Chapter Three: Connective, Muscular, and Nervous
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Connective tissue is the most
Abundant and widely distributed tissues
GF: CT consists of two basic elements
Cells and extracellular matrix
What is the extracellular matrix?
Material located between spaced cells
What does the ECM consist of?
consists of protein fibers and ground substance
Fibers of the ECM are secreted by?
except for?
Its fibers are secreted by fibroblasts, except for blood cells
The structure for extracellular matrix determines what?
Much of the tissue qualities
(GF) Does CT occur on body surfaces?
Mostly no, except for joint cavities
All CT have a good X and are highly X. Except for?
Have a good nerve supply and are high vascular, except for cartilage
What are the two class types of cells of CT?
-blasts or -cytes
(CELLS) what are -blasts?
immature cells, capable of mitotic cell division, and secrete ECM characteristics of the tissue
(CELLS) what are -cytes?
mature cells, lost mitotic ability, but monitor and maintain ECM
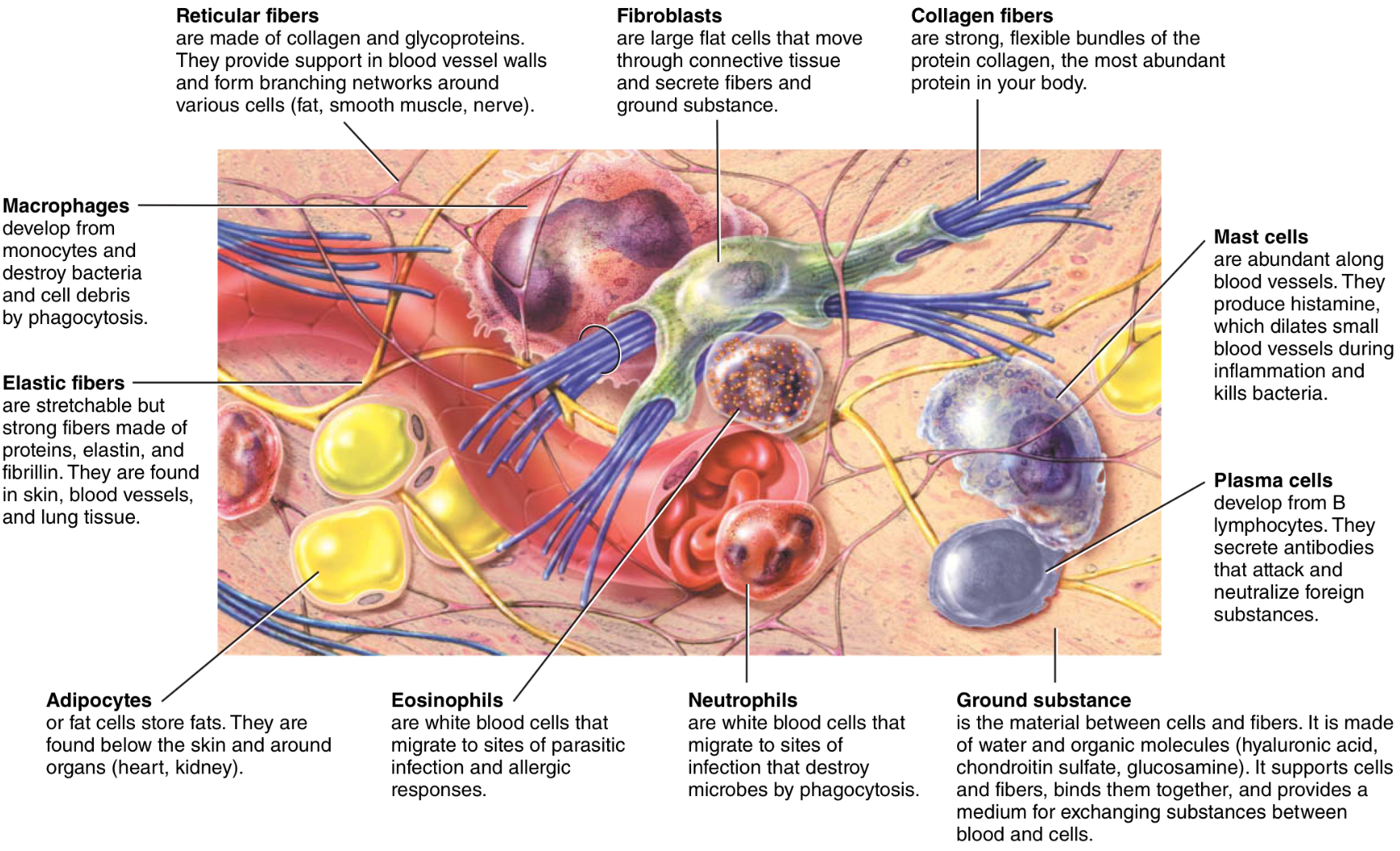
What are the cells of CT?
What are their functions?
Fibroblasts, macrophages, plasma cells, and mast cells
(Cells of CT) Fibroblasts function
move through CT, secrete matrix components
(Cells of CT) What are macrophages what is their function?
are phagocytes that developed from monocytes, destroy bacteria and cell debris
(Cells of CT) Plasma Cells function
Make antibodies
(Cells of CT) Mast Cells function
Inflammatory response; also bind, digest, and kill bacteria
What do mast cells produce?
Histamine
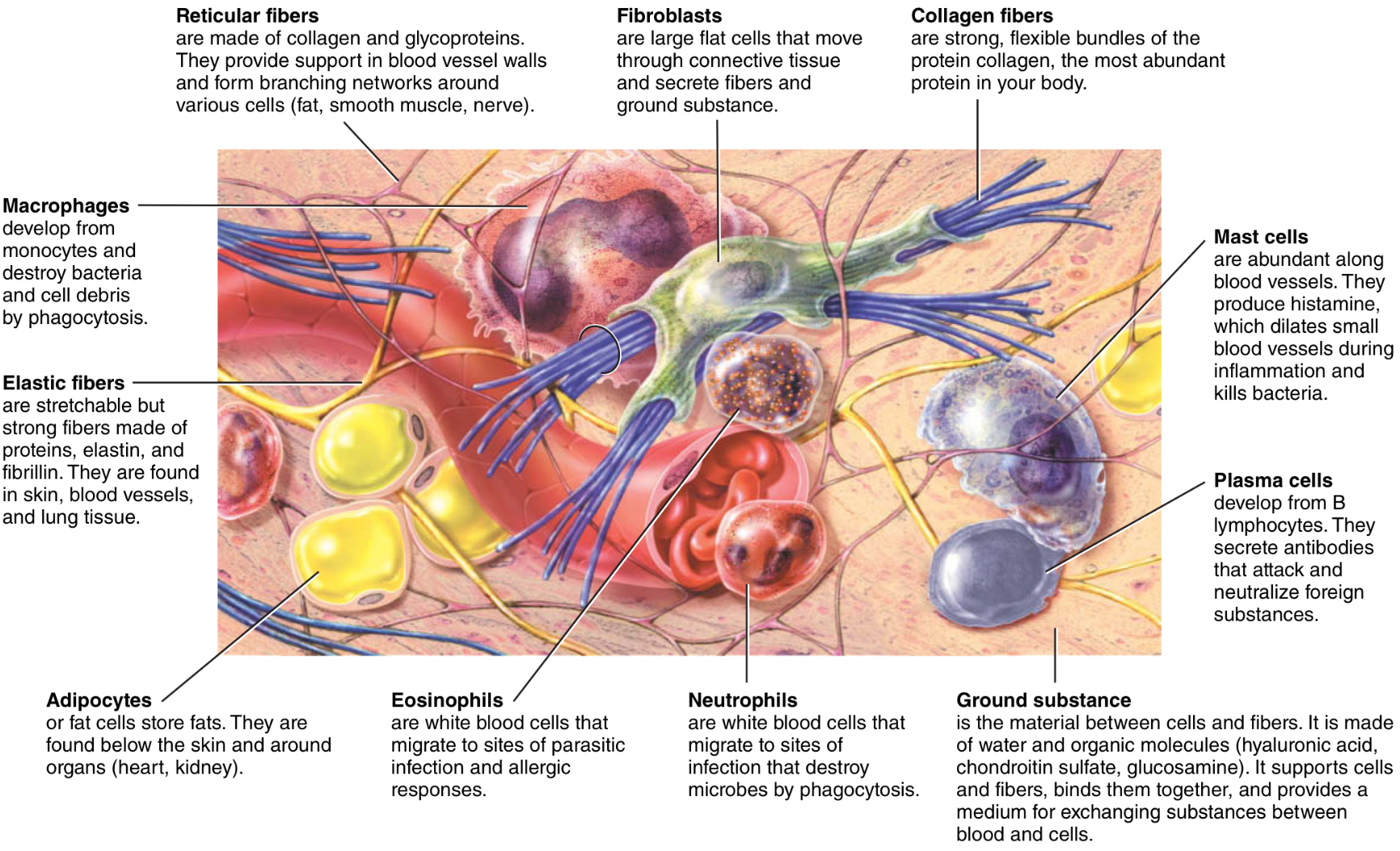
What is the ground substance of the ECM?
What are its different forms?
What is it made out of?
component of a CT between the cells and fibers
may be fluid, gel, or hard
Hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and mineral salts
What are the functions of the ECM?
supports cells, binds them, stores water, and provides a medium for the exchange of substances between blood and cells.
(GS) What is the function of hyaluronic acid?
What is it major in
What is the function of chondroitin sulfate?
Where are mineral salts notable?
binds cells together and lubricates joints
major in synovial fluid
provides support and adhesiveness in cartilage, bone, skin, and BV
notable in bone and teeth
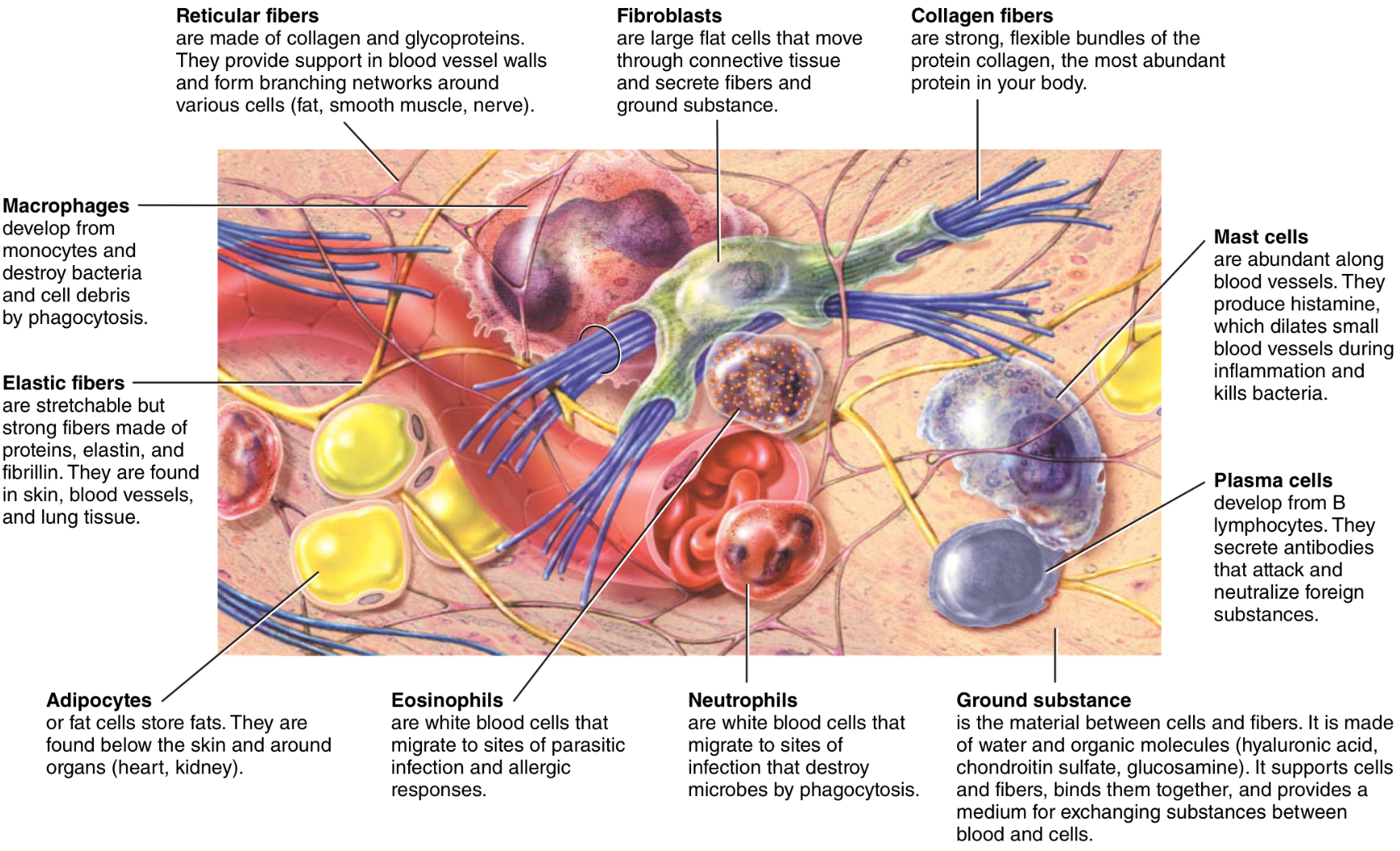
What are the three types of fibers?
Collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers
What are collagen fibers?
They are the most?
Are very strong and resist tensile forces, but still allow flexibility
Are the most abundant protein in the body
What are elastic fibers?
Where are the found?
Form a fibrous network within a tissue, allowing for stretching and ability to recoil back into original shape
Found in the skin, BV walls, and lung tissue
What are reticular fibers?
What are they made of?
What does it form?
Provide strength and support
Collagen with glycoprotein cover
Forms the stroma, the supporting network of organs
What are the different classifications of CT?
Loose CT
Dense CT
Cartilage
What are the types of loose CT?
Areolar, adipose, and reticular
What are the types of dense CT?
Dense regular CT, dense irregular CT, and elastic CT
What are the types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage
What are two other types of CT?
Blood and bone
What is muscular tissue?
What is its function?
What are the different types?
Consists of elongated long cells (muscle fibers/myocytes) that use ATP to generate force
Produces body movements, maintains posture, and generates heat
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
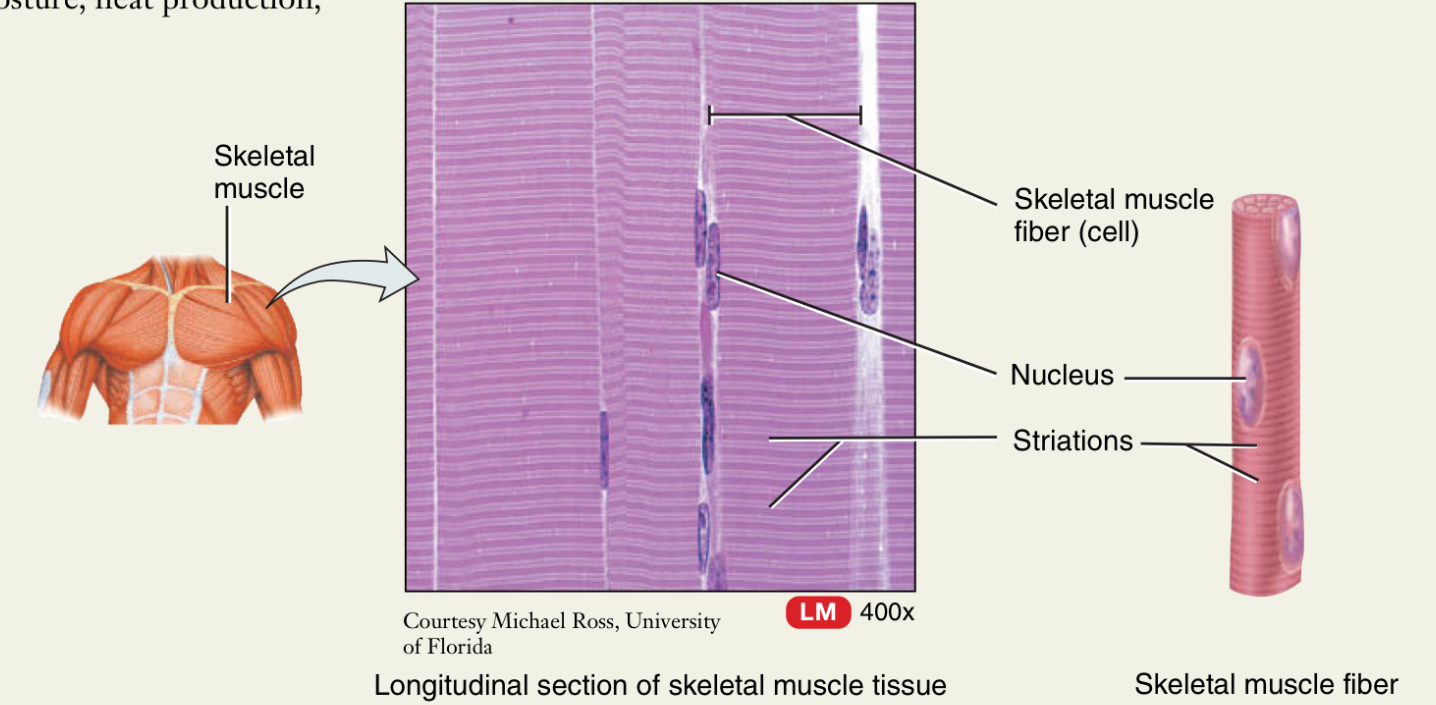
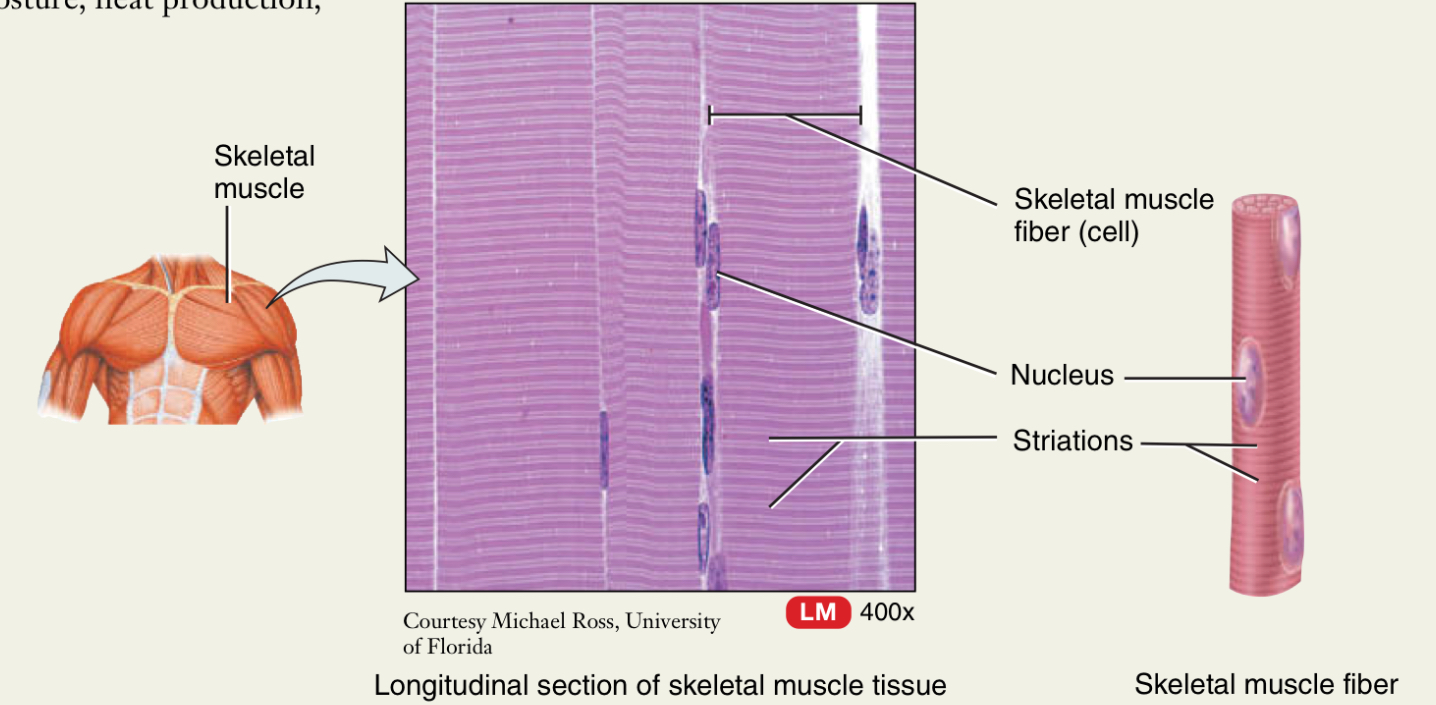
Skeletal Muscle
What is it attached to?
Striated or not? What causes it?
What type of control?
Attached to the bone
Straited because of contractile proteins
Voluntary control, conscious movement
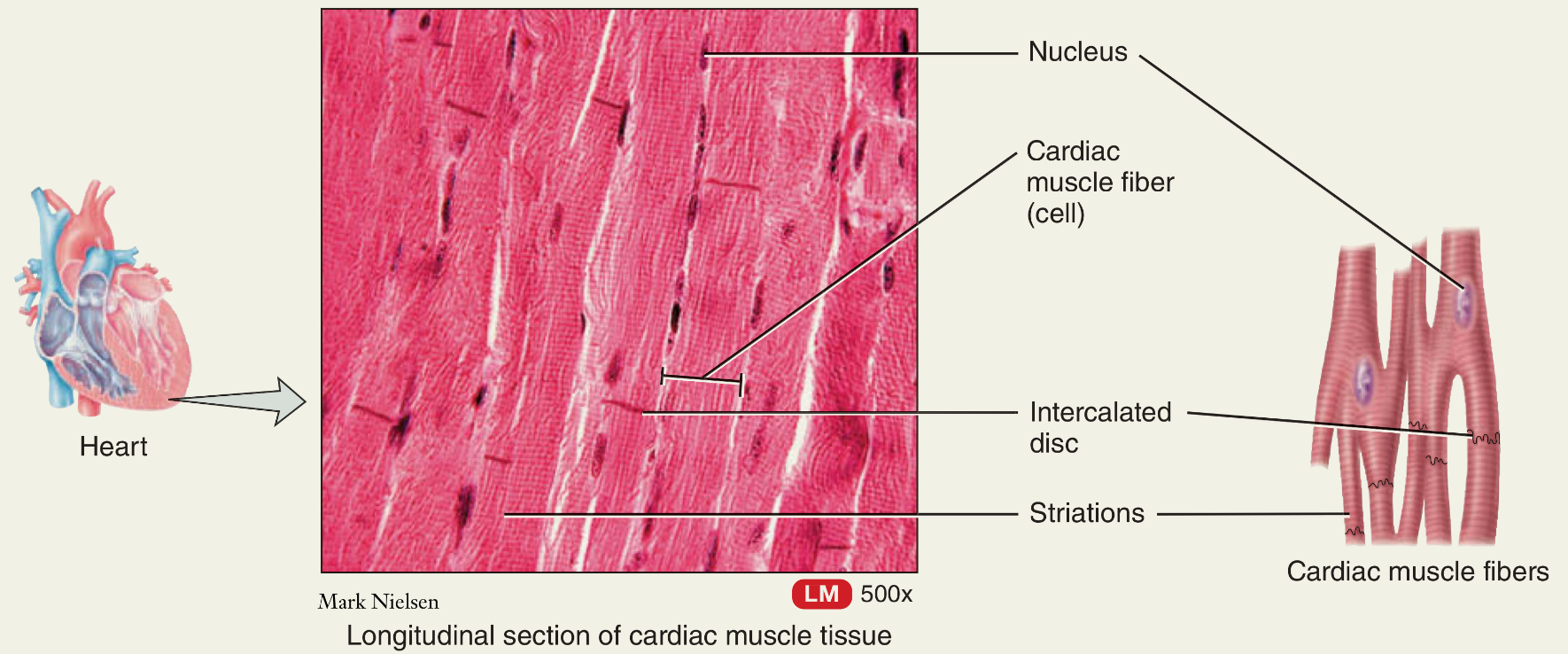
Cardiac muscle
Where is it? What does it do?
Striated?
What type of movement?
Located at the heart, pumps blood to entire body
Is striated and involuntary control
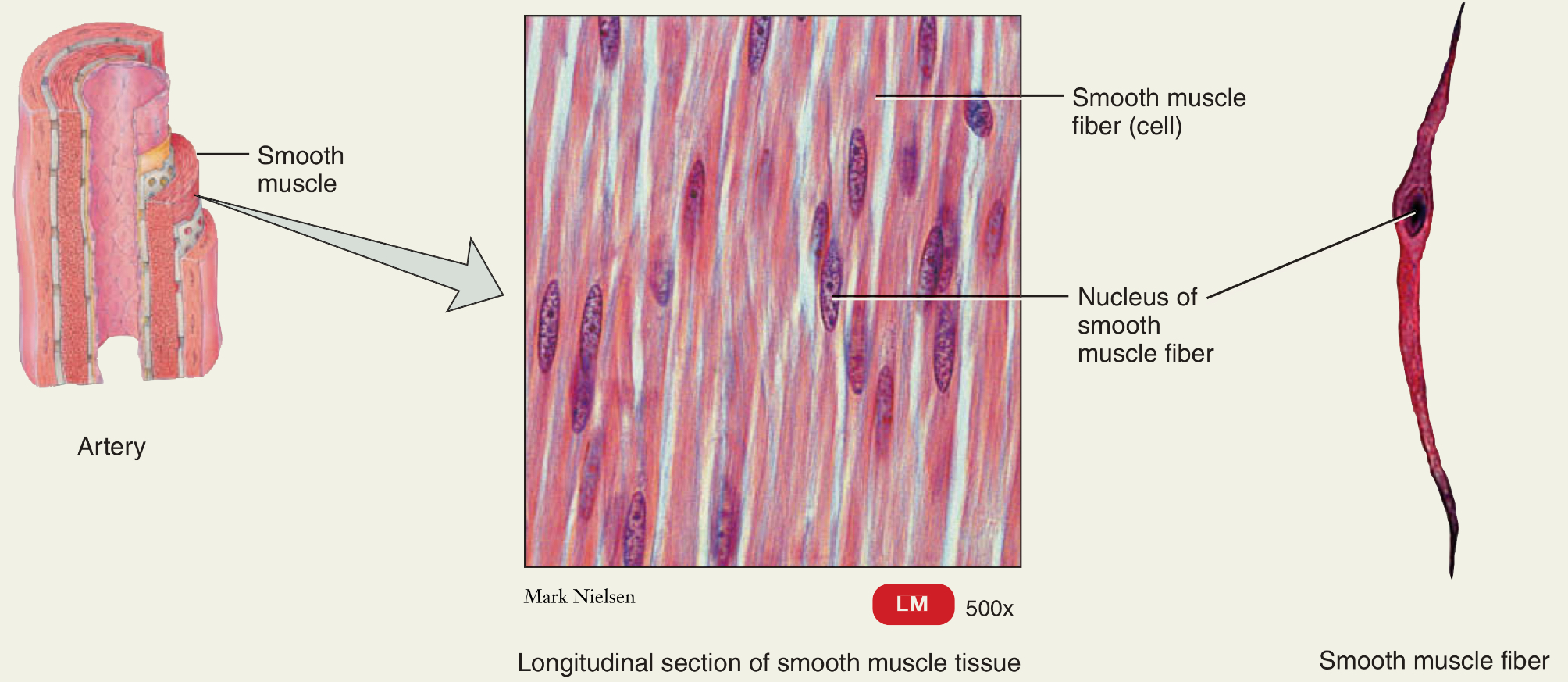
Smooth muscle
Function?
Striated?
What type of control?
Motion
Not striated
Involuntary control
What is nervous tissue sensitive to?
What does it generate?
Nervous tissue is sensitive to stimuli
It generate electrical signals that sends messages to tissues/organs
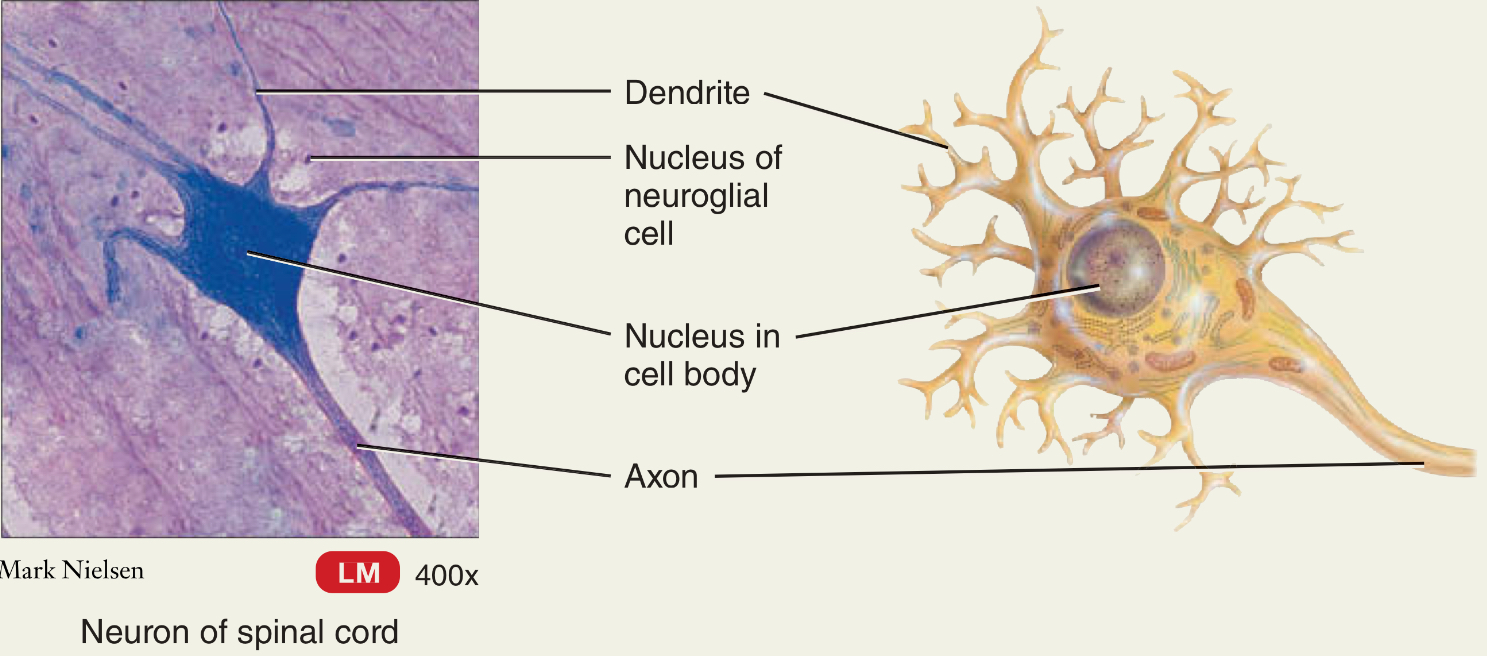
What are the two cells types of nervous tissue?
What are their functions?
Neurons: highly specialized, axons and dendrites
Neuroglia (glial cells): Support the neurons