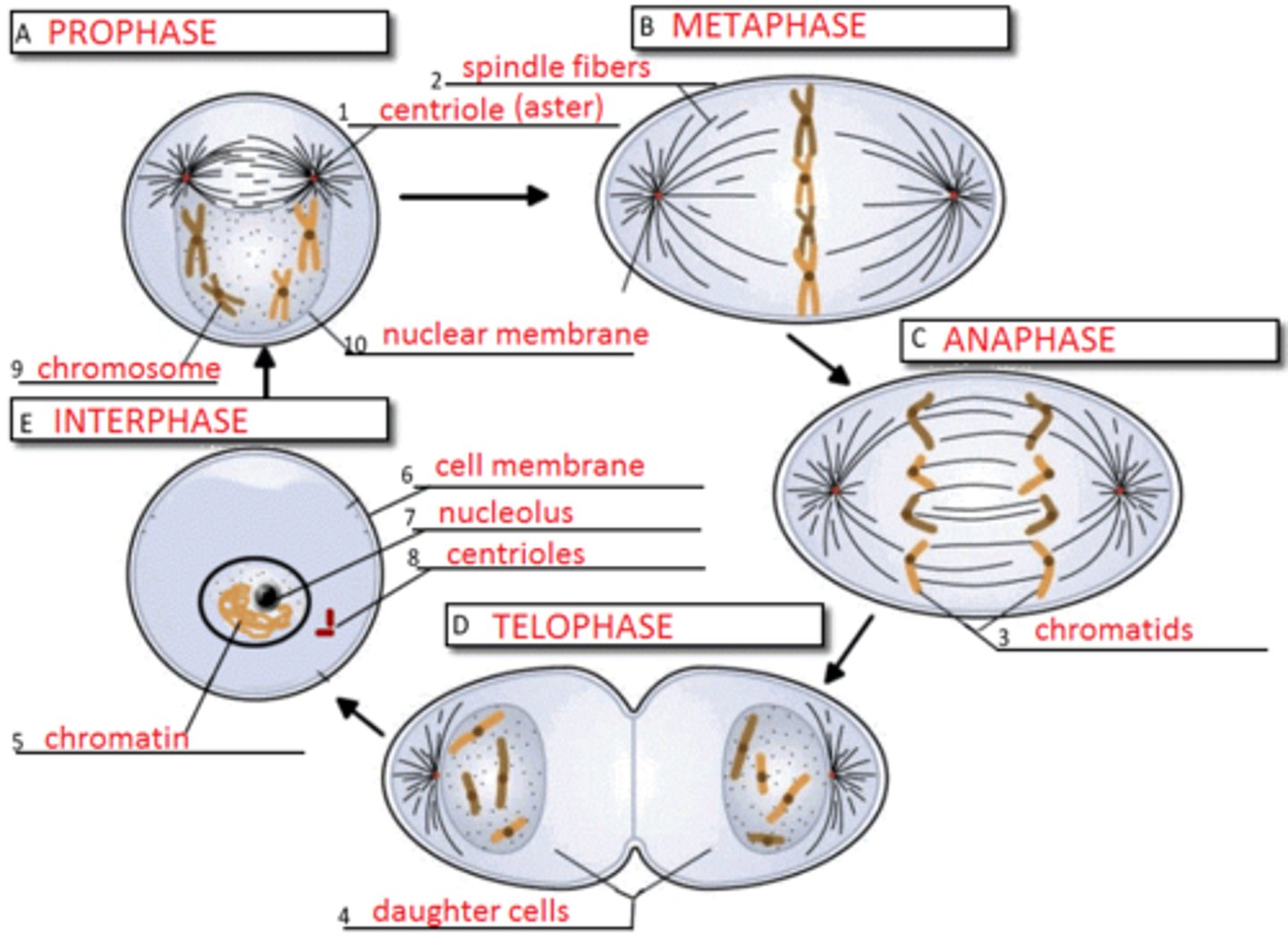
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Sister chromatid
sister chromatid refers to either of the two identical copies (chromatids) formed by the replication of a single chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere. In other words, a sister chromatid may also be said as 'one-half' of the duplicated chromosome.
Which phase of mitosis do the chromosomes line up along the middle
Prophase
What is the role of the spindle fibers
The spindle fibers help separate the chromosomes.
Two main stages of cell division
mitosis, the process of nuclear division, and cytokinesis, division of the cell's cytoplasm