French and Indian War & American Revolution Key Events & Figures
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What was the significance of the Ohio Country during the French and Indian War?
It was important for fur trade, access west via the Ohio River, and was a strategic key to North America.
Who was Governor Duquesne?
The French governor who played a key role in the French and Indian War and was responsible for sending regular French army troops.
What was Fort Necessity?
A fort built by George Washington in 1754 during the French and Indian War, poorly located and later captured by the French.
What was the outcome of Edward Braddock's campaign in 1755?
Braddock's force was annihilated in the western Pennsylvanian forest while attempting to capture the forks of the Ohio.

What role did William Pitt play in the French and Indian War?
As English Prime Minister, he sent additional troops to America, leading to the French being driven out of the forks of the Ohio in 1758.
What was the Proclamation Line of 1763?
A boundary established by Britain to limit colonial expansion westward after the French and Indian War.
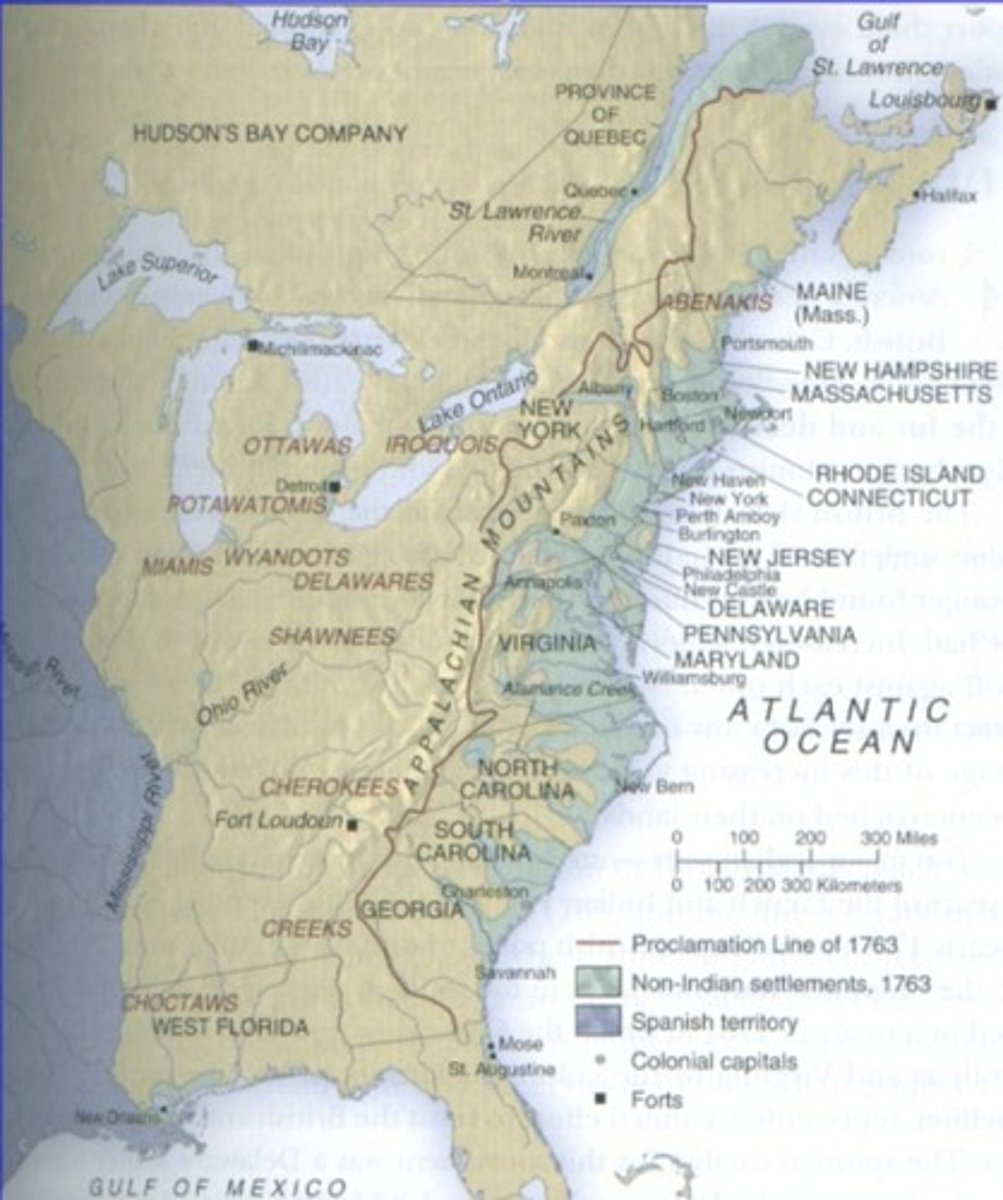
What was the impact of the French and Indian War on England?
England became the dominant power in North America, but was left with significant war debt, leading to tensions with American colonists.
What was Pontiac's Rebellion?
A Native American uprising against British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War.
What was the Stamp Act of 1765?
A law requiring colonists to purchase a stamp for printed materials, which sparked widespread protest and was seen as taxation without representation.
Who were the Sons of Liberty?
A group of American colonists who organized against British policies and taxation, including the Stamp Act and the Boston Tea Party.
What event is referred to as the Boston Massacre?
A confrontation in 1770 where British soldiers killed five colonists, escalating tensions between Britain and the colonies.

What was the Boston Tea Party?
A protest in 1773 where colonists, led by the Sons of Liberty, dumped tea into Boston Harbor to oppose British tea taxes.
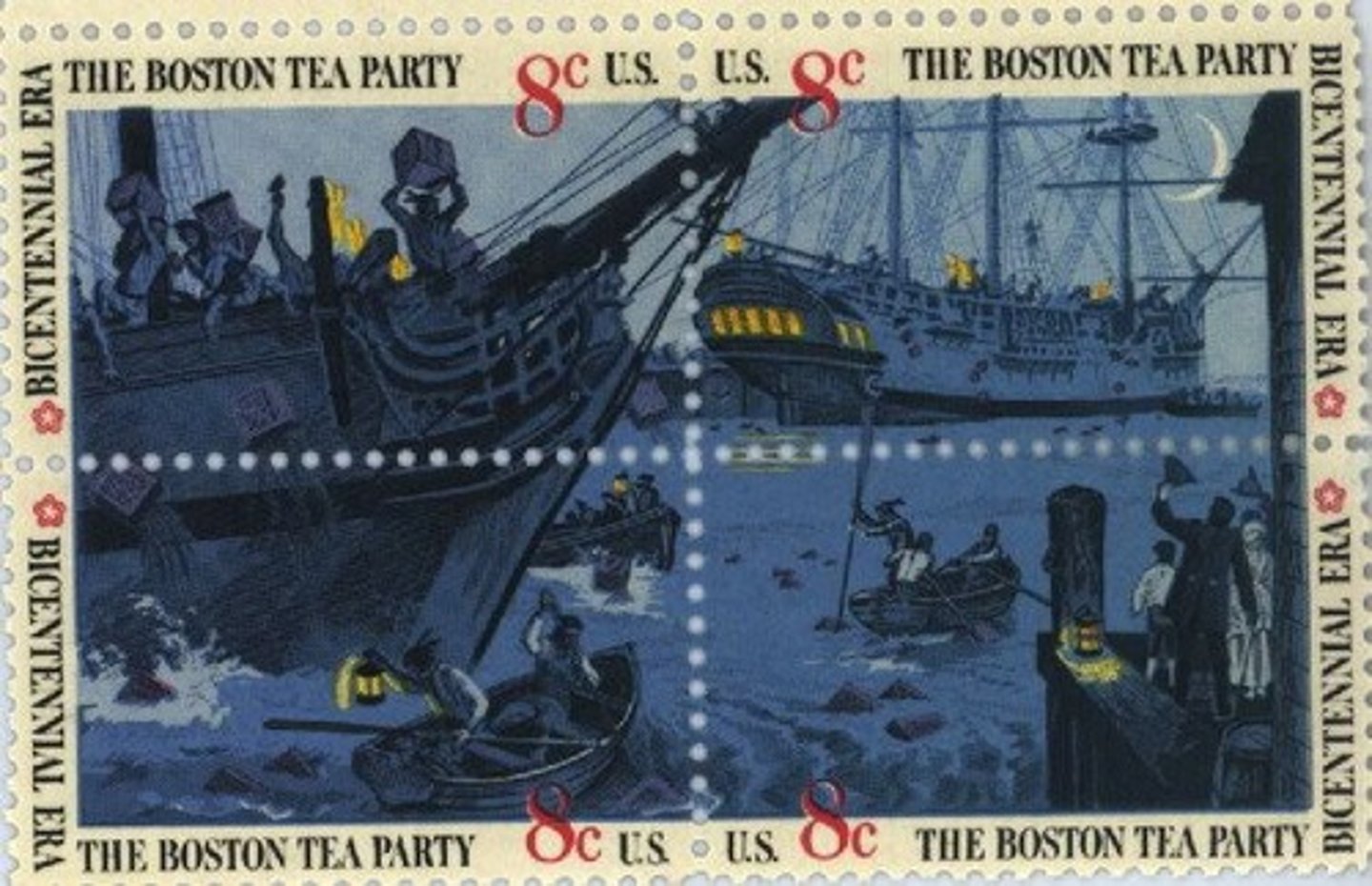

What were the Coercive Acts?
A series of punitive measures imposed by Britain in response to the Boston Tea Party, including closing Boston Harbor.
What was the Quebec Act?
A law passed in 1774 that extended Quebec's territory and granted rights to French Catholics, viewed unfavorably by American colonists.
What was the First Continental Congress?
A gathering of representatives from 12 colonies in 1774 to address colonial grievances and demand the repeal of the Intolerable Acts.
What was the economic impact of the Navigation Acts on the colonies?
The enforcement of these acts led to colonial resentment and was a contributing factor to the American Revolution.
What philosophical ideas influenced the American Revolution?
The ideas of John Locke, particularly regarding natural rights and government by consent, played a significant role.
What was the significance of the year 1766 in the context of colonial resistance?
It marked the repeal of the Stamp Act, reflecting the effectiveness of colonial protests against British taxation.
What were the Townshend Duties?
A series of taxes imposed in 1767 on common products like glass, paint, lead, paper, and tea, leading to further colonial unrest.
Who were key figures in the Sons of Liberty?
Samuel Adams and John Hancock were prominent leaders advocating for colonial rights and resistance against British policies.
What was the impact of the French and Indian War on American nationalism?
The war fostered a sense of unity and identity among the colonies, contributing to the rise of American nationalism.
What was the general colonial response to the imposition of taxes without representation?
Colonists protested vigorously, leading to the formation of groups like the Sons of Liberty and events like the Boston Tea Party.