Psychology Approaches: Psychodynamic approach (1)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the assumption of the psychodynamic approch?
It assumes early childhood experiences hsape adult personlaity and behaviour through unresolved conflicts and fixations
Forms the foundation of Freuds explanation for adult mental health problems
What does fixation mean in the psychodynamic approch?
Becoming psychologically stuck at a psychosexual stage due to over or under gratification
Explains adult habits and personality traits
What is an example of oral fixation?
Smoking, overeacting, nail bititing, sarcasm , neediness
Show show early feeeding experiences influence adult behaviour
What causes defence mechanisms?
Unresolved childhood conflict or anxiety that the ego cannot manage directly
Explains irrational or protective behaviours
What is the unconcious mind?
A hiffen part of the mid containing repressed memories, desires adn unresolved conflict
Central to Freuds explanation of behaviour ouside awarness
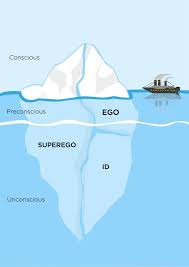
What is the iceberg metaphor?
Unconscious mid is the small visible tip, unconcious is the large hidden mass
Illistrates how most mental activity is unconcious
How do unconscious thoughts reveal themselves?
Through dreams, Freudian slips (error in speech / action / memory), and defence mechanisms
Shows how hidden coflicts influences behaviour
What is the conscious mind?
The part of the mid we are aware of - thoughts and perceptions
Represents the smallest part of mental functioning
What is the preconscious mind?
Material just below awarness, including memories, dreams and slips
Acts as a bridge between unconscious and conscious processes
what is a Freudian slip?
An accidental speech error revealing true, repressed feelings
Evidence for unconscious influence on behaviour
What is the Id?
The instinctive , pleasure seeking part of personality present from birth
Explains impulsive and biological drives
What principle does the Id operate on?
The plesure principle - seeking immediate gratification
Drives early behaviour and urges
What is the Ego?
The rational part of personality that mediates between Id and Superego
Maintains psychological balance
What principle does the ego operate on?
The reality principle - considering what is realistic and acceptable
Prevents harmful or impulsive behaviour
What is the superego?
The moral part of personality, internalising parental rules (laws and authority)
Produces guilt , shame and moral judgement
What does the superego operate on?
The morality principle — enforcing right and wrong
Explains moral behaviour and self criticism
How do the ID ego adn super ego interact?
They work together but often conflict with the ego mediating
Explains internal psychological conflict
What is teh purpose of defence mechanisms in the psychodynamic approch?
To protect the individual from anxiety by managing conflict between Id and super ego
Shows how the Ego prevents psychological overwhelm
Why are defence mechanisms unconscious ?
They operate automatically without awareness
Supporting Freuds claim that hidden processes shape behaviour
Why are defence mechanisms unhealthy long term?
They offer temporary relief but prevent confronting real problems
Explains how unresolved conflicts leads to dysfunction
What is displacment?
Redirecting strong emotions onto safer a target
Shows unconscious conflict distorts behaviour
What is an example of displacmnet?
Shouting at children instead of a boss
Demonstrates misdirected emotional expression
What is repression?
Pushing distressing memories or feelings into the unconcious
EXplains memory gaps and hidden trama
What is an example of repression>
Having no memory of being bullied
Shows how the mid protects itself from pain
What is denial ?
Refusing to accept reality to avoid distress
Explains unrelistic or over positive self presentation
Whats an example of denial ?
Insisting a partner isnt stealing despite evidence
Shows how denial distorts reality