Chapter 2: Chemical Composition of Body
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
atoms
smallest unit of chemical elements
nucleus
Center of an atom
protons and neutrons
nucleus contains
mass number
protons + neutrons =
atomic number
# of protons
number of protons
what determines elements
isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
number of electrons
_________ is equal to number of protons
2 electrons
1st shell can hold
8 electrons
2nd shell can hold
valence electrons
outermost shell of electrons
1
hydrogen - # of electrons in shell 1
1
hydrogen - number of chemical bonds
4
carbon - # of electrons in shell 2
4
carbon - number of chemical bonds
5
nitrogen - # of electrons in shell 2
3
nitrogen - number of chemical bonds
6
oxygen - # of electrons in shell 2
2
oxygen - number of chemical bonds
6
sulfur - # of electrons in shell 3
2
sulfur - number of chemical bonds
covalent bonds
sharing of valence electron pairs
nonpolar bonds
electrons equally distributed between 2 bonds
polar bonds
unequal electrons distributed between 2 different atoms, electrons pulled more towards one direction than the other
more electronegative
the end of molecule towards which electron is pulled in a polar bond is
carbon and hydrogen
two molecules that have similar electronegativity that they are considered the same and nonpolar bonds
polar covalent bond
H2O is what type of bond
nonpolar covalent bond
CH4
ionic bonds
one or more valence electrons from one atom are completely transferred to second atom
ions
atoms that have positive or negative charge
anions
atoms that have negative charged ions
cations
atoms that have positive charged ions
hydrogen bonds
weak attraction between partially negative oxygen and partially positive hydrogen located near each other
heat capacity, surface tensions
hydrogen bonds are responsible for
acid
protons donors
bases
proton acceptors
strong acid
complete dissociation of H+
strong base
complete dissociation of OH-
weak acid
substance that donates proton but does not completely disassociate
pH
-log [H+], molar concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions in moles/liters
high concentration of H+
acid is high or low concentration of H+
low concentration of H+
base is high or low concentration of H+
buffer
stabilizes pH in solution
weak acid and weak base
buffer's two components
organic molecules
contain carbon and hydrogen
hydrocarbons
bonds that contain carbon and hydrogen
linear and cyclic
two common forms of hydrocarbons
functional groups
common molecular arrangements with a carbon hydrogen backbone
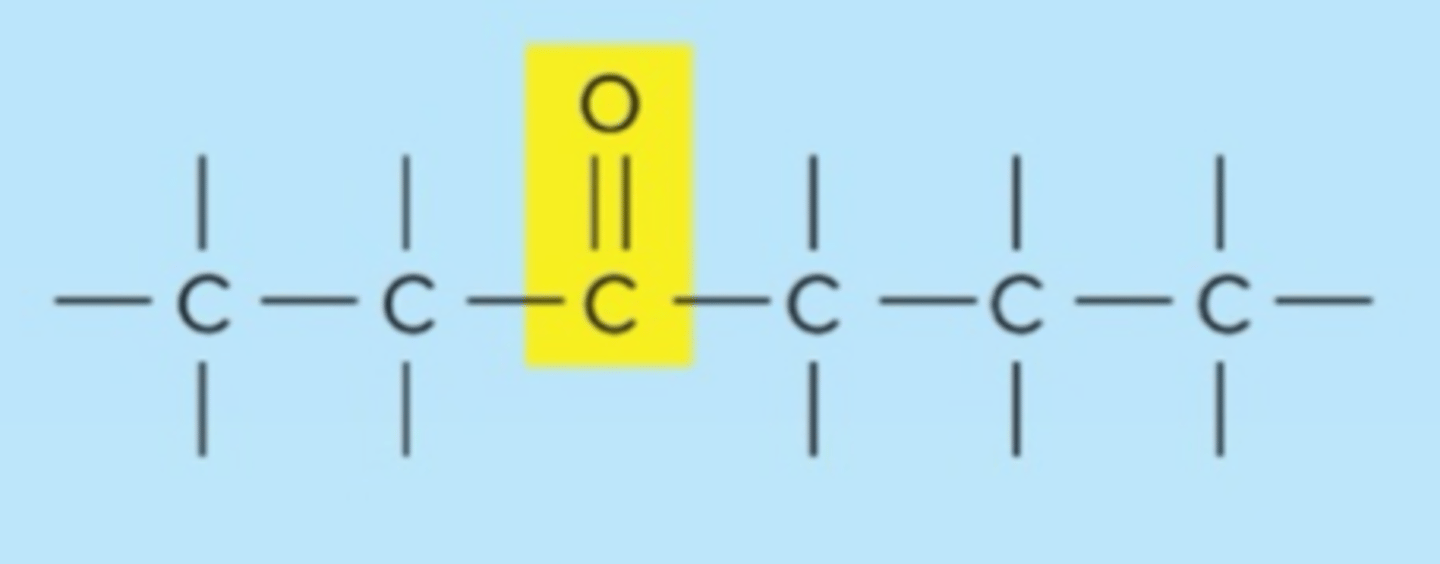
carbonyl
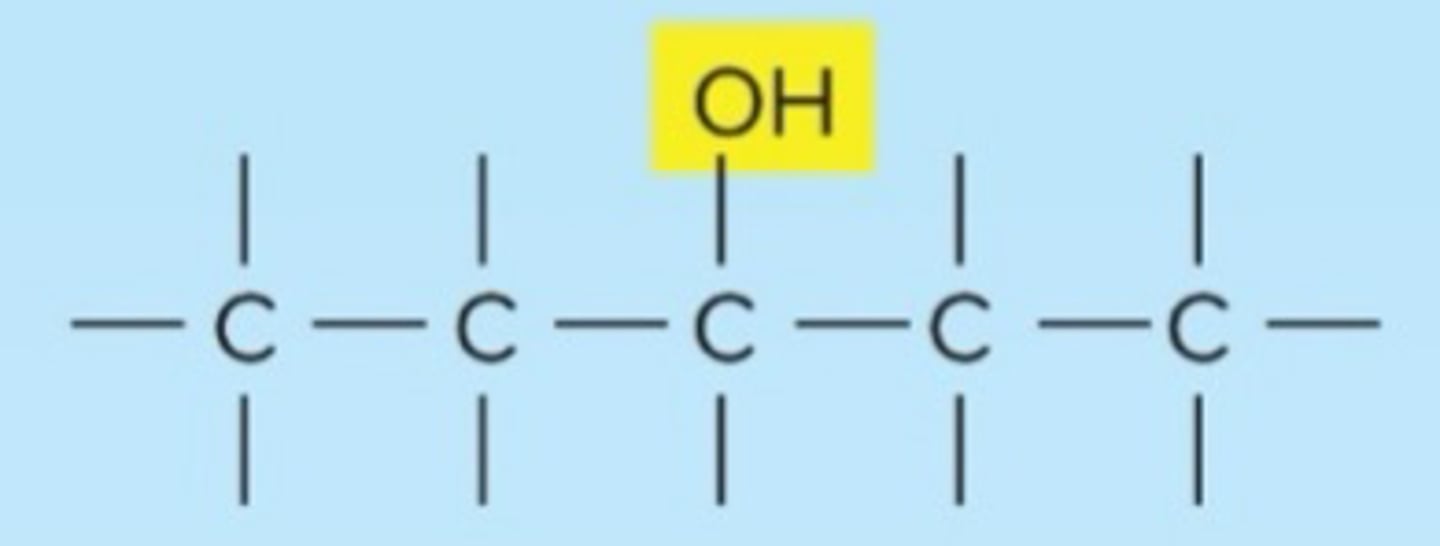
hydroxyl
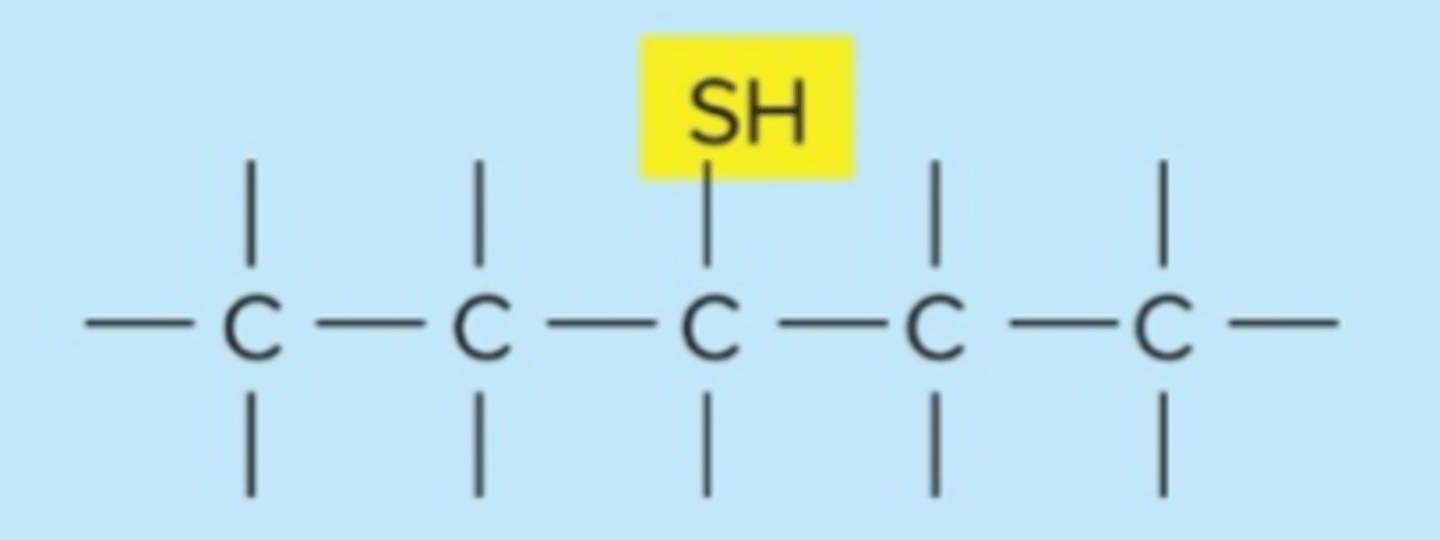
sulfhydryl
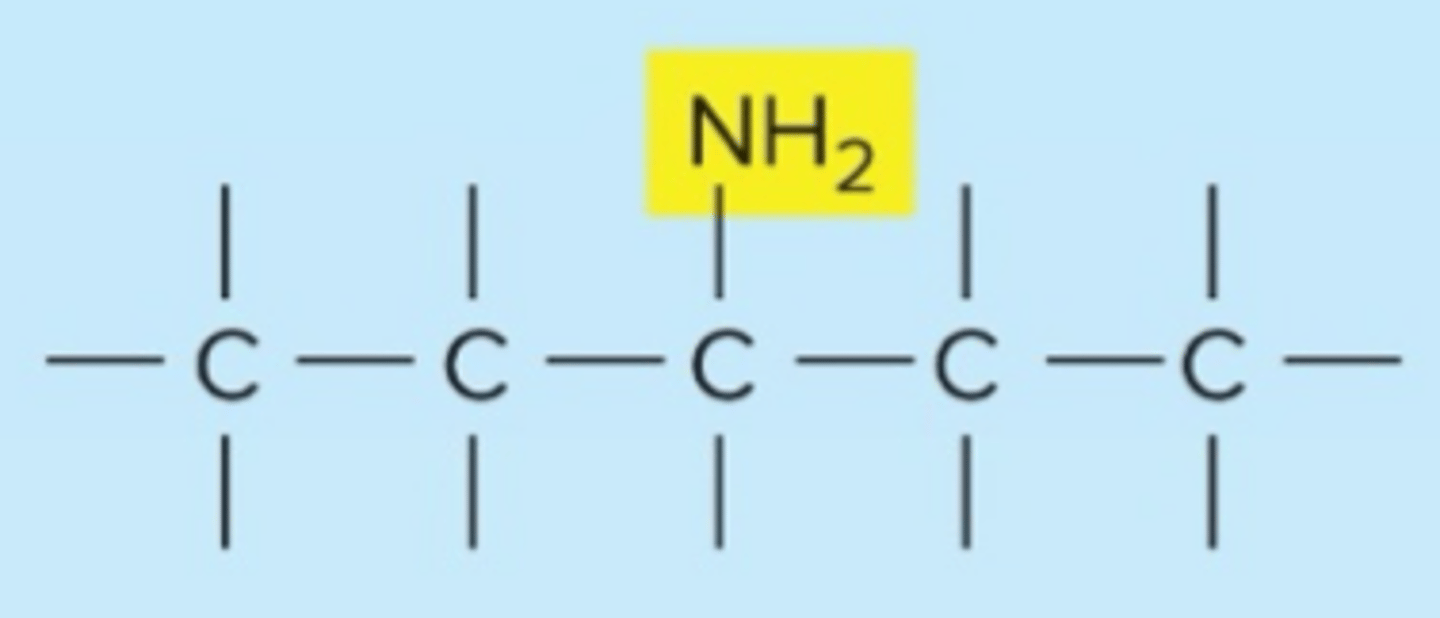
amino
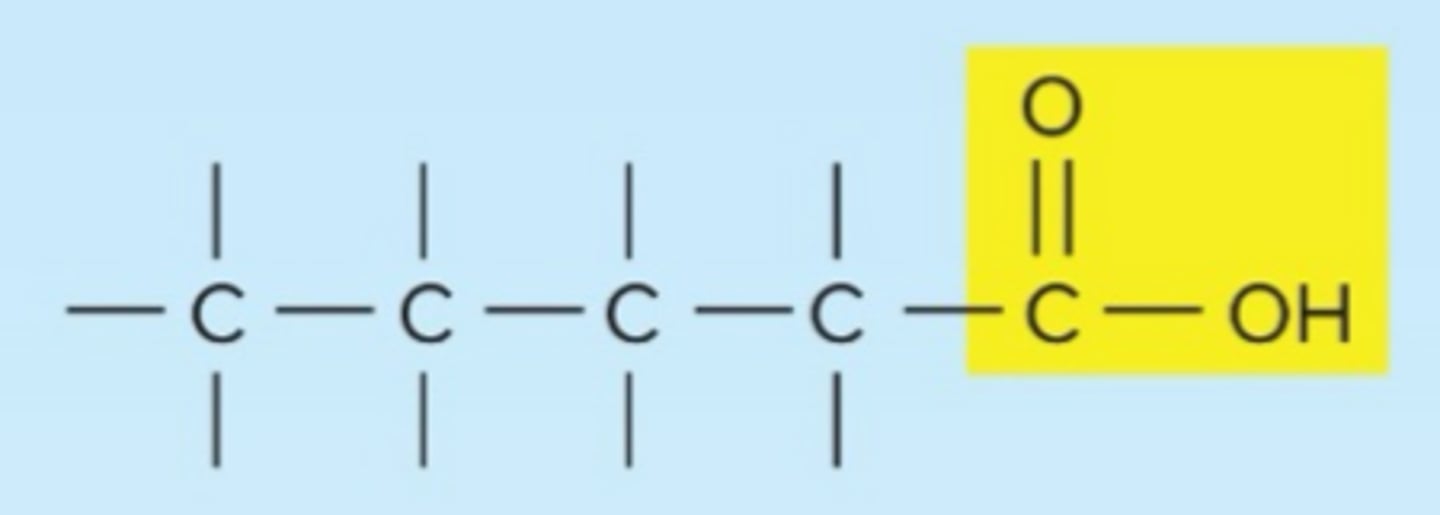
carboxyl
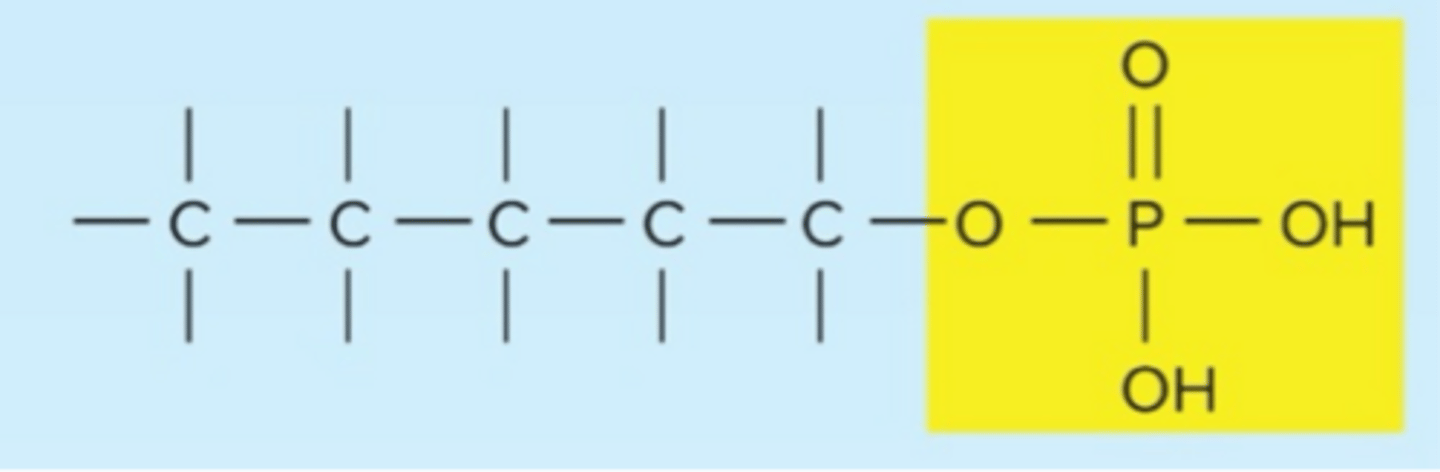
phosphate
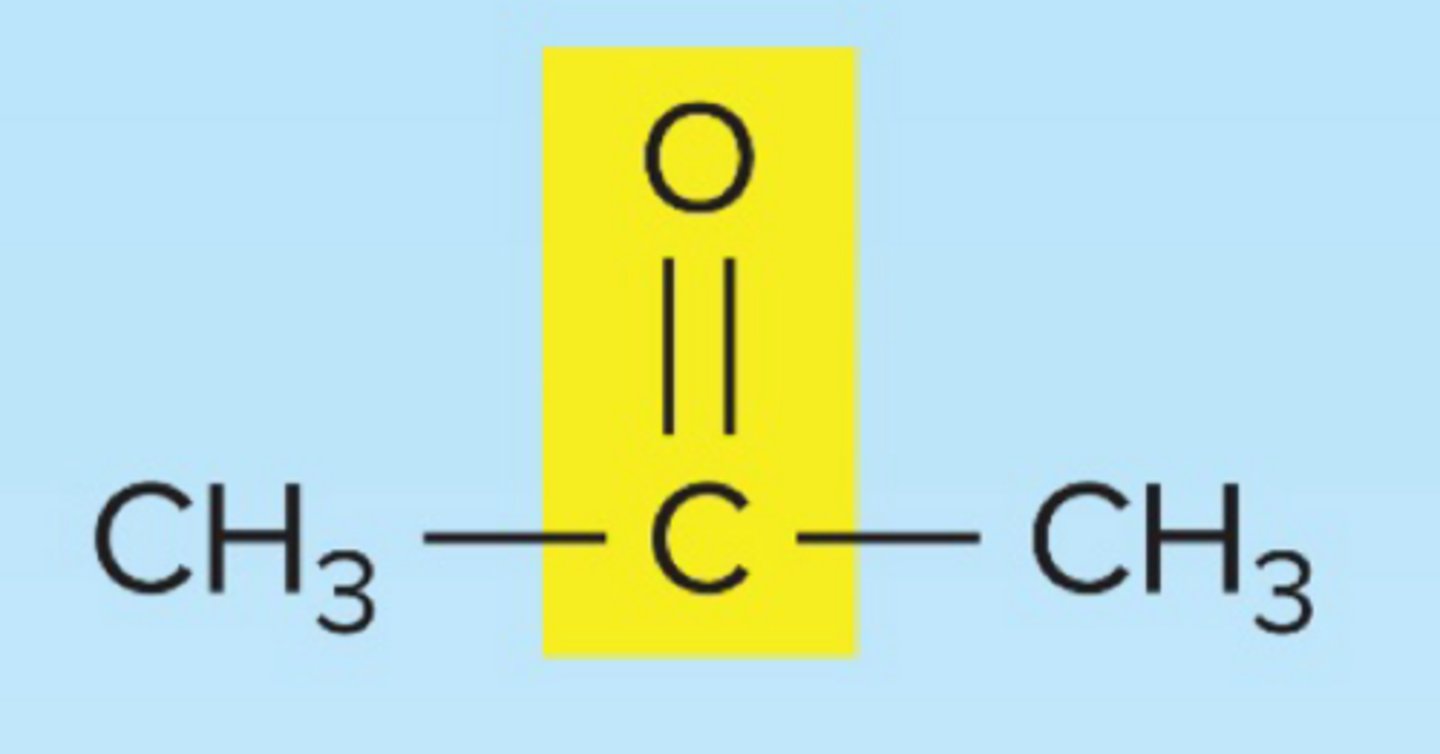
ketone
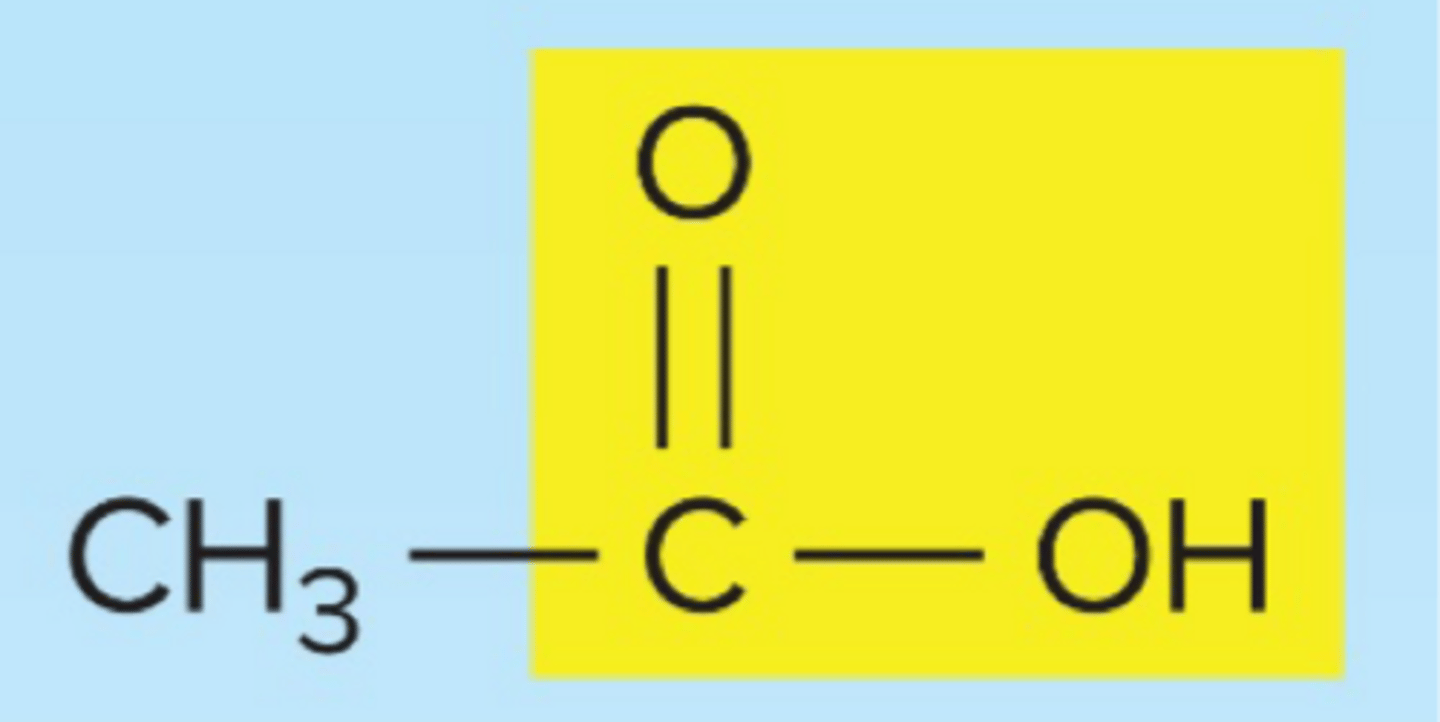
organic acid
aldehyde
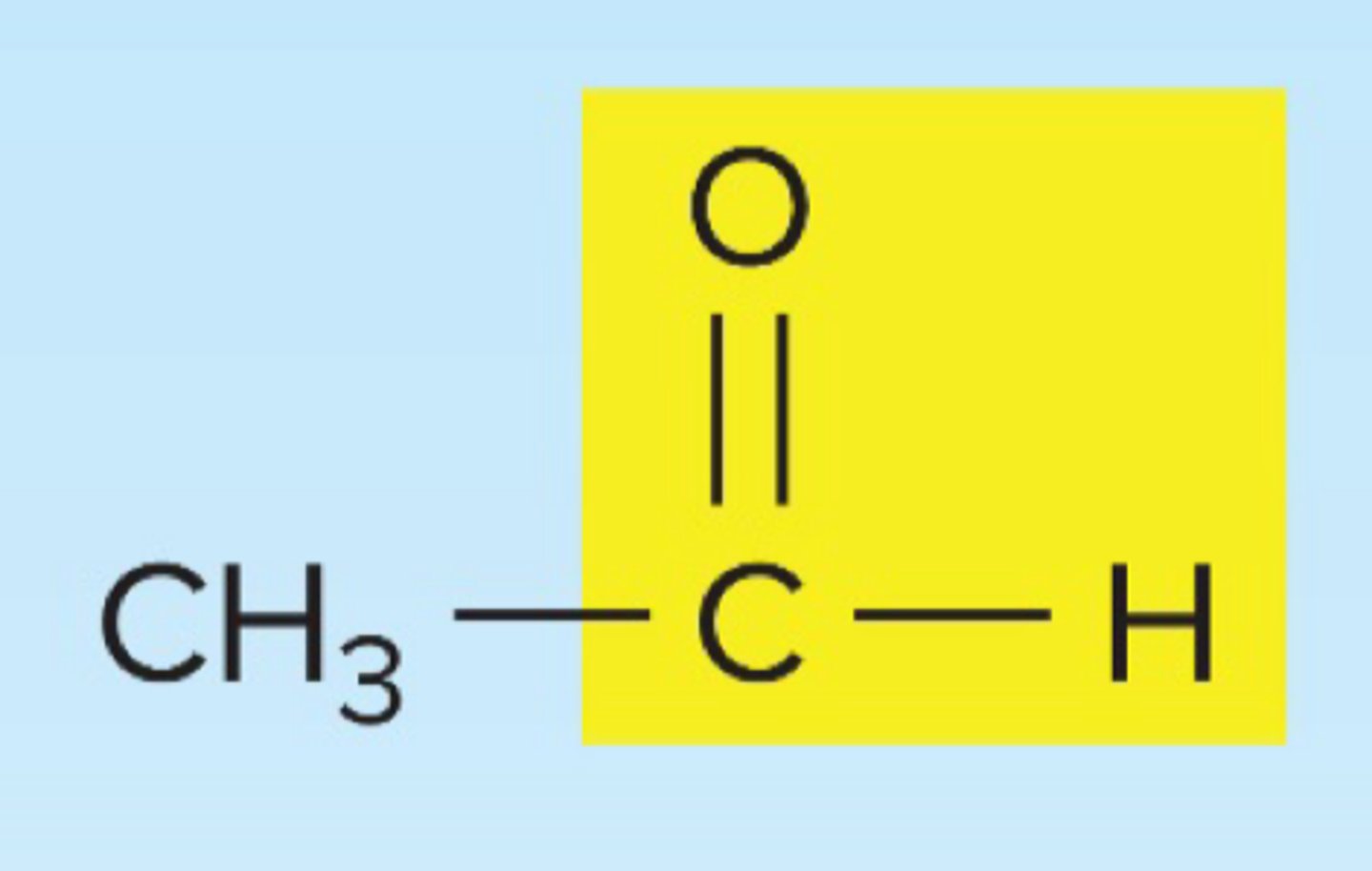
Alchohol
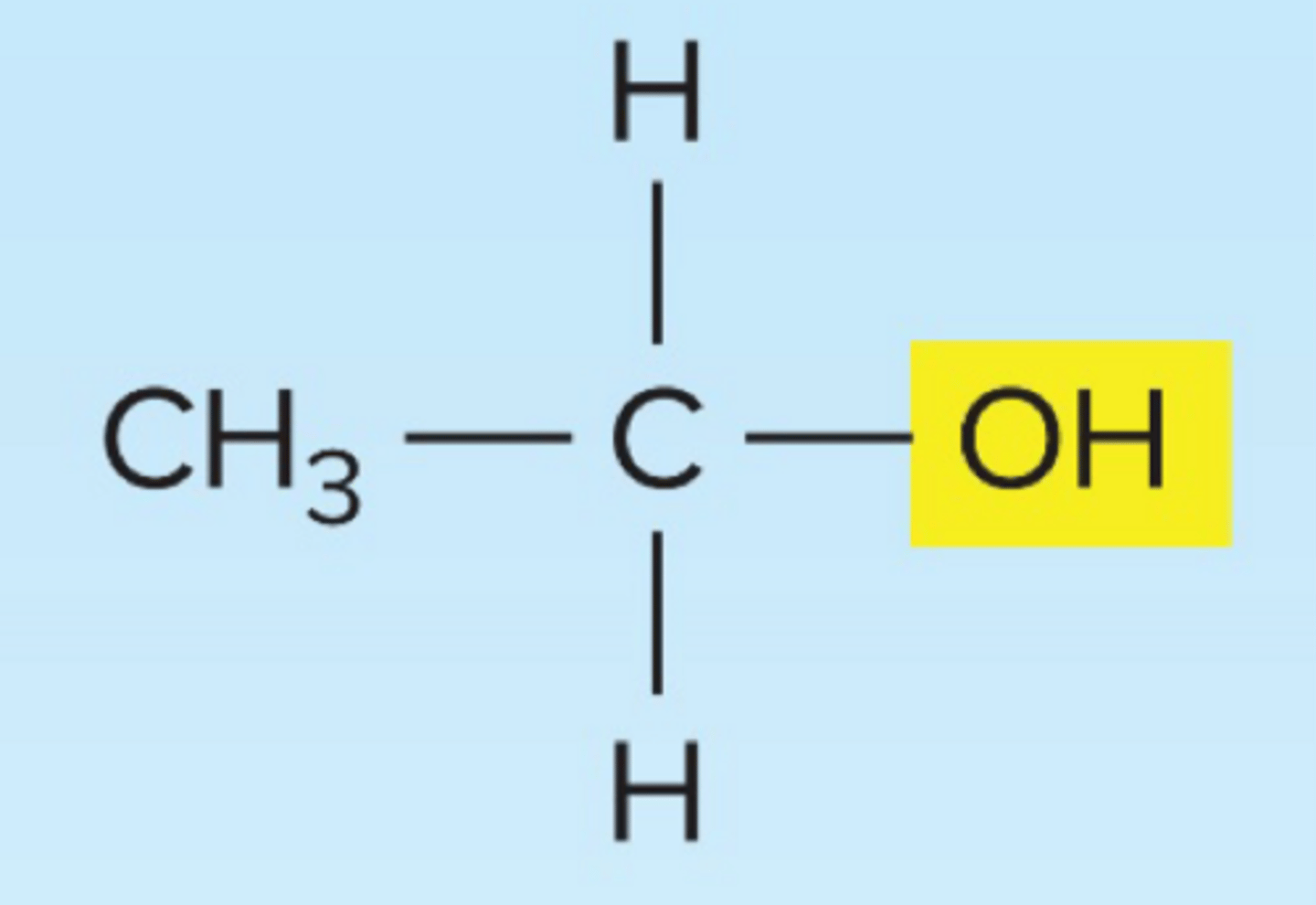
isomer
same molecular formula, different structure
stereoisomers
isomers that have different biological properties depending on configuration
cis vs trans
stereoisomers example
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
4 major macromolecules
monomer
simple molecule, acts as building block to chemically bond with similar molecules to form a polymer
polymer
many monomers built together
energy source and storage, cell recognition, and part of cell structure
carbohydrate function
monosaccharides
monomer of carbohydrates, simple sugar
glucose
example of monosaccharides
linear and cyclic form
carbohydrates exist in what two forms
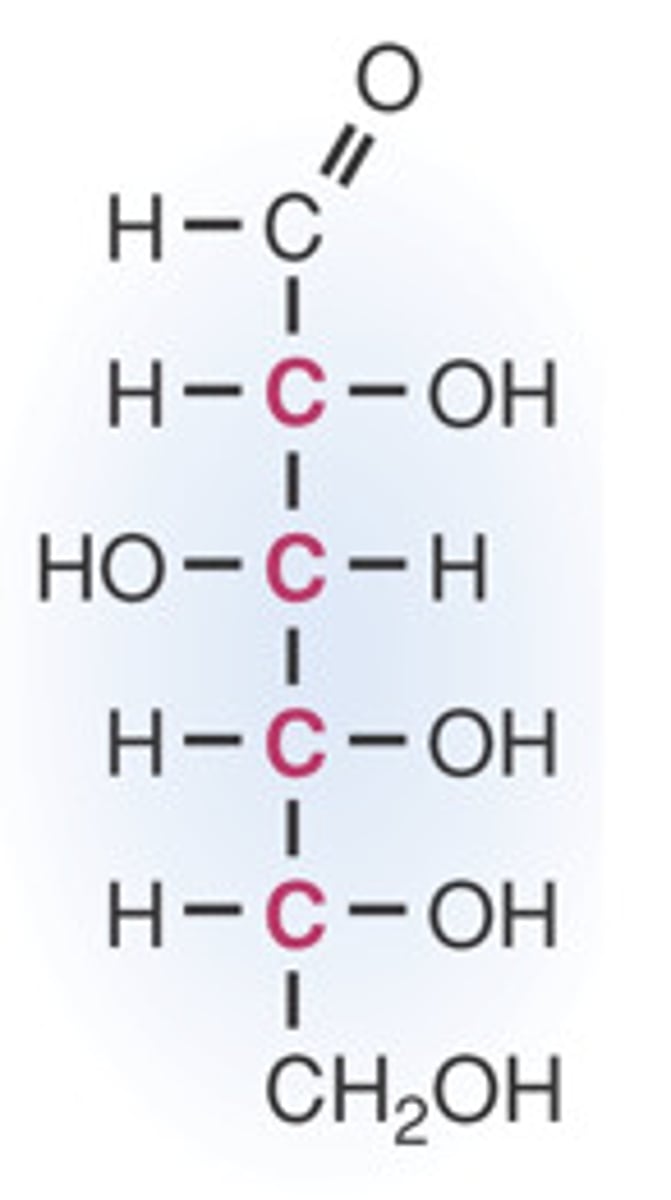
linear form of carbohydrate
contain a carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone) and multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups
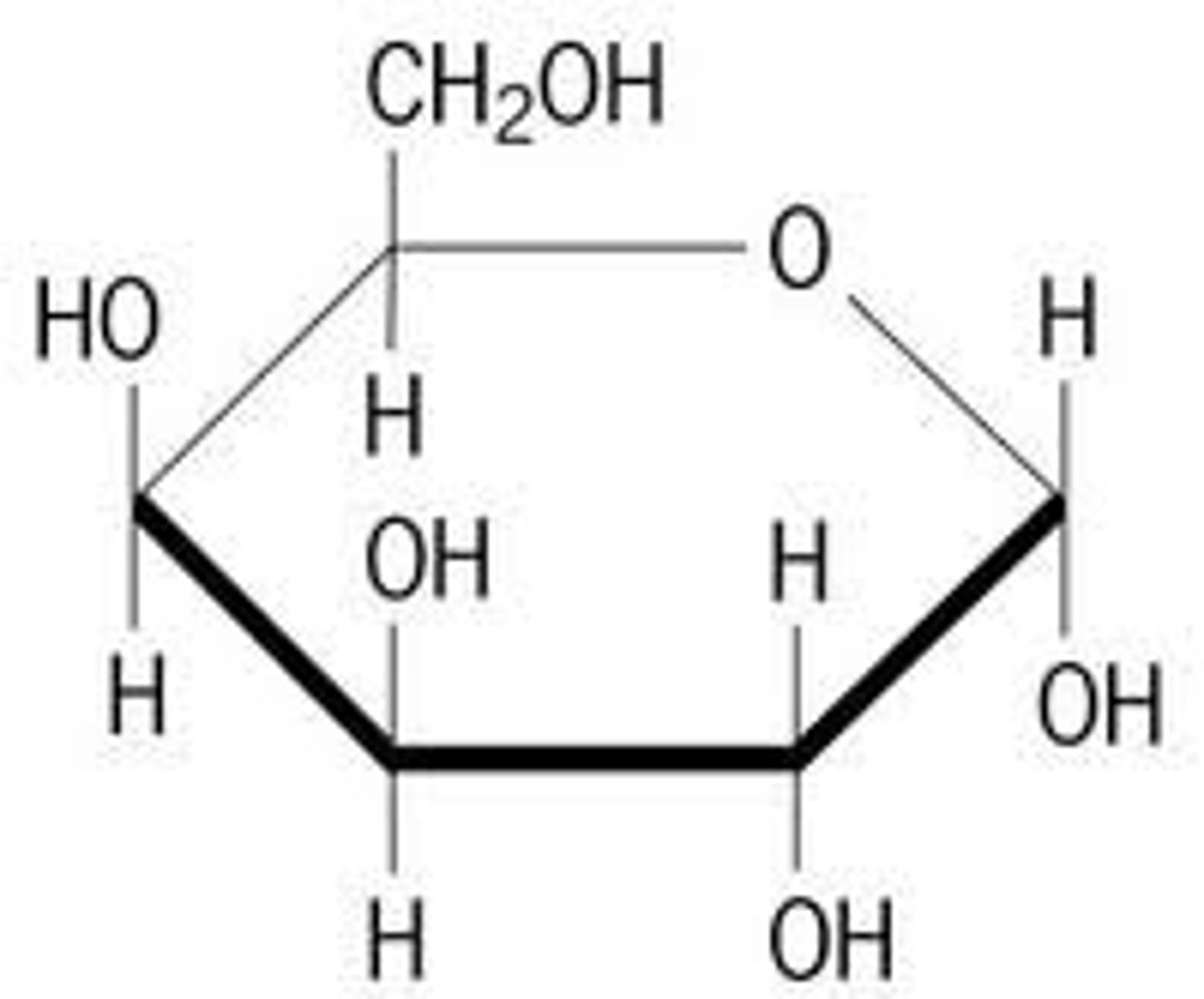
cyclic form of carbohydrate
oxygen included in ring
disaccharides
double sugar, two monosaccharides joined covalently - ie: maltose
polysaccharide, glycosidic bond
polymer of carbohydrates + bond used
repeating glucose subunits
polysaccharides are often
starch
polysaccharide, energy storage in plants - humans CAN digest
glycogen
polysaccharide, energy storage in animals - humans CAN digest
cellulose
polysaccharide, cell wall of plants - humans CANNOT digest
dehydration synthesis
binds monomers together to form polymers by removing a water molecule
hydrolysis
water molecules are used to break down complex compounds into smaller components
lipids
all are insoluble in polar substances (water)
fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, prostaglandins
lipid categories
fatty acid
long hydrocarbon chain with hydroxyl group at end
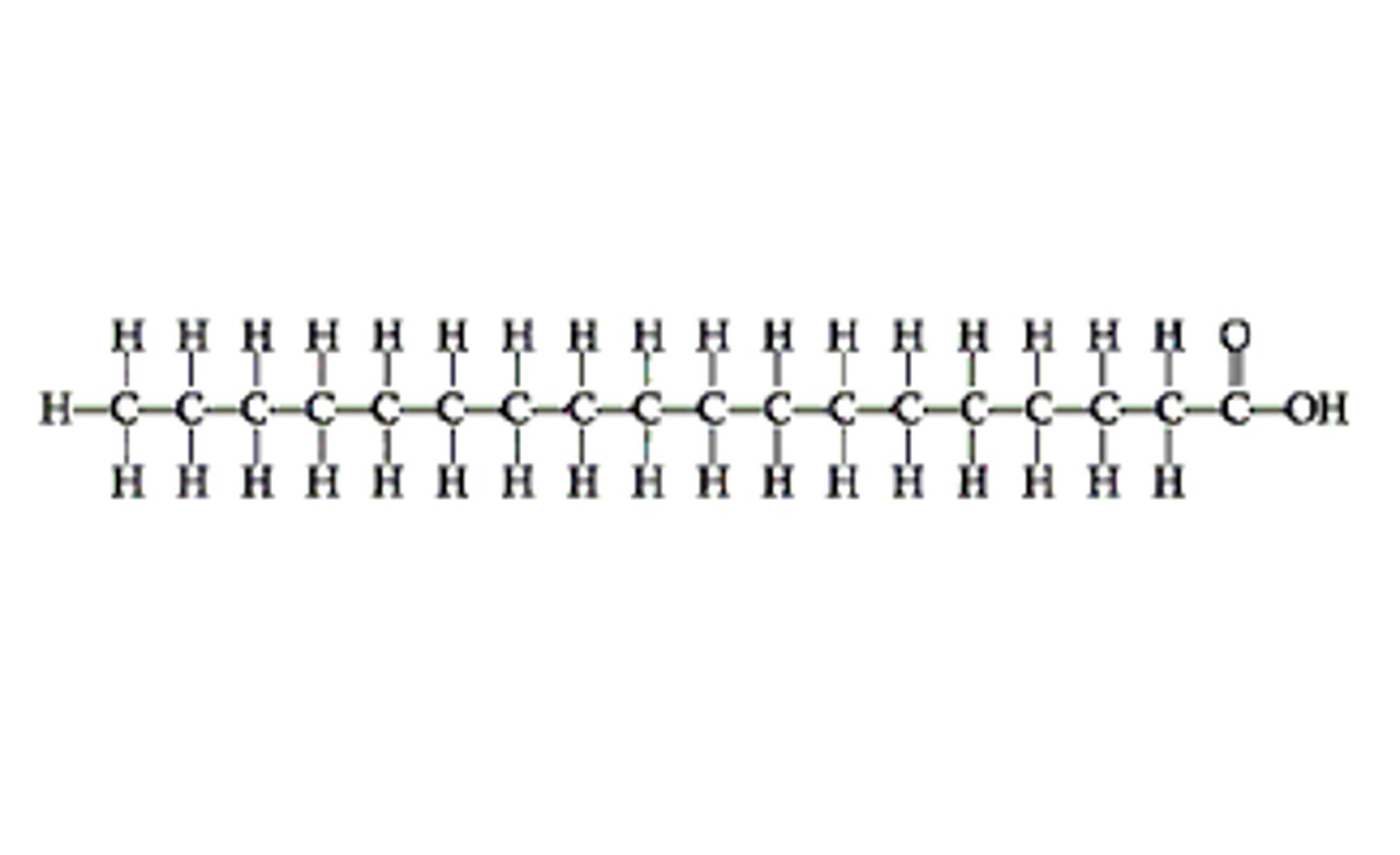
store energy
fatty acid function
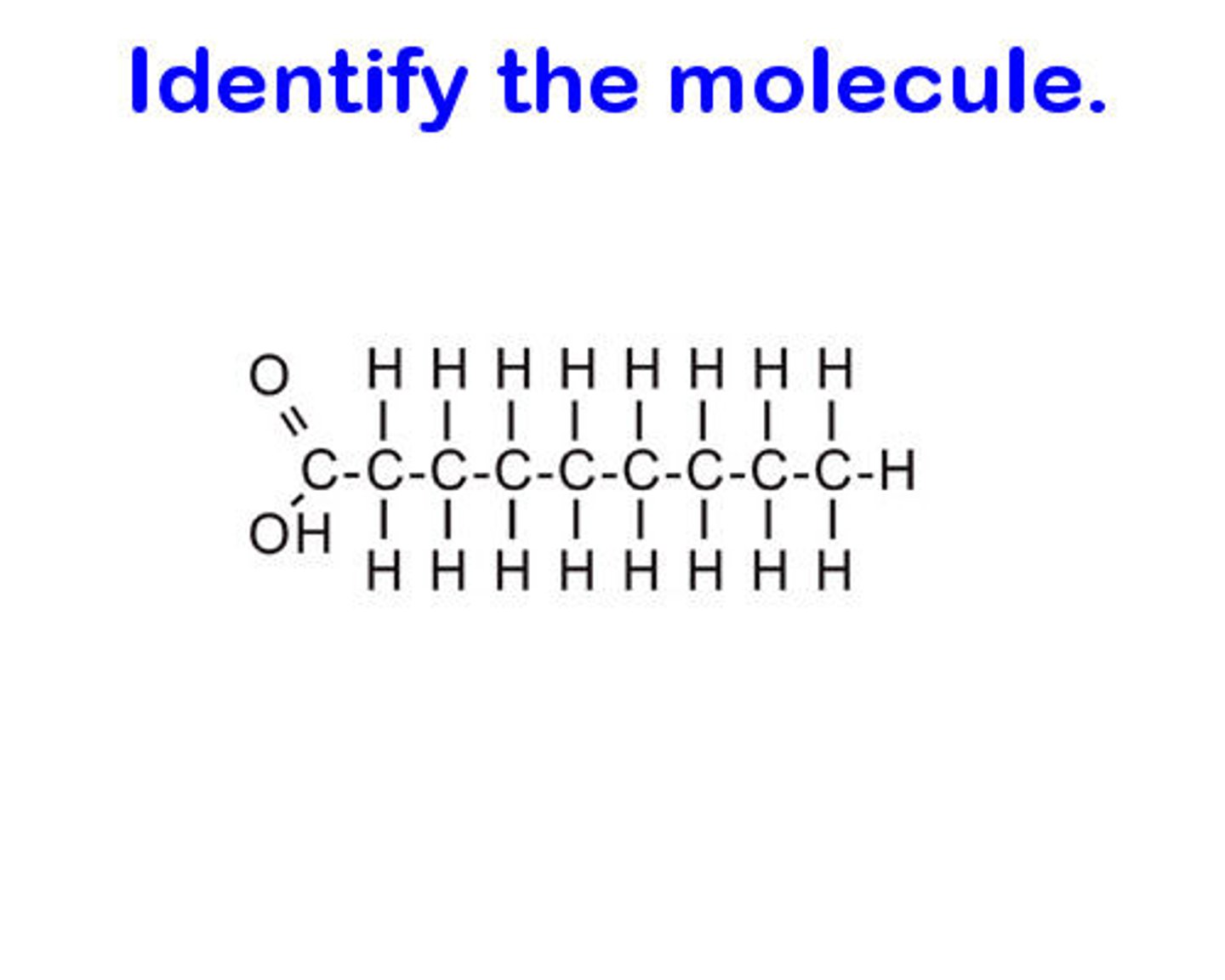
saturated fatty acid
all single bonds
unsaturated fatty acid
contains double bonds
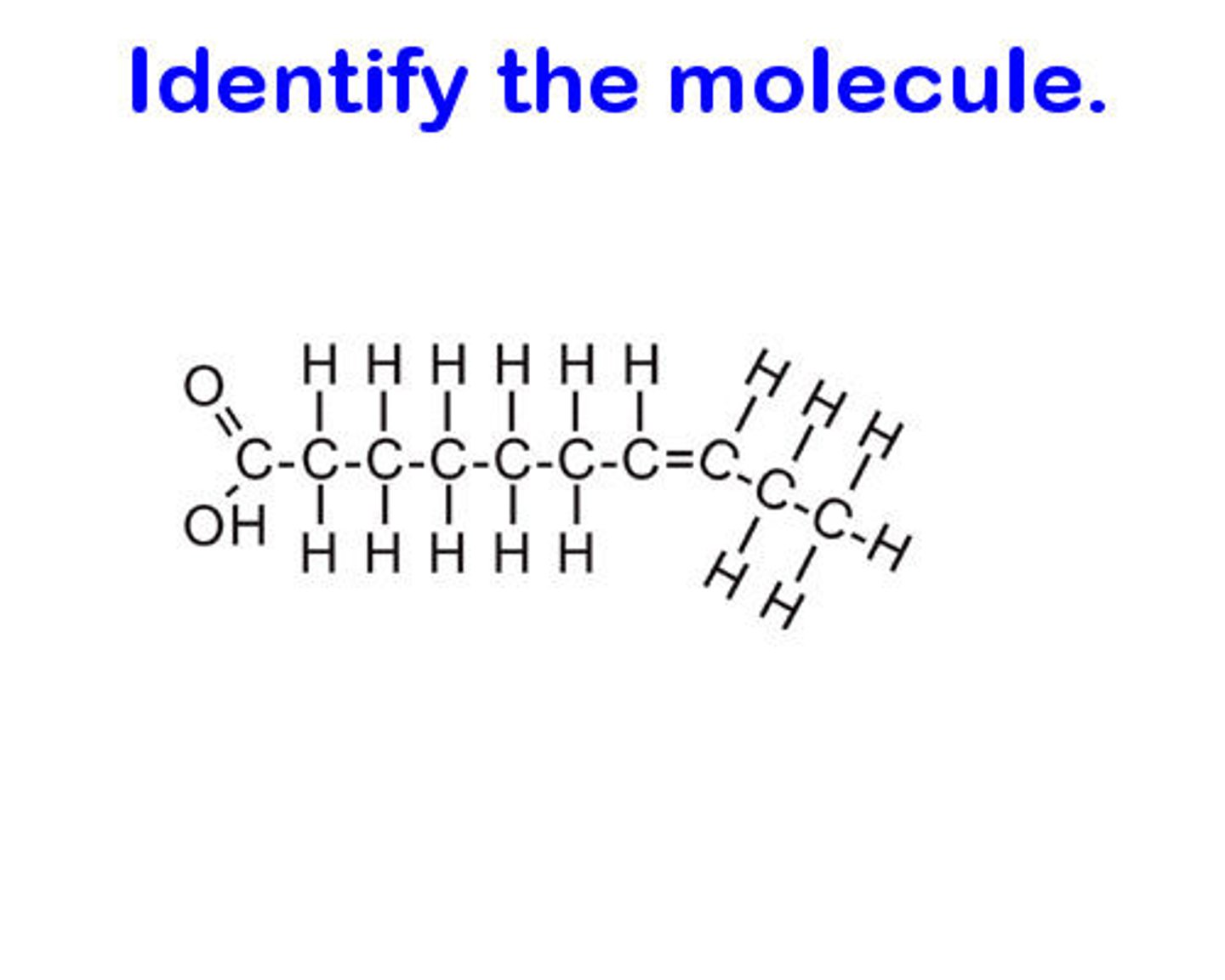
cis unsaturated fatty acid
hydrogen on same side, body CAN digest
trans unsaturated fatty acid
hydrogen on opposite side, body CANNOT digest
triglyceride
1 glycerol with 3 fatty acids
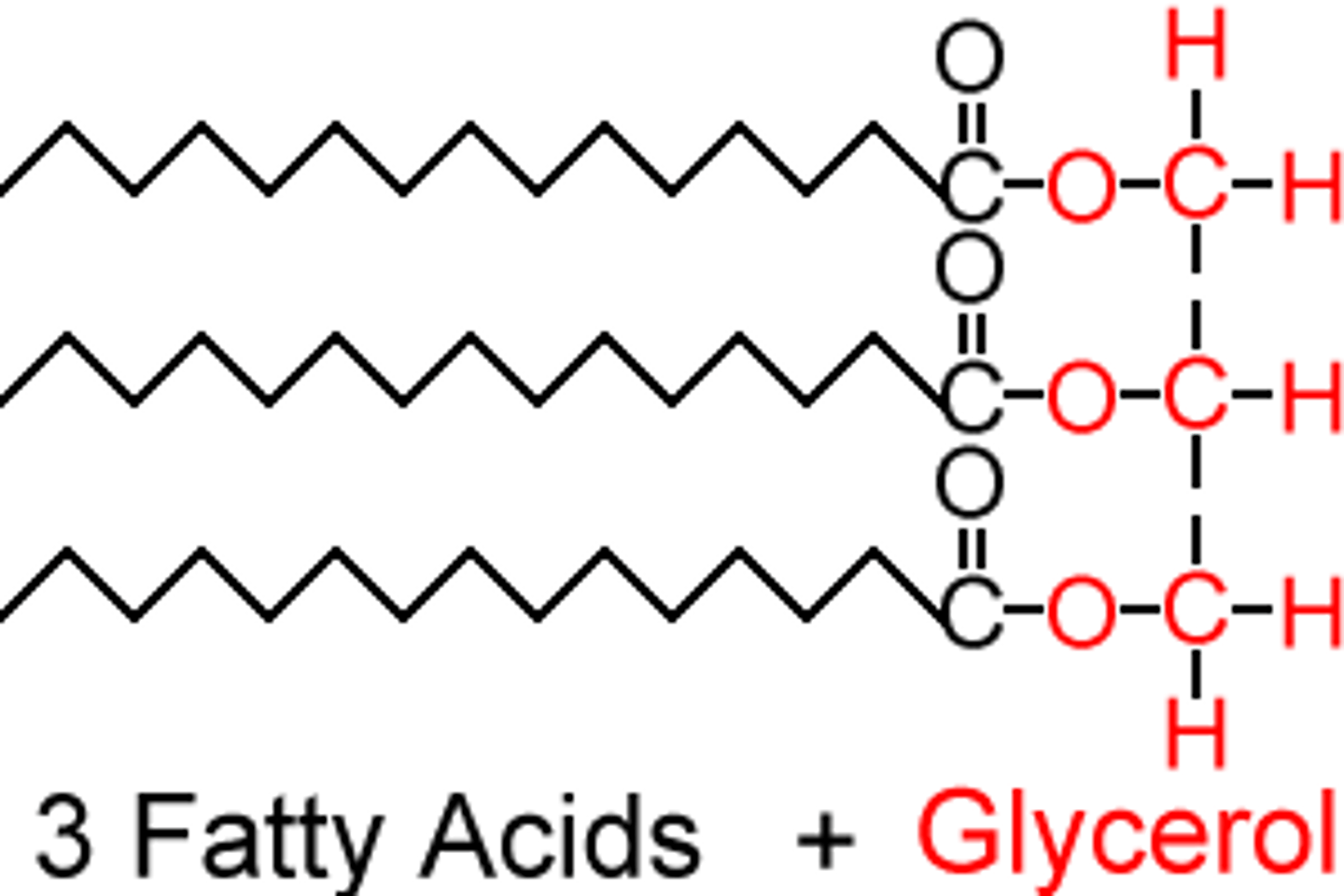
store and transport fatty acids
triglyceride function
ketone bodies
used as alternative to glucose if unavailable
phospholipids
2 fatty acids (hydrophobic) with polar head group (hydrophilic)
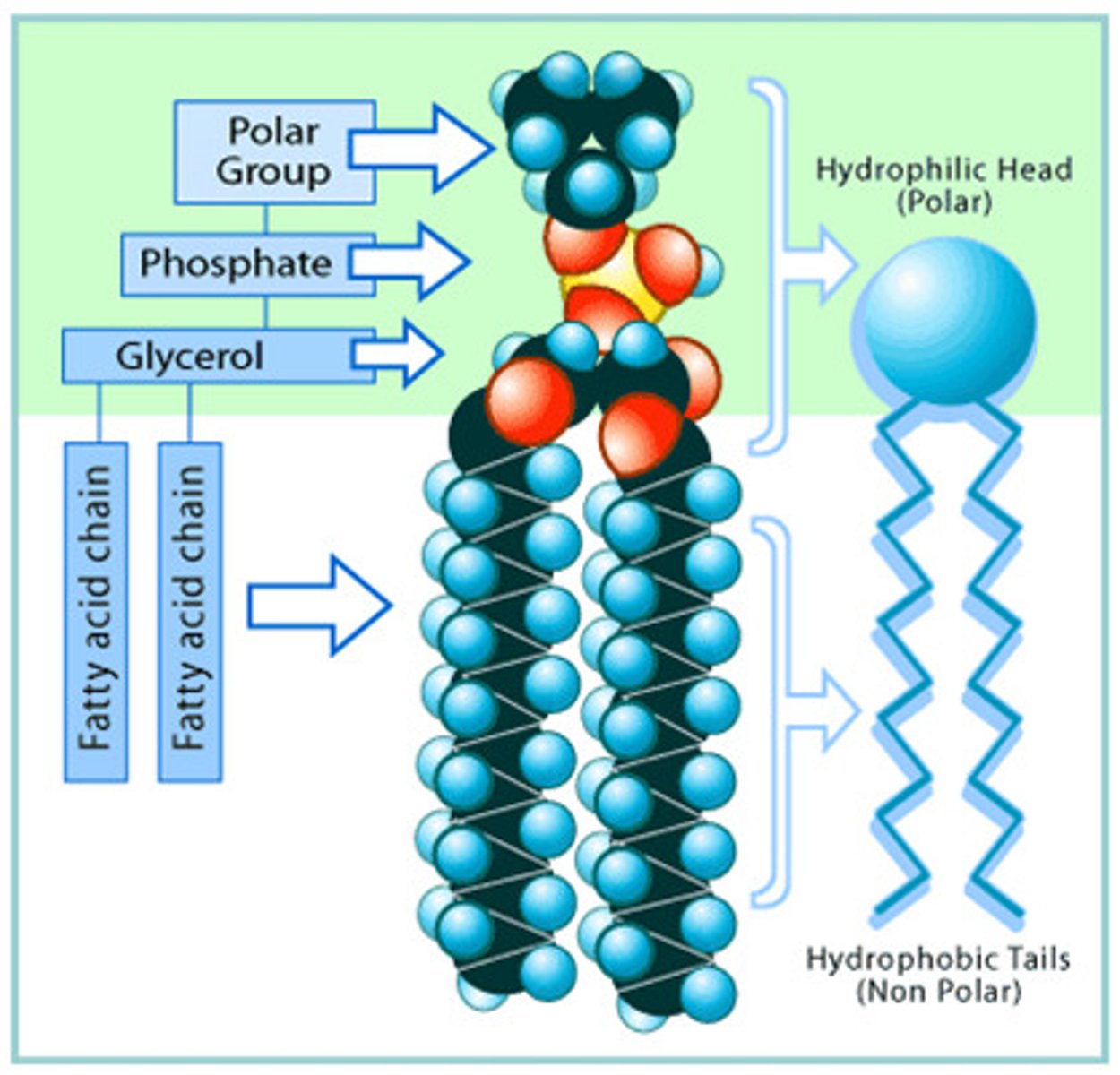
amphipathic
has hydrophobic and hydrophilic portion
forms bilayer of plasma membrane
phospholipids function
hydrogen bond with water
hydrophilic head of phospholipids forms
steroids
3 cyclohexanes + 1 cyclopentane
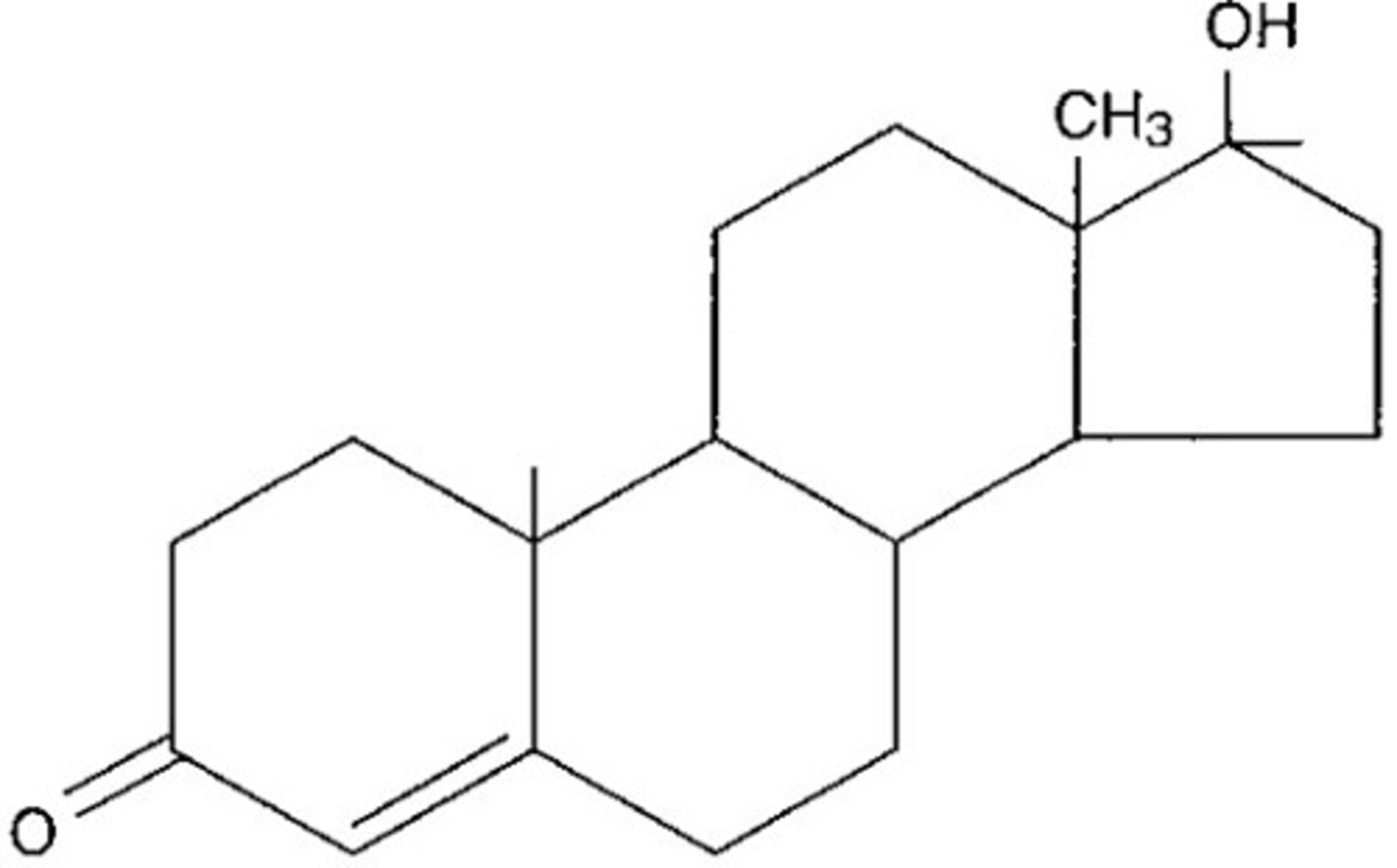
nonpolar and insoluble in water
steroids are
form plasma membrane and found in some hormones
steroid functions
prostaglandins
5 carbon sugar with 2 fatty acid tails
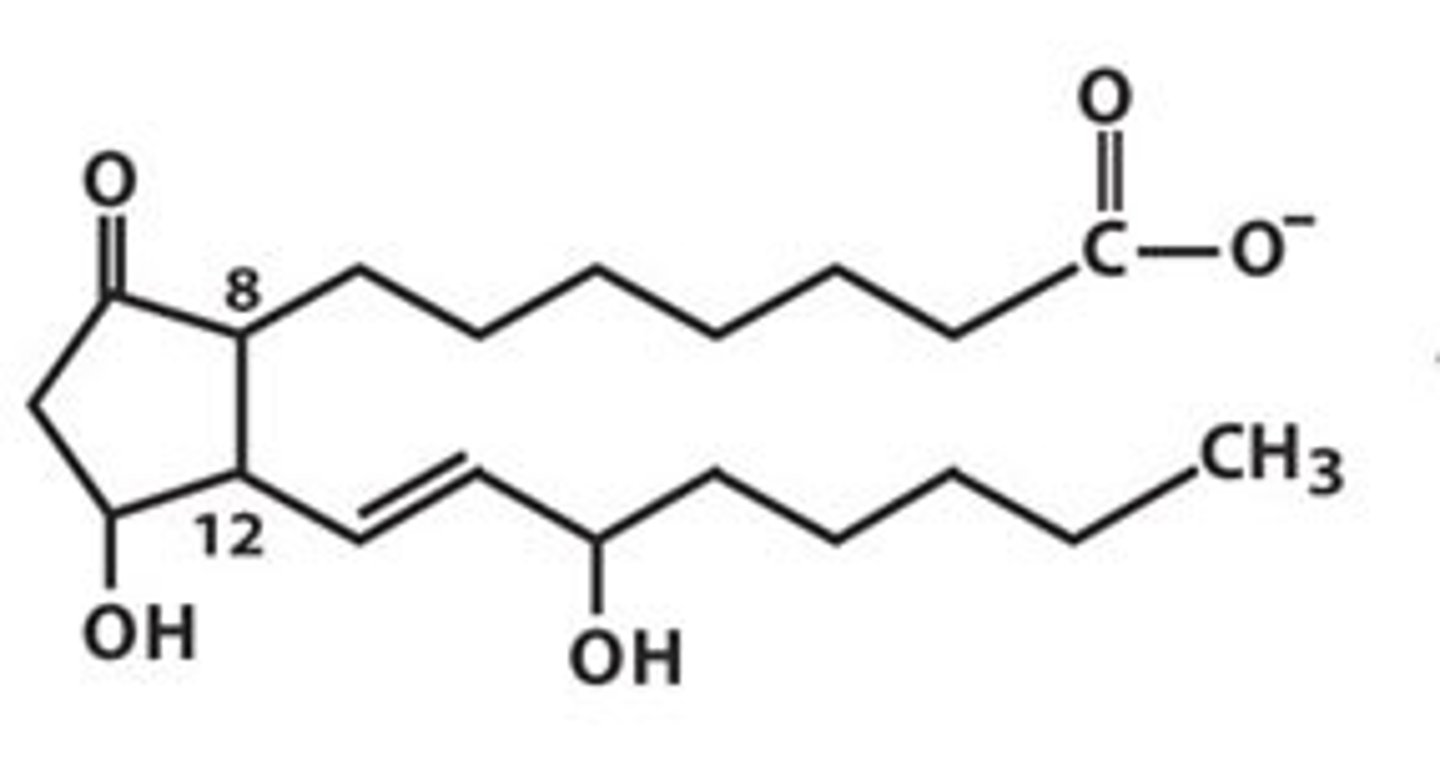
communication molecules between cells locally, regulate vasodilation and vasoconstriction, and uterine contractions
prostaglandins functions
proteins
amino group on one end and carboxyl group on other
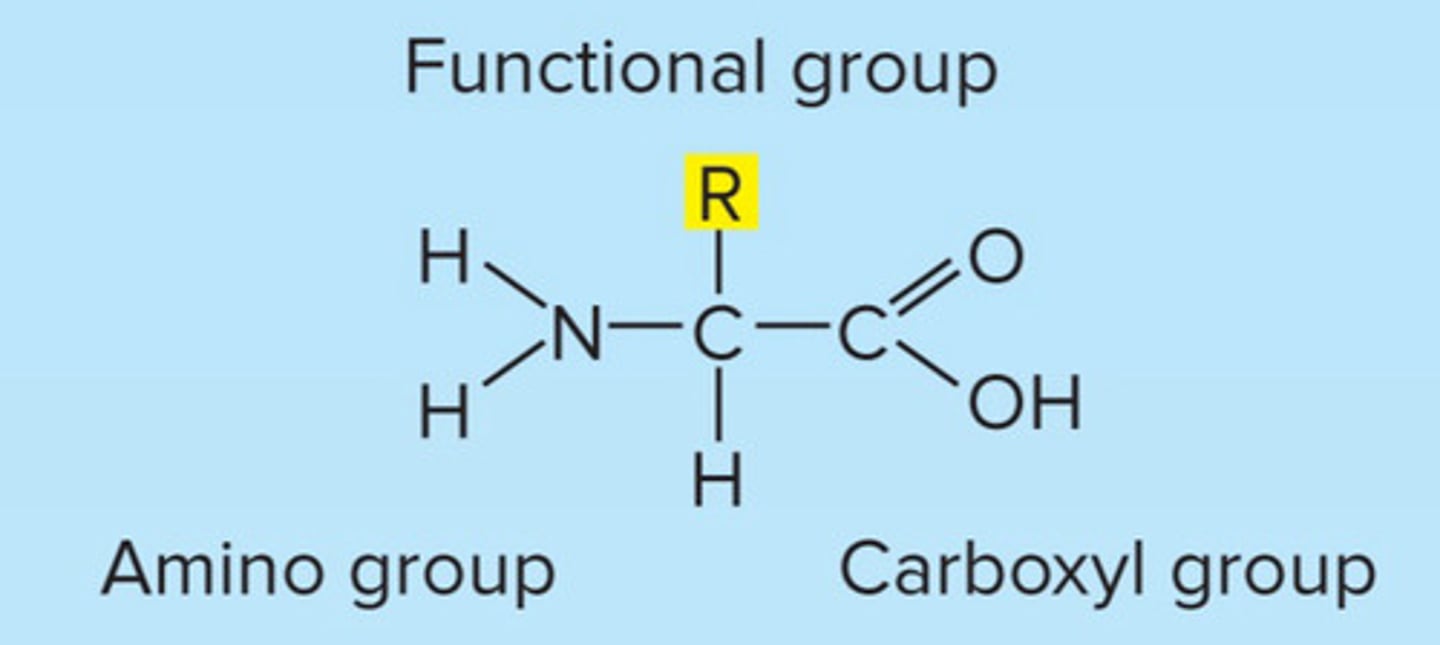
amino acid
protein monomer