structure of crystals and diffraction exam 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
the hallmark of crystalline state is ______ symmetry, ____ range order
translational, long
crystal structure = ____ + ____
lattice, motif
what is the defining characteristic of a primitive unit cell?
only one lattice point
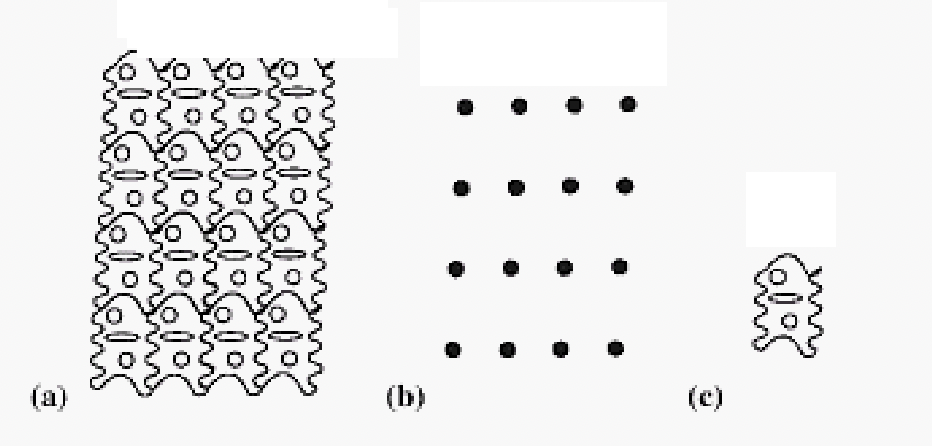
identify a. b. and c.
a=structure, b=lattice, c=motif
What are the symbols for a primitive, base-centered, body-centered, and face-centered unit cell?
P, C, I, F
How many lattice points does a primitive unit cell have and where?
one at 0,0,0
How many lattice points does a base-centered cell have and where?
2 at 0,0,0 and 1/2,1/2,0
How many lattice points does a body-centered cell have and where?
2 and 0,0,0 and 1/2,1/2,1/2
How many lattice points does a face-centered cell have and where?
4 at 0,0,0, 1/2,1/2,0, 1/2,0,1/2, and 0,1/2,1/2
Name the defining symmetry for a triclinic (a) crystal system.
monad (360 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a monoclinic (m) crystal system.
1 diad parallel to [010] (180 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a orthorhombic (o) crystal system.
3 diads parallel to each axis (180 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a tetragonal (t) crystal system.
1 tetrad parallel to [001] (90 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a rhombohedral (R) crystal system.
1 triad parallel to [001] (120 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a hexagonal (h) crystal system.
1 hexad parallel to [001] (60 degree symmetry)
Name the defining symmetry for a cubic (c) crystal system.
4 triads all parallel to <111> directions (120 degree symmetry)
a monad has a ___ fold rotation axis, thus is perfectly asymmetrical
one
a diad has a ___ fold rotational axis, thus looks the same after a ____ degree turn
2, 180
a triad has a ____ fold rotational axis, thus looks the same at ___ degree intervals
3, 120
a tetrad has a ___ fold rotational axis, thus looks looks the same at ___ degree intervals
4, 90
a hexad has a ___ fold rotational axis, thus looks the same at ___ degree intervals
6, 60
fractional coordinates are only used when defining the position of atoms constituting the _____
motif
<> are used for a family of crystallographically equivalent ______ and {} are used for a family of crystallographically equivalent ____
directions, planes
for a cubic system, {100} = what planes?
±(100), ±(010), ±(001)
for an orthorhombic system, {100} = what planes?
±(100)
ZONE LAW: if the dot product of [uvw] and (hkl) = 0 then what
[uvw] vector lies in the plane
how do you represent a negative number in a direction or plane
line above number
what is this equation used to find? D²=(q-p)igij(q-p)j
distance between two points
in an fcc unit cell, a point at 1/2, 0, 0 has how many nearest neighbors? what is its shape?
6, octahedral
in an fcc unit cell, a point at 1/4, 1/4, ¾ has how many nearest neighbors? what is its shape?
4, tetrahedral
what is the volume of a sphere?
4/3 pi r³