MIcroeconomics: Production, Costs & Revenue
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is productivity?
The output for a given input unit (factors of production)
What is labour productivity?
Labour productivity refers to the output produced in a certain amount of time for a given input of labour cost.
What is labour productivity used to measure.
Labour productivity can be used to measure performance and to compare workers with other workers.
What is the formula for labour productivity?
Labour productivity = total output / number of employees or total hours worked
Name 3 ways labour productivity can be improved?
More education
More training
Installing better technology
What is division of labour?
The specialisation of workers on specific tasks in the production process
Why does division of labour help production?
If each person does one job a lot, they are usually better at that one job than if they did four different jobs with a quarter of their time
What is economies of scale?
When the average cost of producing a good or service falls as the quantity produced increases.
What is specialisation?
A worker only performing one task or a narrow range of tasks, which they are more efficient at which improves the productivity of the entire production process.
Give and explain 3 disadvantages of specialisation.
Specialised firms are often not flexible. (Workers may struggle to adapt and do a new role quickly if the environment changes. This is because they are only trained in their specific skill.
Workers may become bored. (This could reduce productivity if they start to do their work more slowly)Risk of structural unemployment due to occupational immobility
Countries may be less self-sufficient and struggle when trade suffers.
Give and explain 3 advantages of specialisation.
Specialisation can lead to economies of scale. (This lowers the long run average costs for the firm)
Specialisation reduces the cost of training workers because they only have to be trained for this particular job.
Specialisation can increase labour productivity. Workers do tasks they're good at and so should produce better quality and/or a higher quantity of products.
Why does specialisation rely on trade?
Specialisation relies on trade because economies need to buy the things that they have not specialised in from other countries.
What is short run production?
When at least one factor of production is fixed.
What is long run production?
When all factors of production are variable.
What are average returns?
Average returns is the total return divided by the number of inputs.
What are marginal returns?
Marginal returns is the output from adding an additional unit of input,
What are total returns?
Total returns is the total return for all inputs (or the total return created by all inputs).
Explain diminishing returns.
As output increases, marginal costs rise and average fixed costs fall.
Initially, the effect of falling average fixed costs outweighs the increasing marginal costs, so average total costs fall.
This benefit diminishes over time, as average total costs rise
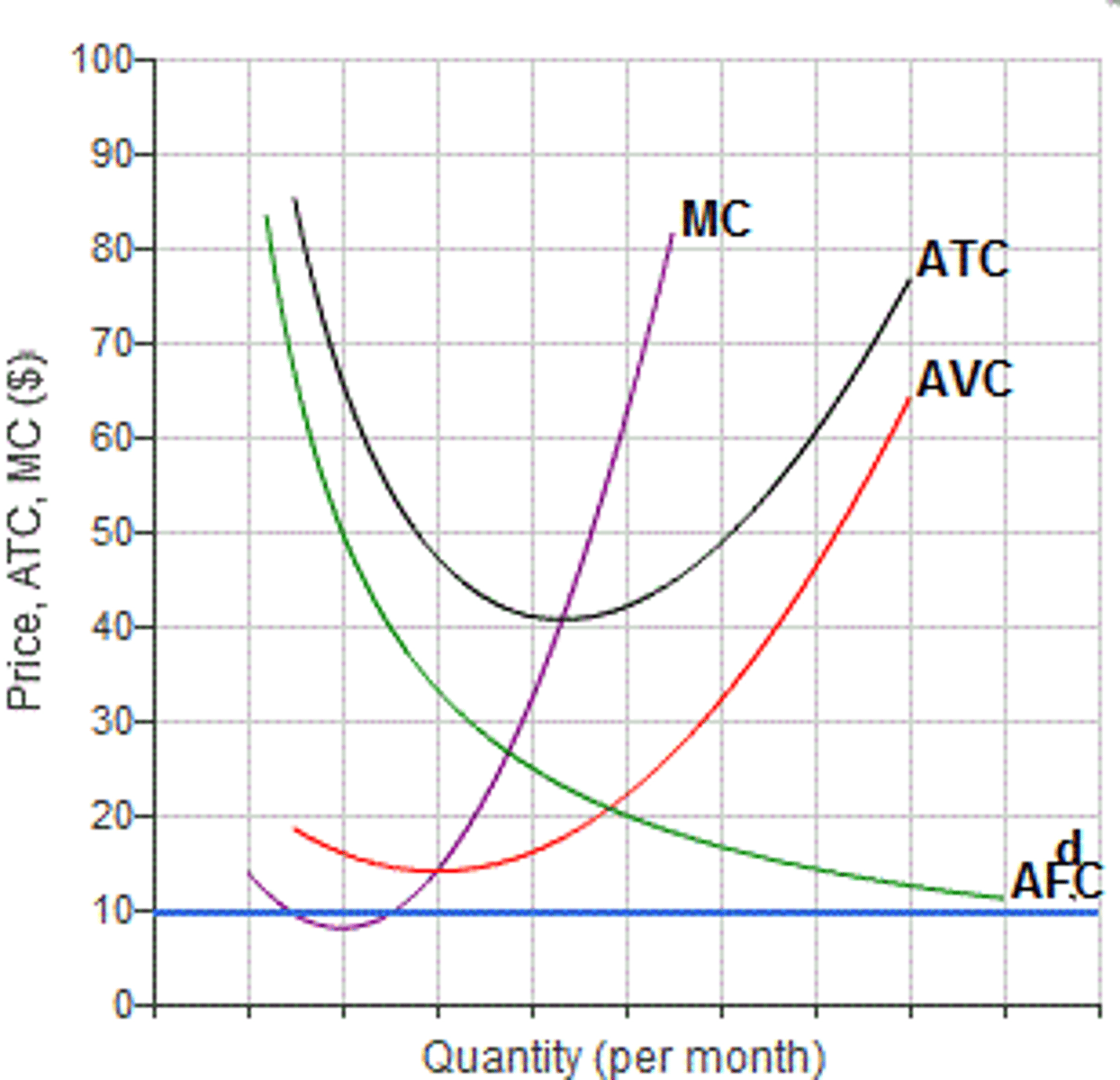
Explain diminishing marginal product.
When firms choose to create goods or services they will select the most productive factors of production to use.
As they produce more goods, the firm will be forced to use less and less productive factors of production.
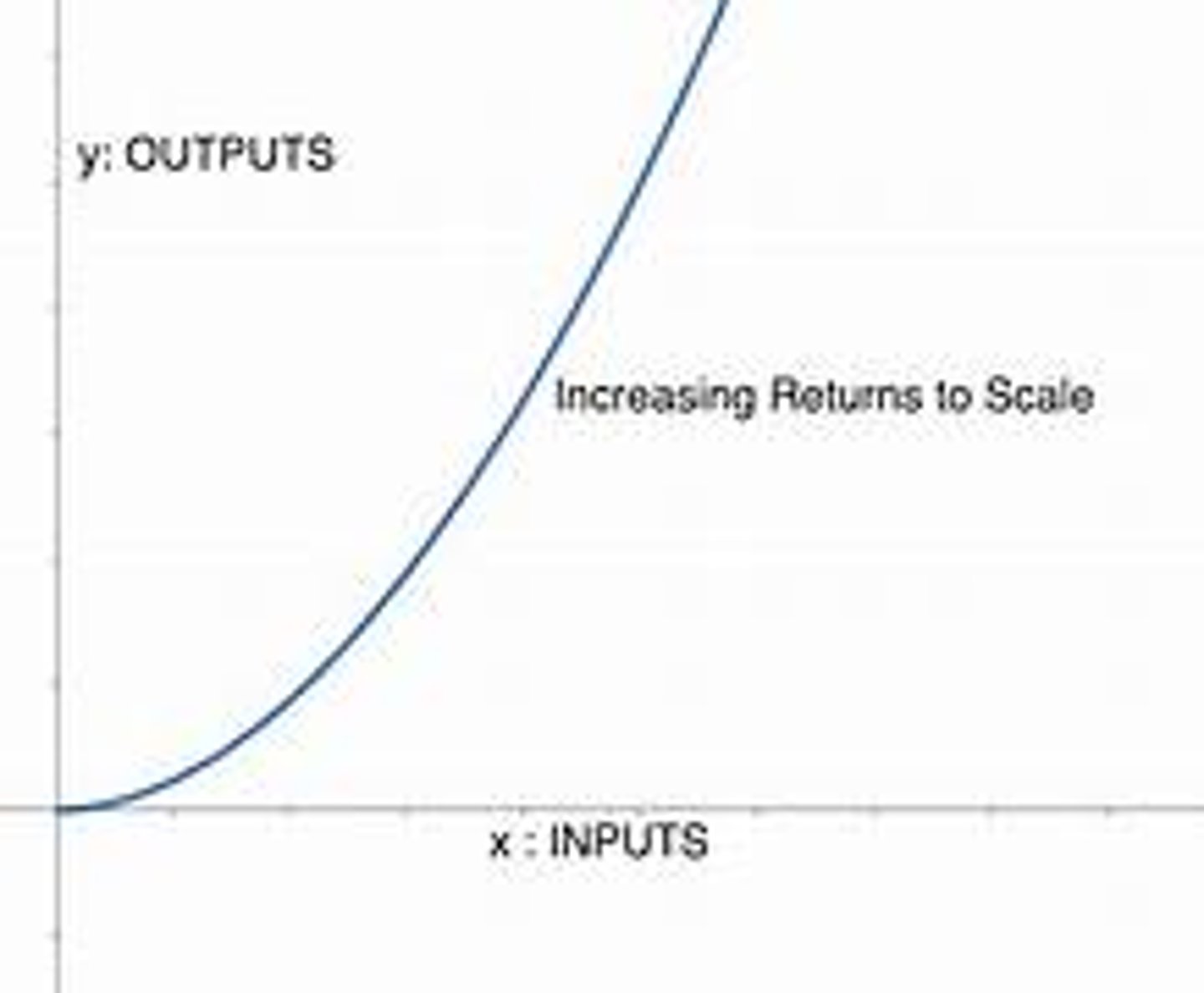
What is increasing returns to scale?
Increasing returns to scale means that for an additional unit of input, there is a more than proportionate effect on output.
e.g. increasing the amount of all inputs by 10% may lead to a 20% increase in output
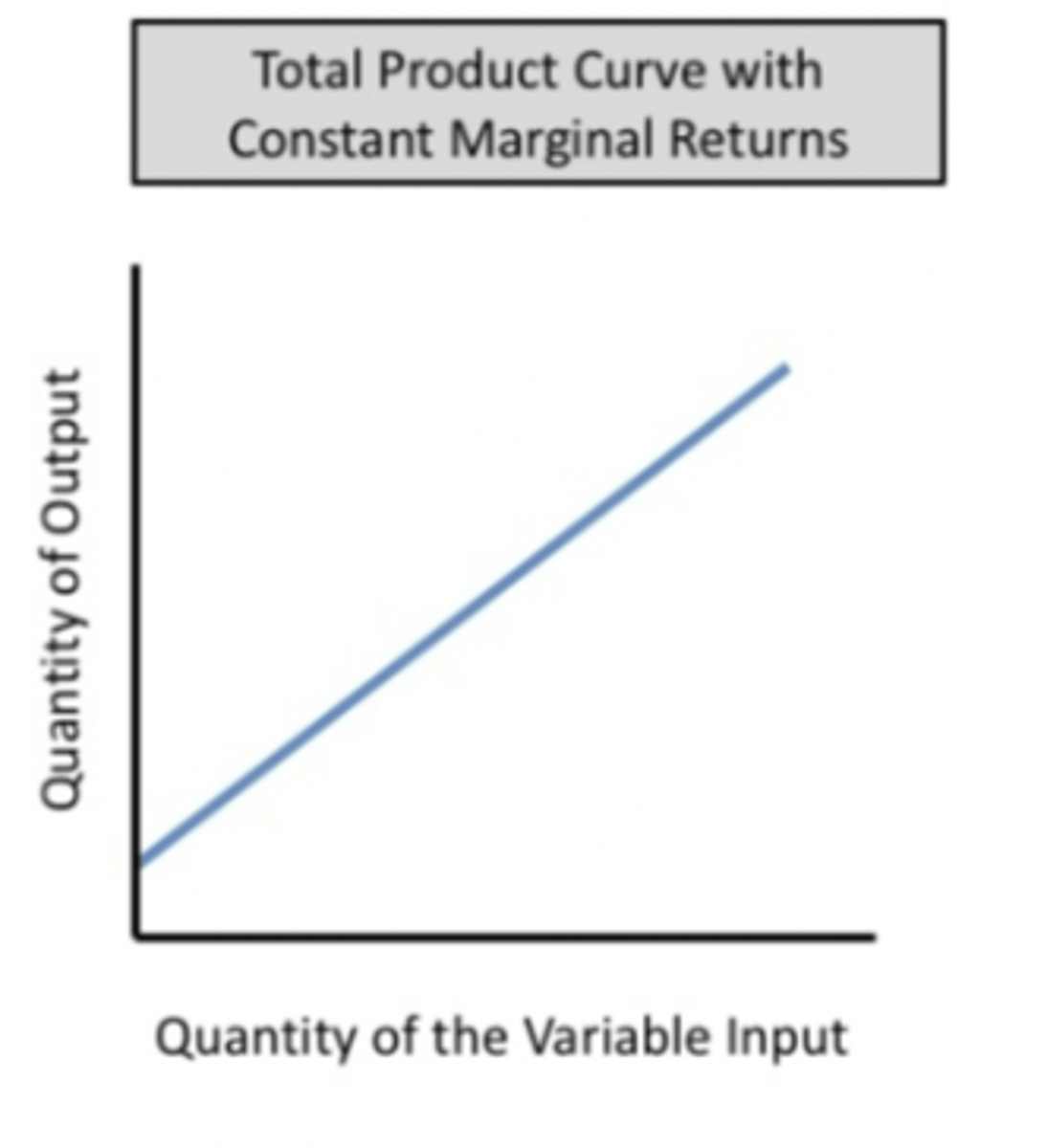
What is constant returns to scale?
Constant returns to scale means that every extra unit of input added leads to a proportionate increase in output.
This means that average cost does not change when output increases.
e.g. increasing the amount of all inputs by 10% will lead to a 10% rise in output
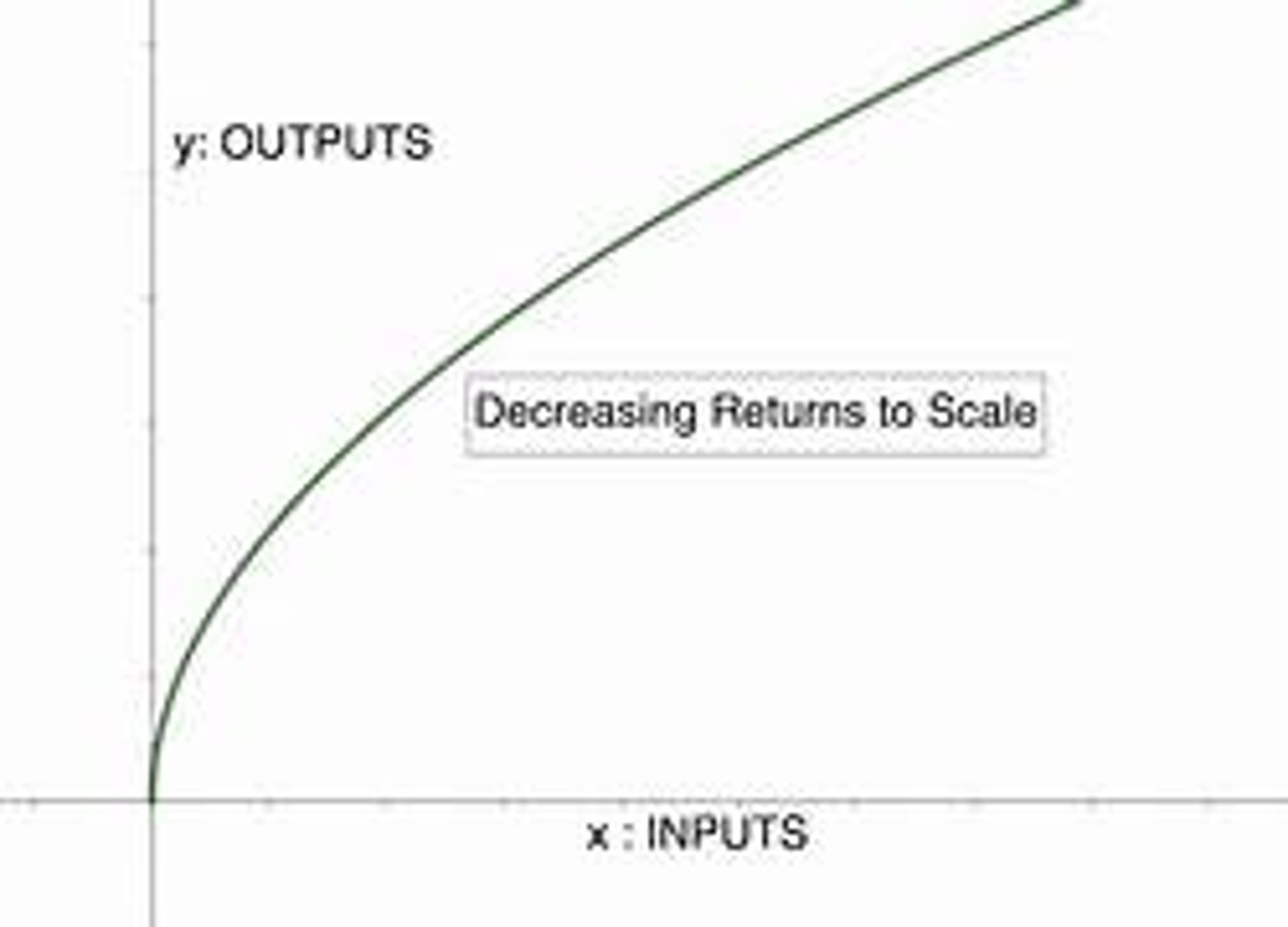
What is decreasing returns to scale?
Decreasing returns to scale means that there is a less than proportionate effect on output for a change in input.
Increasing the amount of all inputs by 10% may only lead to a 5% increase in output.
What is total costs?
fixed costs + variable costs
What are fixed costs? Can they be changed in the short run?
Fixed costs do not change regardless of the level of production (or output)
They cannot be changed in the short run
Where is the lowest average cost on an AC MC graph?
The lowest average cost is where the average cost is equal o marginal costs.
What are marginal costs?
Marginal costs is the change in total costs divided by the change in output for each possible level of output.
These are usually rising.
Only variable costs affect marginal costs.
What are factor prices and how do they affect costs of production?
Factor prices are the prices of factors of production.
Higher factor prices increase the cost of production
How does productivity impact costs of production?
If productivity increases, output will have increased for a given input (or amounts of inputs)
So for the same level of output, the cost of input will have decreased.
Costs of production will have fallen
How does economies of scale impact monopolies?
Having a high output reduces a firm's average costs, then they can sell their products at lower prices than competitors who have lower output.
This can eventually lead to the firm having monopoly power over the market if it's able to force its competitors out the market.
What is internal economies of scale?
Internal economies of scale is the long run process that sees firms learn and adapt, reducing average costs as output increases.
What is External economies of scale?
External economies of scale is when the change that brings about economies of scale happens outside of the firm.
What is technical economies of scale?
Larger firms can afford to invest in specialist technologies (or capital) which reduces the cost of production.
A manufacturing firm can invest in specialist machines to produce their goods more efficiently.
What is purchasing economies of scale?
Larger firms have more power in a market place than small firms.
Suppliers are willing to negotiate discounts on their goods and services to increase the quantities that they sell.
As a result, larger firms can buy more at a lower price per good, reducing their costs, known as bulk buying.
What is specialisation and division of labour economies of scale?
As firms grow, they can designate particular tasks to individuals or groups of workers.
Workers now only have one or a small number of jobs so it is more cost effective to have specific training and equipment makes them more efficient.
Specialised workers are more productive which reduces average costs
What are risk bearing economies of scale?
Large firms are considered less of a risk because they tend to be in more markets.
Firms can be in more markets by diversifying the range of goods and services they produce or by selling to different geographical areas.
Any impact to goods sold or market will have a lesser affect on a large firm
What are financial economies of scale?
Larger firms are viewed by financial institutions as less risky relative to smaller firms.
Banks are therefore willing to lend money at a cheaper rate as they can be more certain that the money will be repaid
What are managerial economies to scale?
Large firms can afford to invest in management technology and employ dedicated managers.
The managers and their systems can improve the productivity of the whole production process by overseeing it effectively.
What are marketing economies of scale?
Mass market advertising on TV and sponsoring large events has a very large cost. Large businesses can spread the cost over a lot of output, whereas the local corner shop would not even be able to access this type of marketing.
What are diseconomies of scale?
When output rises but this causes average costs rise too
What is the minimum efficient scale (MES)
The MES is the lowest output at which average cost is minimised in the long run.
All possible economies of scale have been reached
What is a natural monopoly?
A monopoly that arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms
What is marginal revenue?
This is the additional revenue gained from selling the last output unit.
If marginal revenue is positive, total revenue could be increased from expanding output.
What point is revenue maximization?
Marginal revenue = 0
What are price makers?
Price makers have partial control over the price at which their goods are sold.
What are price takers?
Price takers have no control over the price at which their goods are sold.
What is the equation for profit?
profit = revenue - cost
What is normal profit?
Normal profit is when total revenue is equal to total costs.
How can a firm be sustainable in the long run?
In the long run, normal profit is the minimum a firm can be making to be sustainable.
What market structure makes can only make normal profit?
Perfectly competitive markets.
What is supernormal profit?
When total revenue exceeds total costs, a firm is said to be generating supernormal profits.
What is a signal for firms to enter markets? What affects their ability to enter?
Supernormal profits
Barriers to entry and levels of contestability
What is the shut down point?
The shut down point is the revenue where a firm just covers its variable costs. Below this point the firm will cease production immediately.
What is the difference between short run production and long run production?
Long run production is where all factors of production are variable.
Short run production is where at least one factor of production is fixed/
What should a firm do to increase profit when marginal costs is less than marginal revenue.
Increase output
What should a firm do to increase profit when marginal costs is more than marginal revenue.
Decrease output
What is creative destruction?
Creative destruction is how market structure changes through technological innovation, when markets are destroyed and new one created.
If a new dominant design or product is developed, the structure of a particular industry can reform around it.
Firms who do not incorporate and adapt to the new technology could be forced out of the market.
What are two ways that technology can improve the standard of capital machinery used?
Increased labour productivity
More opportunities to take advantage of economies of scale
How can improvements in technology affect barriers to entry?
Improvements in technology may reduce entry barriers to markets, increasing the level of contestability.
But if the technology is patented, it can create a monopoly through a legal barrier to entry.