Intro to Neurology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Central Nervous System
Includes the brain, spinal cord, and covered meninges
Starts in the CNS and ends in the CNS
Upper motor nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Includes cranial nerves and spinal nerves
Lower motor neurons
Starts in CNS and ends in the PNS
Somatic Nervous system
Subdivision of the peripheral nervous system
Innervates structures of the body such as muscles, skin, and mucous membranes
Autonomic Nervous System (Visceral)
Subdivision of the peripheral nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Controls smooth muscles and glands of internal organs
Returns sensory information to the brain
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest
Top and bottom of spinal cord
Sympathetic
Fight or flight response
Middle of spinal cord
Structures of the CNS
Brain
Cerebrum, Telencephalon, Diencephalon
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Structures of CNS
Spinal Cord
Cord
Conus Medullaris (cone shape lower end of spinal cord)
Cauda Equina (nerve roots at the end of the spinal cord)
Neurons
nerve cells, send signals via retro or anterograde transportation
Interneurons
nerve cells with short axons, send information locally
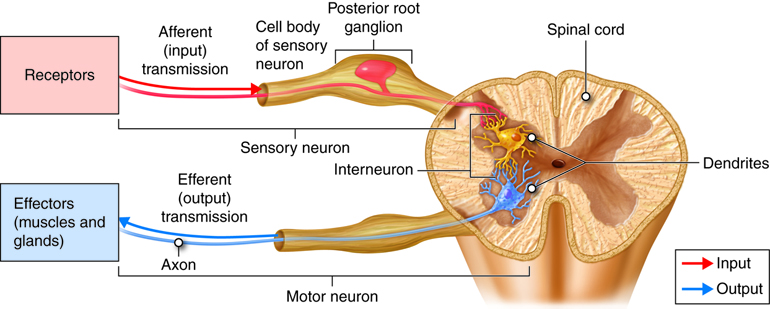
Nuclei
nerve cells with common function, grouped in a cluster, INSIDE the CNS
Glial Cells
Support (physical/chemical) activity of neurons, 10:1, many different types, a lot of glial cells in the brain
Ganglia
Nerve cells with a common function that are grouped OUTSIDE of the CNS
Synapse
chemical transmitters may cause excitation or inhibition
Monosynaptic (reflex)
Polysynaptic (complex behavior)
Efferent - motor information from CNS to PNS
Afferent - sensory information, from PNS to CNS
Tracts (fasciculi)
Columns (funiculi)
Descend
Ascend
Decussate (cross over)
Commissures
Cerebral Hemispheres
Cerebrum
Right Hemisphere
Left Hemisphere
Sagittal sulcus separates left and right hemispheres
Cerebral cortex
Gray matter, cell rich, cell bodies
Nuclei
Cluster of cells, Basal ganglia
White matter
Axons, connecting brain regions
Lobes of the Brain
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Insular ( Sensory motion)
Limbic (Emotion, motivation, memory)
Frontal Lobe
Associated with
Thoughts
Planning
Decisions
Actions
Cortical Motor system
Central Sulcus- everything in front is considered the frontal lobe
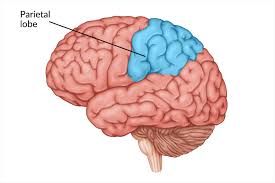
Parietal lobe
Associated with
Sensation (Feeling)
Perception
Sensorimotor System
From central sulcus to parietal occipital sulcus
Occipital Lobe
Dedicated to vision
Dorsal Stream “where” parietal lobe
Ventral Stream “what” temporal lobe
Boundaries: temporal lobe laterally, parietal lobe medially
Temporal lobe
Associated with
Auditory processing
Language
Memory
Object identification (“ what pathway”)
- Separated from parietal lobe and frontal lobes by lateral sulcus . Imaginary line between temporal and occipital lobes.
Subcortical Structures- Thalamus
Sensory information
Basal Ganglia
hyper and hypo movement a lot or a little bit of movement
Hypothalamus
hunger, sleep, thirst
Hippocampal Formation
memory
Amygdala
emotions and fear
Corpus Callosum
Connects right and left hemisphere
Anterior Commissure
Helps connect connect hemispheres
Internal Capsule
Information about movement
Corona Radiata
cerebral hemisphere to brainstem
Brainstem
Midbrain, Pons,Medulla
Connections between the cerebral hemispheres, the spinal cord, and cerebellum
Complex nuclei
Hearing, respiration, arousal, posture, locomotion
Cranial Nerves
Most have nuclei in the brainstem and exit or enter the brainstem
Cerebellum
“little brain”
Posterior and inferior to the cerebellum
Connects to the rest of the nervous system through the brainstem
Cortex, deep cerebellar nuclei, white matter
Motor function (Coordination)
Motor learning (Movement adaptation)
Meninges/layers
Multilayered membranes that enclose the nervous system and separate it from protective bony structures
Deep to superficial (Pia > Arachnoid> Dura)
Ventricles
CSF is within the ventricles
2 lateral ventricles (right and left)
3rd ventricle is midline around the midbrain
4th ventricle is midline and between the brainstem and the cerebellum
Lateral ventricles are connected by the interventricular foramen
3rd and 4th are connected by the cerebral aqueduct
Spinal Cord
Vertebrae
Cervical (7)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacral (5)
Coccygeal (1)
Fiber Tracts
Cord
Conus Medullaris
Cauda Equina
Spinal Nerve Roots
Peripheral Nervous System
31 pairs of spinal nerves
8 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Sacral
1 Coccygeal
12 Cranial Nerves
Myotomes - group of muscles innervated by a nerve root
C5- Elbow Flexors L2- Hip Flexors
C6- Wrist Extensors L3- Knee Extensors
C7- Elbow Extensors L4- Ankle Dorsiflexors
C8- Finger Flexor L5- Long Toe Extensors
T1- Finger Abductors S1- Ankle Plantar Flexors
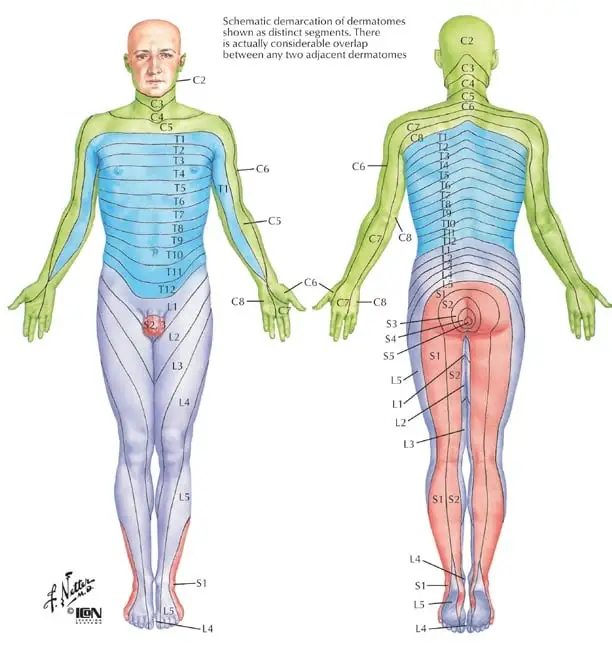
Dermatomes
Area of skin supplied by a nerve root
PNS
Motor and sensory axons coming out of and heading into the central nervous system