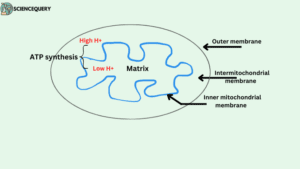
Electron transport chain
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
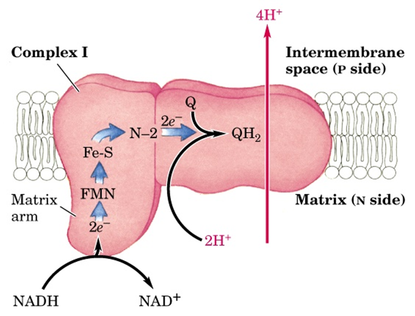
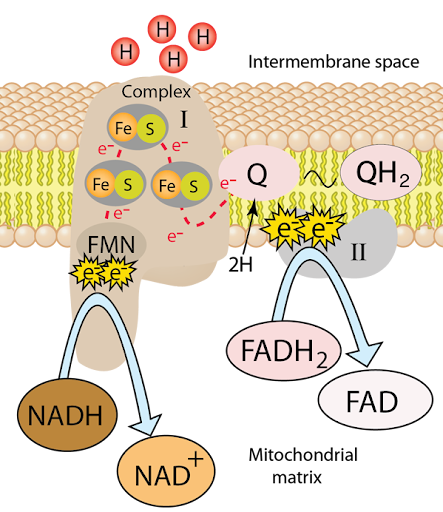
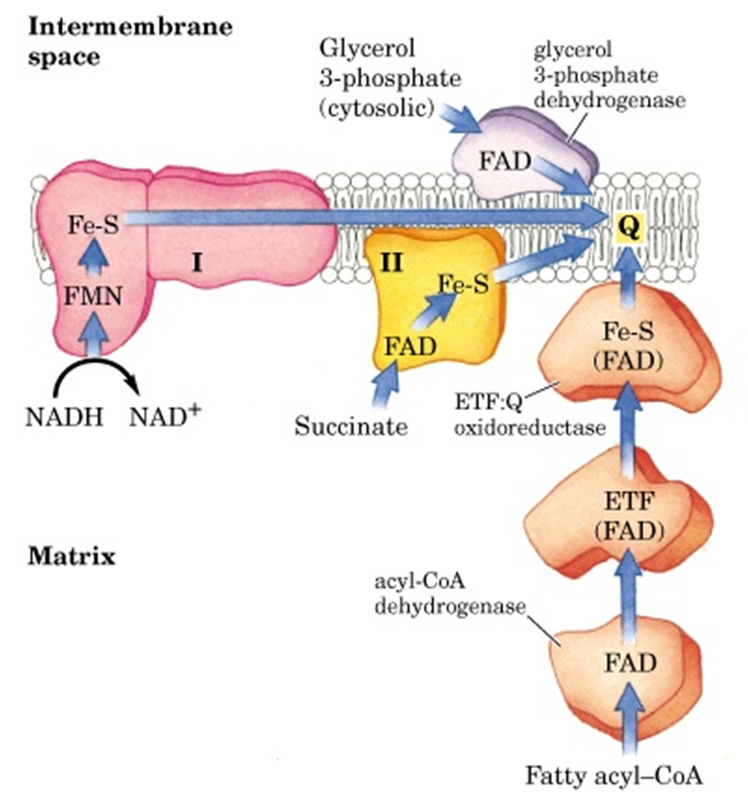
Complex 1
2 electrons will be accepted from NADH
Transfers them to Coenzyme Q
Pumps 4 H+ into the inter membrane
NADH turns into NAD+
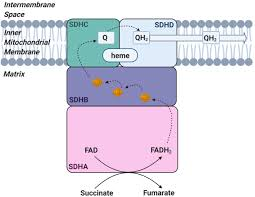
Complex 2/ Succinate Dehydrogenase
Accepts electrons from FADH2
Transfer them to Coenzyme Q
Does not pump protons
FADH2 turned FAD
Coenzyme Q/Ubiquinone
carriers electrons from Complex 1 & 2 into complex 3
Complex 3/Cytochrome Bc complex
Transfer electrons from Coenzyme Q to cytochrome C
Pumps 4 H+
Cytochrome C
Carriers electron one at a time from complex 3 & 4
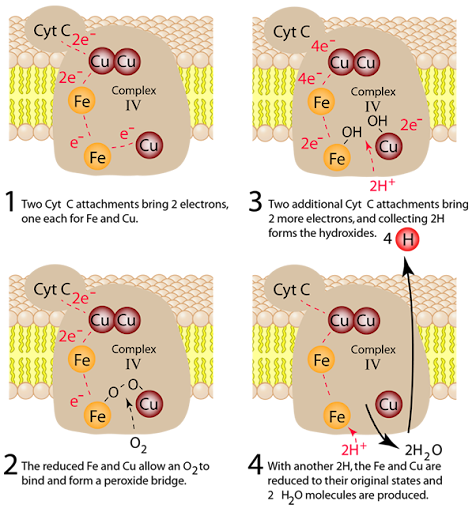
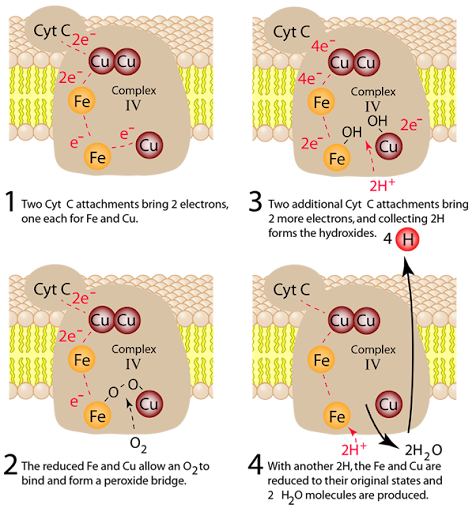
Complex 4/Cytochrome C oxidase
Transfer electrons to molecular oxygen(final electron acceptor
Reduces o2 to h2 O
pumps 2 H+ per pair of electrons
Structure of ATP Synthase( F 0 and F1)
F₀ (membrane-embedded motor)
Forms a proton channel that allows H⁺ ions to flow down their electrochemical gradient.
Contains a c-ring of subunits that rotates when protons pass through.
Acts like an electric motor, converting proton motive force into mechanical rotation.
F₁ (catalytic headpiece)
Located on the matrix side (mitochondria) or stroma side (chloroplasts).
Composed of α₃β₃ hexamer (three α and three β subunits arranged alternately).
The β subunits contain the catalytic sites for ATP synthesis.
Connected to F₀ by a central stalk (γ and ε subunits) and a stator (b subunits) that hold the α₃β₃ hexamer stationary
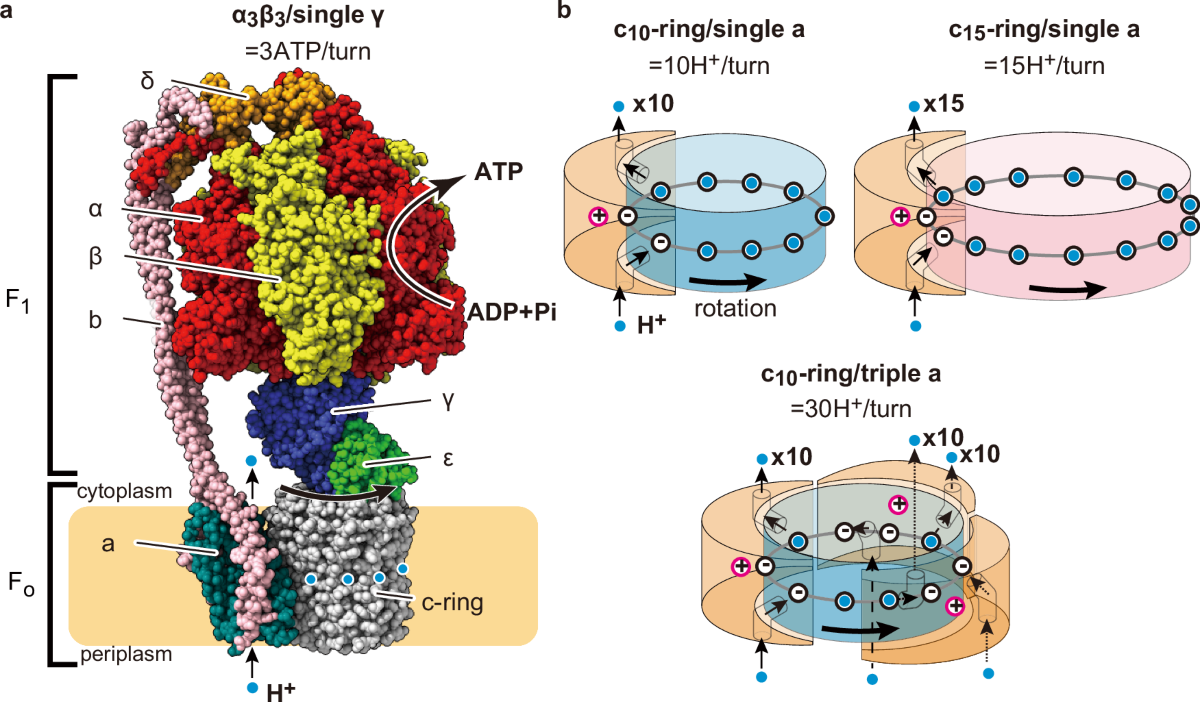
Structure of ATP Synthase(Rotary)
Proton flow through F₀ drives rotation of the c-ring and central stalk (γ subunit).
This rotation induces conformational changes in the β subunits of F₁:
One β subunit binds ADP + Pi.
Another β subunit synthesizes ATP.
The third β subunit releases ATP.
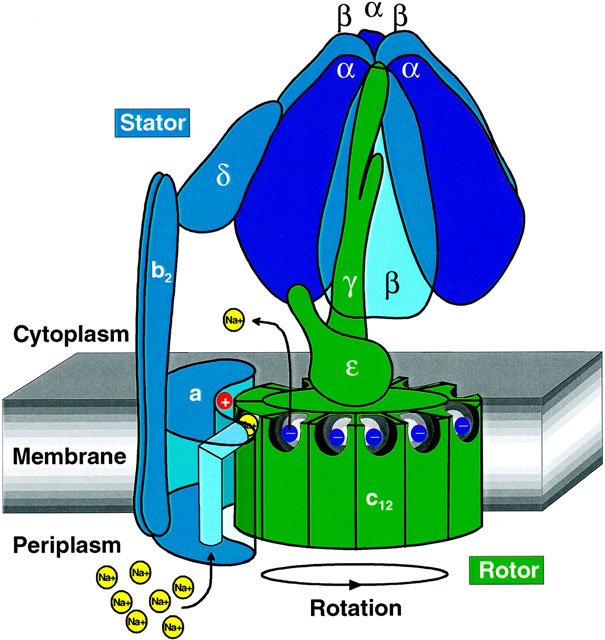
Structure of ATP Synthase(key structure)
Stator arm: Prevents the α₃β₃ hexamer from rotating with the stalk.
Rotor (c-ring + γ subunit): Rotates with proton flow.
Catalytic sites: Located in the β subunits of F₁.
Coupling: Mechanical rotation → chemical synthesis.
net inputs
NADH, FADH2, O2, ADP + Pi
Net outputs
ATP, H2O, NAD, FAD
Location of ATP Synthase
inner mitochondrial membrane