1751 Digestive System Anatomy Parts of Stomach
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
The fundus is located ____ to the body of the stomach
Posterior
The Fundus is the most ___ portion of the stomach
Superior
The pyloric Portion is directly ____ to the body
Posterior
When a patient is supine the barium is in the ___ and the air is in the ___
Fundus; Body and Pylorus
When a patient is prone the barium is in the ___ and the air is in the ___
Body and Pylorus; Fundus
If the patient is erect the barium is in the ___ and the air is in the ___
Body; Fundus
Air that has risen to the top of the fundus is called what
the Gas Bubble
AP Supine position demonstrates
Entire stomach and duodenal loop
PA Prone position demonstrated
Entire stomach and duodenal loop
If patient is in RAO position Barium is in ___ Air is in ___
Pylorus and duodenal bulb; Fundus
RAO Position demonstrates
Pyloric canal and duodenal bulb
If patient is in LPO position barium is in ___ air is in ___
Fundus; Pylorus
LPO Position demonstrates
Fundus and unobstructed view of the duodenal bulb
If patient is in Rt Lateral position barium is in ___ Air is in ___
Pylorus and part of body; Fundus
Rt Lateral Position demonstrates
Retrogastric space, duodenal loop and duodenojejnual junction
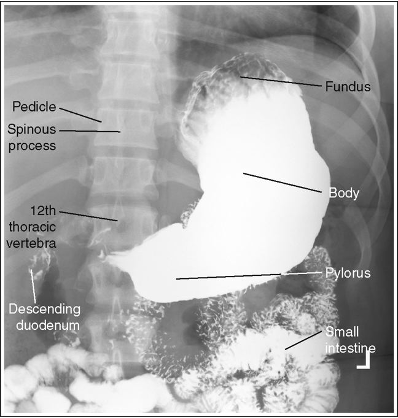
What position is this patient in?
PA (Prone, air in fundus spine is straight)
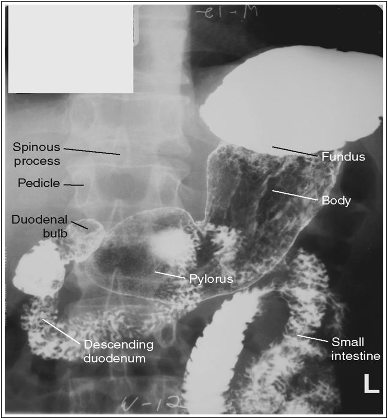
What position is this patient in?
AP (Supine, barium in fundus and spine is straight)
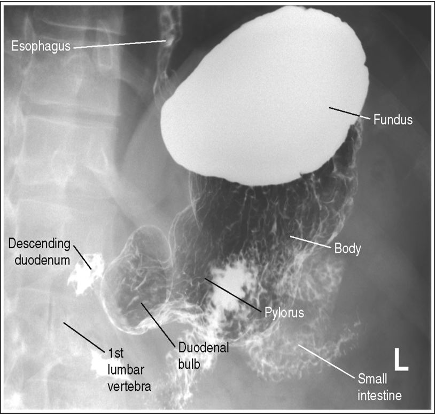
What position is this patient in?
LPO (Supine because barium is in the fundus, spine is not straight so they are rotated)
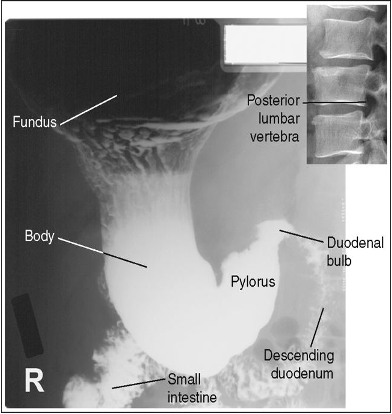
What position is this patient in?
Lateral (Spine is lateral and you see the retrogastric space)
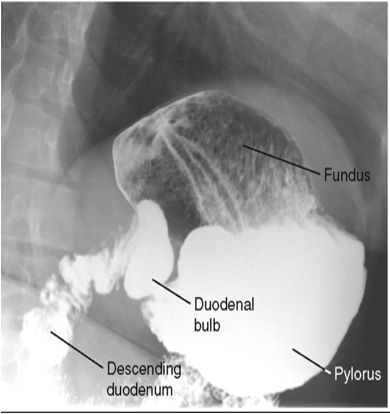
What position is this patient in?
RAO (Patient is PA due to air in fundus, but the spine is rotated so this is an RAO)