JONES- EXAM 1
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
:)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
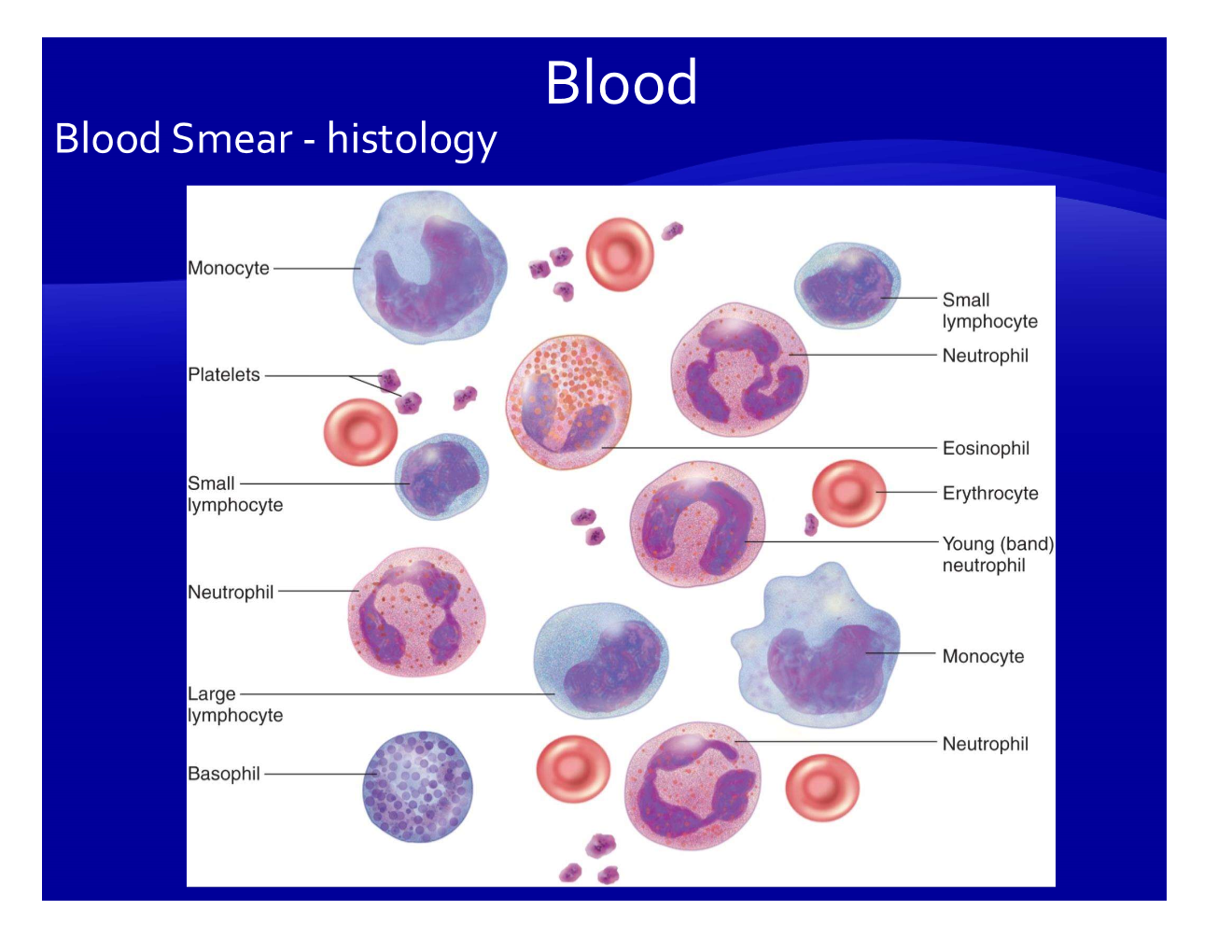
What is blood?
blood= plasma (fluid part) + formed elements (all the cells/cytes in the pic)
Blood proteins are mainly produced by what organ? List some examples of blood proteins.
primarily produced by the liver
examples
albumins
globulins
fibrinogen
What is the main function of albumin proteins?
colloid oncotic pressure
transport
viscosity
pH
When we say we are “measuring serum” what are we actually measuring?
plasma minus fibrinogens
What is hemopoiesis?
production of blood (RBC, WBC, and platelets)
All cells in the blood start from a hematopoietic _________ ____________.
stem cell
Where are most RBC’s made in adults?
bone marrow
Lymphoid tissues (thymus, tonsils, spleen, nodes) produce ________________.
lymphocytes
What is the most abundant formed element/ blood cell in the body?
RBCs or “Erythrocytes”
What is hematocrit? How do we measure it (FYI)? What is the normal range?
hematocrit is the # of RBC’s in the blood
FYI: measured by taking a blood sample—> spin it —> the RBC’s settle at the bottom and you measure the % of the blood sample that is at the bottom
NORMAL RANGE: 42-47%
What are the functions of RBCs/erythrocytes?
CARRY OXYGEN FROM LUNGS TO TISSUES
carry CO2 from tissues to lungs
What is special about the structure of RBCs/erythrocytes?
bi-concave disc
spectrin cytoskeleton—> allows RBC’s to be bouncy
Inside RBC’s, what protein is responsible for gas transport? (responsible for carrying 98% of O2)
HEMOGLOBIN!!
What is the normal range of Hgb in the body?
15-18 g/dL
Describe the structure of hemoglobin:
_____ subunits/chains
each subunit has a ________
4 subunits
each subunit has a heme
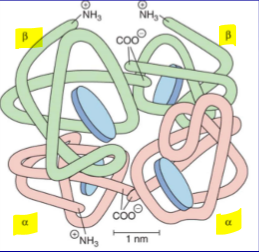
The heme group of each subunit on hemoglobin has what kind of binding sites? What bind to these binding sites?
each heme has IRON binding sites where O2 BONDS
Normal adult hemoglobin has what kind of chains?
2a, 2b
How many oxygen atoms bind to 1 hemoglobin?
4 O2
What is erythropoiesis?
production of red blood cells
What are the intermediate cells between becoming a stem cell and a mature RBC?
stem cell—> CFU —> erythroblast—> reticulocyte—> erythrocyte
In order for a stem cell to become a CFU (colony-forming-unit-erythroid cells) WHAT HORMONE IS ESSENTIAL!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
EPO or erythropoietin
About 0.5-1.5% of reticulocytes are circulating in the blood. What does this mean? If there was a high % of reticulocytes in the blood what would that mean?
reticulocytes in the blood means they escape before maturing
FYI is normal to have some reticulocytes in the blood
high % of reticulocytes in the blood means that more RBC synthesis is stimulated
EPO is mainly released from the kidney when?
when we need RBC’s/ don’t have enough oxygen
How many days does it take to go from a stem cell to a mature RBC’s?
30 days
What are some other requirements for RBC formation?
iron
b-12
folic acid
amino acids
What is hemolysis? What happens to the heme group when an RBC dies?
rupture of RBC
what happens when a RBC dies? Hgb dies, and the heme is broken down into bilirubin and excreted
What is MCV? What does it signify? What is the normal value?
mean corpuscle volume- it’s the average size of your red blood cells
normal value- 87
What is anemia?
decrease # of RBC’s
What type of anemia is when there are larger cells/ larger MCV?
macrocytic/megaloblastic anemia
What type of anemia is when there are smaller cells/ smaller MCV?
microcytic anemia
What type of anemia is when the cells are normal size, but there’s a low #?
normocytic anemia- can be hemolytic if also high reticulocytes
Fill in the following table about causes of different anemias:
Type | Causes |
Microcytic with low/normal # of RBC’s | |
Microcytic with high # of RBC’s | |
Normocytic | |
Macrocytic |
Type | Causes |
Microcytic with low/normal # of RBC’s |
|
Microcytic with high # of RBC’s |
|
Normocytic |
|
Macrocytic |
|
Why do thalassemias lead to an increased # of RBC’s?
thalassemias are characterized by a disorder within the Hgb
If the Hgb is not functioning right, then the RBC can’t carry oxygen as well
this stimulates EPO release
more RBC’s are made, but they still can’t function and carry oxygen properly
What is polycythemia? What are the causes?
polycythemia: an increase in # of RBC’s
causes: cancer of the bone marrow, dehydration, emphysema, altitude, exercise—→ ALL OF THESE INCREASE EPO
Compare hypoblastic and aplastic anemia:
hypoblastic—> decline in # of RBC’s
aplastic—> complete cessation of erythropoiesis
What is sickle cell anemia? List a pharm tx for sickle cell.
a hemoglobin defect—> we can’t make the beta chains of hemoglobin
RBC’s instead of being round become a sickle shape instead and clump together
tx: Hydroxyurea: stimulates HgF (y) and decrease HbS (beta chains)
What are red blood cell antigens?
What do they do?
What are red blood cell antigens? proteins on the surface of RBC’s
What do they do? determine blood type
All blood types technically have what antigen?
H antigen
What are the different blood types and their corresponding antigens?
example: type A has what antigen?
type A- A antigens
type B- B antigens
type AB- A and B antigens
type O- NO A or B ANTIGENS
For each blood type what kind of antibodies do they have?
type A: Anti-B antibodies
type B: Anti-A antibodies
type AB: NO ANTIBODIES
type O: Anti-B and Anti-A antibodies
(people produce antibodies AGAINST the antigens they don’t have
What does Rh+ and Rh- refer to?
the D antigen!
Rh+ = have the D antigen
Rh- = no D antigen, might MAKE anti-D ANTIBODIES
How does a person make anti-D antibodies?
form ONLY when an Rh- person is exposed to Rh+ blood
PRACTICE:
A 26-year-old Rh-negative woman is pregnant for the first time. Her fetus is Rh+. What is must be done during her pregnancy?
a. no treatment is necessary
b. give Rhogan
c. monthly blood tests and checkups
a- (this is the mother’s first pregnancy and she is Rh-negative. even though the fetus is Rh-positive, the mother hasn’t and won’t develop antibodies until the mother and fetus’s blood mix at birth)
PRACTICE:
A 31-year-old Rh-negative woman is pregnant and already has Rh antibodies from a previous pregnancy. Her fetus is Rh+. What is must be done during her pregnancy?
a. no treatment is necessary
b. give Rhogan
c. monthly blood tests and checkups
b. (the mother needs a medication to stop the Rh antibodies from attacking the fetus)
What cells produce platelets?
megakaryocytes
What is the primary job of platelets?
form a plug to seal off damaged vessels
What factor is ESSENTIAL in platelet adhesion and fibrin formation?
vWF
Briefly summarize the factors involved in the intrinsic to common pathway:
Intrinsic: XII—> XI—> IX—> VIII—> X—> active X
Common: prothrombin—> thrombin—> fibrinogen —→ fibrin
What type of bleeding disorder is this:
most common inherited disorder
decreased adhesion of platelets and fibrin formation
vWF disease
Hemophilia A is a deficiency in WHAT CLOTTING FACTOR? ************
factor VIII
Hemophilia B (Christmas disease) is a deficiency in WHAT CLOTTING FACTOR?
factor IX
Hemophilia C (Rosenthal’s) is a deficiency in WHAT CLOTTING FACTOR?
factor XI
Vitamin K deficiency leads to increased clotting time and effects what factors?
II, VII, IX, X
Liver disease leads to increased clotting time and effects what factors? (i don’t think that important)
V, VII, IX, X, XI, XII, fibrinogen and prothrombin