MKTG 650 Consumer Behavior Exam 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is a conjoint analysis?
Most widely used market research method Based on the premise in which the value assigned to products
is based on the combined value of its attribute levels
Uses of Conjoint Analysis
Understand the how much consumers value different
attributes and attribute levels.Figure out the optimal combination of features for different consumers.
Predict market shares for products that have different combinations of features.
• Identify market potential for concepts not yet available.
• Quantify brand value
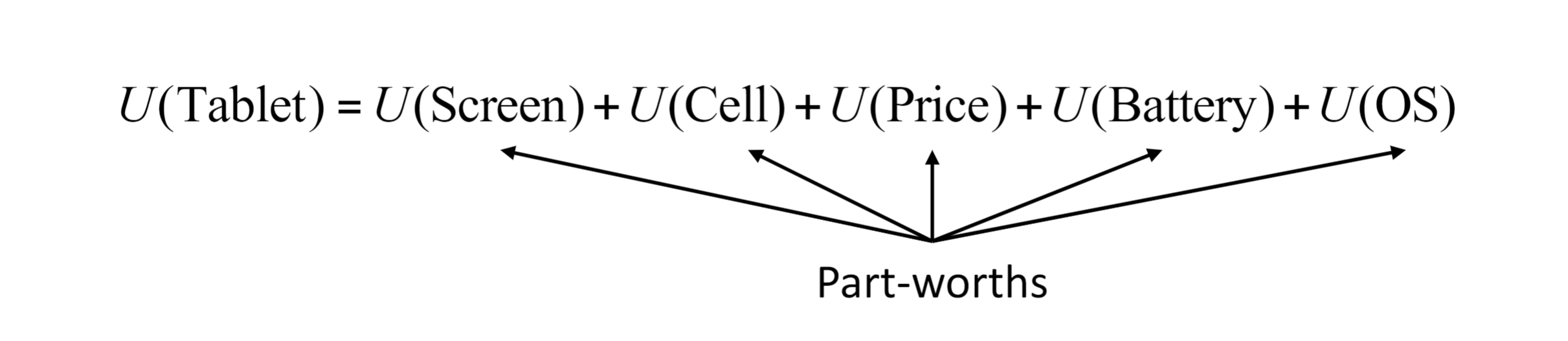
Utility for a Product
Sum of utilities of its attribute levels; The whole is equal to the sum of its parts
Stages in Conjoint Analysis
• Select attributes
• Select levels for these attributes
• Create product profiles
• Collect data
• Estimate partworths
• Derive insights and make predictions
How to Select Attributes
Do not use too many attributes.
• Focus on attributes that impact sales (cell service??).
• Do not use ambiguous descriptors (e.g., $6 to $8).
• Do not use subjective attributes (e.g., aesthetic
appeal).
• Watch out for infeasible combos.
How to Select Attribute Levels
Keep levels similar across attributes
Keep levels realistic
Make sure the range of levels is all you want to asses
Calculating Attribute Importance
The bigger the partsworth, the more IMPORTANT
Attribute Importance Formula
Range / (Sum of Ranges)
Willingness to Pay Formula
1) Price Range / Util Range = Price per Utility
2) Multiply partworth by price per utility to get WTP
Loss Aversion
People are more sensitive to losses than gains
Endowment Effect
People value objects they own more than the same object when they do not own it
Psychological Ownership
The feeling that something is yours that results from control, intimate knowledge and self-investment

Foot-In-The-Door Technique
A two-step procedure for enhancing compliance
in which a minor initial request is presented
immediately before a more substantial target
request.
Agreement to the initial request makes people
more likely to agree to the target request than
would have been the case if the latter had been
presented on its own.

Door-In-The-Face Technique
A two-step procedure for enhancing compliance
in which an extreme initial request is presented
immediately before a more moderate target
request.
Rejection of the initial request makes people
more likely to accept the target request than
would have been the case if the latter had been
presented on its own.

The Beauty Premium
Attractive people are treated better than unattractive people (and people are more likely to listen and comply to them)

Principles of Persuasion - Liking - Similarity
Principles of Persuasion - Liking - Praise

Reciprocity
If someone gives us something, we feel the need to give back even if we didn’t want their initial “gift” in the first place
Consistency
People behave consistently with previous “clear
commitments”

What is a clear committment?
• Requires action
• Voluntary
• Public
Consistency - Rule of 3 Yeses
Ask 3 questions you know you will get a yes to and then ask for what you really want

Principal of Persuasion - Social Proof
People follow the lead of others; use social power when applicable (Monkey see, monkey do)

Principle of Persuasion - Authority
People defer to experts
Principles of Persuasion - Scarcity
People want more of what they can’t have
EX: Bernie Madoff Ponzi Scheme
Scarcity = Limited, Urgency, Exclusivity
Nudge
Any aspect of the choice architecture that
alters people’s behavior in a predictable way without
forbidding options or significantly changing their
economic incentives
Choice Architecture
The method by which choices are presented to people to influence their behavior
Psychological Reactance
A phenomenon that involves a hostile motivational reaction to offers, persons, rules, or regulations that are perceived to threaten behavioral agencies and freedoms
What causes Psychological Reactance?
May occur when a individual feels that someone or something is threatening to limit/control their behavior or choice.
This perceived threat can elicit a hostile response due to them feeling their behavioral freedom being infringed on
Nudges must be ____________ to implement?
Relatively costless

Mapping
The choice from choice to outcome (or welfare)
Paradox of Choice
Less is more; too much can be stressful (Choice Paralysis)

Option Attachment
A sense of ownership when consumers select one
option, they feel a sense of loss for the others.
Increases the attractiveness of the forgone options.
Choosing feels like losing.
Escalation of Expectations
The more choices you have, the greater the expectations
for the option that is chosen.
Becomes harder to meet or
exceed expectations. Leads to dissatisfaction.

Choice Paralysis
The more choices you have, the harder it is to make a decision and the more attractive the choice set is.
Makes people less likely to choose (EX: Jams)

How do you deal with too much choice?
Mindfulness

Mindfulness
Being present here and now, paying attention to thoughts, bodily sensations, emotions, and external environment with kindness and not negativity
Satisficing
A decision-making strategy that aims for
a satisfactory or adequate result, rather than the
optimal solution.
Instead of considering all information, consumers
apply a simple rule of thumb to make a decision that
is “good enough.”
Performance Tactic
Make choices by focusing on one attribute that is
important to you and select the best.
Habit Tactic
Made choices that we last made to simplify our decision making process
What leads to habit formation?
Ubiquity
What is ubiquity?
In general, the term ubiquity means being physically present in several places simultaneously, or being omnipresent. In e-commerce and customer service, ubiquity refers to the fact that your visitors and customers can access your services from anywhere, at anytime, and on any device.
Brand Loyalty Tactic
Repeated purchases of a brand because it satisfies your needs more than other brands
System 1
Intuition and Instinct; Automatic pilot, unconscious
System 2
Rational thinking; takes effort, slow, lazy, logical, indecisive